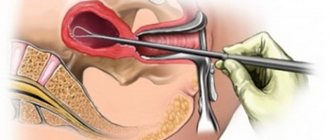
Hysteroscopy of the uterus is both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that allows you to examine the uterine cavity from the inside and, if necessary, perform various medical procedures, for example, remove foreign bodies, polyps, etc. Hysteroscopy is performed using special instruments that are inserted through the vagina.
- Types of hysteroscopy of the uterus
- Indications for performing hysteroscopy of the uterus
- How to prepare for hysteroscopy of the uterus
- How is hysteroscopy performed?
- Contraindications
- Recovery after hysteroscopy of the uterus
- What complications can hysteroscopy cause?
- What procedures can a gynecologist perform during hysteroscopy?
- When can hysteroscopy be performed?
- Risks of hysteroscopy
- What alternatives are there to hysteroscopy?
Types of hysteroscopy of the uterus
- Diagnostic hysteroscopy. As the name implies, this procedure does not involve therapeutic interventions. During diagnostic hysteroscopy, only a visual examination of the internal cavity of the uterus and cervical canal is performed using a special optical system. Since no surgery is performed, significant anesthesia is not required. In most cases, local anesthesia and sedation are sufficient. The recovery period after the procedure is short. No hospitalization required.
- Surgical hysteroscopy is already a therapeutic and diagnostic intervention. It allows you to detect the problem and immediately treat it. This procedure is prescribed when the diagnosis has already been established, or in cases where its probability is maximum. This is already a full-fledged operation, albeit a low-traumatic one. It requires anesthesia and is therefore performed in a hospital setting.
- Control hysteroscopy. It is carried out to monitor the condition of the uterus after surgical treatment.
Indications for performing hysteroscopy of the uterus
- Infertility of unknown etiology.
- Habitual miscarriage.
- Polyps of the uterus and cervical canal.
- Foreign bodies in the uterine cavity, for example, intrauterine contraceptives.
- Pathology of the endometrium - hyperplasia, synechiae.
- Suspicion of uterine malformations.
- Metrorrhagia is non-cyclic uterine bleeding.
- Bleeding after menopause.
Currently, there is a trend away from carrying out invasive techniques purely for the purpose of examination, since this is one way or another associated with certain risks, and the necessary information can often be obtained using safer methods. The same applies to diagnostic hysteroscopy. The procedure is prescribed only if it is impossible to establish a diagnosis using other non-invasive methods.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Hysteroscopy with RDV: pre-registration and price in Moscow
Where can I have curettage performed under hysteroscopy control in Moscow? At the Miracle Doctor clinic you can receive qualified medical care. Our gynecological department employs doctors of the highest category with many years of experience.
Using first-class diagnostic and medical equipment, the capital's leading gynecologists conduct examinations. We have our own histological laboratory, where we can analyze the obtained material for malignant tumors. Find out the price for diagnostic curettage in Moscow and make a preliminary appointment on the clinic’s website.
How to prepare for hysteroscopy of the uterus
Hysteroscopy of the uterus is an invasive procedure that carries certain risks. To minimize them, it is necessary to undergo examination and, if indicated, treatment. As part of the examination, the following tests are prescribed:
- General and biochemical analysis of blood and urine.
- Smear for flora and oncocytology (if not performed within the last year).
- Test for STIs.
- Coagulogram.
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor.
- ECG.
- Determination of markers of infectious diseases: HIV, parenteral hepatitis, syphilis.
If inflammatory gynecological processes are detected, sanitation is carried out.
Hysteroscopy is planned in accordance with the menstrual cycle. It is recommended to perform the procedure in the first days after the end of menstruation, since during this period there is no growth of the endometrium and it is easier to detect its pathology. However, if there are absolute medical indications, the procedure can be performed on any day of the cycle. Immediately before hysteroscopy, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Avoid vaginal sex 1-2 days before the scheduled procedure.
- The last meal should be at least 6 hours before the start of the intervention. This condition is necessary for safe anesthesia. Anesthesia can lead to muscle relaxation and the flow of gastric contents into the airways. This is fraught with the development of asphyxia or aspiration pneumonia, which is difficult to treat.
- You will need to shower on the day of surgery.
- Before the operating room, you must empty your bladder and remove jewelry, dentures, and contact lenses.
Diagnostic and therapeutic studies carried out at CEMH in the field of gynecology
Hysteroscopy –
This is a relatively new word in medicine, which is translated from Latin as examination of the uterus.
