Synonyms: Red cell Distribution Width, distribution of red blood cells by size.
Scientific editor: M. Merkusheva, PSPbSMU named after. acad. Pavlova, medical practice. September, 2021.
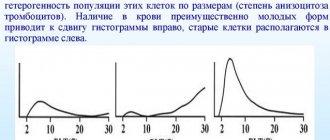
A blood test with RDW indicators is prescribed in cases where it is necessary to determine the degree of heterogeneity of red blood cells.
The bulk of blood is made up of red blood cells - small blood cells that give blood its color. If a person is healthy, they will not differ in size and shape. If there is a pathology in the blood, there may be red blood cells of different sizes. Good blood function directly depends on the diameter of the blood cells.
Changes in the gradation between blood components may be associated with age-related diseases, the presence of malignant tumors, and anemia. In medical circles, a deviation in the form of a change in the size or volume of red blood cells in the blood is called anisocytosis.
Indications for analysis
There are several reasons to perform the RDW diagnostic test. Often this procedure is performed before surgery or if anemia is suspected. In some clinics, RDW is included in the list of routine tests that the patient must undergo regularly.
Together with the MCV analysis, the RDW study is prescribed for:
- differential diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia.
- differential diagnosis of B-12 and folate deficiency anemia and other megaloblastic anemias.
Often, the initial appointment comes with complaints, which become the main indications for examination for RDW:
- constant dizziness;
- poor sleep;
- darkening of the eyes;
- general weakness;
- nausea;
- tinnitus;
- the formation of bruises of unknown origin on the body;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Note: Hip fracture patients who experience large fluctuations in RDW during treatment are at increased risk of mortality within two years.
Increased value
If the average volume of red blood cells is increased, this may mean a disruption in the body’s functioning. Reasons when mcv is elevated can be:
- Liver disease.
- defect in the functioning of the red bone marrow.
- The thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones
- Vitamin B12 deficiency. This deficiency has a particularly negative effect on children under 2 years of age. At this age, you need to focus on eating foods containing high amounts of vitamin B12, for example, sour cream, eggs, liver, beef and others.
- Folic acid deficiency.
- Smoking. Smoking releases a significant amount of carbon dioxide, which impairs blood transport in the body, leading to a deterioration in oxygen supply. Women who smoke are more susceptible to respiratory diseases, which can cause increased red blood cell counts.
- Oncological diseases.
- Taking contraceptive and hormonal medications.
- Inflammatory processes in the body. These can be infectious diseases caused by a virus or some kind of fungus.
- Alcoholism. In this case, the mcv indicator can be brought back to normal; to do this, it is enough not to drink alcohol for 100 days. It is worth saying that in this case only mcv values increase, and the hemoglobin value remains within normal limits.
There is a version that taking antidepressants for a long time can lead to increased levels, but at the moment this version is under study.
An increase in red blood cells in the blood may be temporary and not carry any abnormalities or pathologies. This situation can lead to:
- stress,
- being in high mountains,
- excessive mental or physical work,
- influence of toxins,
- dehydration.
After these factors are eliminated, such important indicators of red blood cells as their average volume will return to normal.
(
1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
RDW standards
The analysis results are calculated using a special analyzer. In most cases, the procedure is performed in combination with the MCV index. This combination helps to determine one or another type of microcytic anemia.
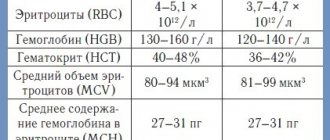
Reference (corresponding to normal) indicators of RDW in human blood range from 11.5% to 14.5%. The optimal coefficient value is 13%. These figures are the same for both adults and children over six months old, i.e. do not change throughout life.
Reference values, %:
- up to 6 months — 14.9-18.7
- over 6 months — 11.6-14.8
If all indicators are normal, the test result is negative.
If the RDW is elevated, the result is considered positive. Important! The interpretation of the results is always carried out comprehensively. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on only one analysis.
Reduced value
If the average volume is reduced, they speak of anemia, i.e. a lack of hemoglobin in the blood.
The most common reasons when red blood cells are below normal are:
- Iron deficiency or iron deficiency anemia. This form of anemia occurs without complications and has the simplest treatment compared to other types of anemia. If a child’s hemoglobin is low and the cause is determined to be iron deficiency, the child is prescribed a special diet with a repeat blood test a month later. If a child’s hemoglobin does not increase after a month, but rather decreases, then in this case, he is referred to a hematologist and drug treatment is prescribed.
- Sideroblastic anemia. Also associated with iron deficiency, responds well to vitamin B6 therapy. This type of anemia develops quite rapidly and requires immediate action; the worst outcome of such a diagnosis can be death.
- alassemia is a genetic disease. Anemia is caused by impaired hemoglobin production.
- Lead poisoning. In case of lead poisoning, the average value of red blood cells decreases due to the fact that the bone marrow begins to fail and a disruption occurs in the body's production of hemoglobin.
- Dehydration of the body. This is due to the loss of fluid from the body, which negatively affects the blood test.
Sometimes there are situations when the average volume of red blood cells is not reduced, but is within the normal range, but clear signs of anemia appear. This often happens if there is:
- the presence of a malignant tumor,
- the presence of chronic infections,
- significant blood loss
- the presence of diseases that cause insufficient production of hormones.
If the mcv is lowered in the analysis, then a qualified consultation with the attending physician or hematologist is necessary.
