Author
Kuibida Oleg Rostislavovich
Leading doctor
Candidate of Medical Sciences
Endoscopist
until September 30
We are giving 1000 rubles for all services for a visit in September More details All promotions
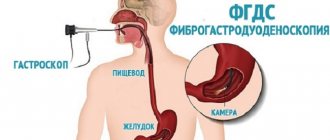
Gastroscopy
(full name -
esophagogastroduodenoscopy
, or
EGDS
) is an endoscopic examination of the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, duodenum.
Gastroscopy is performed using special endoscopic equipment - a gastroscope. A gastroscope is a long, thin and flexible tube with a lens at the end. Since the gastroscope uses optical fiber, it is also called fibrogastroscope, and research with its help is called fibrogastroscopy
(
FGS
). A gastroscope is inserted through the mouth. The image transmitted from the gastroscope lens can be significantly enlarged, and the endoscopist conducting the examination has the opportunity to observe on the monitor a detailed picture of the condition of the patient’s mucosa.
Why is gastroscopy needed?
Gastroscopy allows you to obtain detailed information about the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, identify foci of inflammation, detect ulcers, malignant formations and other lesions. No other instrumental diagnostic method (including ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging) provides such an accurate picture of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroscopy provides the doctor with the opportunity to see the situation with his own eyes, which allows him to make a diagnosis and prescribe the most effective course of treatment.
How to check your stomach using Gastropanel
Indicators determined using Gastropanel
The test panel provides a simple and reliable way to obtain information about the structure and function of the gastric mucosa. The following parameters are determined in the blood on an empty stomach:
- Pepsinogen I, Pepsinogen II and their ratio,
- Gastrin-17 and stimulated Gastrin-17,
- antibodies to gastric parietal cells,
- antibodies to Helicobacter pylori IgG and IgA.
Blood Test Panel Helps Answer Questions
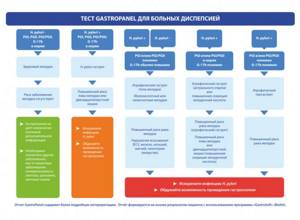
- does the patient suffer from gastritis caused by Helicobacter pylori,
- Is gastritis atrophic and in which part of the stomach are these changes localized?
- whether the patient is at risk of developing peptic ulcers or stomach cancer,
- Is it necessary to do a mandatory esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsy,
- whether there is autoimmune atrophic gastritis with damage to the body of the stomach, which determines a high risk of disorders associated with vitamin B12.
Indications for gastroscopy
Gastroscopy is usually prescribed in the following cases:
- for any diseases of the esophagus, stomach and intestines (including gastritis, peptic ulcers, polyps, tumors) for the purpose of differentiated diagnosis;
- for gastrointestinal bleeding (in order to establish their cause and location);
- in case of impossibility or insufficient information content of an x-ray examination;
- if it is necessary to study the condition of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract (this need may arise in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of some other organs and systems)
There are also a number of contraindications to gastroscopy. Therefore, a referral for gastroscopy should be written by the attending physician who has a complete picture of the patient’s health status.
What does the algorithm for identifying stomach diseases include:
- Clinical examination of the patient (history, heredity, clinical and laboratory data).
- Study of gastric juice acidity:
- 2-hour or 24-hour pH-metry,
- pH-metry during endoscopy,
- pharmacological test or blood test in the test panel.
- Test panel (Gastropanel) or “serum biopsy” (blood test). I’ll tell you more about it below.
- X-ray examination of the stomach (if indicated).
- Endoscopic examination of the stomach and duodenum (esophagogstroduodenoscopy, endoscopy) - detection of erosive and ulcerative process, polyps, inflammation, tumor formations.
- Determination of infection with Helicobacter pylori:
- Helpil test (express test) performed during esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGDS),
- blood test for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori in Ig G and Ig A.
- Helicobacter antigen in stool analysis.
- Blood test for homocysteine. Homocysteine is an early marker of cellular functional deficiency of vitamins B12, B6 and folic acid, as a consequence of the development of atrophic gastritis. When donating blood for homocysteine, you should give up protein foods, vitamins, and hormonal contraceptives for 1 day.
How is gastroscopy performed? Gastroscopy in a dream
Gastroscopy can be performed under local anesthesia, as well as in a state of medicated sleep. Drug-induced sleep should be distinguished from general anesthesia.
If the procedure is performed under local anesthesia, gastroscopy lasts 5-10 minutes. The patient is asked to hold the mouthpiece through which the gastroscope is inserted.
