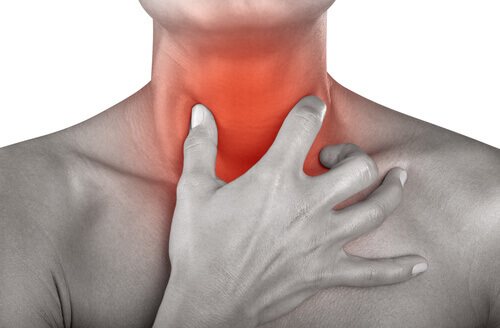
Painful symptoms in the lower back are a common phenomenon. About 80% of people suffer from it, regardless of age, gender and profession. An x-ray of the lumbar spine can help determine the pathology that is the cause of pain symptoms. This diagnostic study is deservedly considered highly informative: it allows you to obtain data on the state of bone structures, changes that have arisen as a result of diseases and injuries, as well as identify pathologies of the spinal column at different stages of their development.
You can take an x-ray of the lumbar spine at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic. Our radiologists practice an individual approach and have modern equipment, thanks to which they consistently achieve high quality and informative X-ray images.
X-ray of the lumbar spine - RUB 2,200.
15 - 20 minutes
(duration of procedure)
Indications for radiography of the lumbar spine
An X-ray examination of the lumbar spinal column is prescribed if any pathological conditions in this area are suspected. They are usually divided into several groups, which are presented in our table.
| Groups of pathological conditions | Specific pathologies and features of x-rays |
| Congenital anomalies of the spinal column | Pathologies such as splitting or fusion of the vertebrae or congenital curvature of the spinal column most often require surgical intervention. Planning the operation requires a standard x-ray examination. |
| Acquired curvature of the spinal column | Spinal deformities often arise as complications of incorrect posture. Correction requires taking measures to fix the vertebrae in the correct position. To prescribe adequate treatment, an x-ray is performed. |
| Degenerative-dystrophic changes | Dystrophic processes in articular cartilage, such as osteochondrosis, lead to the development of pathological changes in the spinal column. Diagnosis requires x-rays and magnetic resonance imaging. |
| Inflammatory pathologies of the spine - spondylitis | The pathology is characterized by primary destruction of the vertebral bodies and the development of complications in the form of further deformation of the entire spine. It occurs as a result of inflammatory processes provoked by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. Diagnosis requires a conventional x-ray. |
| Systemic osteoporosis | The disease is accompanied by a decrease in bone density, the development of its fragility and occurs in a chronic form. If left untreated or if it progresses rapidly, it can lead to loss of mobility and disability. A type of radiography called densitometry is performed, which allows you to determine bone density. |
| Traumatic conditions of the spine | Injuries can occur due to falls from heights and road traffic accidents. They are regarded as dangerous, posing a threat to human health and life. In order to accurately determine the location, nature and severity of fractures, bruises and dislocations, regular x-rays are performed. Contrast x-rays can detect damage to the nervous system. |
Is it harmful to take x-rays?
An X-ray is an invisible electromagnetic wave that has the ability to penetrate any substance. As a result of exposure to radiation, photographic material darkens. Thanks to this effect, the structure of the human body is displayed on photographic film, after which a number of conclusions can be drawn about the state of health of the patient’s internal organs and bones.
Despite the wide range of applications of X-ray radiation in such branches of medicine as traumatology, pulmonology, gastroenterology, etc., this research method has a significant drawback. It has been established that the maximum dose of X-ray radiation allowed for an adult is 150 mSv (millisievert) per year. For a child under 16 years of age, the maximum radiation dose using various methods is no more than 50 mSv, and research is carried out only in emergency cases.
When carrying out standard X-ray examination procedures that must be done annually (in particular, fluorography), an adult patient receives a radiation dose not exceeding 20 mSv.
