Participation of uric acid in purine metabolism
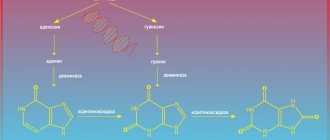
Purines are the main components of important amino acids from which DNA molecules are synthesized. As a result of purine metabolism, uric acid is obtained. After cell destruction, purine bases are degraded. With the blood flow, breakdown products enter the liver, where they are converted into uric acid crystals under the influence of enzymes.
It is excreted from the body in 2 ways:
- A small part is disposed of through the gastrointestinal tract with its other contents.
- The main part of urates (crystals) undergo filtration in the renal tubules and are then excreted from the body through the urinary system.
Previously, physiologists believed that the presence of uric acid in the body was useless, and an excess completely poisoned the body.
Today it is known that the functions of uric acid crystals are:
- Antioxidant. Forms non-toxic compounds by binding free radicals, then such compounds are removed from the body.
- Central nervous system stimulant. Takes part in the synthesis of adrenaline and norepinephrine. Increases the period of exposure of nerve fibers to these hormones.
The norm is the constant presence of uric acid crystals in the blood. Any deviations from the norm are a reason to do an examination and consult a doctor.
Please note that uric acid and urea are completely different substances that should not be confused.
Serum uric acid
Uric acid is a breakdown product of nucleic acids and purine bases under the influence of enzymes. Most of it is excreted into the gastrointestinal tract, and a smaller part is eliminated through the kidneys in the urine.
Synonyms Russian
Purine-2,6,8-trione, product of purine base metabolism, trihydroxypurine, 2,6,8-trioxypurine, heterocyclic urea ureide.
English synonyms
Uric acid, UA, Uric A.
Research method
Colorimetric photometric method.
Units
μmol/L (micromoles per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Uric acid is a product of the catabolism of purine bases, which are part of the DNA and RNA of all cells of the body. Purines appear mainly after natural cell death, and a smaller part of them comes from food (liver, red meat, legumes, fish) and liquids (beer, wine). Uric acid is transported in the blood from the liver (where the enzyme xanthine oxidase interacts with it) to the kidneys, where about 70% of it is filtered and excreted in the urine, the rest enters the gastrointestinal tract and is eliminated in the stool.
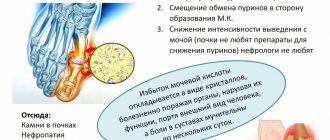
If too much uric acid is produced or not enough is excreted in the urine, it accumulates in the body, resulting in high concentrations in the blood (hyperuricemia). Persistently elevated levels of uric acid can cause gout, an inflammation of the joints in which uric acid crystals are deposited in the joint (synovial) fluid. In addition, the deposition of urate and the formation of stones in the urinary system are also a consequence of high levels of uric acid in the blood.
Elevated uric acid levels may be caused by increased cell death (due to cancer therapy) or less commonly by an innate tendency to overproduce uric acid. Insufficient excretion of uric acid usually results from decreased kidney function when kidneys are damaged. In many cases, the exact cause of excess uric acid accumulation remains unknown.
Accelerated processes of cell death, as well as a decrease in the rate of excretion of uric acid by the kidneys, cause hyperuricemia - an increase in the concentration of uric acid in the blood. As a result, it is deposited in the joints and soft tissues, and inflammation spreads to intra-articular urate crystals. In addition, stones form in the urinary system.
What is the research used for?
- For the diagnosis of gout.
- For periodic monitoring of people undergoing radiation and chemotherapy, frequent cell death with these types of treatments can lead to increased concentrations of uric acid.
When is the study scheduled?
- If you suspect gout (the main symptom is pain in the joints, most often in the big toe).
- During antitumor therapy.
- When monitoring the results of gout treatment.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Floor | Reference values |
| Male | 202.3 - 416.5 µmol/l |
| Female | 142.8 - 339.2 µmol/l |
Causes of elevated uric acid levels
The most common mechanisms for the development of hyperuricemia:
1) frequent death of a large number of cells and their no less intensive renewal (in this case, there is an active exchange of genetic information, and therefore nucleic acids, the degradation products of which are nitrogenous bases, and then uric acid, which is formed in large quantities),
2) a decrease in the rate of filtration and excretion of uric acid by the kidneys.
Based on this, the main reasons for increased uric acid levels are:
- malignant neoplasms with metastases, multiple myeloma, leukemia - almost all oncological diseases are characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and division,
- radiation and chemotherapy of neoplastic processes in the body,
- chronic renal failure.
