Orthopedic traumatologist > Articles > 10 things you need to know about arthroscopy
To correctly prescribe treatment, the doctor needs to analyze the condition of the knee joint. For this purpose arthroscopy . The medical term refers to a highly informative visual technique that allows for a high-quality examination and treatment of the joint in a closed manner. For this, puncture portals are used, which greatly alleviates the severity of surgical trauma.
Doctors consider the key advantage for the patient to be minimizing pain and reducing the rehabilitation period. The operation was first used at the beginning of the 20th century. To this day it is indispensable. What is its essence and beneficial advantages?
How does the procedure work?
First, a special tube is inserted into the joint cavity. It is synchronized with ultra-strong lenses. A powerful light source is connected. Next comes a direct study with visualization of the picture on the display. The picture is displayed on the monitor in an enlarged size, so you can recognize the pathology and choose the right treatment. According to scientists, arthroscopy is a progressive technique in terms of diagnosis. So far there is no alternative to it in terms of information. The device clearly visualizes the condition of the joint down to the smallest detail. Moreover, they may not be noticed when doing CT and MRI.
The fact that the procedure is used not only for diagnostic purposes is also positive. It is good to use in the treatment and restoration of joints. Having discovered a violation, the doctor is able to immediately act on the affected areas using surgical manipulations. However, as with any operation, there are indications and contraindications.
Efficiency of the technique
Arthroscopy today is used more and more often, gaining ground from other methods of treating diseases of the knee joint. The advantages of the method are:
- short rehabilitation period;
- low risk of complications;
- high efficiency, good treatment results;
- the ability to use the method for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Arthroscopy surgery in Moscow can be performed in most medical centers. The average price is 20 thousand rubles. The cost depends on the type and purpose of the intervention, and the level of the clinic. It is necessary to clarify how much the operation itself, the stay in the ward, and the prices for the necessary studies will cost.
Who should not have arthroscopy?
Experts note the following categories of people with contraindications.
- Surgery is not performed on hypertensive patients.
- The obstacle is diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation and an impaired balance of blood clotting.
- Disorders of the lungs and cardiac system.
- The technique is not prescribed to people with local skin inflammatory signs.
Arthroscopy is performed with caution, since the consequences can be unpredictable if you are allergic to the anesthetic.
Concept and advantages of the procedure
The surgery is performed using specialized, state-of-the-art fiber optics integrated into an innovative device called an arthroscope. Thanks to the unique device, the procedure got its name. The process involves an internal study of bone and cartilage tissue, menisci, tendons, muscles, ligaments, connective tissue elements, and synovial fluid.
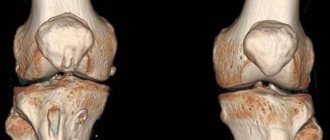
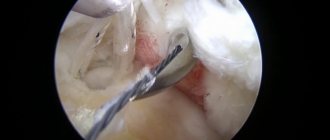
Image of the joint cavity.
For the purpose of highly informative diagnostics, a specialist, through a microportal, inserts the working tube of the device into the joint, into which a system of ultra-strong lenses, a powerful light source and digital video recording equipment are mounted. All structures that the arthroscope “sees” are visualized on the screen in a “live” form, and the image is received in a many times enlarged format. The doctor can find the exact location of the injury or degenerative changes, determine the nature of the pathology, the severity and take action.
Arthroscopy has been proven to be superior to any existing diagnostic methods. It clearly shows from the inside all the structural units of the bone connection in the smallest detail, allowing you to identify even small hidden damage that cannot be detected using standard fluoroscopy or arthrography, ultrasound, MRI, CT and other popular imaging methods.
The method is used not only as a diagnostic tool, but also as a therapeutic and restorative tactic. Having discovered certain violations of the cartilage surface, the doctor can immediately eliminate them. He will perform surgical manipulations through an additional incision (about 6 mm in size) using microsurgical instruments, and he will perform the entire process while looking at the monitor.
Who does the doctor prescribe arthroscopy for?
- In the case when the cause of the pathological symptoms is not clear and other methods do not help to establish them.
- Clinic clients with ligament ruptures and damaged tendons are also prescribed arthroscopy.
- Dislocation of the cup or the presence of loose bodies in the joint cavity.
In addition, this manipulation helps with intra-articular fractures, arthritis and arthrosis. Serious reasons for surgery are meniscus injury, inflammation in the synovium and necrosis of the articular head.
How risky is knee arthroscopy?
The operation is low-risk, but complications after such a diagnosis of arthrosis do occur. Among them are:
- increased bleeding, including inside the knee joint;
- wound infection after manipulation;
- breathing difficulties caused by anesthesia;
- allergies to anesthesia or medications injected into the joint;
- formation of a blood clot in the leg.