The main contraindication to x-ray examination is exceeding the safe and recommended by experts radiation dose. The consequences of exposure to electromagnetic rays on the human body can be different: from skin burns (erythema) to infertility, the appearance of tumors and even radiation sickness.
The negative impact of X-ray radiation on the human condition exists, however, if precautions are taken, exposure to electromagnetic radiation during X-ray examinations can be reduced.
Contraindications to X-ray of the lumbar spine
Conventional radiography has minimal contraindications due to the risk of negative effects of radiation on the patient’s body in cases where he is in certain conditions. They are relative, which means that if a diagnosis can save the patient’s life, it is carried out. Radiography using a contrast agent has a number of absolute contraindications due to its use.
| Groups of contraindications | When is diagnostics prohibited? |
| Contraindications to standard radiography |
|
| Contraindications to the procedure with contrast |
|
What device do you use for radiographic examination?
The Clinic on Komarova uses the latest generation universal X-ray complex - AGFA DX-D 300 (2016), the only one in the Far East. Modern digital technologies make it possible to obtain images of the highest quality with minimal radiation exposure, which have undeniable diagnostic effectiveness.
For comparison, when performing digital chest radiography AGFA DX-D 300, the radiation exposure is only 0.03 mSv (millisievert) per procedure, which is 17 times lower than with conventional fluorography (0.5 mSv), 10 times lower than with conventional radiography (0.3 mSv) and 2 times lower than with digital fluorography of the chest organs (0.05 mSv).
One of the unique features of the AGFA DX-D 300 is an individual approach to research. The German company has thought through everything to improve the level of patient comfort. The maximum flexibility and motorization of the AGFA DX-D 300 allow the equipment to independently take a position in space relative to the patient during the examination. This unique feature makes it easy to carry out a wide variety of examinations on any population, be it children, the elderly or patients with limited mobility.
Preparation for x-ray of the lumbar spine
Diagnostics requires certain preparation from the patient, aimed at cleansing the intestines in order to obtain clear images. To do this, 72 hours before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude black bread, legumes, dairy products, fresh vegetables and fruits from the diet. Depending on the situation, the doctor may prescribe a cleansing enema or taking enterosorbents, which help cleanse the intestines. X-rays are taken on an empty stomach: the last meal can be taken 12 hours before.
Preparing for a colonoscopy:
Option 1:
- On the eve of the study at 14-00 - a full lunch.
— At 17-00, take 60-80 g. castor oil.
- At 20-00 and 21-00, perform enemas of 1.5 liters each.
- On the morning of the study at 07-00 and 08-00, perform enemas of 1.5 liters each.
- If there was stool after enemas, rinse with clean water.
Option 2:
— Use of the drug “Fortrans” (in sachets).
— If the patient weighs less than 100 kg. for preparation, 4 sachets of “Fortrans” are required (calculation for 20-15 kg 1 sachet).
— Dissolve 1 sachet in 1 liter of water and drink gradually over 1 hour, one glass at a time for 15 minutes (it is NOT possible to change the proportions or reduce the amount of liquid you drink!). To improve the taste, you can add lemon juice, or juice, sour jam syrup (without seeds and peels) to the solution.
- Approximately 1-1.5 hours after the start of treatment, painless loose stools will appear.
- In the evening, on the eve of the study (from 18 o'clock), drink 3 sachets. Bowel movement will end with the release of clear or slightly colored liquid 2-3 hours after taking the last dose of Fortrans solution.
— On the morning of the test, drink the 4th sachet.
Preparation for survey urography:
- three days before the test, exclude from the diet: brown bread, milk, peas, beans, cabbage, fresh vegetables, fruits and sweet foods;
- on the eve of the study, no later than 18-00 - a light dinner, then 2 cleansing enemas at 19-00 and 21-00;
- on the day of the examination - another cleansing enema 2 hours before the examination;
- come on an empty stomach (do not eat, do not drink).
