Synonyms: Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase, AT-TPO, microsomal antibodies, anti-thyroid, antibodies to microsomal antigen, ATPO.
Scientific editor: M. Merkusheva, PSPbSMU named after. acad. Pavlova, medical practice. Proofreader: M. Mazur, KSMU named after. S. I. Georgievsky, therapist
The thyroid gland plays a responsible role in the body - the production of biologically active substances that are responsible for the process of energy exchange between cells. Their secretion occurs with the participation of a special enzyme - thyroid peroxidase (TPO), it is involved in the formation of the active form of iodine, without which the biochemical synthesis of thyroid hormones T4 and T3 is impossible.
Antibodies (AT) to TPO are formed when the enzyme is detected by the body as a foreign protein. The AT-TPO analysis is a highly accurate marker that determines the level of aggression of the immune system towards its own body, and allows for timely diagnosis of autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland: diffuse toxic goiter, thyroiditis, thyroid dysfunction in infants.
General information
To thyroid peroxidase, which is located on the surface of thyrocytes (cells that produce T3 and T4), i.e. directly in the thyroid gland, the immune system does not react in any way. But only up to a certain point. When this enzyme enters the blood, and this happens in the case of damage to the thyroid gland, provoked by external or internal factors, the active synthesis of autoantibodies to peroxidase (AT-TPO) begins in the body.
Provoking factors:
- radiation therapy (in the treatment of cancer), systematic irradiation of the body (occupational hazard);
- trauma to the thyroid gland as a result of a bruise, blow, fall, puncture, etc.;
- unsuccessful surgical intervention on the gland;
- deficiency or excess of iodine in the body;
- inflammatory processes, infectious and viral diseases.
When the amount of antibodies increases, massive destruction of peroxidase and thyroid follicular cells secreting T3 and T4 begins. As a result, the concentration of these hormones in the blood increases sharply. This condition is diagnosed as autoimmune thyrotoxicosis. Then, over the course of 1.5-2 months, T3 and T4 are washed out of the body, and their levels in the blood drop. At the same time, there is no possibility of replenishing the hormone deficiency, because the cells that produce them are completely destroyed. Hypothyroidism develops.
If the amount of AT has increased moderately, then over the course of decades they will gradually destroy thyroid cells and gradually reduce the volume of hormones produced. As a result, the patient will develop insufficient thyroid function, and there will be a deficiency of the most important iodinated hormones (T3 and T4). This is the same hypothyroidism.
The AT-TPO test makes it possible to accurately diagnose pathological conditions, the correction of which requires the use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT). With the correct dosage of synthetic hormones (levothyroxine), such treatment tactics provide a stable and long-lasting clinical effect.
Antibodies to thyroglobulin (AT-TG)
Thyroglobulin is a glycopeptide that is a precursor to T3 and T4. It is synthesized exclusively by the thyroid gland and accumulates in its follicles in the form of a colloid. When hormones are produced, thyroglobulin enters the bloodstream in small concentrations. Due to currently unknown reasons, it can transform into an autoimmune agent, to which the body begins to form antibodies. This becomes a trigger for the development of an inflammatory process in the organ. ATTG can interfere with normal hormonal functioning, leading to hypo or hyperfunction.
According to statistics, ATTG is detected in 40-70% of people with chronic thyroiditis and in 75% of patients with hypothyroidism. At the same time, a slight increase in its normal value may not indicate a disease (quite common in older people). Analysis for AT-TG is of particular importance in the diagnosis of diffuse toxic goiter, toxic nodular goiter and Graves' disease. If during pregnancy a woman is diagnosed with a thyroid lesion or other autoimmune pathology, an ATTG test is prescribed in the first trimester and a few days before the planned birth. This was based on minimizing the risk of thyroid damage in the newborn.
Indications for analysis
In addition to direct indications (diagnosis of autoimmune thyroid diseases), an endocrinologist may prescribe an anti-TPO antibody test in the following cases:
- when the patient complains of: uncontrolled weight gain or loss, chronic fatigue, constantly low or, conversely, increased body temperature, increased sweating, increased anxiety, insomnia.
- if the results of other tests (T3, T4 and/or TSH) indicate thyroid dysfunction.
