There are people who are not only afraid to undergo diagnostics, but also to visit doctors in general. We usually delay visiting a medical professional for fear of identifying a dangerous disease. However, you should not postpone the appointment, because this will only worsen your health situation. Previously, there were a large number of myths about magnetic resonance imaging, which drove into people’s heads that diagnostics using such equipment was something scary. Those who did not know were afraid to undergo the scan because they thought they would have to lie in a closed booth for a long time without light in the presence of loud noise.
It is much more difficult for patients with claustrophobia to be examined. This condition is not considered an absolute contraindication to MRI, since the diagnostic value of testing justifies the discomfort during the session. The fear of doing tomography in children and adults is not considered a rare phenomenon in medical practice, but we will now tell you how to overcome it.
Briefly about MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is a highly informative diagnostic procedure that is performed non-invasively and does not cause pain in the patient. However, some people who are new to CT scans report fear that prevents them from relaxing and remaining still during the scan. During the preparatory period, the doctor explains to the patient how not to worry when diagnosing using closed-type equipment. In some cases, open-plan equipment is used, but not all clinics have such devices, and the quality of the results is inferior to the first type.
Electromagnetic tomography is performed without the use of radiological radiation, therefore it is absolutely safe for the patient’s health. Screening results can visualize hidden pathologies that did not even provoke symptoms in the patient. The images are issued in electronic or printed form with a detailed examination report. You can select medical centers in a specific area or near a specific metro station, find out the current prices for MRI and make an appointment at a discount remotely.
Why are patients afraid of MRI?
There are several main reasons why subjects are afraid of diagnosis. Let's look at each of them in detail.
Fear of noise from tomography equipment
Some patients, especially children, are frightened by the large size of the device and the loud sounds it creates. Progressive devices that are installed in the clinics presented on our service have a minimal noise level. This makes them as comfortable as possible for adults and children. The tomographs are equipped with light bulbs inside for good illumination. The patient always has the opportunity to contact the physician during the session.
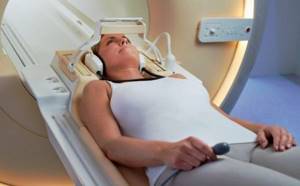
You can get rid of the noise arising from a functioning device using earplugs or headphones. Most tomography rooms have the ability to change the sound and light environment in the room. Patients who choose headphones will be able to listen to their favorite tracks directly during the diagnosis. To do this, provide the diagnostician with access to the virtual player so that the medical officer can play the selected playlist during the examination.
Fear of enclosed spaces
In some cases, patients experience discomfort from being confined inside the scanner. Screening is especially difficult for people suffering from:
- claustrophobia;
- panic attacks.
In such cases, it is worth choosing a medical center equipped with an open-type tomograph. In such a device, the patient will not have to fit into a narrow scanner tunnel, which will significantly reduce the load on the nervous system. The patient may ask the doctor to lie on his stomach during the screening. It is believed that in this position the discomfort goes away. Additionally, you can take sedatives to help you relax and not worry.
Fear of studying from the MRI machine
Patients who encounter magnetic resonance diagnostics for the first time mistakenly assume that MRI is a dangerous and harmful procedure. We hasten to reassure all alarmists - electromagnetic tomography is not capable of causing any harm to human health. MRI screening has been used by doctors around the world since the 1970s. During this time, millions of people completed the study:
- adults;
- children;
- babies;
- pregnant women.
Global science says that there is no negative impact on patient health from MRI. This is due to the fact that during screening the device operates without radiation exposure. Tomography is carried out not with ionizing rays, but by generating a magnetic field.
Fear of contrast
According to indications, to improve the quality of images and their detail, doctors prescribe MRI with an additional amplifier. The drug enters the patient's body intravenously before starting the device. In addition to the banal fear of an injection, which is quite realistic to endure, some subjects develop a fear of poisoning with a substance. There is no reason for the development of such a phobia.
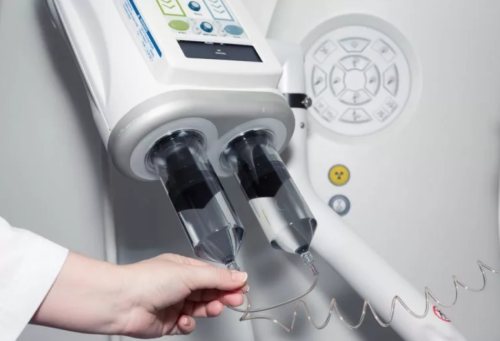
The contrast reagent is made from rare earth gadolinium salts. The composition is non-toxic. It is hypoallergenic and is quickly eliminated from the body. After scanning, the substance leaves the body through the urinary system after 24 hours. However, there are restrictions on who can receive the supplemental booster. Contrast is not prescribed to persons:
- with an allergy to the substance;
- with renal and liver failure;
- pregnant women.
High tech
In the first years of its use, magnetic resonance imaging was called differently: NMR imaging, from the words “nuclear magnetic resonance.” It was renamed after 1986, when, in connection with the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, people began to fear anything containing the word “nuclear” in the name.
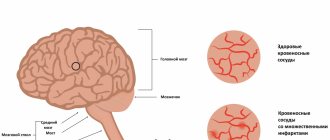
The principle, however, remains the same. It has nothing to do with radioactivity. The electromagnetic field that the tomograph generates affects the nuclei of hydrogen atoms present in any tissue of the human body. They generate a response signal, which is recorded by the device.
