Our fears depend on us
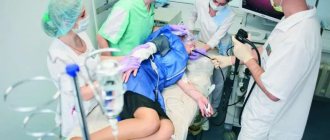
This procedure cannot be called pleasant, especially remembering the methods used ten to twenty years ago: nausea, gag reflex, and drooling were almost impossible to avoid. Now the situation has changed for the better: very thin endoscopes have appeared, which in our clinic are inserted through the nose - nasal gastroscopy. Is it worth using anesthesia, because it “does not hurt”, “is not scary”, “is calm”? It’s not for nothing that all the epithets are put in quotation marks, because they are most often caused by our attitude towards examination - what we inspired ourselves to do is what we got. To paraphrase the famous phrase of Faina Ranevskaya: “all fears and illnesses come from nervous experiences and our attitude towards them.” If you take the examination calmly, and do not conduct surveys of your friends about “was it scary, did you feel very sick,” then the procedure will turn out to be the most ordinary, if the doctor’s hands turn out to be skillful, and the specialist is experienced - like our doctors.
FGDS without stress: the doctor spoke about the advantages of medicated sleep
For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, doctors often prescribe endoscopic examinations to patients: FGDS, video gastroscopy, colonoscopy and others. They help make an accurate diagnosis, identify pathological changes in the early stages and create an effective treatment plan.
But most people perceive such procedures as very unpleasant and put off going to the doctor, wasting precious time. At the “Alone” medical clinic, at the patient’s request, they can be carried out in a state of medicated sleep. We learned about the features of this service from the endoscopist, head of the endoscopy department, Andrey Drozdov.
What is medicated sleep?
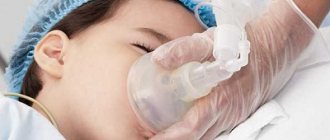
- This is a state close to physiological sleep. The patient is given a special drug intravenously. In our clinic we use Propofol, it is an ultra-short-acting hypnotic. It does not contain any potent or narcotic substances. It begins to act 20-30 seconds after intravenous entry into the body. Medication-induced sleep must be carried out under the supervision of an anesthesiologist and nurse anesthetist. The patient wakes up a few minutes after the end of the procedure and fully comes to his senses and recovers within 30-60 minutes. The time depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
What are the benefits of medicated sleep?
— It helps relieve pain and other unpleasant sensations during the examination. Especially in people with a high pain threshold and a labile mental state. The patient is asleep and does not feel anything. Medication-induced sleep is often requested by patients who have had a routine EGD or colonoscopy in the past and have experienced stress or pain. For some it even became a real psychological trauma.
There are advantages for the doctor too. After all, during a routine examination, he works in a nervous environment: the patient is uncomfortable, and the specialist has to carry out the procedure as quickly as possible. And thanks to medicated sleep, you can do this calmly, carefully studying your health status.
Do you need any documents or opinions from other specialists to carry out medicinal sleep?
— Permission to carry out medicated sleep is given by an anesthesiologist. It is necessary to provide the list of tests indicated on the clinic’s website and the result of an ECG study - no more than two weeks old. You can take tests and perform an ECG directly in our clinic.
Surely there are contraindications?
- Of course. Not all patients can tolerate medicated sleep without harm to health. The main contraindications include:
— hypertension in crisis stage;
- severe degree of respiratory failure;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- heart failure and acute myocardial infarction;
- acute cerebrovascular accident;
— recovery period after myocardial infarction and stroke;
- aneurysms of large vessels (aorta, carotid sinuses, heart);
- serious mental disorders.
How do patients usually tolerate it?
You need to understand that with medicated sleep, the patient falls asleep before the procedure and wakes up after it. As a rule, after waking up there is no lethargy or lethargy, or problems with orientation. However, you should not drive a car for the day after the test, make important decisions or sign legal documents, or drink alcohol or take sleeping pills.
Is it possible to undergo gastroscopy and colonoscopy under medicinal sleep in one visit?
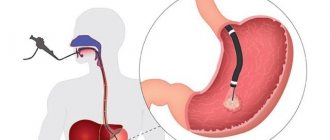
“Most of our patients prefer to do this. First, videogastroscopy is performed with a gastroscope, and then videocolonoscopy is performed with a colonoscope. During the study, a test for Helicobacter may be taken, and if tumors are detected, they are removed, or a biopsy is performed with further histological examination.
In total, the Naedine clinic employs 6 endoscopists. All endoscopic procedures are performed using expensive Japanese expert equipment. The Endoscopy Center is open daily, seven days a week.
To learn more about medicinal sleep and to sign up for an endoscopic examination, please call: 8 (8332) 32-7777.
Kirov, st. Dzerzhinsky, 6.