Hysteroscopy is a modern method for diagnosing and treating the vast majority of gynecological diseases. Examination of the uterine cavity “from the inside” allows you to clearly visualize the nature of the pathological process and, if necessary, perform minimally invasive surgical intervention.
Get an endoscopic examination of the uterus and fallopian tube area. Our specialists will conduct a full diagnostic examination in comfortable conditions - short-term intravenous anesthesia. On average, the procedure lasts from 10 to 30 minutes, during which a specialist examines the walls of the uterus and the area of the fallopian tubes; also, within the framework of one study, tissue samples can be removed or treatment may be carried out.
Indications for examination:
infertility, bleeding, polyps, fibroids, removal of tumors, routine examination.
Contraindications:
pregnancy, inflammation of the pelvic organs, cervical cancer.
Hysteroscopy technique:
Hysteroscopy is performed using a special device - a hysteroscope (a long tube with video-optical equipment at the end, connected to a computer monitor), which is inserted into the uterine cavity. The device consists of an eyepiece head and interconnecting hard or soft tubes. The optics of the hysteroscope are located in the inner part of the tube. Between the optical and outer tubes there is a fiber light bundle, through which illumination is supplied to the surgical field. All data is displayed on the screen in “real time” with an increase of approximately 25 times, which allows the doctor to examine all the walls of the uterus and the area where the fallopian tubes exit. Visual data from the examination are recorded or can be presented in the form of photographs, which the patient receives in his hands for subsequent assessment by other specialists
Preparing for the study
For more information on preparing for hysteroscopy, see here
Before a planned historoscopy, the patient undergoes all the necessary tests, which are carried out on an outpatient basis. On the basis of the department of outpatient and operative gynecology of the Central Medical Research Center, patients have the opportunity to undergo full preparation for surgical minimally invasive interventions in one day; a quick examination has been developed (see price list - “preparation for surgical minimally invasive gynecological interventions”). namely:
- Initial examination and consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences, with a set of examinations:
- Liquid cytology of cervical and cervical canal scrapings with determination of HPV types 16,18,31,33,35,39,45,51,52,56,58,59 (SurePath FocalPoint)
- Gynecological smear for flora
- Tests: hematological hospital extended complex pre-hospitalization
- hematological screening (can be expanded individually depending on the medical history) - clinical blood test with leukocyte count and ESR with microscopy of a blood smear to detect pathological changes, total protein, glucose, glycated hemoglobin, ALT, AST, total bilirubin, potassium (K+), sodium (Na+), chlorides, creatinine, urea, total cholesterol, hepatitis B, HBs Ag (quality), hepatitis C, anti-HCV amounts. (quality), AT and AG to HIV 1/2 (screening, quality), syphilis sum. AT (IgG and IgM) (quality), blood group, Rh factor, INR (+PTT and PTI), fibrinogen + general urine test
- Preoperative consultation with an anesthesiologist
- Electrocardiogram
Please note: when performing emergency historoscopy, all necessary tests and studies are carried out immediately from the moment of admission to the hospital.
Important to know: The patient is admitted to the hospital in the morning and on an empty stomach. For those patients who have problems with varicose veins, and simply to reduce the risk of developing thrombosis, it is recommended to use compression stockings. Also, before the study, the patient needs to shave her bikini and genital area. Immediately before the procedure, the patient must empty her bladder. If the patient wears dentures, they need to be removed.
The final stage of preparation for the procedure is an examination by an anesthesiologist.
Research technique:
Histoscopic examination is carried out under short-term intravenous anesthesia. Anesthesiologists at the CEMH Medical Center select an individual program scheme for short-term anesthesia for each patient. This approach ensures a gentle effect of anesthesia on the body and a trouble-free recovery from it (without headaches, nausea, etc.).
After the patient is immersed in a state of sleep, the actual study begins. The gynecologist dilates the cervical canal, and after preliminary supply of a sterile solution (for better visualization), inserts a hysteroscope into the uterine cavity and conducts a thorough examination and analysis of the mucous membrane.
To establish an accurate final diagnosis after the hysteric stage, the doctor performs curettage of the cervical canal and separate curettage of the uterine cavity.
Please note: At CEMH, hystoscopic examinations are carried out using the latest expert-class equipment, which gives the doctor the opportunity to identify even the most minor pathological processes at an early stage, which will subsequently facilitate treatment for patients.
After hysteroscopy:
For detailed recommendations after gynecological operations, see here
After completion of the hystoscopic procedure, the patient remains in a special rehabilitation ward for another 2 hours. If necessary, the patient is given additional painkillers. After the patient’s condition returns to normal, she is allowed to leave the hospital.