For those who are wary of this procedure, the doctors at Family Doctor recommend using the “sleep gastroscopy” service. This service is provided in a surgical hospital setting. Abroad (in Europe, Israel, the USA, Japan), gastroscopy during medicated sleep is the basic version of the procedure, which is abandoned only if there are contraindications.
To perform gastroscopy in your sleep, it is advisable to approach 30 minutes before the time for which the procedure is scheduled. In this case, you must have a fresh and deciphered electrocardiogram on hand. You will be examined by an anesthesiologist who will determine whether there are any contraindications to the study. To put you to sleep, the drug “Proviv” is used, which is administered under the supervision of an anesthesiologist. When the drug is administered, the patient falls asleep and wakes up almost immediately after the end of the administration. After 15-20 minutes, complete recovery occurs, however, the doctors at “Family Doctor” still recommend staying under the supervision of a doctor for another hour or two, which can be done in our comfortable hospital. It is considered acceptable to drive a car two hours after waking up from sleep, but it is better to drive no earlier than 6 hours later.
During the study, it may be necessary to carry out therapeutic and diagnostic manipulations (biopsy - taking a tissue element for laboratory analysis, removal of polyps, etc.). Similar manipulations are carried out during the study using a gastroscope. The biopsy material is sent to the Family Doctor’s own laboratory, which significantly speeds up the process of obtaining results.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound examination makes it possible to determine anatomical and histological changes in the esophageal tube. It is prescribed during the study:
- hiatal hernia
- suspicion of the development of neoplasms;
- achalasia of the cardinal sphincter;
- esophagitis;
- developmental anomalies of the esophageal tube;
- diverticulum.
Since pathologies are often combined with pathologies of the stomach, examination of these organs is carried out simultaneously.
To prepare for the study, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that cause gas formation in the stomach. The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach, the last meal should be no later than 19 hours on the eve of the ultrasound.
The ultrasound procedure is selected by a specialist individually for the patient, taking into account the data of the clinical study, previously performed diagnostic procedures and the anatomical characteristics of the patient.
This could be an ultrasound:
- percutaneous;
- intraesophageal;
- with water-siphon sample;
- endosonoscopy.

Before the study, the patient is informed about the method, features of its implementation and effectiveness.
Ultrasound establishes:
- erosions and ulcerative lesions of the walls of the esophageal tube;
- the condition of the organ mucosa to confirm or exclude the presence of esophagitis;
- exact location of polyps ;
- presence of gastroduodenitis ;
- degree of effectiveness of the treatment.
When is pediatric gastroscopy and FGDS needed?
The technique is quite stressful for children, so it is routinely carried out only for certain indications, which include:
- pain when swallowing;
- vomiting with blood or bile;
- the appearance of blood in the stool;
- periodic abdominal pain;
- frequent heartburn and belching;
- pathological reflux (regurgitation) in infants;
- poor appetite;
- pain after eating;
- previously identified gastrointestinal pathologies.
Emergency reasons for gastroscopy of the stomach in children may be life-threatening conditions:
- bleeding from the upper digestive tract;
- suspected life-threatening congenital malformations;
- child ingestion of dangerous objects or suspicion of it.
How to prepare for research
Before gastric endoscopy, the child must be properly prepared so that the examination is as informative and comfortable as possible. A special diet is not required, but 2-3 days before the test it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that take a long time to digest and increase gas formation. Gastroscopy of the stomach for children is usually done in the morning, before breakfast and strictly on an empty stomach. Infants can be given some clean water or breast milk, but not less than 2 hours before the test.
An important point: children who will be examined under local anesthesia must be told what the doctor will do and how, how long they need to wait and why this is important. Preliminary psychological preparation and parental support are the key to the comfort and tranquility of the little patient.
You don’t need to take anything with you to gastroscopy; the only thing you can take for your child is your favorite toys or books to keep your baby occupied while he is under the supervision of doctors after the procedure.
Before endoscopy, your doctor may prescribe:
- general blood analysis;
- blood clotting test;
- group and Rh factor;
- analysis for the hospital group and ECG during the procedure under sedation.
Rehabilitation after gastroscopy
The first meal after an endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract is possible after 1.5–2 hours. It is advisable to give your child warm, liquid and soft foods that are easier to swallow and do not require long chewing. Experts recommend feeding children more often, but in smaller portions, for 2-3 days after the procedure, and be sure to actively drink clean water or other safe drinks.
For the first few days after the procedure, you will have to limit outdoor games, running, jumping and other physical exercises. There are no other special rules of behavior, but the doctor will give individual nutritional recommendations or prescribe supportive drug therapy.