The nuclear magnetic resonance technique is used not only in medicine - it can be used to study the structure of almost any substance. But it was for its adaptation to the study of living organisms that American scientists Paul Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield received the Nobel Prize in 2003. The research itself that led to the creation of the tomograph was carried out in the late 1960s and early 1970s.
In science, it often happens that some idea is “in the air.” The use of nuclear magnetic resonance in medicine was explored at that time not only by Lauterbur and Mansfield. Back in 1960, the first prototype of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner was developed by Vladislav Aleksandrovich Ivanov, a graduate of the Leningrad Air Force Engineering Academy named after A.F. Mozhaisky. Unfortunately, the finalization of the device and the subsequent receipt of a patent took more than ten years, so Western scientists received an advantage in time - and therefore the laurels of discoverers.
How to get an MRI if you are afraid of confined spaces?
When booking a place at the diagnostic center, you must inform the operator about your fear of the examination and possible episodes of panic attack. In this case, the support center manager will suggest alternative ways to undergo a tomography scan with minimal discomfort.
You can undergo an MRI if you are afraid of closed spaces as follows:
- Choose an open or semi-open type tomograph instead of a closed one.
- Take a sedative before the procedure.
- Go for diagnostics with an accompanying person.
- In special cases, tomography is done under anesthesia or sedation.
Prepare yourself mentally for the examination, think about the good and put aside your worries. In the clinics on our list, the patient is in complete safety under the supervision of qualified diagnosticians. If there is the slightest discomfort or deterioration in well-being during the study, doctors will stop the session. No one will torture a sick person.
Which sedative should I choose?
Self-selection of sedatives before MRI screening is prohibited. The choice of medications is made by the attending physician, based on the diagnosis and clinical picture of the patient. Some sedatives affect the functioning of the heart, blood vessels, and nervous system, and also lead to pressure surges and can even distort diagnostic results. A number of drugs contribute to the formation of side effects and make it difficult to study abnormal reactions in the body. Such factors are taken into account when a patient is afraid to do an MRI of the head, legs, spine, and blood vessels.
If there is a pronounced fear of closed spaces, an unstable psycho-emotional state, as well as anxiety and the inability to use alternative diagnostic methods, premedication and tomography under anesthesia in a hospital are needed.
Every person has their own phobias, including the fear of closed spaces. try to find out the source of fear. Don’t let it influence your life, because even a routine diagnosis in such a situation becomes a sophisticated test. Before an MRI, prepare yourself for the procedure: take a relaxing bath, meditate, assess the situation sensibly and understand that the tomography is useful and will not harm you in any way.
Indications for MRI diagnostics
Neurology and neurosurgery:
- tumors of the brain and spinal cord;
- disorders of cerebral and spinal circulation;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- malformations of the brain and spine.
Traumatology and orthopedics:
- joint injuries and diseases (including arthritis);
- injuries and inflammatory diseases of the spine;
- osteochondrosis, tumors of bones and soft tissues.
Gynecology:
- pathology of the uterus and appendages (tumors, cysts, inflammatory diseases, dyshormonal conditions).
Urology:
- tumors of the bladder, prostate gland;
- inflammatory diseases of the bladder, prostate gland;
- urolithiasis disease.
Gastroenterology:
- tumors of the liver, pancreas, spleen;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- pancreatitis;
- cholelithiasis.
How to choose a clinic for MRI?
Use the search and information service to select a medical center based on specific criteria in a few minutes. The portal contains a list of clinics that perform magnetic resonance scanning using open and semi-open circuit devices, with and without contrast. Additionally, on the service you will find out the following information about specialized institutions in Moscow:
- rating;
- schedule;
- level of qualification of medical staff;
- price lists;
- stock;
- technical parameters of the equipment;
- visitor comments;
- information about the admission of children;
- photos.
Call the resource hotline for advice on issues of concern, clarification of the addresses of the nearest diagnostic organizations, as well as current prices for MRI. Registration for examination is open daily from 8 am to 12 midnight. To track your reservation, service news and bonus offers from partners, register in your personal account using your phone number.
How much to hang in a Tesla?
The magnetic field induction of the tomograph is measured in Tesla. The unit is named after the inventor Nikola Tesla, who clarified much about the nature of electricity and magnetism. The more Tesla markings a tomograph shows, the more powerful it is and the more detailed images it can provide. Typically in medicine, tomographs with induction from 0.2 to 3 Tesla are used; high power is not required. Still would! The magnetic field induction of sunspots is only 3 times higher.
- 0.23-0.35 Tesla (low-floor) - preliminary diagnostics only. For example, such a tomograph will be able to determine whether there is a tumor or not, but will provide almost no information about its structure;
- 1 Tesla (mid-field) - such a tomograph will not allow you to examine the smallest details, but it is quite enough to get a general idea of the location and severity of the damage.
- 1.5-3 Tesla (high-field) – visualization of small areas of tissue. Such a tomograph will help to find metastases and determine whether there is a pathological change in the tissue around the joint capsule or inside the mammary glands after the installation of implants.
Author: Svetlana Yastrebova Published: October 19, 2021