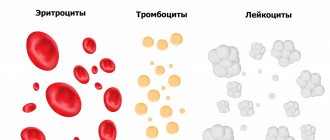
The norm of red blood cells in the blood
Anemia is a decrease in the total number of red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin in the blood, as well as a decrease in the blood's ability to carry oxygen.
Anemia can range from mild to life-threatening depending on hemoglobin levels and symptoms. Some of these symptoms are more severe than others. But if even mild symptoms occur, you should consult a specialist.
Red blood cells are the most common cells in human blood. The body produces millions every day. Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow and circulate throughout the body for 120 days. They then go to the liver, which breaks them down and processes them into cellular components.
Approximately 84% of the cells in the human body are made up of 20–30 trillion red blood cells. Almost half of the blood volume (40% to 45%) is red blood cells.
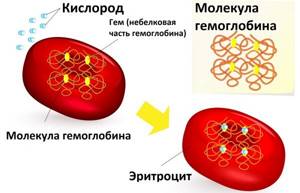
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which collects oxygen from lung cells and transports it to tissues. The main purpose of red blood cells is to ensure a normal supply of oxygen to tissues and organs.
Normal red blood cell counts range from 4.7 to 6.1 million cells per microliter for men and 4.2 to 5.4 million cells per microliter for women. These ranges may vary depending on age, gender and factors such as lactation, menstruation, pregnancy.
A high red blood cell count is most often caused by:
- smoking cigarettes;
- heart problems;
- dehydration;
- kidney problems;
- bone marrow dysfunction;
- difficulty breathing;
- side effects from medications;
- staying at high altitude.
The bone marrow continuously produces red blood cells. If the body doesn't get the nutrients it needs, red blood cells can become deformed or die faster than the body can replace them.
A lower than normal red blood cell count may occur with:
- frequent bleeding, injuries, cuts;
- bone marrow failure;
- malnutrition and deficiency of nutrients necessary for the synthesis of red blood cells;
- kidney disease;
- overhydration – swelling, excessive fluid consumption;
- pregnancy;
- influence of side effects from medications.
Low red blood cell counts or anemia cause you to feel tired and weak. When a person's red blood cell count is below normal, the body has to work harder to provide oxygen to the cells. A low red blood cell count can cause a variety of symptoms and health complications.
The most serious complications of low blood cell counts include:
- Infection. With a low white blood cell count, and in particular a low red blood cell count, people are at high risk of developing an infection. If an infection develops when white blood cell levels are low, the body will not be able to protect itself. In severe cases, infection can be fatal.
- Anemia. A low red blood cell count is anemia. The most common symptoms of anemia are fatigue and shortness of breath. Anemia can be relieved with blood transfusions or medications that increase the body's production of red blood cells.
- Bleeding. A low number of platelets in the blood can cause bleeding. You may have heavy bleeding from a small cut or spontaneous bleeding from your nose or gums. In rare cases, dangerous internal bleeding may occur.
Detailed description of the study
Folates are salts of folic acid, which plays an important role in hematopoiesis. With insufficient folic acid, a special type of anemia develops - folate deficiency anemia. The most common causes of low folate levels in the blood are:
- impaired absorption of folic acid in the gastrointestinal tract (resection of the stomach, intestines, malabsorption syndrome, etc.);
- insufficient intake of folic acid from food;
- increased consumption of folic acid (pregnancy, lactation, active growth and maturation in children, fever, sepsis, etc.);
- alcoholism;
- some kidney diseases;
- taking medications that interfere with the absorption of folic acid (hormonal contraceptives, aspirin, cytostatics, etc.);
- oncological diseases;
Elevated levels of folate in the blood are rare and are usually associated with long-term use of medications containing folic acid.
Folate is a natural form of vitamin B9. The source is the intestinal microflora. Partially comes from food (spinach, lettuce, beans, asparagus, grains, wholemeal). One of the most important functions of vitamin B9 in the body is the regulation of hematopoietic processes. Folates are necessary for the differentiation of red blood cells and for the normal functioning of the bone marrow and nervous system.
