After the operation, are they given a certificate of incapacity for work and how many days are they paid for?
The patient’s sick leave is issued from the moment she is admitted to the hospital and preparations for the operation begin.
The duration of the disability period will include time spent in the hospital and rehabilitation at home if needed. Surgery can be performed in two ways, each of them has its own characteristics.
Laparoscopy of ovarian cyst or fallopian tubes, removal of ovary
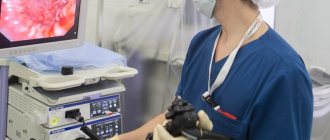
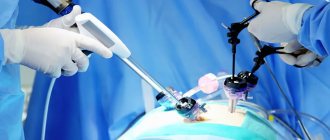
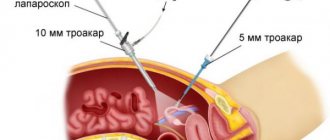
Laparoscopy is the most gentle method of surgical intervention , in which the risk of complications is minimal. To carry out this manipulation, an incision in the abdominal cavity is not required; several small punctures (5-7 mm) are sufficient, through which the optical device laparoscope and manipulator are inserted.
Most often, laparoscopy is used to remove cysts of the fallopian tubes or ovaries. Surgeries to remove the organs themselves are more complex, but they can also be performed using this method.
The duration of sick leave depends on the patient’s condition in the postoperative period. On average, the patient is under observation in the hospital for 2 to 5 days. If recovery goes well, the patient is discharged from the hospital. In this case, she may be issued sick leave for up to 10 days for full recovery at home. This is usually done when a woman’s work involves heavy physical exertion.
Laparotomy
Laparotomy is an abdominal operation that involves an incision into the abdominal cavity (horizontal or vertical). Recovery after such an intervention is much slower, so the laparotomy method is used in particularly difficult cases when it is impossible to perform the operation in any other way. Sometimes the transition to laparotomy is unplanned and forced (for example, if bleeding began during laparoscopy).
After the operation, the patient remains in the hospital for at least 5 days, and the maximum period depends on the severity of the particular case. The sick leave is opened for the entire period of stay in the hospital, extended for recovery on an outpatient basis for no more than 15 days, and beyond this period only by decision of the medical commission.
HOW IS THE RECOVERY PERIOD IN THE HOSPITAL?
Laparoscopy is a method of surgery with a low degree of trauma. Instruments are inserted into several punctures in the abdominal cavity. Special manipulators - instruments equipped with lighting and a camera - can reduce the risk of complications and speed up rehabilitation.
On the first and second days, the woman’s body experiences discomfort and even pain associated with the use of carbon dioxide, which is filled with the abdominal cavity during the operation. Gas pressure can provoke pain in the heart, liver, even in the neck. Then the gas is gradually eliminated from the body, and the discomfort stops. During this time, you can take analgesics and mild painkillers.
You are given up to a week in the hospital for the entire postoperative period. Discharged from the hospital on the 7th day after surgery. Once at home, women are given sick leave from 10 to 18 days.
What affects the length of a newsletter?
The length of the period of incapacity depends on:
- what kind of ovarian surgery will be performed;
- how;
- how successful it will be.
Grounds for extension and possible extension dates
The likelihood of complications after surgery is always present, so not only the period of the manipulation itself, but also the time after the intervention is very important. When everything goes well, the duration of sick leave is minimal. But in case of complications, more time is required for treatment and recovery.
The grounds for extending sick leave may be:
- complications during the operation itself;
- poor health in the postoperative period (fever, pain, discharge, weakness and dizziness);
- sudden deterioration of condition after discharge from hospital.
The total duration of outpatient sick leave is 15 days. In case of complications, by decision of the commission, the sick leave is extended once for another 15 days. In especially difficult circumstances, the commission will decide to extend the sick leave for several months (up to 10, and maximum no more than 12, according to clause 13 of Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated June 29, 2011 N 624n (as amended on November 28, 2017) “On approval of the Procedure for issuing certificates disability").
