Chronic leukemia
With this type of disease, blood cells have time to grow, but cannot fully perform their functions.
A blood test shows the presence of a high number of white blood cells, but these cells cannot protect the child’s body from infections. After some time, there are so many granule cells that normal blood flow is disrupted. Symptoms of leukemia in children do not appear when it is chronic. This disease can be discovered completely by accident during a laboratory blood test for another disease.
Chronic leukemia stages have the following:
- Monoclonal. Only one clone of pathological cells is present. This phase can last quite a long time, for many years, and is characterized as benign.
- Polyclonal. At this stage, secondary clones appear. It is characterized by a fast flow. A large number of blasts are formed, and a crisis ensues. It is at this moment that more than eighty percent of patients die.
Diagnostics
A patient with symptoms resembling acute leukemia is prescribed:
- blood tests - general, biochemical, coagulogram;
- removal of bone marrow from the ilium or sternum, followed by cytochemical analysis, immunophenotyping, and morphological analysis of cells;
- puncture of bone marrow and cerebrospinal fluid for cytological and histological examination;
- instrumental studies of internal organs - ultrasound, radiography, CT, MRI to assess the extent of their damage by malignant cells;
- consultations with a neurologist, otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist and other specialists.
A little about the problem
Leukemia is a disease of the circulatory system. It is considered malignant. The reproduction and increase in leukocytes in the blood, bone marrow, and internal organs cannot be controlled. Initially, the tumor grows in the bone marrow, and then begins to “attack” the blood circulation.
As the disease progresses, it entails the appearance of other ailments associated with increased bleeding, internal hemorrhages, weakened immunity, and infectious complications.
In children, this disease is considered from the point of view of the mutation of healthy cells into pathological ones. Every day there are more and more of them. Patients may develop different types of deficiencies of some blood cells.
Symptoms
The first signs by which one can suspect the onset of the disease are the same for all its forms.
- Noticeable weight loss not associated with food restriction or exercise.
- Fatigue, deterioration in general health.
- Constant weakness, apathy, drowsiness.
- A feeling of heaviness after eating, often concentrated in the left hypochondrium and independent of the amount and calorie content of what was eaten.
- Frequent infectious diseases.
- Increased sweating, especially at night.
- Increased body temperature.
As malignant cells grow in the blood, the symptoms of acute leukemia become more pronounced.
- Pale skin, shortness of breath due to lack of oxygen carried by the blood, anemia.
- Frequent bleeding from the nose and gums, bruising on the skin and mucous membranes, in women - heavy periods.
- Dysfunction of the affected internal organs with its own specific manifestations.
- Severe pain in bones and joints.
- Increased size of the spleen and liver.
- Constant swelling of the hands and face.
Clinical signs are not differentiated in accordance with the classification of acute leukemia, so the form of the disease can only be determined using laboratory tests.
General blood analysis
A general analysis can determine the presence of many diseases, inflammations and abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs and body systems. If the picture of the main elements in the analysis does not change, then the body works without deviations or disturbances. The following elements are taken into account for diagnosis:
- An increased ESR is observed - this indicates the presence of possible pathologies. To confirm blood cancer, you need to compare other indicators.
- White blood cells may be higher than normal or lower. In acute or chronic leukemia, the level depends on the stage of the process and the form of the pathology. Acute leukemia is characterized by aggressive cell division, which is expressed in an increase in the rate from normal. In a preschool child and a teenager, there is often a difference in the readings of leukocyte levels.
- Identification of cells with different sizes indicates the presence of anisocytosis.
- With leukemia, platelets are reduced by 10-15 times (the norm is 180-320). The initial stage may show normal levels.
- A decrease in red blood cells to 1-2*109/l indicates an oncological process in the body. The cell is responsible for transporting oxygen to tissues and organs. A lack of transport provokes shortness of breath and headaches in humans. The malignant process at an early stage does not affect the number of red blood cells in the blood.
- Reticulocytes are the germ cells of red blood cells. A low rate is present at an early stage of the tumor.