Other less common causes of elevated uric acid levels include:
- acute heart failure,
- hemolytic and sickle cell anemia,
- hypoparathyroidism,
- hypothyroidism,
- diabetic ketoacidosis,
- hyperlipidemia, obesity,
- exacerbation of psoriasis,
- lead poisoning,
- Down Syndrome,
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
Causes of low uric acid levels:
- liver disease (impaired uric acid metabolism due to deficiency or decreased enzyme activity),
- Fanconi syndrome (decreased tubular reabsorption of uric acid due to a defect in the development of renal tubules),
- toxicosis,
- alcoholism,
- Wilson-Konovalov disease,
- xanthinuria (little uric acid is formed due to deficiency of the enzyme xanthine oxidase),
- syndrome of pathological secretion of antidiuretic hormone.
What can influence the result?
- Falsely elevated readings can be caused by: stress, intense physical activity and a diet rich in purines,
- anabolic steroids, nicotinic acid, epinephrine, thiazide diuretics, beta-blockers, furosemide (table), ethacrynic acid (table), caffeine, vitamin C, cyclosporine, cisplatin, small doses of acetylsalicylic acid, calcitriol, asparginase, clopidogrel, diclofenac, isoniazid, ethambutol, ibuprofen, indomethacin, piroxicam.
- low purine diet, coffee and tea,
Important Notes
- People with gout and/or urolithiasis should avoid foods high in purine (meat, fish, mushrooms, etc.). It is worth significantly limiting your alcohol intake, because it slows down the removal of uric acid from the body.
- The results of a test for uric acid in the blood cannot serve as a 100% basis for making a diagnosis of gout.
- Normally, one third of all uric acid is processed by bacteria of the intestinal biocenosis.
- During pregnancy, an increase in uric acid levels is an alarming sign of the possible development of preeclampsia and eclampsia in the near future.
- High levels of uric acid in the blood do not always lead to severe symptoms; in 10% of adults, hyperuricemia is asymptomatic. People with a family history of gout, stones, or kidney damage should be prevented for these diseases even though they have no symptoms.
- Some studies show that too much uric acid increases the risk of heart disease. It is believed that this plays a role in the course of diabetes, in the deterioration of lipid metabolism, increased blood pressure and increases the likelihood of stroke and eclampsia. But the immediate consequences of hyperuricemia are 2 conditions: gout and urolithiasis.
Also recommended
- Uric acid in daily urine
- Urea in the blood
- Creatinine in blood
- Urea in urine
- Creatinine in urine
Who orders the study?
Therapist, rheumatologist, gynecologist, hepatologist, oncologist, nephrologist.
What is the normal level of uric acid?
In many ways, standard norms depend on the gender and age of the subject. Concentrations are known to be lowest in adolescents and children. Further, during the development and growth of the body, the level of expended resources increases, and all the synthesized protein is spent on the formation of the skeleton and muscles.
The female body does not synthesize a lot of protein, and, therefore, there is a small amount of protein breakdown products in the blood. An exception may be women who play sports or whose work requires a lot of physical activity.
Men are the most active, so the highest concentration of urates is found in their blood. Protein metabolism in the male body occurs much faster and more intensely due to more developed muscle mass.
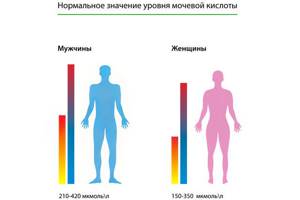
| Age and gender | Concentration (µm/l) |
| Children | 120-320 |
| Men | 210-420 |
| Women | 150-350 |
| Over 90 years old | 130-460 |
These indicators are considered the physiological norm. It should also be noted that changing your usual lifestyle may affect changes in the amount of uric acid. Hypouricemia is a state of reduced concentration of crystals, diagnosed by taking special tests.
How to determine the exact level of uric acid?
A biochemical blood test will show the level of uric acid in the blood; it is carried out both for healthy people, for possible detection of diseases, and for people suffering from metabolic disorders - urolithiasis, diabetes, gout, etc.
There are certain recommendations for obtaining an accurate analysis result:
- Eliminate all high-protein foods from your diet 8 hours before the test.
- Do not drink alcohol or take medications the day before the collection.
- Blood is drawn on an empty stomach.
- Avoid physical activity the day before the test.
Blood is taken from a vein. Most often, the result is ready the next day. If the result is reduced, a repeat analysis is prescribed. After confirming the deviation from the norm, the doctor prescribes a full examination and, based on its results, makes a diagnosis.
Factors that may affect the result of the analysis:
- Taking diuretics:
- Hormonal drugs
- Diet with minimal protein content.
Before the study, it is imperative to exclude such factors.
Uric acid in daily urine
Uric acid in urine is uric acid from the blood filtered through the kidneys.