Tel.: 8 (8332) 32-7777
Website: clinic-naedine.rf
“In Contact”: https://vk.com/knaedine
License No. LO-43-01-002713 dated January 24, 2018. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Negative effects of anesthesia on the body
In addition, anesthesia (sedation) is not a completely safe method and can have rather dire consequences, which are called postoperative cognitive dysfunction, which has a negative effect on the brain. There are a lot of symptoms, they are usually associated with:
- disturbances of memory, sleep, hearing and even speech - you must agree, it is much more unpleasant than waiting out two or three minutes of nausea;
- decreased concentration - which is especially important for people who work with machinery or drive cars;
- deterioration in learning ability - unacceptable for the younger generation;
In some cases, symptoms go away within a few hours, and in some cases they last up to 12 months! Although in fairness, we note that the more time passes from the moment of administration of anesthesia, the weaker they appear.
The main risk groups here are elderly patients, people receiving repeated anesthesia for a short period of time or heading for long-term surgery, as well as those with infectious and respiratory diseases.
You should know that colonoscopy and gastroscopy must be carried out in different rooms, ensuring that the devices are used strictly for their intended purpose, so that the colonoscope does not accidentally end up in the esophagus and vice versa. This guarantees patients peace of mind and confidence since both devices are very similar, only the first one is longer; if the space is not demarcated, there is a possibility of confusing them.
What the patient should know
Another feature when conducting gastroscopy is that the doctor conducting the study must be in contact with the patient, which is why anesthesia is not acceptable here. And an additional danger to its implementation may be the presence of an allergy status to any component of anesthesia, which a person may not know about and be subjected to severe anaphylactic shock, the consequences of which can lead straight to the Sklifosovsky Institute. The formalities of sedation include the mandatory presence of a medical institution with a special drug license, the availability of which many patients simply do not consider necessary to check and are exposed to even greater risk.
There is an alternative to anesthesia - transnasal endoscopy!
The nasal endoscope is much thinner than a conventional gastroscope, its diameter is less than 4 mm, which allows the device to be inserted through the nose. Such an intervention is easily tolerated not only by adults, but also by small patients, reducing the likelihood of unpleasant sensations to a minimum.
The advantages of the study include not only the elimination of the gag reflex, but also low trauma, the ability to exclude local anesthetics, since the transnasal endoscope is also more flexible, with its help you can not only examine the required area, but also perform therapeutic manipulations.
Gastroscopy under anesthesia
Share information with your Facebook friends
VK
Anesthesia is usually understood as turning off the patient’s consciousness for the duration of one or another medical procedure using narcotic and psychotropic substances, i.e. acting on the central nervous system. The effect of these substances on the human brain has not been sufficiently studied, and their circulation is under strict control.
Anesthesia is used when it is impossible to conduct one or another endoscopic examination, which is necessary to make the correct clinical decision, if the patient is agitated, or is not adequate due to impaired brain function, if these are infants and up to 5-7 years of age, when the child does not have a clear self-awareness. In this case, the drug propofol is used, which allows you to control sleep, literally on a needle. As soon as the effect of this drug on the person’s brain weakens and he begins to wake up, the anesthesiologist adds a little propofol and the patient goes back to sleep.
However, a clear understanding has entered into practice that gastroscopy under anesthesia is performed solely at the whim of the patient, due to the unwillingness to experience unpleasant sensations and not to injure oneself with negative emotions associated with the gag reflex.
This is not entirely true, because during gastroscopy under anesthesia with the patient’s calm behavior due to the switched off consciousness, the endoscopist clearly and quickly examines all the necessary areas, using washing of the walls and aspiration, and can carefully and accurately perform various diagnostic manipulations (biopsy, removal of foreign material). body, contrasting bile ducts, chromoscopy, etc.). Therefore, endoscopists love to work in this mode.
Before performing a gastroscopy under anesthesia, the anesthesiologist must carefully ask the patient about concomitant diseases and pathologies, medications used, and familiarize himself with a general blood and urine test.
To be fair, it should be noted that most routine screening and diagnostic endoscopic examinations, for example, in Japan, are performed without sedation or anesthesia. This is due, first of all, to a critical approach to the use of narcotic anesthetics and strictly according to indications and, secondly, to the mentality of the nation, in which, traditionally, the doctor has a very large weight and patients are ready for all tests on the advice of a doctor.
In Europe and Israel, on the contrary, they do not perform endoscopy without sedation.
print version
Endoscopy
Cost of services Customer reviews Our doctors
Directions in endoscopy
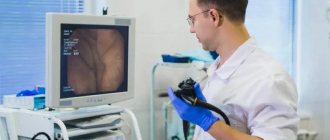
Modern international endoscopic diagnostic methods have switched from fiber optic to video endoscopic devices in the HD system. The Scandinavia Clinic has completely abandoned FEGDS, FCS, FBS, switching to such modern techniques as video esophagogastroduodenoscopy (VEGDS), video colonoscopy (VCS), video bronchoscopy (VBS).