Note:
- In order to eliminate the risk of inflammatory processes, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics over the next 5-7 days after the examination.
- After hysteroscopy, not very painful pulling sensations in the lower abdomen are possible, as well as scanty bleeding from the genital tract for 10-14 days.
- For 10-14 days, especially with unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen, visiting baths and saunas is contraindicated for patients. Doctors also recommend abstaining from sexual activity for this period.
- The day of hystoscopic examination is considered the first day of menstruation.
Important to know: Histoscopic examination is the most effective method for diagnosing and treating intrauterine pathologies. Histoscopy is a 100% way to diagnose endometrial cancer.
Conization of the cervix:
A minor, non-traumatic surgical procedure performed on the cervix in which the cone around the external os or part of the canal connecting the uterine cavity and vagina is removed. It can be done in different ways: traditional surgical, laser, ultrasound or radio wave method. It is performed either under local anesthesia or in a state of sedation (sleep).
Indications:
diagnosis, additional examination, treatment of cervical dysplasia, cervical cancer (cervical cancer).
Contraindications:
pregnancy and lactation, cancer with a wide spread of the malignant process, electronic implants, infectious or inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
Extended colposcopy:
This is a detailed examination of the cervix using special equipment - a colposcope, which is a magnifying system with backlight located on a tripod. The procedure is painless and does not require much time. Indicated for all women over 30 years of age. This study is the earliest way to diagnose cervical pathologies.
RDV or Separate diagnostic curettage:
Can be used to diagnose or stop uterine bleeding.
The procedure involves the removal of the surface layer of the endometrium and the epithelium of the canal connecting the uterine cavity and vagina (cervial). It is carried out in a state of short-term medicated sleep - sedation. Tissues are removed mechanically.
Indications for the procedure:
diagnosis, incomplete abortion, uterine bleeding, polyps.
Contraindications
acute inflammatory processes.
In our center, you will not only undergo all the necessary examinations, but also receive subsequent consultation with a high-class specialist who will be able to select an adequate course of treatment or additional diagnostics.
How is hysteroscopy performed?
An hour before the patient is admitted to the operating room, premedication is administered, the purpose of which is to reduce anxiety, increase tolerance to anesthesia and reduce the secretory activity of the glands. For this purpose, a combination of drugs is prescribed, containing narcotic analgesics, antihistamines, anticholinergics and sedatives.
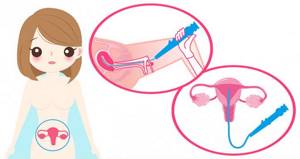
In the operating room, the patient is placed in a gynecological chair and anesthesia is administered. The type of anesthesia is discussed in advance, taking into account contraindications, recommendations of the anesthesiologist and the wishes of the patient.
Next, proceed directly to hysteroscopy:
- The cervical canal is expanded using special instruments.
- A sterile liquid or gas is injected into the uterus through an enlarged canal. This is necessary to expand its cavity and make it accessible for inspection and manipulation.
- Next, a hysteroscope is inserted through the cervix - a thin tube with a diameter of about 5 mm with an optical system that transmits an enlarged image to the monitor. As it is introduced, the cervical canal, intrauterine cavity and its angles are examined.
- After the diagnosis has been established, treatment is carried out using the same hysteroscope, which has a special channel for inserting surgical instruments. In this way, removal of polyps, submucosal myomatous nodes, dissection of synechiae, curettage of the endometrium, etc. can be carried out.
- After all interventions are completed, the hysteroscope and the injected liquid or gas are removed. The patient is sent to the intensive care ward, where she recovers from anesthesia under the supervision of medical staff.
Preparing for anesthesia
12 hours before anesthesia, it is necessary to exclude meat products and juices from the diet, and significantly limit water consumption. Precisely limit it (30-50 ml of still water per hour), and not exclude it! If necessary, you can take water into your mouth, rinse your mouth and spit without swallowing. Patients taking medications on a regular basis are required to continue taking them according to the previous regimen, with a small amount of water. You can take light yogurt or a couple of bananas with you.
A conversation with an anesthesiologist is an integral part of the patient’s psychological preparation before anesthesia. The anesthesiologist is obliged to examine the patient, interview him in detail, assess his condition and readiness for anesthesia. Do not hide the presence of chronic diseases, bad habits and addictions from the anesthesiologist. Remember, the anesthesiologist takes responsibility for your safety and must be well informed to make decisions in the event of an emergency.