Endoscopy of the stomach: an informative method for studying the gastrointestinal tract - MEDSI
Table of contents
- Key points of the procedure
- What can be seen during gastrointestinal endoscopy
- Preparing for endoscopy
- Indications and contraindications
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
An endoscopic examination
is a type of examination that involves inserting a specialized device (endoscope) into the patient’s body to examine organs from the inside. Modern endoscopes can be equipped with a video camera as well as an ultrasound sensor.
For endoscopic examination of the esophagus and stomach, the device is usually inserted through the patient's mouth. To examine other organs of the gastrointestinal tract, an endoscope can be inserted through the rectum.
Key points of the procedure
Endoscopic examination of the esophagus and organs of the upper segment of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out as follows:
- The patient lies on his left side on the couch and pulls his right leg bent at the knee towards his stomach
- The tube of the device is slowly inserted into the esophagus
- At the right moments, the doctor will inform the patient about the need to perform swallowing movements
- The specialist examines tissues, mucous membranes and blood vessels for damage, pathologies, and foci of infection.
- If necessary, tissue samples can be taken for laboratory testing
- After the examination, the doctor carefully removes the device
- The patient is recommended to spend about one and a half hours in a horizontal position
When inserting the endoscope, it is important that it does not touch the trachea. Otherwise, the patient may start coughing, and all manipulations will have to be repeated again.
The procedure itself is painless, but discomfort and discomfort may occur during the insertion of the device tube.
For a more accurate diagnosis, in addition to a biopsy, photography and video can be used, the results of which the doctor can subsequently examine in more detail.
The total duration of endoscopy is about 5 minutes.
What can be seen during gastrointestinal endoscopy
Endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract allows us to determine the presence of diseases, pathologies and injuries, as well as the degree of their development and prevalence. This examination is more informative for identifying problems at an early stage.
The examination shows the following violations:
- Ulcer and erosion
- Neoplasm (benign and malignant)
- Excessive wall thickening and polyp formation
- Inflammation of the mucous membranes
- Incorrect functioning of blood vessels in the walls of organs
Due to the close location of the gastrointestinal tract organs, a disease or other pathology can spread throughout all of them in a short time. Therefore, the doctor conducts a comprehensive examination using various methods. This approach avoids complications.
Preparing for endoscopy
- You should tell your doctor in advance if you have any allergies to medications.
- The day before the procedure, you must stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
- 10 hours before the test – stop eating
- During the remaining time, you can drink still water in small quantities.
- Half an hour before the test, the patient is given the necessary medications.
- Sedatives may be used if the patient is overly nervous
- If the patient has severe sensitivity, local anesthesia may be used
The doctor also tells you in advance what the procedure is, how it will happen, and what the patient should do.
Indications and contraindications
Endoscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out for the following indications:
- Detection of inflammation of the mucous membrane and other tissues, as well as its localization
- Determining the location of a foreign body
- The need to remove polyps in the gastrointestinal tract
- Detection of ulcers, gastritis, colitis, etc.
- Finding and treating the site of blood vessel damage (if bleeding is present)
- Carrying out a biopsy of tissues that show signs of malignant cells
- Determining the cause of food obstruction in the stomach
- Inspection of tissues previously damaged due to disease for the presence of adhesions, scars, etc.
- Identifying the causes of anemia
- Monitoring the effectiveness of therapy
There are two types of contraindications to gastrointestinal endoscopy: in the first case, such a study is strictly prohibited, but in the second, it is allowed with the utmost caution.
Absolute contraindications to the procedure:
- Previous stroke or heart attack
- Heart or pulmonary failure (grade I or II)
- Pathological narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus
- Varicose veins in the walls of the esophagus or stomach
- Atherosclerosis
- Atony, weakness
- Hemorrhagic diathesis
- Excessive body weight
- Mental illness
Endoscopic examination of the esophagus and stomach is used with caution in the following cases:
- Presence of an inflamed larynx, tonsils, or pharyngeal tissue
- Chronic asthma
- Angina pectoris due to stage III hypertension
- Probability of perforation of peptic ulcer in the acute stage
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- Clinic specialists use modern equipment - video endoscopic systems and instruments from the Japanese company Olympus and the German Xion, which allows them to make the diagnosis most accurately
- Application of various types of endo-procedures: polypectomy, chromoendoscopic and histological studies
- If necessary, doctors of related profiles are involved in making a diagnosis
- To schedule a consultation, call 24/7 8 (495) 7-800-500
- There are more than 20 MEDSI clinics located in Moscow and the region
Do not delay treatment, consult a doctor now:
- Endoscopy
- Endoscopy Center at the CDC on Krasnaya Presnya
- Treatment of gastric ulcer
- Treatment of gastrointestinal diseases