Synonyms Russian
Purine-2,6,8-trione, product of purine base metabolism, trihydroxypurine, 2,6,8-trioxypurine, heterocyclic urea ureide.
English synonyms
Urine Uric Acid, Urine Uric Acid Quantitative (24-Hour), Uric Acid in urine.
Research method
Enzymatic method (uricase).
Units
mmol/day (millimoles per day).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Daily urine.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate alcohol from your diet the day before donating urine.
- Do not eat spicy, salty foods, or foods that change the color of urine (for example, beets, carrots) for 12 hours before the test.
- Do not take diuretics 2 days before the test (as agreed with your doctor).
- Avoid physical and emotional stress during the collection of daily urine (during the day).
General information about the study
Uric acid is formed as a result of cell renewal and also enters the body with food. Most of it leaves the body in urine, less in stool. With excessive formation of uric acid, its concentration in the urine can increase significantly, and if the kidneys are unable to filter blood in normal volumes, it can decrease.
Consistently high levels of uric acid cause the formation of uric acid crystals in the joint cavity. This painful pathological condition is called gout. If left untreated, uric acid crystals inside joints and adjacent tissues can form deposits that appear as hard bumps on the surface of the body.
Persistently high levels of uric acid in the urine can lead to stone formation.
Uric acid, which is dissolved in the blood, is delivered to the kidneys, where, after filtration, it is excreted in the urine. If the body produces too much uric acid over a long period of time or does not eliminate it well enough, a person may experience problems urinating, fever, chills, fatigue, and joint pain.
A condition in which the level of uric acid in the urine is elevated is called hyperuricosuria. This can cause kidney stones to form, blocking the normal flow of urine in the kidney tubules, ureter, and bladder.
What is the research used for?
- To assess uric acid metabolism.
- To identify disorders affecting uric acid production.
- To determine the severity of kidney damage.
When is the study scheduled?
- If necessary, find out the cause of the formation of kidney stones.
- When monitoring the condition of patients with gout.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 1.48 - 4.43 mmol/day.
Causes of increased concentration of uric acid in urine:
- eating large amounts of food rich in purine bases (meat, especially offal),
- gout (increased production or insufficient excretion of uric acid),
- urolithiasis disease,
- polycythemia vera (excessive production of blood cells),
- Lösch–Nyhan syndrome (increased uric acid synthesis),
- Wilson–Konovalov disease,
- viral hepatitis,
- sickle cell anemia,
- malignant neoplasms with metastases, multiple myeloma, chronic myeloid leukemia (uncontrolled cell growth and division),
- Fanconi syndrome (decreased tubular reabsorption of uric acid due to a defect in tubular development).
Reasons for low concentration of uric acid in urine:
- chronic kidney diseases, such as chronic glomerulonephritis,
- xanthinuria (little uric acid is formed due to xanthine oxidase deficiency),
- lead intoxication (due to a pronounced decrease in kidney function),
- chronic alcoholism,
- folic acid deficiency.
What can influence the result?
Falsely inflated results are contributed to by:
- stress and intense physical activity,
- injuries,
- beta-blockers, caffeine, vitamin C, large doses of acetylsalicylic acid, calcitriol, asparaginase, diclofenac, isoniazid, ibuprofen, indomethacin, piroxicam, paracetamol, lithium salts, mannitol, mercaptopurine, methotrexate, nifedipine, prednisolone, verapamil.
A falsely low result can be caused by:
- allopurinol, glucocorticoids, imuran, contrast agents, vinblastine, azathioprine, methotrexate, spironolactone, insulin, small doses of acetylsalicylic acid, furosemide, ethambutol, pyrazinamide.
Important Notes
- 20-25% of people with nephrolithiasis develop hyperuricosuria.
Also recommended
- Serum uric acid
- Urea in serum
- Serum creatinine
- Urea in urine
- Creatinine in urine
Who orders the study?
Therapist, rheumatologist, gynecologist, hepatologist, oncologist, nephrologist.
Causes of decreased uric acid
If uric acid in the blood is low, then they speak of hypouricemia. The following main reasons for the decrease in uric acid concentration levels are identified:
- Fanconi syndrome - absorption of the renal tubules is impaired, the disease is congenital
- Hepatocerebral dystrophy is an inherited pathology characterized by problems with the metabolism of microelements (copper in particular). The central nervous system and liver are the first to be affected.
- Acquired xanthine oxidase deficiency. The main cause of the disease is impaired liver function, medications containing the substance allopurinol. The production of enzymes responsible for acid synthesis is affected by the active substance of the drug.
- Hereditary deficiency of xanthine oxidase - the body cannot synthesize uric acid on its own. It is less common than the acquired one.
- Alcoholism.