Recovery after hysteroscopy of the uterus
The recovery period after hysteroscopy is divided into two stages. In the early recovery period, tissues damaged during the procedure are restored—the mucous membrane of the uterus, the muscular wall, and the cervical canal. This period lasts about 2-3 weeks.
The second period takes about six months. At this time, the new endometrium will be regenerated, which must meet the functions assigned to it - grow and be rejected in the process of changing the phase of the menstrual cycle.
Bloody discharge after hysteroscopy
Moderate bleeding is possible in the first 2-3 days after hysteroscopy. This is normal, since during the procedure the cervical canal, endometrium and muscular layer of the uterus are injured. Gradually, the discharge lightens, acquires a yellowish color and continues for about 2-3 weeks. If heavy bleeding develops, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this may be a symptom of serious complications.
Painful sensations after hysteroscopy
Mild to moderate pain after hysteroscopy is normal. They are localized in the lower abdomen and can radiate to the sacrum or lower back. They arise due to stretching of the uterine cavity and injury to the cervix. To alleviate the condition, it is recommended to prescribe “strong” NSAIDs such as ketorol or indomethacin. If the pain increases and becomes unbearable, you should seek medical help immediately, as this may be a sign of serious complications.

In order for the recovery period to go smoothly, you must adhere to several rules:
- Take all medications prescribed by your doctor. As a rule, we are talking about antibiotics that are prescribed prophylactically to prevent the development of infections.
- Avoid vaginal sex until your next period.
- During the period of bleeding, it is better to use pads. Tampons are strictly prohibited.
- Also, during the recovery period it is not recommended to use vaginal suppositories, tablets and creams.
- Refrain from intense physical activity.
- Don't forget about personal hygiene. Toilet of the genital organs should be performed at least 2 times a day, and ideally after each urination and defecation.
- To prevent the development of constipation, follow your diet. Don't forget to empty your bladder in a timely manner.
Hysteroscopy to remove polyps
Polyps are often found in the cervix and uterine cavity. Polyps are pathological neoplasms on the mucous membrane. They are attached to the uterus by a base or stalk and have a smooth or ribbed surface. The presence of polyps in the uterus can cause many problems for women and is characterized by the following manifestations: spotting between menstrual cycles, nagging pain in the lower abdomen or pain during sexual intercourse. Therefore, timely treatment of these formations is necessary. The most effective method of solving this problem is hysteroscopy. Preparation for the operation and the procedure itself were described above. After the doctor finds the site of attachment of the polyp, he cuts off the stalk of the polyp using flexible scissors. Then the doctor clamps the cut polyp with forceps and carefully removes it from the uterine cavity.
What complications can hysteroscopy cause?
As with any invasive intervention, complications may develop after hysteroscopy. The most formidable and dangerous of them is perforation of the uterine wall, which is accompanied by bleeding. To eliminate the perforation, repeated surgery is required to suturing the defect. If left untreated, peritonitis may develop.
There may also be other complications:
- Hematometra is the accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity due to the impossibility of its drainage. Clinically manifested by increasing spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen and deterioration in general well-being. For treatment, conservative methods can be used (prescription of drugs that improve uterine contraction or antispasmodics for pathological contraction of the cervix), or surgical methods, in which repeated intervention is performed with evacuation of the intrauterine contents.
- Infectious complications. They are manifested by an increase in body temperature, symptoms of intoxication, and pain in the lower abdomen. A little later, pathological discharge appears, which may have a foul odor.
- Bleeding. Possible after therapeutic hysteroscopy, when, for example, myomatous nodes or polyps are removed. If you experience heavy bleeding, especially if it lasts several days, you should consult your doctor.
In general, hysteroscopy is a low-traumatic intervention and the likelihood of complications after it is much lower than with other, more extensive treatment methods.
Contraindications to hysteroscopy
Like any surgical intervention, hysteroscopy has a number of contraindications:
- developing pregnancy;
- malignant neoplasms in the cavity and cervix;
- infectious diseases (sore throat, flu, pneumonia, etc.);
- acute inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- cervical stenosis;
- uterine bleeding;
- serious chronic diseases of internal organs (heart, liver, kidneys).
What procedures can a gynecologist perform during hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy is a diagnostic procedure, however, during it some additional manipulations can be performed, including therapeutic ones:
- Biopsy is a procedure during which a piece of pathologically changed tissue is removed and sent to the laboratory for histological and cytological examination. This allows you to establish a more accurate diagnosis, confirm or exclude the presence of a malignant tumor in the uterus.