RDW increased
An increase in RDW values indicates the presence of such abnormalities in the body as:
Isolated RDW increase:
- Deficiency of iron, vitamin B-12 and folic acid;
- Macrocytic anemia (B-12 deficiency, folate deficiency)
- Sickle cell anemia
- Myelodysplastic syndrome (high risk of developing acute leukemia)
- Bone marrow metaplasia
- Metastases to the bone marrow
- Chronic liver failure
Increase RDW and MCV
- Iron deficiency anemia;
- Sideroblastic anemia;
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia;
- Chemotherapy;
High RDW and low MCV:
- Iron deficiency
- Sickle cell beta thalassemia
- Iron-deficiency anemia ;
- megaloblastic anemia (lack of vitamin B12, folic acid);
- Liver dysfunction;
- Lack of vitamin B12;
- Folate deficiency (water-soluble B vitamins).
Anemias that are not characterized by an increase in RDW:
- Anemia in chronic diseases, in renal failure;
- Anemia due to acute blood loss;
- Hemolytic anemia;
- Aplastic anemia
- Genetically determined diseases (thalassemia, congenital spherocytosis, presence of hemoglobin E)
When decoding, other blood parameters are also taken into account, which will help the doctor specify the problem and make an accurate diagnosis.
Why is MCV lowered?
If the MCV indicator in a blood test is low (does not reach the required 80 fl), most often this indicates that the child or adult is developing some form of anemia, that is, a lack of hemoglobin in red blood cells. Thanks to the compensatory properties of blood, the number of red blood cells themselves can increase, but all of them will poorly supply oxygen to the tissues and organs of a sick person.
The reasons for the decrease in the average volume of red blood cells may be the following conditions and pathologies:
- Iron deficiency anemia (grade 2-3) is a lack of iron, which the body receives from food or in the form of vitamin-mineral complexes. Often develops against the background of gastrointestinal diseases and microelement absorption disorders, intestinal tumors, gastritis with low acidity. Pregnancy can also lead to iron deficiency.
- Lack of folic acid, often also associated with pregnancy.
- Chronic diseases associated with constant blood loss: hemorrhoids, nosebleeds, peptic ulcers, etc.
- If the indicator in women is below normal, this may indicate the development of uterine tumors (fibroids, fibroids, or malignant ones). These diseases are characterized by frequent bleeding not associated with menstruation.
- A pathology of the red bone marrow that results in insufficient production of normal blood cells (congenital sideroblastic anemia). In addition to the congenital form, the disease can develop due to lead poisoning and taking a number of medications.
- Thalassemia, hemoglobinopathy and other hereditary blood diseases. Characterized by a decrease in the average size of red blood cells to 65 fl.
- Hemolytic anemia associated with increased destruction of blood cells (transfusion of blood incompatible with the patient’s group or rhesus, hereditary forms, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome).
Important information: Why are there elevated leukocytes in the blood of a newborn baby (causes and consequences)
When the MCV value in the blood is below normal, but no pathologies are detected, the cause may be conditions associated with blood loss in large quantities:
- surgical intervention;
- trauma with injury to soft tissues and blood vessels;
- donation
Often, a decrease in the volume of red blood cells is also caused by metabolic disorders or endocrinological disorders (increased thyroid function, etc.). These conditions are distinguished from anemia by the normal hemoglobin content. Only a doctor can correctly decipher a blood test and determine the presence of any abnormality.
If you find a reduced reading of the average volume of red blood cells, it is recommended to visit a physician, especially if you have painful symptoms.
MCV and RDW
For example, if RDW is normal, but MCV is low, this may indicate the following diseases:
- anemia in chronic diseases
- malignant formations;
- post-traumatic splenectomy (removal of the spleen);
- hemorrhage (bleeding);
- thallesemia (disturbances in the structure of normal hemoglobin);
- Hemoglobin-E-pathy
- blood transfusion (blood transfusion).
If the opposite is true, RDW is higher than normal, and mcv is lower than normal, then this may indicate a lack of iron in the body, and sickle cell anemia. When both erythrocyte indices are high, vitamin B12 deficiency and various types of anemia are diagnosed.
Depending on what the test results show, the attending physician refers the patient to a specialized specialist, for example, a hematologist, or writes out referrals for additional tests and prescribes the necessary treatment.
Normal values
The complete blood count contains the MCV value, or the mean volume of red blood cells in the blood. If the MCV is low, then the size of the red blood cells is lower than normal.
Doctors judge the normality or decrease in the volume of red blood cells quite arbitrarily. The size of the red blood cell changes even during the day due to physiological reasons: after work, a tired person’s blood cells increase in size, and after rest they become smaller. At 8 o'clock in the morning, when most tests are carried out, the size and volume of the bodies reaches a minimum.
The volume of red blood cells and their size in an adult are determined in femtoliters (fl) or µm³. Normal values change throughout life. In middle age (40-59 years) they range from 80-100 fl for women and 81-94 fl for men. Indicators in younger patients differ slightly (a little more), so 80 fl is most often taken as the average norm. In men over 65 years of age, the normal value can range from 78-103 fl.
Red blood cells with normal volume are called normocytes, and those with low and high volume are called micro- and macrocytes, respectively. The size of the cells is regulated by the body itself depending on their number in the blood: if there are a lot of red blood cells, then the MCV is lower.
Important information: What does it mean that the average hemoglobin content in a red blood cell is reduced (normal)
Normal for a child
In the first month of life in children, the normal size of a red blood cell is more than 105 fl. By six months this value drops to 90, and by 1 year - to 78-80 fl. This is a normal physiological process during which fetal hemoglobin is replaced with the new one that adults have. At 5-12 years of age, the average volume indicators again increase slightly (up to 89 units), but by the age of 18 they reach the adult norm.