- Hemoglobin decreases in later stages of the disease. A reading of 50 or 60 g/l is considered the main sign of leukemia. But for this, the doctor excludes the reasons for the decrease associated with other diseases - deficiency of vitamin B12 with iron and severe bleeding.
- The absence of basophils and eosinophils indicates the presence of oncology that has affected the body’s hematopoiesis.
Clinical analysis is carried out in the same way for patients, regardless of age. This type of diagnosis is a mandatory event in the anamnesis collection program. In children, acute leukemia is lymphoblastic in nature, in adults it is mainly myeloblastic. Chronic leukemia occurs in people over 45 years of age.
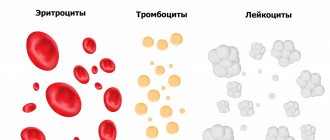
Leukocytes
White blood cells are cells responsible for protecting the body from infectious and viral substances in the body. During the disease, the shape and structure of leukocytes undergo changes that affect their functionality. The disease can increase or decrease the number of cells. A blood test with bone marrow puncture allows you to detect the extent of damage to the body.
- General blood analysis
Any changes in indicators indicate the presence of the disease. Lymphocytes are heterogeneous in structure and differ in appearance. Low or elevated levels (leukocytosis) not only with leukemia. This is possible during other diseases - internal inflammation or viral damage. There is an example of the course of the disease against the background of a normal number of lymphocytes. But the leukocyte system shifts towards agranulocytes or granulocytes. Granulocytes mainly increase during an infectious disease.
Platelets
Platelets in the blood circulation perform an important function - they stop bleeding. When a vessel is injured, the system quickly forms a blood clot to stop bleeding. Normally, they should be contained from 180 to 360 in men and women. Leukemia affects differently - an increase (thrombocytosis) or a decrease (thrombocytopenia) is possible. A dangerous diagnosis is thrombocytopenia - decreased clotting function (DIC syndrome).
A decrease in platelets is possible with leukemia, hepatitis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Increased levels occur with erythremia, cancer of the pancreas, and after surgery.
Platelets in the blood
Red blood cells and hemoglobin
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin to transport oxygen to human tissues and organs. The level of red blood cells depends on the amount of hemoglobin. Normally there should be 4-5*1012/l. In the last stages of leukemia, the rate drops to 1-2*1012/l.
A decrease in hemoglobin causes an acute state of anemia, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- You feel very tired and have decreased performance.
- The skin becomes dry and pale.
- Nail plates become brittle and thin, hair falls out.
- Light physical activity is accompanied by rapid heart rate and shortness of breath.
- There is a change in taste preferences.
- There are extraneous noises in the ears, attacks of nausea and dizziness.
- Unstable emotional background.
These symptoms worsen the patient’s condition, complicating the treatment process.
Hematocrit
Hematocrit is the ratio of red blood cell volume to plasma. The indicator is directly related to the number of red blood cells. The disease affects the entire hematopoietic composition.
Hematocrit helps detect the degree of anemia. The development of anemia reduces the amount to 25% and below. Severe blood loss with blood transfusion does not take into account hematocrit data due to the late reaction to the change of basic elements. You also need to take the test correctly, since the value changes depending on the position of the body.
ESR during illness
ESR is the value of the erythrocyte sedimentation process. The speed of this process is taken into account. Against the background of cancer, the picture does not look the same as in a normal state. Usually the speed increases. This is due to a disruption in the functioning of the immune system and the presence of a secondary infectious lesion. Based on this value, the doctor can understand the patient's condition.
- Detailed description of each sign of leukemia in adults
Device for blood ESR analysis
Leukocyte formula
Diagnosing a patient with leukemia also includes assessing the leukocyte count. It is not the number of leukocytes that is taken into account here, but it is important to identify a qualitative change. The quantity often remains unchanged, but there is a qualitative imbalance. The analysis shows mature and young forms, without the presence of intermediate forms.