- determining the risk of neonatal hypothyroidism (thyroid deficiency in newborns), if the mother has a history of thyroid disease or antibodies to TPO are detected;
- screening in the first trimester of pregnancy to determine the risk of developing thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland);
- screening in pregnant women with TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) concentration >2.5;
- determination of the degree of risk of miscarriage, spontaneous termination of pregnancy (miscarriage);
- diagnosis of female infertility and unsuccessful attempts at artificial insemination;
- assessment of the structure and condition of the thyroid gland before prescribing medications (HRT, amiodarone, interferon, lithium or iodine preparations, etc.);
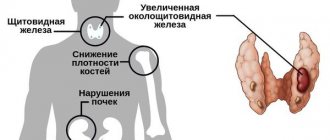
- diagnosis of hypothyroidism, goiter (enlargement of the gland), thyroiditis, thyrotoxicosis (excessive secretion of iodinated hormones);
- clarification of ultrasound results that revealed a disorder of the structure (heterogeneity) of the thyroid gland;
- to examine the thyroid gland in newborns to ensure that there are no abnormalities if the mother has been diagnosed with antibodies to thyroid peroxidase or postpartum thyroiditis.
AT to TPO is increased - reasons
A high level of antibodies exceeding the norm is usually observed in the following diseases:
- various viral diseases;
- chronic renal failure;
- thyroiditis;
- Graves' disease;
- thyroid injuries;
- autoimmune diseases of a hereditary nature;
- diabetes;
- rheumatism.
Also, elevated antibodies to TPO occur if, shortly before the tests, the patient underwent radiation therapy in the head and neck area. It should be said that the analysis for these antibodies is not used as part of the measure to monitor the therapy being carried out. The examination is necessary only to determine whether pathology is present or not.
AT-TPO test for pregnant women
Sometimes an increase in AT-TPO occurs during pregnancy, during the restructuring of the immune system for bearing a fetus. At this time, the thyroid gland becomes more active, producing more hormones. This is sometimes regarded by the immune system as a disorder and promotes the synthesis of antibodies to TPO.
Testing for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase during pregnancy is carried out for expectant mothers for preventive purposes. If the concentration of antibodies to TPO is high, then the risk of developing postpartum thyroiditis increases by 50%.
According to statistics, pathology develops in 5-10% of women after childbirth. The thyroid gland is gradually destroyed under the influence of AT, after which thyrotoxicosis develops (oversaturation of the body with iodinated hormones). Sometimes the function of the gland is restored on its own, but 1/3 of patients may develop hypothyroidism - chronic hormone deficiency, which requires systematic use of hormonal medications.
If the level of other thyroid hormones (T3, T4, TSH) is elevated in the first trimester, then the endocrinologist prescribes an AT-TPO test.
During pregnancy, antibodies to TPO can significantly affect the development of the thyroid gland of the unborn child, since they are able to penetrate the placental barrier from the mother’s blood into the fetus’s body and cause neonatal hypothyroidism.
Important! The interpretation of the results is always carried out comprehensively. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on only one analysis.
Diseases of the thyroid gland that require testing for elevated thyroglobulin
An analysis for elevated thyroglobulin is done in the following cases:
• For thyroid carcinoma. But it should be remembered that only a third of patients with thyroid cancer have an increase in the concentration of this protein;
• For the purpose of early detection of metastases or relapses of tumors after surgical treatment has already been performed. A relapse of both malignant and benign thyroid tumors may be indicated by increased thyroglobulin in the blood plasma;
• Determination of the effectiveness of radioactive iodine therapy for the metastatic process in thyroid tumors;
• For the diagnosis of artificial thyrotoxicosis (against the background of hormone replacement treatment);
• Thyroglobulin, the norm of which is increased, is assessed in children to determine the origin of congenital hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
• As a tumor marker and a means for assessing the effectiveness of treatment of thyroid tumors;
• To assess the activity of thyroiditis or confirm previous inflammation of the thyroid gland in the next 2 years;
• For mass studies in conditions of iodine deficiency.
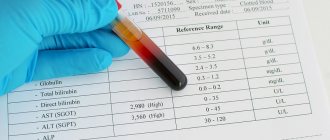
Standard for AT-TPO
All endocrinological studies (instrumental and laboratory) must be carried out in the same medical institution, since the reference values of AT-TPO in different laboratories may be different.
- According to the independent laboratory Invitro, for antibodies to thyroid peroxidase the indicator is set to 5.6 U/ml.
Standard reference values
The generally accepted norm (including abroad) is the indicator
- 0-34 IU/ml
However, there are also extended reference intervals:
Women:
- up to 50 years – 0-34 IU/ml.;
- after 50 years – 0-100 IU/ml;
Pregnant:
- at the 12th week of pregnancy – no higher than 25 IU/ml;
- in the 2nd and 3rd trimester - from 30 IU/ml to 56 IU/ml;
Men:
- up to 50 years - 0-34 IU/ml;
- after 50 years - less than 85 IU/ml.