Special offers for endoscopic examinations
Read more >>>
Endoscopic ultrasound is a transabdominal ultrasound that is performed through the anterior abdominal wall. Endoscopic ultrasound is a hybrid technology - a combination of ultrasound and endoscopy. If with conventional ultrasound recognition is performed through the skin, then endoUS is performed by inserting a special ultrasound endoscope into the esophagus and directed to the organ that needs to be examined.
More about endoscopic ultrasound
More details
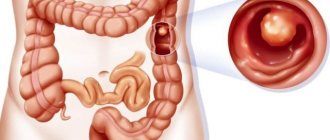
Video esophagoscopy (VGDS, video gastroscopy) is a type of endoscopy that allows you to examine the esophagus, stomach and duodenum in order to diagnose diseases such as hiatal hernia, gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, polyps, tumors. When performing VEGDS, it is possible to determine the presence in the stomach of the microorganism Helicobacter pylori, which plays a leading role in the development of peptic ulcers and gastric tumors. In addition, with VEGDS, gastric acidity can be determined. Additional studies for VEGDS are necessary for a more accurate diagnosis and prescribing the most effective treatment.
No special preparation is required for IGDS. The procedure is performed on an empty stomach and is accompanied by anesthesia with modern anesthetics.
Videocolonoscopy (VCS) is performed to identify diseases of the colon, the most common of which are colitis, diverticulosis, and tumors.

Preparation schemes for video colonoscopy:
The study is scheduled until 11:30 a.m. (using the drug Fortrans) The study is scheduled until 11:30 a.m. (using the drug Endofalk) The study is scheduled until 11:30 a.m. (using the drug Eziklen) The study is scheduled until 11:30 a.m. (using the drug Picoprep) Study scheduled before 11:30 a.m. (using the drug Moviprep) Study scheduled after 12 a.m. (using the drug Fortrans) Study scheduled after 12 a.m. (using the drug Endofalk) Study scheduled after 12 a.m. (using the drug Picoprep) ) The study was scheduled after 12 a.m. (using the drug Moviprep) The study was scheduled after 12 a.m. and is used in patients with constipation The study was scheduled after 12 a.m. and is characterized by a small amount of the main laxative drug (according to indications) The study was scheduled after 12 a.m. (with using the drug Esiclene)
One-day regimens for colonoscopy in the afternoon and with a small amount of solution using the drug Picoprep:
One-day scheme Fortrans 12.00 - 17.00 One-day scheme Fortrans 15.00 - 20.00 One-day scheme Endofalk 12.00 - 17.00
Video bronchoscopy (VBS). Indications for VBS are all lung diseases, but, first of all, this type of study is advisable to carry out in the presence of long-term pneumonia against the background of intensive drug treatment, the appearance of blood streaks in the sputum, or if aspiration of a foreign body is suspected. VBS is performed on an empty stomach, with premedication (carried out in the clinic), under anesthesia.
The clinic performs endoscopic operations to remove benign formations of the gastrointestinal tract or foreign bodies.
All types of gastroscopy are performed using the modern Pentax Hi Line HD+ video endoscopic system. Endoscopy rooms are equipped with video stands. Thanks to modern endoscopic equipment, the examination is high-quality, informative, quick and painless. If the patient wishes, endoscopies can be performed under general anesthesia.
When performing endoscopic procedures, disposable sterile consumables are used. The endoscopes themselves are treated with modern disinfectant solutions and sterilants, allowing for high-level disinfection and sterilization after procedures. Endoscopic instruments are subjected to mechanical cleaning using a Japanese ultrasonic cleaner, followed by sterilization by autoclaving or the most effective modern sterilants. The quality of cleaning and sterilization of endoscopic equipment allows us to completely eliminate the possibility of infection during endoscopic procedures.
Previously, the word gastroscopy was associated with unpleasant swallowing of a tube, and the abbreviation FGDS made even the most persistent shudder. The only way out to avoid some unpleasant sensations could be an FGDS under anesthesia. At the Scandinavia clinic, during VEGD, superficial general anesthesia and short, superficial sleep are performed, which does not leave memories of nausea and lack of air.
Forget about the fear of the upcoming examination. We do not use FGDS, FCS and FBS, causing harm to the health of our patients, but provide only modern safe video endoscopic examination technologies.
In August 2017, the endoscopy department of the clinic on Liteiny was equipped with new endoscopic equipment from PENTAX. The world's first video processor (OPTIVISTA EPK-i7010) was launched, combining digital and optical amplification functions using a new optical filter that transmits light in a limited spectral range. These improvements make it possible to improve the quality of endoscopic examination by obtaining a clearer image of blood vessels, gland ducts and the gastrointestinal mucosa. (Photo of the processor is attached below.)