Folate deficiency can lead to spontaneous miscarriages, premature birth, and premature placental abruption. Lack of folate can also cause congenital intrauterine malformations (CHD) of the cardiovascular and nervous systems of the fetus. Supplementing with folate during pregnancy can reduce the risk of neural tube defects by 85%. Folate absorption disorders can be caused by an unbalanced diet low in fresh fruits and vegetables, old age, taking medications, and celiac disease. Folate reserves in the body are relatively small, and therefore deficiency can develop within 1 month after cessation of its supply, and anemia - after 4 months.
The first symptoms of folate deficiency are weakness, irritability, decreased concentration and loss of appetite, followed by inflammation of the mucous membranes, anemia and neurological disorders. Folic acid and atherosclerosis. Folate deficiency is one of the main causes of hyperhomocysteinemia. And it, in turn, is an independent risk factor for the early development of atherosclerosis. Determination of folate levels can be carried out as part of an analysis of the risk of developing coronary heart disease.
Nutritional supplements
Dietary supplements (dietary supplements) can help raise red blood cells in the blood. Nutritional supplements contain substances that increase the production of red blood cells or support related processes in the body. Nutritional supplements interact with medications, so you should consult a doctor before starting a course. You cannot take a dosage greater than that specified in the instructions.
Nutritional supplements your doctor may suggest include:
| Name | Norm | Action |
| Iron | Women need about 18 milligrams (mg) per day. Men only need 8 mg per day. | Iron deficiency usually causes low red blood cell production. |
| Vitamin E | The average adult requires about 15 mg of Vitamin E per day. | Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant by trapping free electrons that can damage healthy cells. It enhances immune function and prevents the formation of blood clots in the heart arteries. |
| Copper | Women need 18 mg per day and men need 8 mg per day. | Copper deficiency causes the production of defective red blood cells, disruption of the myelin sheath of nerve tissue, and destruction of connective tissue. |
| Vitamin A | Women need 700 mcg per day. For men, the recommended amount increases to 900 mcg. | Vitamin A is involved in the formation of blood cells and the absorption of iron, necessary for the synthesis of red blood cells. |
| Vitamin B6 | Women need about 1.5 mg each day, and men need about 1.7 mg. | It affects not only the circulatory and cardiovascular systems, but also mainly the nervous system. In turn, adequate functioning of nerve cells helps to increase the level of red blood cells. |
| Vitamin B9 | The average person needs 100 to 250 mcg per day. Women during menstruation are recommended to take 400 mcg. Pregnant women need 600 mcg per day. | Folic acid is used to create new cells. Not only red blood cells, but also hair, skin and nail cells. Therefore, it is recommended that women consume more Vitamin B9. |
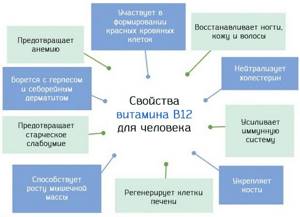
| Vitamin B12 | Ages 14 and older require 2.4 mcg of this vitamin per day. For pregnant women, the recommended dosage increases to 2.6 mcg. For women during lactation, it increases to 2.8 mcg. | Vitamin B12 is important for maintaining healthy metabolism, blood cells and nerves. |
What else is prescribed with this study?
Vitamin B12
4.4. Venous blood 1 day
960 RUR Add to cart
Homocysteine
1.53. Venous blood 1 day
RUR 1,890 Add to cart
Clinical blood test with leukocyte count and ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear to detect pathological changes) (venous blood)
3.9.1. Venous blood 1 day
720 RUR Add to cart
Folate metabolism
GNP047 Venous blood, DNA extraction 3 days
RUR 3,750 Add to cart
Lifestyle
Timely intake of nutritional supplements, vitamins and combination with a healthy diet is the basis for raising the level of red blood cells in the blood.
An integrated approach includes:
- Reduce alcohol consumption to 1 drink per day for women and 2 drinks per day for men. A serving of alcohol is 10 g of pure alcohol. For example, 1 serving of alcohol will be contained in 100 ml of wine 12%.