After arthroscopy, patients undergoing treatment for osteoarthritis sometimes complain of stiffness in the knee. Unfortunately, there are cases when, due to inept manipulation, cartilage, ligaments, menisci, blood vessels or nerve endings in the knee are damaged. To avoid this, you should undergo the procedure in reliable clinics.
Arthroscopy – jewelry work
Preparing the patient for surgery
The preparatory stage is the most important on the path to success. It consists of collecting tests and the need to conduct a thorough examination of the patient using instrumental and laboratory testing. The doctor must make sure that the operation is safe and weigh the pros and cons. Without this, it is impossible to carry out it. What else is important?
Patient requirements
- The patient must undergo specialist examination, including a cardiologist, endocrinologist, an allergist and a pulmonologist.
- A preliminary diagnosis of an allergic reaction to anesthesia may be necessary.
- It is necessary to undergo an ECG examination, the patient must have fluorography.
- Traditional urine and blood tests.
Medical professionals recommend that patients do not eat food 12 hours before surgery. Anticoagulant medications should be stopped several weeks before the procedure. This list includes heparin and aspirin. You should forget about bad habits for a while. It is recommended to stop smoking and drink alcohol, even in minimal doses, two weeks before the procedure.
Interesting fact! In the USA, up to 700 thousand knee arthroscopy is performed per year, in England up to 150,000 operations are performed.
Except knee, arthroscopy
done on the elbow, shoulder, hip joint. This manipulation is performed on the temporomandibular joint; the ankle and wrist are also examined. What is useful to know about diagnostic surgery?
How is recovery going?
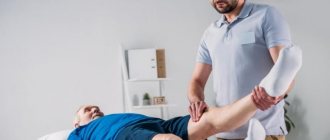
Recovery from this minimally invasive procedure takes only a few hours. You can return home on the same day, and in some cases, a little later, within three days. To relieve pain, it is recommended to apply an ice pack to the knee, which will reduce swelling and reduce pain. On the first day, it is important to protect your leg from stress and provide it with complete rest. Also, to relieve swelling and pain, analgesics, manual or lymphatic drainage massage are prescribed, and anticoagulants are prescribed to prevent deep vein thrombosis.
A person can move independently without crutches on the second day. The stitches are removed after about two weeks. At your scheduled consultation, the surgeon will recommend a set of exercises. It will help strengthen your muscles and restore your range of motion.
Subtleties of diagnostic arthroscopy
This type of manipulation is an intervention using instruments into the joint cavity in order to clarify the pathology. This invasive procedure compromises the integrity of the joint capsule as an instrument is inserted. This cannot be avoided, since x-rays/tomography do not show some pathologies. During diagnostic tactics, the doctor can use a targeted biopsy, choosing the most suspicious area of the capsule. The procedure is prescribed in more complex and questionable situations. Diagnostic arthroscopy is performed before complex surgical operations on the joint. Moreover, it works even in case of joint damage with hemorrhage into the cavity under anesthesia.
A little about anesthesia
Patients who come to the clinic are interested in the question of anesthesia. In this case, three types of techniques can be used.
- The operation is performed under local anesthesia with the participation of lidocaine, novocaine and other painkillers into the skin. These remedies provide an analgesic effect, although they will not completely eliminate the discomfort, but they can be tolerated.
- Regional anesthesia is used, which involves the use of anesthesia in the cerebrospinal fluid. The person remains conscious, without discomfort from touching the skin or pain. The ankle, hip, and knee are examined.
- General anesthesia is also applicable if surgery is unavoidable. The person is in an unconscious position; this technique is used when it is necessary to carry out a long operation.
Why is arthroscopy better than arthrotomy?
The key reason for using this advanced method is minimal tissue damage. In addition to less trauma during manipulation, doctors note the following advantages over arthrotomy.
- The manipulation can be carried out in an outpatient department.
- It takes a little time to recover.
- Low risk of postoperative complications.
- Surgical scars are barely noticeable.
- The intervention is performed with high precision thanks to a good overview thanks to the operation of a micro-video camera.
Indications may be:
- damage (and rupture) of the meniscus of the knee joint;
- damage to articular cartilage (the damaged area is smoothed or treated using high-frequency cold ablation; large areas of damage are usually treated with microfracture (formation of many holes in the subchondral bone);
- removal of the free intra-articular body (cartilage, bone) on the joints;
- resection of inflamed synovial tissue (synovectomy);
- reconstruction (restoration or plastic surgery) of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee joint.
Historical reference.
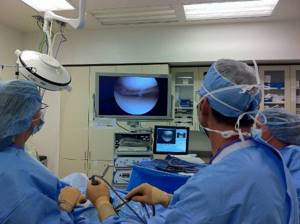
Arthroscopy allows you to see the internal condition of the joint on a monitor in great detail.
