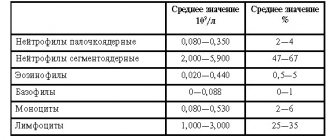
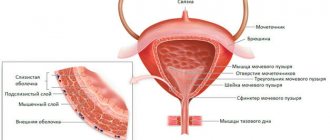
Inflammatory diseases of the MPS as a cause of increased levels of leukocytes in smears
Inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system are the main reasons for the quantitative increase in the number of leukocytes in smears.
We are talking about the participation of sexually transmitted infections, prostatitis, urolithiasis, bacterial urethritis, tuberculosis, cystitis.
Very often, the cause of prostatitis is a bacterial infection, and it always causes an increase in the level of leukocytes in smears.
With urolithiasis, there is also inflammation in the kidney tissue, in particular, and at the same time the level of leukocytes in smears increases.
Bacterial urethritis, as the name implies, is an inflammatory disease in the urethra of an infectious nature.
When they occur, the number of leukocytes in smears from the urethra increases.
Tuberculosis damage to the genitourinary organs also leads to a significant increase in the number of leukocytes in smears from the urethra.
Cystitis is an inflammatory disease of the genitourinary tract and promotes an increase in the number of leukocytes in smears from the urethra.
From anterior and total urethritis, the number of leukocytes in the smear also increases.
Clinical forms
- Typical;
- Atypical;
- with macrosymptoms;
- with microsymptoms;
- Asymptomatic form;
It is very difficult to establish the real incidence of damage to the internal genital organs in both women and men, since in 25-40%, and according to some data, in 60% of patients, the disease occurs without subjective sensations. It can be assumed that this pathology occurs much more often than it is diagnosed.
With herpes of the internal genitalia there may be no complaints. Sometimes they note periodically appearing light mucous discharge from the urethra and vagina. During laboratory examination of smears of the cervical canal, vagina and urethra, an increased number of leukocytes is periodically noted (30-40 in the field of view of the urethral discharge, 200-250 or more in the field of view when examining smears from the vagina), indicating the presence of an inflammatory process.
The asymptomatic form of genital herpes of the internal genitalia (asymptomatic shedding of the virus) is characterized by the absence in patients of any complaints about the genital area, objective clinical data confirming inflammation. During a laboratory examination of the discharge of the urogenital tract, HSV is isolated, while in smears there are no signs of inflammation (leukocytosis). In 25-30% of men with idiopathic (when the cause of infertility is not clear) infertility, HSV is isolated from semen.
It is known that genital herpes, in 70-80% of cases, occurs in the form of a microbial association, in combination with chlamydia, urea-, mycoplasma, strepto-, staphylococci, fungal flora. It is possible that the genitals may be affected by HSV, gonococcus, treponema pallidum, and viral diseases transmitted through sexual contact, which indicates the need for a thorough examination of patients to exclude STIs and HIV infection.
What additional tests need to be taken if the level of leukocytes in urethral smears is elevated?
To obtain an informative and more reliable result, the level of leukocytes in a smear from the urethra must be confirmed by tests for the content of leukocytes in the blood and urine.
In the blood of adults, normal levels of leukocytes are considered to be four and a half to eleven thousand units per milliliter.
A drop of male urine normally contains no more than three white blood cells.
According to norms, women’s urine may contain them slightly higher, up to seven pieces per drop.
If there are seven to ten of them, then this is already bad.
And more than ten are already signs of obvious inflammation.
To clarify the suspicion of signs of inflammation in the genitourinary tract, it is considered necessary to conduct a urine test according to Nechiporenko.
For him, indicators of two thousand white blood cells contained in one milliliter of urine, or rather its sediment, are considered normal.
Effective antibiotic therapy for elevated levels of leukocytes in urethral smears
Fluoroquinolones and nitrofurans are considered effective antibiotics for the treatment of inflammatory diseases that lead to an increase in the level of leukocytes in smears.
They are also successfully treated with fosfomycin and trimethoprim.
Methods for determining the most effective antibiotics for treatment are being improved every day.
Based on these studies, conclusions are drawn about the most effective ones for each specific pathology.
The presence of pyelonephritis as the cause of an increased level of leukocytes in a smear from the urethra
With pyelonephritis, since this is an inflammatory disease, the level of leukocytes in a smear from the urethra, urine and blood also increases.
In general, with any inflammatory disease of the genitourinary organs, there may be an increase in the level of leukocytes in smears from the urethra, urine and blood.
The presence of pyuria is generally a very characteristic symptom of pyelonephritis.
A smear from the urethra may also contain not only an increased level of leukocytes, but also traces of pus.
The level of leukocytes in all liquid media with pyelonephritis increases significantly.
How do injuries to the organs of the urinary tract affect the level of leukocytes in urethral smears?