Oncology provokes a decrease in reticulocytes. The peculiarity of the leukocyte picture depends on the type of leukemia - an increase or decrease is possible.
Analysis in children
Children are susceptible to acute forms of the disease. The age group at risk is from 2 to 5 years. In the chronic type, symptoms are often not detected, but the disease can be determined by the values of the main blood elements. The development of a malignant tumor can be recognized by the following signs:
- A sharp decrease in the level of hemoglobin with red blood cells;
- Red blood cells settle at a high rate;
- The number of reticulocytes decreases;
- Unstable leukocyte count;
- Platelets shift towards decrease.
Doctors recommend taking an annual blood test to determine the clinical picture and tumor markers.
Types of disease
Oncohematologists, depending on the nature of the cell pathology, distinguish two main types of acute blood leukemia.
- Lymphoblastic. Accounts for approximately 15-20% of cases. First, malignant cells affect the bone marrow, then spread to the lymph nodes, thymus gland and spleen, and then throughout the body. A characteristic feature is that mutated cells lack lipids, esterase, and peroxidase. It most often develops in children aged from one to six years and in adults after forty years. In turn, it is divided into two types: B-form with a favorable prognosis for a third of adults and two-thirds of sick children, and T-form with an extremely severe course and a sad outcome.
- Myeloblastic. The disease usually develops in adulthood and affects men and women equally. The treatment prospects are quite optimistic: partial remission can be achieved for 80% of patients, complete recovery occurs in at least 20%.
The full classification of acute leukemia includes many subtypes that differ in morphological, genetic and other characteristics that require specific treatment.
Stages of acute leukemia
There are only three of them:
- Initial stage. During this period, all biochemical blood parameters may be normal or slightly change. A slight weakness appears, chronic diseases, bacterial and viral infections return.
- Expanded stage. During this period, with a disease such as blood leukemia, the symptoms are pronounced. There are two options for getting out of this situation: there is an exacerbation of the disease or remission. During an exacerbation, a transition to the terminal stage occurs; during remission, it is necessary to wait time. Only after five years or more can we talk about a complete cure.
- Terminal stage. The hematopoietic system is completely suppressed, and there is a high probability of death.
Causes and risk factors
The etiological factors that inevitably become the “trigger” for malignant cell mutation have not yet been precisely established. However, the risks of developing acute leukemia increase significantly if:
- radiation exposure to which a person is exposed;
- infection with certain viruses that suppress the immune system (Epstein-Barr disease, T-lymphotropic virus, etc.);
- unfavorable heredity;
- smoking tobacco;
- prolonged exposure to certain chemical compounds, including medications;
- stress, depression;
- environmental pollution.
Treatment
Since the list of the most aggressive malignant diseases includes acute leukemia, treatment should begin immediately after diagnosis. The patient is placed in an oncohematology hospital in a ward with special ventilation to remove pathogenic microflora. The main method, as a rule, is chemotherapy, which is supported by transfusion of blood components, detoxification therapy, and prevention of infections. The treatment regimen consists of the main stages:
- induction of remission - exposure to chemotherapy that destroys blast cells in order to achieve the maximum possible remission;
- consolidation - consolidation of achieved results;
- prevention of relapse - preventing the return of the disease.
In certain forms of the disease, bone marrow stem cell transplantation, performed after destruction of blasts using chemotherapy and radiation therapy, has a good effect.
The first stage of treatment takes from 4 to 6 weeks, during which time the patient receives massive therapy. At the consolidation stage, two or three courses of treatment are carried out, after which maintenance measures continue for several years, which are necessary to prevent relapses. Complete remission is achieved when the clone of pathological cells is destroyed and the normal hematopoietic process is restored.
Rehabilitation
The list of clinical recommendations for acute leukemia during the rehabilitation period includes:
- measures to improve immunity;
- balanced diet;
- detoxification therapy;
- restoration of intestinal microflora;
- anti-stress psychotherapy;
- improving sleep quality.
During the recovery period, it is important to follow all the orders of the attending oncologist and complete the recommended treatment courses on time and in full.