Severin Nordentoft, a doctor from Denmark, first reported in Berlin at a surgical congress in 1912 about the possibility of examining the knee joint without opening its cavity. For the first time, the scientist Kenji Takagi (Japan) managed to examine the knee using a device with a diameter of 7 mm in 1919. At the same time, the Tokyo “school of arthroscopy” was founded. Takagi subsequently reduced the diameter to 4 mm and was able to perform an intra-articular biopsy under vision guidance. In 1931, the first photographs of the formations from the inside were obtained. Scientists continuously worked to improve the device and methodology.
The Swiss Eugen Bircher worked on the creation and development of arthroscopy for about 10 years, and in the 1920s he was able to carry out diagnostic operations on the knee joint using a laparoscope. His numerous studies and attempts to improve the device made a huge contribution to the development of endoscopic surgery. Dr. Masaki Watanabe developed the first arthroscope to be mass produced in 1960. He performed operations and created the first atlas on arthroscopy. Later, Dr. Heshmat Shahriaree began performing arthroscopic meniscal resections. Over time, thanks to the development of fiber optics, the instruments were significantly improved and became widespread. And a new method of surgical treatment has become available in advanced clinics.
Stages of implementation
As a rule, the duration of arthroscopy does not exceed 1 hour, but it all depends on the purpose of the procedure. All surgical procedures are carried out in a special sterile operating room, which is equipped with all the necessary equipment, including medical monitors for image display. Then they begin anesthesia, the types of which vary. This or that type of anesthesia is selected strictly individually and depends on the purpose of arthroscopy, the duration of the operation, the wishes of the patient and the preferences of the surgeon.
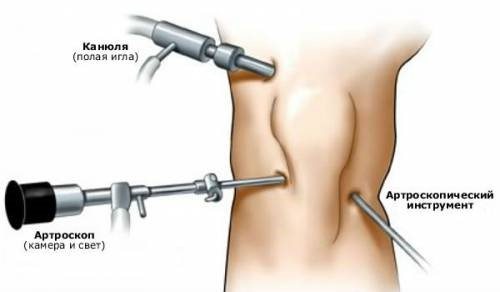
Then the arthroscopist performs an antiseptic treatment of the surgical field and makes three small incisions (3-5 mm) in the projection of the knee, through which arthroscopic instruments are introduced into the joint cavity - a camera with a light source, a tube for filling the joint with a special liquid, which allows you to enlarge and straighten the joint cavity and main working tool. Then the operation itself is performed. After completing all the necessary manipulations in the joint cavity, the fluid is pumped back and the instruments are removed.
Recommended behavior after knee arthroscopy
Day of surgery. | 1. After spinal anesthesia, strict bed rest must be observed. 2.After awakening from intravenous anesthesia, with clear consciousness, you can walk on crutches without putting any weight on the operated leg. |
1 day. | 1. Move on crutches without putting any weight on the operated leg. 2.After dressing, start performing the following set of exercises: Exercise Ι — “playing with the patella” — is tensing and relaxing the quadriceps femoris muscle on the operated leg 10-15 times 3-4 times a day. Exercise ΙΙ - flexion-extension movements of the foot 20-30 times every hour. Exercise ΙΙΙ - active lifting of the straightened sore leg 10-15 times 3-4 times a day. |
2 days. | 1. Walk with the help of crutches, balancing the supporting load on the leg with your own pain sensations, the magnitude of the load is brought to the mass of the limb, i.e. You can “put your foot” on the floor when moving with crutches. 2. Continue the same exercises. |
3 days. | 1. Walk with the help of crutches, balancing the supporting load on the leg with your own pain sensations, the magnitude of the load is equal to the mass of the limb, i.e. You can “put your foot” on the floor when moving with crutches. 2. Add one more exercise to the set: Exercise ΙV - active flexion-extension movements in the knee joint with a gradually increasing amplitude. The exercises are performed in a supine position, while the patient must keep his leg raised at an angle of about 45° to the plane of the bed. The duration of exercises and range of motion should be determined and limited by the patient himself, depending on the degree of pain and fatigue of the thigh muscles. |
4 days. | 1. Walk with the help of crutches, balancing the supporting load on the leg with your own pain sensations, the load is brought to half the body weight (walking with one crutch). 2. Continue the same exercises. |
5-7 days. | 1. Walk with additional support from a cane, gradually and smoothly increasing the load on the operated leg. 2. Continue the same exercises. |
8-9 days. | 1. Gradually and smoothly increase the load on the operated leg and bring it to full (walk without additional support). 2. Continue the same exercises. |