Traumatic injuries to the organs of the genitourinary system cause inflammatory reactions in them, which leads to an increase in the level of leukocytes in smears from the urethra, blood and urine.
Injuries to the MPS organs can also contribute to the occurrence of other inflammatory diseases, which also increase the level of leukocytes.
Thus, we realized that any inflammatory diseases, including those caused by sexually transmitted infections, lead to an increase in the level of leukocytes.
Clinical features of herpetic infection in women
Herpes of the urethra and bladder
Herpetic urethritis in women is subjectively manifested by pain and cramping at the beginning of urination, and a frequent urge to urinate. With herpetic cystitis, hematuria, pain at the end of urination, blood in the urine, and pain in the bladder area appear.
Herpetic cystitis
In a woman, the first and only sign of HSV infection may be in the genitourinary tract. It often occurs in the first 1-3 months after the start of sexual activity or a change of sexual partner.
Herpes of the anal area and rectum
The lesion in the anal area usually represents a recurrent fissure, which is often a reason for diagnostic errors. Such patients with an erroneous diagnosis of “anal fissure” end up with surgeons. The itchy form of herpes anus and herpetic lesions of hemorrhoids are also difficult to diagnose.
The list of diseases etiologically associated with HSV is constantly growing. According to the literature, in 3.6% of women suffering from treatment-resistant colpitis and cervical leukoplakia, HSV is one of the etiological factors of the disease. A new form of latent intrauterine HSV-II infection with localization of the pathological process in the glandular epithelium of the endometrium is described. It has been proven that HSV can cause the development of endometritis and salpingoophoritis.
The asymptomatic form of herpes of the internal genitalia is detected in 20-40% of women suffering from herpes of the buttocks and thighs. This important circumstance must be taken into account when planning pregnancy in women with this form of GC due to the existing likelihood of developing complications of HSV infection during pregnancy.
The etiopathogenetic role of HSV in cervical cancer has been established. The above emphasizes the growing etiological role of HSV in the structure of diseases of the pelvic organs in women.
Herpes and pregnancy
The prevalence of HSV among pregnant women in the United States is 22-36%, in Europe 14-19%. Viremia in women during pregnancy can cause fetal death, stillbirth, and premature birth. Herpes viruses cause up to 30% of spontaneous abortions in early pregnancy and over 50% of late miscarriages; they are second only to the rubella virus in terms of teratogenicity (the development of fetal deformities).
The most severe forms of neonatal herpes develop when a newborn is infected with the herpes simplex virus during childbirth. With primary herpes in the mother, from 30% to 80% of children are infected, with recurrent herpes – 3–5%. Infection of the fetus during delivery, if the mother had herpetic eruptions at the end of pregnancy, occurs in 50% of women with RGG; however, 60–80% of infected children develop encephalitis.
Treatment regimens for diseases with an increase in leukocytes in the smear
The diseases listed above are all treated differently.
But antibiotic therapy or antiviral therapy is almost always needed to suppress infectious agents.
Antiseptics are widely used for local treatment of urethritis and cystitis.
They reduce inflammatory reactions and help reduce the level of leukocytes in smears, blood and urine.
Pyelonephritis is treated with antibiotics and nitrofurans, as well as all kinds of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Urolithiasis is a metabolic disease.
But when stones appear in the kidneys, infectious agents settle on them, which cause inflammatory diseases in the body.
Treatment of genital herpes
INITIAL CONSULTATION
from 2,400 rub.
A pronounced therapeutic effect in more than 90% of patients during treatment is achieved thanks to:
- Decades of experience in treating recurrent herpes;
- An integrated approach to therapy;
- Individual selection of antiviral treatment (drugs and regimens) and immunomodulators;
- Experience with anti-relapse therapy;
Herpes can and should be treated
The result of treatment largely depends on the experience and skill of the doctor, as well as on the patient’s patience and careful compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. The treatment methods we use can significantly reduce the duration of treatment without losing the quality and effectiveness of therapy.
IT IS POSSIBLE, because the existing arsenal of antiviral and immune drugs allows us to solve many problems that arise in people suffering from recurrent forms (genitals, face, buttocks, and other rarer localizations). The correct methodological approach to examination and therapy will allow:
- quickly stop acute manifestations of the disease;
- carry out effective immunocorrection;
- reduce the frequency and intensity of clinical manifestations of subsequent relapses;
- significantly increase the duration of inter-relapse periods and achieve many months of clinical remission;
NECESSARY, because timely treatment is the prevention of the development of possible complications of herpetic infection:
- pain syndrome that develops when the nervous system is involved in the infectious process;
- spread of infection, when almost all organ systems can be involved in the infectious process;
- pathologies of pregnancy, fetus and newborn;
Your guarantee is our positive 18-year experience of working with patients suffering from severe complicated forms. We know almost everything about modern medications (imported and domestic) and existing treatment methods. We identify and eliminate the causes that led to the development of the disease.
