X-ray is a research method carried out to diagnose a particular disease, and also involves radiation exposure to the human body. The latter provokes special restrictions in terms of the frequency of such diagnostics.
Radiography is divided into overview, intended for the study of some significant system or part of the body in general, and targeted radiography, for a more detailed, extensive study of a structure or organ.
Indications
X-rays are usually performed according to indications such as:
- treatment control;
- checking for pathological conditions;
- making an accurate diagnosis.
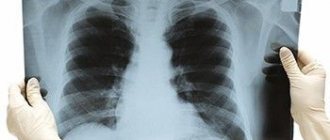
However, indications for radiography may vary depending on the part of the body or organ being examined. For example, when asked how often an X-ray of the lungs is done and when, we can say that it is necessary if pneumonia, pleurisy, bronchitis, tuberculosis or cancer are suspected. Also, this kind of diagnosis of the respiratory system is carried out for shortness of breath, dry cough of unknown etiology, pain in the back and chest area, general weakness and high temperature of an unexplained cause.
X-ray of the digestive system is prescribed to assess the large intestine and the patency of the small intestine, detect foreign bodies in the stomach, esophagus or intestines, exclude various gastrointestinal diseases, as well as prepare for surgery and much more. Speaking of the urinary system, here to study the ureter and kidneys, the urethra and the bladder itself. Musculoskeletal – for examining bones and joints, as well as recognizing deformations and injuries visible in the image, identifying fractures, detecting osteoporosis, dysplasia, dislocations, neoplasms and curvatures. Cardiovascular - for studying the heart and blood vessels, as well as if there is a suspicion of any disease of the corresponding system, with heart defects and impaired blood flow.
In general, studies that involve X-rays include fluorography, HSG (hysterosalpingography) and CT, densitometry and mammography.
3-D Dental Scanning
The advent of volumetric imaging (3-D scanning) has changed everything when it comes to the radiation dose in a 3D dental image. As we saw above, the real reason why the dose of X-rays has always been considered very low is that it is projected onto a small X-ray.
But 3D dental scanners use fan beam technology and their detectors are different from the technology used for hospital CT scanners. This provides some dose reduction compared to traditional CT machines, but many of the technical parameters are the same. It is difficult to directly calculate and compare the dose of dental 3-D scanners with traditional X-ray scanning in dental clinics.
It is important to train staff and inform them that low doses will change if a positioning error is detected or unusual anatomy is identified in the patient and unintended body parts are also irradiated during the scan.
It must be remembered that manufacturers of dental 3D scanners may take into account the salivary glands and other anatomical structures that are in the radiation field, but the lenses of the eye or the thyroid gland are usually not exposed to radiation.
The truth is that there's nothing magical about the X-rays used to create stunning 3D images in new dental scanners. Detectors have improved significantly over the years and require less radiation than in the past to reconstruct these 3D images.
Background radiation
The most common way dentists explain the dose from their x-rays to interested patients is by relating it to background radiation. If you just look at the numbers, you can say that one oral X-ray equals only 20 minutes of background radiation. At first glance this may seem correct, but it is not a direct comparison. One concentrated burst of X-ray radiation on a small area of skin in one tenth of a second is not the same as the entire body being bathed in a regular stream of radiation for 20 minutes. Technically it may be the same amount of radiation if it is listed as a dose in the table, but it is applied to the body differently.
Cancer risk
On the Visited Cancer website you can even enter the effective equivalent dose of radiation you receive from a dental examination and it will calculate it will give you the increased risk of cancer as a result of that examination. Because the risk calculation is based on the main biological effect of ionizing radiation.
No one really knows whether one small x-ray from a dental examination can be extrapolated to the whole body dose received by atomic bomb survivors.
Our discounts and promotions
What are the harms of radiography?
X-rays must pass through an organ, structure, or body of a person to produce the final image on film. They, penetrating every cell of the body, have a destructive effect, the degree of which depends on the duration and, of course, the power of the radiation itself. In addition, it is not perceived by our senses in the form of the skin, eyes and ears, nose and tongue, as well as the vestibular apparatus, which is, in fact, dangerous. But it is worth noting that this danger is often exaggerated.
Of course, ionizing radiation can provoke a temporary change in the composition of the blood, premature aging of cells, the resumption or emergence of pathological conditions, disruption of the normalization of the process of maturation and vital activity of cells, as well as changes in the structure of proteins. That is why, to the question of how often you can do an x-ray without harm, we will answer - no way, it is there, but still not as great as it seems. Moreover, different tissues of the body have different sensitivity to this radiation.

In which studies is the dose load higher?
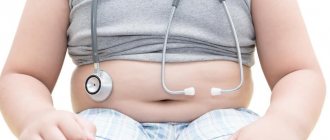
According to the doctor, during radiography, the volume of dose load is influenced by body parameters, for example, the state of a person’s fatty tissue. When examining the same organ, the dose load in an obese patient will be greater than in a slender one.