BAU/ml – new standard for measuring IgG antibodies against COVID-19
In a laboratory assessment of the protectiveness of immunity against coronavirus infection, antibodies to the S-protein region or the so-called RBD antigen are examined, which protect against the invasion of SARS-CoV-2.
IgG are antibodies that represent an “archive” where the body stores information about a past infection or vaccination. This is the so-called immunological memory. In different people, such protective antibodies last for different periods of time (from 3 to 6 months or more), as this depends on many individual factors.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has approved an international standard of measurement - First WHO International Stendart for anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulinum (human), with the unit of measurement BAU - “binding antibody units”.
This alignment will help standardize SARS-CoV-2 serological methods and facilitate ongoing studies of the immune response to the virus associated with natural infection, vaccination and therapeutic treatment.
The NAJA laboratory works with test systems for diagnosing the new coronavirus infection, which are standardized against the WHO International Standard for immunoglobulin against SARS-CoV-2 (human). Therefore, now the result of the ELISA IMMUNO ASSAY (ELISA diagnosis) will differ from the one given previously. When assessing the strength of humoral immunity, a level of specific IgG antibodies less than 10 BAU/ml should be regarded as a negative result.
Interpretation of the result according to the new standard for assessing immune status
:
- < 10.0 BAU / ml - negative
- ≥ 10.0 BAU/ml – positive.
Approximate gradation according to the manufacturer according to the level of virus-neutralizing antibodies in the results
:
- from 0 to 10 BAU/ml = negative result, no antibodies;
- at >150 BAU/ml = virus neutralizing activity is clearly expressed in 100% of cases (sufficient level for protection, vaccination is not required);
- at 80-149.9 BAU/ml = the virus-neutralizing effect is effective only in 50% of cases (control over time);
- at 11-79 BAU/ml = low virus neutralizing effect (vaccination decision);
- 500 and above = the maximum level of antibodies has been developed (vaccination is not required).
For example, if the result, which was calculated relative to the new standard, in BAU/ml = 86 means that the result is positive (since more than 10), there is immunity, but the virus neutralizing effect in such individuals is observed only in 50% of blood samples (observation is recommended ).
When the amount is 49 VAU/ml = the result is positive (since more than 10), but the virus neutralizing effect is low, a decision is made on the need for vaccination.
253 VAU/ml = vaccination is not required, the virus-neutralizing effect is pronounced.
The cost of the study remains unchanged - 650 rubles for the analysis + 150 rubles for blood sampling.
Do you want to test your immunity to a new viral infection or are you planning vaccination?
Get diagnosed at one of the NAJA branches in Surgut:
- Tyumensky tract, 6 Mon-Fri ⌛️ 09:00-15:00, Sat ⌛️ 09:00-11:00
- st. Bezverkhova, 3/7 Mon-Sat ⌛️ 08:00-14:00
- Melik-Karamova, 76V Mon-Fri ⌛️ 08:00-14:00, Sat ⌛️ 08:00-13:00
The exact cost of diagnostic tests for coronavirus infection and details of the provision of services can be found out from the administrators of the medical center by calling (3462) 771-003
AT-TPO is higher than normal
A significant deviation of the results from the norm is typical for:
- diffuse toxic goiter (Graves disease);
- nodular toxic goiter;
- thyroiditis (autoimmune, subacute (de Crevin's disease), chronic (Hashimoto's disease));
- postpartum thyroid dysfunction;
- idiopathic hypothyroidism;
A slight or moderate increase in AT-TPO levels may indicate the presence of:
- diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent);
- rheumatoid arthritis (damage to joints and connective tissue);
- lupus erythematosus (an autoimmune pathology that affects connective tissue and skin);
- vasculitis (damage to vascular walls) and other autoimmune diseases.
Increase in AT-TPO during pregnancy
- Positive test results during pregnancy indicate the possibility of hyperthyroidism in the child (during intrauterine development or after birth)
The following factors can cause a false increase in AT-TPO:
- hereditary predisposition;
- a course of treatment with iodine or other drugs;
- chronic diseases in the acute stage;
- trauma or surgery in the thyroid gland.
For reference: about 5% of the world's population suffers from autoimmune thyroid diseases. This is about 350 million patients. In 10% of the remaining antibodies to TPO can be elevated without affecting the gland or caused by other systemic and autoimmune processes.