- Hysteroscopy allows you to remove various pathological formations protruding into the uterine cavity, such as polyps and fibroids.
- The source of bleeding can be eliminated using electrocoagulation and low temperature (cryosurgery).
- Place contraceptive devices in the fallopian tubes.
The Euroonko clinic in Moscow offers special comprehensive programs for women, for example, hysteroscopy with separate diagnostic curettage of the cervix and uterine body. The cost of the service includes a 6-hour stay in a comfortable hospital, meals, and all related procedures.
What happens during hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy can be performed either under general anesthesia, which means you will sleep during the entire procedure, or with local anesthesia. If you have a local anesthetic, you will remain awake. You may be given a sedative, which will not make you sleepy but may help you feel more calm. You may be advised to take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pain reliever, such as ibuprofen, about 1 hour before your appointment to help reduce pain immediately after the procedure. If you have a local anesthetic you may be asked to see photographs from the hysteroscope if you wish. Some people don't want to do this, but others find it useful.
Your doctor may use a speculum (the same instrument used in the cervical screening test) so that he or she can see the neck of the womb (cervix). When the doctor passes a hysteroscope through your cerivx into your uterus. The hysteroscope is connected to a camera and a TV screen, the inside of the uterus is visible. Certain gases or liquids can be pumped into the uterus to make it wider. This makes it possible to see the lining of the uterus. After this, the doctor may take a small piece of tissue from the uterine cavity (biopsy). Which will be sent to the laboratory for examination under a microscope. Sometimes polyps found can be removed during the test. After completion of the procedure, the hysteroscope is carefully removed.
Hysteroscopy takes from 5-30 minutes. If you wake up, you may feel something like a cramp in several stages. Many women feel no discomfort or only minimal discomfort.
When can hysteroscopy be performed?
Most often, gynecologists prescribe hysteroscopy in the following situations:
- Detection of atypical cells based on PAP test results.
- Vaginal bleeding between periods, postmenopause.
- Infertility is when you cannot get pregnant after a year of regular sexual activity.
- Frequent miscarriages.
- The need to clarify the condition of the uterus with scars and fibroids.
- The need to confirm or rule out certain diagnoses using biopsy.
Risks of hysteroscopy
Overall, this is a safe procedure. For two days after hysteroscopy, you may experience slight bleeding from the vagina and cramps in the lower abdomen - this is normal. More serious complications are very rare, occurring in no more than 1% of cases.
At Euroonko, the research is carried out by a highly qualified specialist - Natalya Evgenievna Levchenko, oncogynecologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. The clinic uses equipment for hysteroscopy from the world's leading manufacturers, which allows the examination to be carried out as comfortably and safely as possible.
What can I expect after hysteroscopy?
If you underwent hysteroscopy under general anesthesia, then you need to rest until the effects of anesthesia wear off. You will need to negotiate with someone to take you home. Bring a friend or relative to stay with you for the first 24 hours.
If you have a hysteroscopy with local anesthesia, you are usually able to go home after a short rest. You'll feel well enough to walk, ride a bus or train - you probably won't need a sedative to drive home.
There may be a period of cramping and moderate bleeding. Bleeding is usually mild and should end within seven days. To reduce the risk of infection, you should use sanitary pads rather than tampons. Be careful for the first one or two days, and take pain medications as needed.
What alternatives are there to hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy can be replaced by some other diagnostic procedures, but not in all cases:
- Transabdominal ultrasound of the pelvic organs through the anterior abdominal wall helps to identify diseases that lead to pelvic pain, menstrual irregularities, vaginal bleeding, and infertility.
- Transvaginal ultrasound is performed with a special probe inserted through the vagina. It allows you to obtain more informative images of the uterus and its appendages.
- Aspiration biopsy of the myometrium. This procedure does not require hysteroscopy: using vaginal speculum, the cervix is visualized and a tube connected to an aspirator is inserted through it.
All these studies are not as informative as hysteroscopy. However, if you start the diagnosis with them, in some cases endoscopic examination of the uterus may not be required. Sometimes these diagnostic methods are used as an alternative if there are contraindications for hysteroscopy for one reason or another.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Contraindications
- The presence of decompensated chronic diseases that may interfere with anesthesia, for example, cardiovascular pathology.
- Presence of STIs and vulvovaginitis.
- The presence of diseases accompanied by a tendency to bleeding.
Euroonco specialists closely monitor the condition of patients not only in the postoperative period, but also at the initial stage. In this regard, we perform the procedure only after we are convinced that the patient has no contraindications. You can make an appointment for a consultation about uterine polyps by calling:
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78