- Poor nutrition.
Often, a decrease in the concentration of crystals is observed in women expecting a child. This is due to an increase in the amount of blood in pregnant women. And the concentration of cells and dissolved minerals decreases. Another reason is an increase in estrogen, which affects the formation of acid crystals.
Uric acid

Uric acid is a breakdown product of nucleic acids and purine bases under the influence of enzymes. Most of it is excreted into the gastrointestinal tract, and a smaller part is eliminated through the kidneys in the urine.
Research method
Colorimetric photometric method.
Units
μmol/L (micromoles per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood.
General information about the study
Uric acid is a product of the catabolism of purine bases, which are part of the DNA and RNA of all cells of the body. Purines appear mainly after natural cell death, and a smaller part comes from food. Uric acid is transported by the blood from the liver to the kidneys, where about 70% of it is filtered and excreted in the urine; the remainder enters the gastrointestinal tract and is eliminated in the stool.
If too much uric acid is produced or not enough is excreted in the urine, it accumulates in the body, resulting in high concentrations in the blood (hyperuricemia). Persistently elevated levels of uric acid can cause gout, an inflammation of the joints in which uric acid crystals are deposited in the joint (synovial) fluid. In addition, urate deposition and the formation of stones in the urinary system are also a consequence of high levels of uric acid in the blood.
What is the research used for?
For the diagnosis of gout.
- For periodic monitoring of the condition of people undergoing radiation and chemotherapy.
What do the results mean?
| Floor | Reference values |
| Male | 202.3 - 416.5 µmol/l |
| Female | 142.8 - 339.2 µmol/l |
Causes of elevated uric acid levels
The most common mechanisms for the development of hyperuricemia:
1) frequent death of a large number of cells and their no less intense renewal,
2) a decrease in the rate of filtration and excretion of uric acid by the kidneys.
Based on this, the main reasons for increased uric acid levels are:
- malignant neoplasms with metastases, multiple myeloma, leukemia - almost all oncological diseases are characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and division,
- radiation and chemotherapy of neoplastic processes in the body,
- chronic renal failure.
- acute heart failure,
- hemolytic and sickle cell anemia,
- hypoparathyroidism,
- hypothyroidism,
- diabetic ketoacidosis,
- hyperlipidemia, obesity,
- exacerbation of psoriasis,
- lead poisoning,
- Down Syndrome,
Causes of low uric acid levels:
- liver diseases,
- toxicosis,
- alcoholism,
- Wilson-Konovalov disease,
- syndrome of pathological secretion of antidiuretic hormone.
Important Notes
- People with gout and/or urolithiasis should avoid foods high in purine (meat, fish, mushrooms, etc.). It is worth significantly limiting your alcohol intake, because it slows down the removal of uric acid from the body.
- The results of a test for uric acid in the blood cannot serve as a 100% basis for making a diagnosis of gout.
- During pregnancy, an increase in uric acid levels is an alarming sign of the possible development of preeclampsia and eclampsia in the near future.
What is dangerous about low uric acid in the blood?
Sufficient levels of uric acid are important for normal metabolism. A low acid level over a long period of time negatively affects the entire condition of the human body. Urates are antioxidants that bind free radicals. In case of metabolic disorders, there is a possibility of poisoning by decay products.
In addition, uric acid directly affects the functioning of the central nervous system; it controls the period of influence of norepinephrine and adrenaline on the system. With a long-term decrease in concentration, patients show noticeable deviations from their usual psycho-emotional state due to the influence of these hormones.
A decrease in the level of acid crystals in itself does not cause complications, since almost always the diagnostic parameter is secondary. The basic disease forms the main dangers.
As a result, the following consequences may occur:
- Hematuria and arthritis.
- Nephropathy and urolithiasis.
- Kidney failure.
- Myopathy and arthropathy.
- Uropathy with obstruction
- Urinary tract infection.
In any case, you need to see a doctor, take a biochemical blood test, and after a diagnosis is made that uric acid is low in the blood, specific treatment will be prescribed.
How to increase uric acid?
The first thing you should do after diagnosing low uric acid levels is to find out the reason for its drop. It is impossible to do without drug treatment for a hereditary disease. If the cause is liver or kidney disease, then treatment should begin with them.
Improper diet is one of the most common causes of hypouricemia. By adding protein-containing foods to your daily meal, you can quickly bring your urate levels back to normal.
The following foods are high in protein:
- Legumes.
- Nuts.
- Fish.
- Cottage cheese.
- Meat and offal.
In addition, it is recommended to avoid fatty and fried foods. It is better to use fractional meals in small portions around five to six times a day. And drinking plenty of fluids will help, in addition to everything else, to overcome the disease.