Preparation
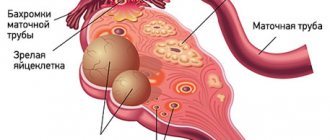
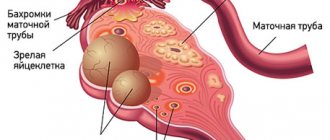
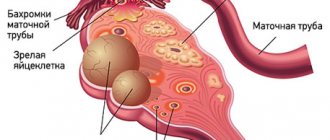
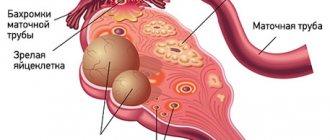
Ovarian cysts are usually detected during an ultrasound examination. In order to better assess the size, location and internal structure of the neoplasm, the condition of the ovary, they usually resort to not only transabdominal (through the abdominal wall), but also transvaginal (using a special sensor inserted into the vagina) ultrasound.
In rare cases, usually when a malignant nature of the formation is suspected, computed tomography and diagnostic laparoscopy are prescribed. of cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) in the blood testifies in favor of cancer . But this analysis is unreliable, since a positive result can be obtained for uterine fibroids, endometriosis and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
Based on the examination results, the doctor advises the woman and explains which treatment tactics will be optimal in her case. If laparoscopic surgery is indicated, a date for hospitalization is set. You need to undergo a preoperative examination. It usually includes the following diagnostic methods:
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- General urine analysis.
- Blood test for hormone levels.
- Tests for infections.
- Cervical smears - cytological, flora.
- Blood clotting study.
- Determination of blood group AB0, Rh factor.
- Electrocardiography.
- X-ray of the lungs.
Laparoscopic removal of ovarian cysts is performed under general anesthesia - endotracheal anesthesia. The woman is hospitalized in the hospital the day before surgery. You can’t eat anything for 8 hours before surgery, and you can’t drink anything in the morning. Some time before anesthesia, premedication : the woman is given drugs that help her relax and calm down.
Decor
The patient’s sick leave is issued by the attending physician at the hospital where the operation was performed. The column “cause of disability” is filled in with code “01”, which stands for “illness that prevents the employee from attending the workplace.”
It is paid in the same way as other certificates of incapacity for work. The amount of compensation depends on the average salary and total length of service at the enterprise.
Regardless of the severity of ovarian surgery, in the postoperative period it is necessary to protect yourself from excessive physical exertion and heavy lifting. In order for the body to fully recover, a careful attitude towards it is required. Unfortunately, not all employers treat their employees with understanding. However, a woman must understand that personal health is more valuable than any workplace.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Grounds for extradition
If a patient has undergone laparoscopic surgery, the doctor is required to issue him a sick leave certificate. This right is regulated by Federal Law No. 255.
An exception may be cases if a person is unemployed or works without official registration and, accordingly, the employer does not make contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for such an employee. Also, the issuance of a certificate of temporary incapacity for work will be refused if the person undergoing surgery is already on sick leave , including for pregnancy and childbirth.
Peritonitis
The appearance of peritonitis usually occurs after a hysterectomy, which was performed for emergency reasons, for example, necrosis of a myomatous node.
In this case, the woman’s condition worsens sharply:
1. The temperature rises to 39 - 40 degrees.
2. There is a pronounced pain syndrome.
3. There are signs of peritoneal irritation.
In this case, massive antibiotic therapy is performed (2-3 drugs are prescribed) and infusion of colloidal and saline solutions.
Prognosis after hysterectomy
Hysterectomy not only has no effect on a woman’s life expectancy, but even significantly improves its quality. Having forever gotten rid of the problems associated with diseases of the uterus and/or appendages, having forgotten forever about the issue of contraception, many women literally blossom.
More than half of the patients talk about liberation and increased libido. A woman is not granted disability after removal of the uterus, since the operation does not reduce her ability to work. A disability group is assigned only in the presence of severe uterine pathology, as well as when hysterectomy was followed by radiation or chemotherapy, which significantly affected the woman’s ability to work and health.
hysterectomy, women's health
Early complications after hysterectomy
The course of the early period after surgery is considered smooth if there are no complications at all. Early postoperative complications may include the following:
- inflammatory process on the skin in the area of the postoperative scar (swelling, redness, purulent discharge from the wound, as well as suture dehiscence);
- cramps or pain during urination caused by traumatic urethritis (damage to the mucous membrane of the urethra);
- bleeding of varying degrees of intensity;
- pulmonary embolism is a dangerous complication that causes blockage of the branches or the artery itself, and this is fraught with pulmonary hypertension, pneumonia and even death in the future;
- peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum, spreading to other internal organs, dangerously with the possible appearance of sepsis;
- hematomas (bruises) near the stitches.
Risks and complications of hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is a major surgery and carries some risks.