Preparation for x-ray of the lumbar spine:
- three days before the test, exclude from the diet: brown bread, milk, peas, beans, cabbage, fresh vegetables, fruits and sweet foods;
- on the eve of the study, no later than 18-00 - a light dinner, then 2 cleansing enemas at 19-00 and 21-00;
- on the day of the examination - another cleansing enema 2 hours before the examination;
- come on an empty stomach (do not eat, do not drink).
Preparation for fluoroscopy of the stomach:
- three days before the test, exclude from the diet: brown bread, milk, peas, beans, cabbage, fresh vegetables, fruits and sweet foods;
- on the eve of the study, no later than 18-00 - light dinner;
- come on an empty stomach (do not eat, do not drink, do not brush your teeth, do not take medications).
ULTRASONIC INVESTIGATIONS:
Preparing for an abdominal ultrasound:
2-3 days before the examination, it is recommended to switch to a slag-free diet, exclude from the diet foods that increase gas formation in the intestines (raw vegetables rich in plant fiber, whole milk, brown bread, legumes, carbonated drinks, as well as high-calorie confectionery products - pastries, cakes ). On the eve of the study - a light dinner no later than 18 hours, excluding the intake of rough, difficult to digest food;
For patients with problems with the gastrointestinal tract (constipation), it is advisable to take enzyme preparations and enterosorbents (for example, festal, mezim-forte, activated carbon or espumizan, 1 tablet 3 times a day) during this period of time, which will help reduce the manifestations of flatulence;
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs must be performed on an empty stomach; if the study cannot be performed in the morning, a light breakfast is allowed; on the day of the study, do not drink, do not take food, or take medications;
If you are taking medications, notify the ultrasound doctor;
You cannot conduct research after gastro- and colonoscopy, as well as R-studies of the gastrointestinal tract.
You must have replacement shoes, a towel, directions, and the results of previous examinations with you.
Preparation for ultrasound of the pelvic organs (bladder, uterus, appendages in women):
- on the eve of the study - a light dinner no later than 19:00;
— the study is carried out with a full bladder, so it is necessary not to urinate for 3-4 hours before the study and drink 1 liter of non-carbonated liquid 1 hour before the procedure;
— no special preparation is required for transvaginal ultrasound (TVS). If the patient has problems with the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to perform a cleansing enema the night before.
You must have replacement shoes, a towel, directions, and the results of previous examinations with you.
Preparation for ultrasound of the bladder and prostate in men:
— the study is carried out with a full bladder, so it is necessary not to urinate for 3-4 hours before the study and drink 1 liter of non-carbonated liquid 1 hour before the procedure;
Ultrasound of the prostate gland is performed using two methods:
- transabdominal: the study is carried out with a full bladder, so it is necessary not to urinate for 3-4 hours before the study and drink 1 liter of non-carbonated liquid 1 hour before the procedure;
— transrectal (TRUS): this method should be the main one when examining the prostate gland. TRUS does not require bladder filling. On the eve of the study, a cleansing enema is required.
Preparation for ultrasound of the mammary glands:
It is advisable to carry out examination of the mammary glands in the first 5-10 days of the menstrual cycle (phase 1 of the cycle). You need to have directions with you.
Preparation for ultrasound of the lumbar spine:
— the study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach after a 4-hour fast;
- provide a slag-free diet in two days;
- cleansing enema the night before and in the morning, directly on the day of the study.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, lymph nodes and kidneys:
- do not require special preparation of the patient. The patient must have with him:
— data from previous ultrasound studies (to determine the dynamics of the disease);
— referral for an ultrasound examination (purpose of the study, presence of concomitant diseases);
- a large towel or diaper.