Also, the dose load varies with x-rays of different regions of the body. “When examining the abdominal organs, the volume of radiation that passes through the human body is greater than when examining the hand. In order for the X-ray beam to pass through the abdominal cavity and the diagnostician to obtain a result that will allow him to write a conclusion on the current clinical situation, a large load on the X-ray tube is needed,” explains Kharlamov.
How often can I have x-rays?
Adults and pregnant women
Apart from direct medical indications, for which X-rays can and sometimes need to be taken more often than required by usual preventive measures, it is worth carrying out such an examination as part of a periodic examination once a year. People working in the food sector or in direct contact with children should undergo a similar examination every six months. If you are wondering how often an adult can have an x-ray for serious illnesses that imply an exceptional need for x-rays (a complex form of pneumonia, for example, etc.), we note that the importance of doing this here can include 2-3 times a month. Sometimes, this is actually a forced and the only measure to assess the patient’s condition and the dynamics of therapy.
X-rays during pregnancy are, of course, very undesirable, but due to urgent need, for example, they are carried out. In this case, the stomach is protected by covering it with a special apron (lead).
For children
Before the age of 18, this type of x-ray examination is not recommended due to the influence of radiation and the still developing organism. In general, the younger the child, the greater the danger that such ionization by the corresponding rays will negatively affect the body. Therefore, children need such diagnostics only according to strict indications.
Note that for children, less powerful radiation is often used, and, if possible, the most gentle type of x-ray diagnostics is chosen.
Is it dangerous
X-rays are often prescribed not only at the diagnostic stage, but also during the treatment of arthrosis of the knee, hip or other joint. Many fear that radiation will harm the body and trigger irreversible processes in it, for example, the degeneration of cells into malignant ones, and weaken the already weak immunity of an elderly person. Is it possible to take x-rays often?
The harm from radiation on modern devices is minimal if all safety rules are followed. The dose of radiation is comparable to that which we receive daily from television or while flying on an airplane. Therefore, you should not refuse the examination if the doctor insists. The main thing is to take precautions.
How dangerous is x-ray and who is strictly contraindicated to undergo this examination? The answers are in the video below:
Preparation
Typically, preparation involves freeing the area of the body that will be examined from clothing, as well as removing other “obstacles” to the passage of rays such as bandages, tubes, patches, etc. In addition, it is important to remove all metal objects from yourself and provide protection for those areas that are not subject to study (due to a special apron). For examination of a specific system or organ, there are preparation measures, which the doctor who prescribed the procedure will tell you about.
Is it true that a visiograph is safer than a regular film photograph?
When asked about such a comparison, they mean the radiation exposure that the patient receives when using different techniques. In this sense, indeed, a visiograph is preferable, since its sensor is much more sensitive than the best film. Therefore, to obtain a high-quality image using a visiograph, much shorter shutter speeds are needed. To take a picture on film, the shutter speed is 0.5-1.2 seconds. To obtain the same image using a visiograph sensor – 0.05-0.3 sec. Those. 10 times shorter. As a result, the radiation exposure received by the patient when using a visiograph is reduced to an insignificant minimum.
Conclusion
In general, there is no such thing as “permissible radiation exposure.” X-rays are performed strictly for medical reasons, and as a preventive measure - only for adults. Of course, when it comes to a person’s life and the extreme need for this diagnostic procedure, it is carried out in the quantity required, including for children.
Today, modern radiologists and equipment are somewhat encouraging, because they provide a minimal dose of ions, compared, for example, with equipment of past decades. Also, this radiation exposure now becomes more accurate and allows you to study very specific selected areas.
Dental Imaging
Extraoral imaging allows the dentist to see a complete picture of the inside of the patient's mouth. Panoramic and 3D imaging assist in diagnosis, treatment planning and evaluation of certain dental conditions.

Dental systems using flat panel detectors have the advantage of providing highly detailed images for more accurate diagnosis. Modern high-speed, high-sensitivity flat panel detectors are an attractive option for dentists and are used for imaging in:
- Periodontal bone loss or disease detection
- Extraoral exams
- Planning a dental implant
- Visualization of abnormal teeth
- Jaw and face assessment
- Cleft palate assessment, dental cavity diagnosis
- Endodontic diagnostics, including root canals
- Diagnosis of dental trauma
And also offers beam computed tomography, also known as CBCT. Dental CBCT systems allow manufacturers to optimize their system to provide fast images while reducing radiation dose to patients. CBCT provides three-dimensional information and images compared to the two-dimensional image obtained with conventional x-ray images. 3D imaging can be especially useful in diagnosis, treatment planning, and evaluation of certain dental conditions.
Our discounts and promotions