Ability to have children
After a hysterectomy, a woman is deprived of an organ designed to carry a fetus, making pregnancy impossible. There will be no more periods. If the ovaries are removed along with the uterus, menopause occurs.
Posthysterectomy syndrome
The uterus is an important organ of the female reproductive system; after its removal, a number of disorders develop in the body. They are combined with the term “posthysterectomy syndrome” . Even if the ovaries remain, blood circulation in them is disrupted, and this affects their function.
Posthysterectomy syndrome includes the following symptoms:
- Emotional disorders, depression.
- A disorder of the autonomic nervous system, which manifests itself in the form of hot flashes, sweating, poor tolerance of high temperatures, palpitations, chills, poor sleep, and increased blood pressure.
- Increased fatigue, low performance.
- Increased anxiety, fear of death.
- Tendency to swelling.
- Deposition of adipose tissue in the abdomen and waist.
- Bone loss, osteoporosis.
- If a woman previously suffered from arterial hypertension, the course of the disease is aggravated.
Sex after hysterectomy
Typically, after a hysterectomy, a woman can have sex as before and enjoy it. Many women note that their sex life has even improved. Most likely, this is due to the fact that the pain and other painful symptoms that the disease caused are no longer bothersome.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
How is a hysterectomy performed?
The most common open surgery is through an incision that can be horizontal along the bikini line or vertical along the midline. The average incision length is between 12 and 17 cm. The advantages of this approach are that it provides a good view for the surgeon and does not require complex equipment. Disadvantages: relatively high risk of complications and long recovery period.
The uterus can be removed laparoscopically, through punctures in the abdominal wall. This operation is less traumatic, after it the risk of some complications is lower, and the woman returns to her normal life faster. But laparoscopic hysterectomy cannot always be performed; factors such as the size of the uterus, the presence of scars from previous operations, obesity and concomitant diseases play a role.
Some clinics perform robot-assisted interventions. Instruments connected to the robot’s “arms” are inserted through punctures in the abdominal wall, and the doctor controls them using a special remote control and monitors the process on the device’s screen.
In some cases, a vaginal hysterectomy is possible. The incision is made inside the vagina, leaving no scars on the skin. Sometimes laparoscopy is performed simultaneously for control.
What determines the cost of intervention on uterine fibroids?
From many factors. Moreover, some of them (the efficiency of the examination, the comfort of the room, etc.) are in no way related to medical activities or the experience of the operating endovascular surgeon. Thanks to this, you can always count on professional assistance at the best price.
You can also contact the administrators of the clinics where Professor Kapranov works. Specialists will clarify the cost of abdominal surgery, talk about the conditions of hospital stay, and the qualifications of the personnel.
Request a call back Get a free consultation
How is laparoscopy performed?
Laparoscopic intervention is performed through several punctures in the abdominal wall. Through one of them, in the navel area, a laparoscope - an instrument with a miniature video camera. It broadcasts an enlarged image onto the screen. For better visualization during surgery, the abdominal cavity is filled with gas.
Special laparoscopic instruments are inserted through additional punctures, and the cyst is removed with the help of them.
Depending on the specific situation, the scope of the operation varies:
- Often it is possible to remove only the cyst, preserving the ovary.
- In some cases, it is necessary to remove the entire ovary - to perform an oophorectomy (oophorectomy) - while the second ovary can be saved. This has to be done if a malignant tumor is suspected, or if the cyst is in an “inconvenient” location, when it is difficult to remove it separately.
- In rare cases, both ovaries may have to be removed. This operation is performed only in extreme cases, especially in women of reproductive age, since menopause occurs after removal of both sex glands. The levels of female sex hormones decrease, and this can lead to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, hot flashes, etc.
Don't hesitate to ask your doctor questions before surgery. Ask what is the likelihood that during the operation you will have to remove both ovaries, what negative consequences this threatens, and how to cope with them.
Types of hysterectomy surgeries
Depending on the extent of the surgical intervention, there are three types of hysterectomy:
- Radical . As a rule, this operation is performed only for cancer. The surgeon removes the uterus, its cervix, part of the vagina, surrounding tissue, and lymph nodes. Often the ovaries and fallopian tubes are excised at the same time - a salpingo-oophorectomy .
- Total . This is the most common intervention option. The uterus and its cervix are removed, the ovaries are left.
- Subtotal . Only the body of the uterus is removed, the cervix is left behind.