Our employees (dermatovenereologists, obstetricians-gynecologists, urologists-andrologists) are the authors of methodological recommendations, textbooks and courses of lectures, which are used by doctors in Russia; take part in international trials on herpes problems.
Which doctor should you treat if you have an elevated level of leukocytes in urethral smears?
If the level of leukocytes in a smear from the urethra increases, then it is necessary to treat inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract by a urologist or nephrologist.

Women also need to consult a gynecologist.
If you make a timely and correct diagnosis and carry out adequate treatment, you can avoid serious complications and the level of leukocytes in the smear will return to normal.
The price and timing of treatment for inflammatory diseases depend on many factors.
They are determined not only by the diagnosis, but also by the duration of the disease, what complications it causes and the price of drugs and additional procedures.
And also the cost of treatment from the required specialist.
For example, treatment of urolithiasis comes down to frequent mechanical removal of stones from the kidneys or ureters.
Lipotripsy is performed both surgically and using, for example, a laser.
The operation itself, depending on the complexity of the stones being removed, in Moscow will cost at least forty thousand rubles.
Preparation for the procedure
As a rule, any procedure must be carefully prepared and taken seriously:
- Mandatory hygiene procedures. It is advisable to perform genital hygiene immediately before bed, but not before visiting a specialist. The use of hygiene products significantly distorts the obtained test result. If a man experiences heavy discharge from the genital organ, then genital hygiene is performed immediately before a visit to the urologist, but it is strictly forbidden to use alkali-containing detergents.
- If a procedure is prescribed - taking a smear, then strictly abstain from intimate life for two days;
- A week in advance, or better yet 10 days in advance, stop using medications prescribed by your doctor. This is especially true for medicines related to antibiotics. Taking medications can significantly distort the picture of the analysis results obtained;
- For a clear picture, a smear is performed only when the bladder is full. Therefore, two hours before the procedure, you should not urinate;
- Stop drinking alcoholic beverages in advance.
Prevention of inflammatory diseases of the urethra and other organs of the bladder
Prevention of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system consists, first of all, in eliminating or minimizing the possibility of contracting infectious diseases, including STIs, using condoms.

It is necessary to prevent overheating, hypothermia and the like.
You should also avoid drafts and adverse weather influences whenever possible.
Anything that helps reduce the body’s immune defense mechanisms increases the risk of getting inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
What tests should a sexual partner take if there is an increased level of leukocytes in urethral smears?
If an STD is detected, then the sexual partner needs to do the necessary testing to detect such an infection.
First of all, for very contagious infections - Trichomonas, gonococcus and mycoplasma.
They are often asymptomatic and the sexual partner may not even know that they are sick.
Testing for the presence of these infections must be carried out using the PCR method.
No earlier than three months after unprotected sex, it is necessary to donate blood for the presence of HIV infection, treponema pallidum and hepatitis B and C viruses.
Other sexually transmitted infections are not all classified as STIs and tests for their presence are not necessary.
It is advisable to repeat the HIV test six months after unprotected sex.
Since three months after unprotected sex, there may still be no specific antibodies.
Diagnosis of genital herpes
Laboratory diagnostic methods are fundamentally divided into two groups:
- isolation and identification of the herpes virus (on cell culture) or identification of the herpes simplex virus antigen from infected material (in immunofluorescence reaction, polymerase chain reaction “PCR”, etc.);
- detection of herpes-specific antibodies (IgM, IgG) in blood serum.
When diagnosing herpes, you must remember that:
- To reduce the likelihood of a false-negative diagnosis, especially with genital herpes and asymptomatic forms of the virus, it is necessary to examine the maximum number of samples from one patient (vaginal discharge, cervical canal, urethra, prostate juice, semen, urine), because the herpes virus is rarely detected simultaneously in all environments.
- If a herpetic infection is suspected, it is necessary to conduct multiple virological studies of the discharge of the genitourinary system in patients, because a negative result of a single virological test cannot completely exclude the diagnosis.
- The frequency of virus isolation in women largely depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. In more than 70% of patients suffering from herpes, the virus is released at the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
- Detection of specific immunoglobulins IgM in the absence of IgG or with a 4-fold increase in titers of specific IgG in paired blood sera obtained from a patient with an interval of 10-12 days indicates primary infection.
- The detection of specific immunoglobulins IgM against the background of IgG in the absence of a significant increase in IgG titers in paired sera indicates an exacerbation of chronic herpetic infection.
- Detection of IgG titers above average is an indication for additional examination of the patient and detection of herpes virus isolation in the media.