- Adding regular physical activity. Simple aerobic exercise will be effective in increasing the level of red blood cells. For example, walking, Nordic walking or running.
- Balanced diet. One reason for low red blood cell levels is a lack of nutrients. Such as, for example, iron or folic acid.
- Timely intake of nutritional supplements and medications.
- Healthy sleep.
- Adequate water intake. Dehydration is one of the reasons why the level of red blood cells in the blood can be disrupted. Therefore, it is so important to drink at least 1 liter of clean water per day or 1.2–1.5 liters with coffee, tea and liquid food.

Regular consumption of alcohol in excess of the norm, which will not harm a person, leads to the destruction of blood cells. Alcohol can affect red blood cell production because it reduces the number of progenitor cells in the bone marrow, resulting in fewer mature red blood cells being produced.
Alcohol also affects the maturation of red blood cells, causing cell abnormalities or dysfunction. Alcohol also causes abnormally large cells to form, which are destroyed more quickly.
Alcohol affects the absorption of nutrients from food. Malnutrition caused by alcohol usually leads to a deficiency of iron and folic acid, which are necessary for the proper formation of hemoglobin. When hemoglobin is not produced properly, red blood cells cannot carry enough oxygen and the number of red blood cells decreases.
Regular exercise can raise red blood cells in the blood. This is the key to red blood cell production. Vigorous exercise causes the body to need more oxygen. When more oxygen is needed, the brain signals the body to create more red blood cells.
The best workouts to increase the level of red blood cells in the blood are aerobic:
- fast walk;
- run;
- swimming.
Unnecessary contact with germs should be avoided whenever possible. To do this, it is useful to wash your hands frequently or use disinfectants, avoid contact with sick people, and do not use public transport.
A balanced diet is important to maintain normal red blood cell levels. The body needs all the vitamins and nutrients every day that it cannot produce on its own. A healthy diet - more fruits and vegetables.
If you have difficulty eating - nausea, vomiting - you need to use nutritional supplements or prepare foods in a different way. For example, instead of frying potatoes, you can boil and puree them. Potatoes are rich in vitamin C, which is also necessary for increasing the level of red blood cells in the blood.
The point is not that a certain diet increases the level of red blood cells, hemoglobin or improves digestion. The body simply needs vitamins to produce blood cells.
What affects the level of red blood cells?
It is immediately necessary to clarify that the body independently regulates the number of red blood cells produced based on the amount of oxygen received.
The less it is, the more red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow to prevent oxygen deficiency. And vice versa - the higher its concentration in the air, the fewer red blood cells are synthesized in the bone marrow.
Nutrition affects the production of red blood cells only indirectly. But in some cases, it is possible to normalize a low or high level of red blood cells only by adjusting the diet.
But how does diet affect red blood cell concentration? In fact, the cell is fully formed after the synthesis of the hemoglobin molecule. And according to research , the formation of hemoglobin requires iron, some groups of amino acids, vitamins A, C, E, B-groups. The red blood cells themselves consist primarily of protein complexes.
Accordingly, consuming foods rich in the above elements helps stimulate the production of red blood cells (if the body needs them).
The exclusion of such products contributes to a slight decrease in the concentration of red blood cells. A normal level is considered to be from 3.7 to 5.15 million cells per microliter of blood.
Nutrients to Increase Red Blood Cells
Eating foods rich in these nutrients will raise your red blood cell levels. Most often, anemia occurs due to malnutrition.
A balanced diet is better than taking dietary supplements, since the human body absorbs substances from food better than those synthesized in laboratories.
Products containing useful substances contain not just one vitamin, but a whole group of excipients, without which the absorption of the necessary microelement will be difficult.
Iron
Regular consumption of foods that contain iron can increase red blood cells in the blood. The average person's body contains about 3 grams of iron, 75% of which is found in the blood.

Iron is not synthesized by the body, but comes from food.
Primarily from the following products:
- beef;
- beef and pork kidneys;
- beef and pork liver;
- spinach;
- cabbage;
- prunes;
- raisin;
- beans;
- egg yolks.
