High-quality and timely diagnosis is the key to successful and effective treatment. That is why in the modern world not a single medical and diagnostic institution can do without an X-ray machine. Managers of medical centers are often faced with the question of choosing this equipment, but how to determine which X-ray machine from the great variety of options on the market is suitable for the clinic? What parameters should you use to choose and buy an X-ray machine? How not to overpay for unnecessary functions and not miss the main thing? Does the price of an X-ray machine affect the quality of it?
Today, outdated “film” installations are increasingly being replaced by digital X-ray machines, increasing the throughput of the room and minimizing the radiation dose. Should I make a choice in their favor or work “the old fashioned way”?
In this article, we will tell you what types of X-ray machines there are and how they differ from each other, about their advantages and features that are important to know for those who decide to buy an X-ray machine.
Types of X-ray machines
In accordance with the operating conditions, the X-ray machine can be stationary or mobile (ward).
Specialized types of X-ray machines are also presented:
- C-arms, used in operating rooms for surgical interventions,
- angiography machines,
- for mammography,
- dental x-rays for dental departments.
There are also portable, small-sized devices that are used for simple x-ray examinations in an ambulance or at the patient's home. The scope of portable devices is extremely limited due to their very low power, so they cannot replace either a mobile or, especially, a stationary X-ray device.
Mobile X-ray units are used mainly in wards, which is why they are often called “ward X-ray machines”. The power of mobile X-ray machines ranges on average from 12.5 kW to 32 kW. The power of classic stationary devices starts from 40 kW.
Some medical centers that have significant restrictions on the installation of a stationary X-ray machine use a mobile (ward) X-ray with a power of 32 kW for radiographic examinations in the radiology department.
Stationary X-ray systems are designed for use in specially equipped rooms - X-ray rooms. Based on the type of design, there are devices for two workstations (a table and an image stand), remote-controlled rotary tables-tripods, and devices of the U-arm type (“yoke”).
An X-ray machine of the U-arm type is an X-ray machine with an emitter and detector located on a single rotating stand. An X-ray transparent gurney is used for photographs in the supine position. This type of stationary X-ray machines is most often used in rooms with a small area.
X-ray units based on a remote-controlled tripod table are the most expensive type of stationary x-ray equipment. These are 3 in 1 units for the X-ray department of any modern medical institution. They allow all possible radiographic and fluoroscopic examinations to be carried out. An excellent example of this type of device is the multifunctional digital X-ray device FLEXAVISION F3 from Shimadzu (Japan).
The most common type of stationary X-ray systems in medical centers are classic two-station X-ray machines. The main components of such systems are an X-ray tube (with ceiling or floor mounting), an imaging table for the lying position, an imaging stand for the standing position, and a generator.
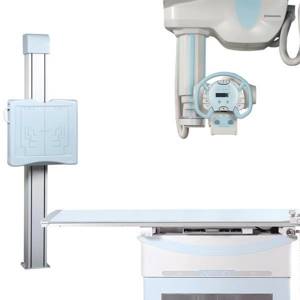
When purchasing an X-ray machine, it is important to decide on the profile of the examination and the location of the equipment. Having chosen the type of X-ray machine, you can proceed to assessing its technical parameters.
What does an X-ray machine consist of?
Of course, there are a large number of configuration variations. But there are basic elements that make up the base:
- One or more X-ray tubes (beam generators).
- A high-voltage device that includes high-voltage and filament tube transformers, as well as a system for rectifying current.
- A device for converting radiation into an image. May include a display, a cassette with an x-ray membrane, an enlarger, an optical inspection part, a photographic camera, a video camera.
- Control panel.
- Special tripods.
- Radiation protection equipment.
- Additional accessories.
In addition, X-ray machines contain tubes, filtering surfaces, separating grids, and self-acting X-ray exposure meters.
Important technical characteristics of x-ray machines
Generator power
When choosing an x-ray unit, you should take into account the main technical characteristics. The higher the power of the feeding device, the shorter the exposure time, the lower the radiation dose, and in some studies the higher the image quality. This is especially important when examining obese patients.
For stationary X-ray machines, the generator power range is on average from 40 kW to 80 kW. The most widely used configurations are those with a power supply of 50 kW - this is enough to carry out the vast majority of studies. But it is important to take into account that the power of the generator must be consistent with the operating power of the X-ray tube foci, which determine the operating power of the “generator – X-ray tube” system.
Generator type
When choosing an X-ray machine, it is also important to consider the type of generator: high-frequency power supplies are characterized by a slight pulsation of the anode voltage, which increases the life of the X-ray tube and reduces the radiation dose for the patient.
Technical solutions implemented in the design of the best modern generators provide X-ray images with high contrast and spatial resolution, as well as maximum research safety by minimizing “soft” X-ray radiation that is not involved in image formation.
For example, stationary X-ray machines from Shimadzu (Japan) are equipped with such generators; they are capable of producing almost ideal rectangular pulses, which directly affects the quality of the resulting images.
X-ray tube parameters
Before purchasing an X-ray unit, pay attention to the main characteristics of the X-ray tube, the most important of which are the effective focus sizes.
The value of the theoretically achievable spatial resolution decreases as the focal size increases. With a focus size of 2 mm, according to various estimates, up to 3 line pairs/mm can be recognized, even if the detector has better characteristics (X-ray film, for example, can distinguish 10-15 line pairs/mm). All tubes have two working focuses. The lower the focus size of the X-ray tube, the clearer the resulting images will be, but decreasing the focus size also reduces operating power.
It is important that the power of the X-ray machine generator matches the operating power of the foci of the supplied tube.
Another characteristic of X-ray tubes is the heat capacity of the anode, which affects the resource intensity of the system. The higher this indicator, the greater the number of studies before the tube overheats and the longer it will last.
Maximum permitted load on the imaging table
When choosing a stationary X-ray machine, you should pay attention to the characteristics of the imaging table.
In the production of imaging tables with a high maximum permitted load, the most expensive and reliable components are used. A good indicator is considered to be a maximum permitted load on a table of 200 kg, but some manufacturers produce optional table models with a permitted load of up to 290 kg or even higher.
The X-ray unit can also be equipped with an imaging table that has a “lift” option, which allows you to move the table surface in a vertical plane - on average in the range of 500-850 mm from the level of the floor covering.
As a rule, manufacturers offer several models of imaging tables to choose from. For example, you can buy a Shimadzu X-ray machine for two workstations with imaging tables with a maximum permitted load on the table of 200 kg and 295 kg.
Tube mounting options
For stationary X-ray machines with 2 workstations, there are two options for mounting the tube - on a floor stand and on the ceiling.
The most common option in private medical centers is to mount the tube on a floor stand. It is easier to install and does not have serious restrictions on the minimum ceiling height and area of the X-ray room.
Ceiling mounting of the tube is a more expensive option, including installation, but also more reliable and convenient to use. If the dimensions of the room, the ceiling and the budget allocated for the X-ray machine allow, then if there is a large planned flow of patients, it is better to choose the option of ceiling mounting of the tube.
If, with a large flow of patients, you plan to purchase an X-ray machine with a floor-mounted tube, you should pay attention to options with a reinforced floor-mounted stand.
We offer our clients reliable Shimadzu X-ray machines for two workstations, both with a floor-mounted tube (model RADspeed MF) and a ceiling-mounted one (model RARspeed MC).
Advantages of digital X-ray machines
In recent years, diagnostics are increasingly carried out using new generation digital X-ray equipment. It provides instantaneous acquisition of images, eliminates the development process, allows you to store images and carry out diagnostics using computer technology.
A digital X-ray machine is distinguished by the fact that images of anatomical structures obtained using X-ray irradiation are processed digitally.
The main advantages of this modern diagnostic method are:
- the highest quality of the resulting images: the ability to digitally process them allows you to reveal important details;
- speed and ease of operation: immediately after the procedure, the image is available for analysis;
- ease of storage and space saving by creating mobile and easily accessible x-ray archives,
- lower cost of research due to the absence of film and reagents, and environmental safety due to the elimination of the development stage.
It is also important for patients that a modern digital X-ray machine minimizes radiation exposure during the examination procedure.
X-ray machines equipped with a digital system are more expensive than analogue ones, but do not require a developing machine with consumables and a special darkened room for it.
The transition to digital technology can significantly increase the throughput of the X-ray room, reduce the dose load on the patient, and also reduce the waiting time for the result for the patient. It becomes possible to edit and process the resulting images to make it easier for specialists to determine the diagnosis and specifics of the disease.
Digital X-ray machines are classified by detector type. Today, there are two main types of digital systems:
- CR - systems with a digitizer, also called a "digitizer",
- DR - systems with a flat panel detector.
The system based on semiconductor flat panel detectors is the latest technology with higher resolution.
CR systems use the principle of phosphor sensitivity. Outwardly, this is an ordinary X-ray machine, in which, instead of a film cassette, a CR cassette based on memory phosphors is used. After taking the picture, the cassette must be removed from the device and placed in a special reading device - a digitizer. At the end of the reading process, the digitizer transmits the resulting digital image to the laboratory assistant’s workstation, and the cassette will be cleaned and ready for the next study.
DR systems use semiconductor flat panel detectors. A digital X-ray machine for two workstations can be equipped with either one wireless flat-panel detector, which must be moved from the table to the image rack, or two - for both the table and the image rack.
It should be taken into account that a flat panel detector should never be dropped, and its cost makes up the majority of the entire DR system, unlike CR, where the cost of an individual cassette is insignificant.
After the image is taken, almost instantly, the flat panel detector transmits the digital image to the laboratory assistant's workstation. There is no link in the chain in the form of a digitizer, which significantly reduces the time it takes to obtain a digital image, as well as the reliability of the entire system.
Systems with a flat panel detector (DR) are more expensive than systems with cassettes with a digitizer (CR), but they are justified when there is a large flow of patients, as they significantly increase the throughput of the X-ray room, are more reliable, and also allow obtaining images of the best quality.

In addition to the laboratory assistant's workstation, which is usually included in the delivery of CR or DR systems, to equip the radiology department with a digital X-ray machine, you will need a doctor's workstation, equipped with a high-resolution medical monitor, and a special printer for printing X-ray images.
We offer our clients reliable printers from Fujifilm (Japan) and various options for workstations based on Osirix (Switzerland), Machaon (Russia) software or a premium solution based on PAX Synapse from Fujifilm. The doctor's workstation software allows you to make a full diagnosis, including all the necessary measurements, send the image for printing or record it electronically on an external storage device.
If the clinic already has an analog X-ray machine, then there is no need to replace it to switch to digital technology. It is enough to buy one of the digital systems - CR or DR and combine it with this device. On our website you can get acquainted with CR systems (digitizers) and DR systems (based on flat panel detectors) Fujifilm (Japan). Over time, it will be possible to change the X-ray unit by connecting a new one to this digital system.
Inspection and inspection complexes (IDC)
In order to conduct research on large objects, inspection and inspection complexes are used, which differ from standard introscopes primarily in their size. In addition, they have a much greater power of penetrating ionizing radiation, which means that using such installations it is possible to examine large objects at customs. IDK is suitable for inspection of cars and trucks, shipping containers, railway cars and so on.
Such installations are much more advanced; they allow you to identify objects by type of material. For example, identify metal, plastic, organic compounds. They will appear in different colors on the operator's screen. And potentially dangerous substances and objects can be highlighted with special markers.