Vitamin B9
Adding certain vitamins to your diet may also be beneficial.
Foods high in vitamin B9 (folic acid) include:
- whole wheat bread;
- whole grain cereals such as pearl barley;
- persimmon;
- spinach;
- cabbage;
- beans;
- lentils
- peas;
- nuts.
Vitamin B12
Steady intake of the vitamin can help raise red blood cell levels and prevent symptoms of depression. Vitamin B12 is essential for the development, myelination and function of cells of the central nervous system, the formation of healthy red blood cells and DNA synthesis.

Intestinal microflora is responsible for the synthesis of Vitamin B12. Dysbacteriosis or long-term use of antibiotics can become an obstacle to the normal absorption of the substance.
Foods High in Vitamin B12:
- beef;
- fish;
- milk;
- cheese;
- eggs.
Copper
Copper does not directly contribute to the production of red blood cells, but is involved in the absorption of iron, which is necessary for the production of red cells. Copper plays an important role in tissue respiration.
Copper is also known for enhancing oxidative processes in cells and tissues, which increases the level of red blood cells in the blood.
This is a list of foods that contain high amounts of copper:
- Domestic bird
- shellfish
- liver
- beans
- cherry
- nuts
Vitamin A
A fat-soluble substance that is easily destroyed in its pure form. It is found in both meat and vegetables. It is synthesized by the body provided that there are no metabolic pathologies.

Vitamin A is capable of raising red blood cells in the blood. It supports the production of red blood cells and is involved in maintaining immunity. Necessary for the formation of visual acuity for children and adolescents.
Foods rich in vitamin A include:
- spinach;
- beef liver;
- cabbage;
- sweet potatoes;
- carrot;
- red pepper.
Drug therapy
| Name, release form | Release form | Action | Contraindications |
| Aeprin | Solution for intravenous administration. | The active substance is epoetin alfa. An artificial form of protein that helps the body produce red blood cells. | Epoetin alfa may cause serious side effects, including heart attack or stroke. May accelerate tumor growth. |
| Binocrit | Injection. | The active substance is epoitin alfa. It is a stimulator of red blood cell production. | Affects the cardiovascular system. Before taking it, you should consult a specialist. |
| Pyridoxine | Tablets, injections. | Pyridoxine is used to treat or prevent vitamin B6 deficiency. | Do not take the medicine in larger or smaller quantities, or for longer than recommended. |
| Maltofer | Drops, syrup, tablets, chewable tablets. | Iron and vitamin complex helps produce more red blood cells. | Some vitamins may harm an unborn baby. Dosage requirements may also differ during breastfeeding. |
| Totema | Solution, 20 ampoules of 10 ml | Among the active ingredients are gluconates of iron, manganese and copper. All of these substances are involved in hematopoiesis and the formation of red blood cells, and also have antioxidant properties. | Use with caution with other medications. Also, do not combine with medications containing copper. |
| Ferrum lek | Syrup 50 mg/5 ml 100 ml; Ampoule solution 5 pcs. 2 ml. | The active substances are iron polymaltosate hydroxide, a whole macromolecular complex of fortified iron. | Use with caution during lactation and pregnancy. |
| Fenyuls | Capsules, 10 pcs. | The iron contained in Fenyuls capsules activates the synthesis of blood cells. A vitamin complex with B vitamins improves their absorption and also affects other organ systems. | It is worth carefully studying the list of added vitamins to avoid overdose. |
| Ferretab comp | Capsules, 30 pcs. | The active ingredients are ferrous fumarate and folic acid, which help increase the level of blood cells. Folic acid improves iron absorption. | It is not recommended to consume more than the recommended dose or exceed the treatment period specified in the instructions. |
| Tardiferon | Tablets, 30 pcs. 80 mg. | Among the active ingredients is ferrous sulfate, which normalizes the production of red blood cells. | It is not recommended to combine it with a diet high in iron or take iron-containing multivitamins at the same time. |

Anemia is often associated with cancer. If tests show low hemoglobin levels, you should consult a doctor. It is not recommended to immediately use medications to raise the level of red blood cells in the blood without a prescription.
Author: Svitkevich Julia
Causes of low red blood cell levels
One of the main reasons for a decrease in the level of red blood cells in the blood is anemia
Deviations from the norm are provoked by a number of serious pathologies. Therefore, test results should be taken seriously and measures should be taken at the first signs of the disease.
One of the most common diseases, which results in a low level of red cells, is anemia and all its types. Low hemoglobin levels go hand in hand with low red blood cell counts.
Anemia is divided into several types:
- Iron deficiency anemia - this disease occurs due to blood loss, pregnancy, or disruption of the absorption of iron from the gastrointestinal tract. This type of anemia is considered the most common.
- Sideroblastic anemia - this type of anemia does not imply a lack of iron, but of the enzyme by which iron is synthesized. This disease is not common, but is serious because it is incurable. A person takes a number of medications throughout his life to maintain his health.
- Deficiency of B12 and folic acid - vitamins B12 and B9 enter the body with food; they are not produced by themselves. The lack of these elements leads to anemia. More often it affects people who do not consume meat and dairy products at all, as well as pregnant women. Deficiency can occur due to gastrointestinal diseases; vitamins are not absorbed. The disease is treatable.
- Posthemorrhagic anemia - develops in response to large or small blood loss, chronic or acute. Chronic posthemorrhagic anemia occurs against the background of gastrointestinal diseases (ulcers, polyps, hernias), neoplasms, kidney and liver pathologies. This type of anemia is dangerous because it cannot be detected immediately. Usually a person seeks help when he feels really bad.
- Hemolytic types of anemia - this disease involves the destruction of red blood cells, which occurs much faster than the generation of new blood cells to replace them. Such anemias are divided into those that are acquired or inherited.
- Sickle cell anemia - this anemia means an abnormal or defective shape of the hemoglobin molecule, which leads to hemolytic crises - dizziness, shortness of breath, tinnitus, low blood pressure, fainting.
- Thalassemia is a hereditary disease due to which hemoglobin molecules are formed at a very low rate. The disease cannot be cured.
- Hypoplastic type - this disease differs from all others in that there is a deficiency of not only red blood cells, but also all other cells that make up the blood as a whole. The pathology is hereditary and acquired.
In addition to anemia, diseases such as erythroid leukemia can cause a low level of red cells. These are malignant tumors in the bone marrow, where the production of red blood cells occurs. Young cells undergo transition to malignant cells. Why this process occurs has not yet been established, but one of the factors identified is chemotherapy and radiotherapy procedures. Unless a person has been exposed to these factors, the reasons why cells in the bone marrow become malignant are not known.
You can learn more about anemia from the video:
Read: Useful tips: how to take a blood sugar test correctly
The main cause of a low level of red blood cells is considered to be anemia and all its types. Therefore, the symptoms of such conditions are similar:
- With anemia, dizziness, headaches, low blood pressure, fainting, nausea, weakness, increased fatigue, insomnia, along with a drowsy state are observed.
- Gastrointestinal diseases, enlargement of the liver and spleen develop in almost all cases.
- There may be problems with memory, loss of coordination, and conditions may develop about which a person says “woolly legs, arms,” or “goosebumps.”
- Problems with the cardiovascular system arise.
Depending on the type of anemia, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment, recommends following a certain diet and following a regimen. The success of therapy depends on a correct diagnosis and strict adherence to all the doctor’s instructions.
Traditional treatment regimen
Treatment for anemia usually requires taking medications to increase red blood cell levels. Depending on the type of disease, either iron-containing or combination medications are prescribed.
In advanced cases, the patient is offered inpatient treatment, which will necessarily be accompanied by injections - iron-containing or combined solutions, B vitamins (12, 9).
The therapy will also include taking medications aimed at curing the main disease that provokes a decrease in red cells in the blood. For complex diseases, such as leukemia, treatment is carried out only inpatiently and may require a bone marrow transplant. The treatment regimen will always be different, as it depends on many factors that only a doctor can take into account.