ENDOSCOPIC STUDIES:
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS):
how to prepare properly:
Show up at least 5 minutes before your scheduled time.
in the morning on the day of the study before FGDS it is PROHIBITED:
- have breakfast and take any food, even if the study takes place in the afternoon;
in the morning on the day of the study before FGDS IT IS NOT RECOMMENDED:
- smoke and take medications in tablets (capsules) orally;
in the morning on the day of the study before the FGDS is ALLOWED:
- brush your teeth;
— do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and other organs;
- take medications that can be dissolved in the mouth without swallowing or taken with you;
- give injections if you do not need to eat after the injection and it is not possible to do it after FGDS;
The night before: an easily digestible (no salads!) dinner before 6:00 p.m.
No special diet is required before FGS (FGDS), but:
- exclude chocolate (chocolate candies), seeds, nuts, spicy foods and alcohol for 2 days;
- when examining from 11 o'clock and later - preferably in the morning and 2-3 hours before the procedure, drink in small sips one glass of still water or weak tea (without jam, sweets, cookies, bread, etc.).
It is important that:
- the clothes were loose, the collar and belt were unbuttoned;
— you did not use perfume or cologne (eau de toilette);
— You promptly warned the doctor about the presence of drug, food or other allergies.
The patient must have with him:
- medications taken on a regular basis (take after the examination, and under the tongue or spray for ischemic heart disease, bronchial asthma.. - before the examination!);
— data from previous FGDS studies (to determine the dynamics of the disease) and biopsy (to clarify the indications for repeat biopsy);
— referral for an FGDS study (purpose of the study, presence of concomitant diseases...);
- a towel that absorbs liquids well or a diaper.
If you are unable to show up at the appointed time, please call the doctor or the medical organization’s reception desk in advance.
COLONOSCOPY:
How to prepare properly:
Preparation for colonoscopy using the drug "Fortrans" two days before the study:
Recommended diet : boiled white fish or chicken, eggs, cheese, white bread, butter, cookies, potatoes. It is recommended to drink a sufficient amount of fluid - up to 2.5 liters per day (if you do not have diseases for which heavy drinking is contraindicated, consult your doctor).
It is not recommended to eat: fruits and berries with seeds, red meat, vegetables, cereals, salad, mushrooms, nuts, grain bread, sweets.
The day before the test:
In the morning - a light breakfast of the products recommended above. After breakfast, you cannot eat solid food until the end of the study; you are only allowed to drink. After breakfast, before 17-00, it is recommended to drink a sufficient amount of liquid to cleanse the intestines - up to 2 liters (you can drink water, low-fat broths, fruit drinks, juices without pulp, tea with sugar or honey, compotes without berries). It is not recommended to take milk, jelly, kefir. At 17:00 you need to prepare the Fortrans solution. For this:
— Dilute 1 packet of Fortrans in 1.0 liter of boiled water at room temperature. The prepared Fortrans solution must be drunk within one hour (from 17:00 to 18:00). Fortrans should be taken in small portions, 1 glass every 15 minutes, in small sips. At 18.00, drink the second packet of Fortrans using the same method. At 19.00, drink the third packet of Fortrans using the same method. 1-3 hours after starting to take the Fortrans solution, you should have copious, frequent, loose stools, which will facilitate complete cleansing of the intestines. If loose stools do not appear 4 hours after the start of treatment or signs of an allergic reaction appear, you should contact medical personnel and refrain from taking the drug again.
On the day of the study:
In the morning at 7.00 it is necessary to repeat taking Fortrans to completely cleanse the intestines of contents (1 packet of Fortrans). Drink the resulting solution in separate small portions within 1 hour (07-00 to 08-00). You will again have loose stools, which should last until the intestines are completely empty and cleansed. By 12-00 you will be ready for research. When preparing for a study with Fortrans, enemas are not required!
You need to have with you:
Referral for colonoscopy (if you were referred from another medical organization), conclusions and protocols of previously performed endoscopic studies, ECG (if you have cardiovascular diseases).
The key to a successful colonoscopy is proper preparation of the patient. Preparation for an intestinal examination begins 2-3 days before the scheduled date of the examination. Additional means used to prepare the intestines for examination are recommended.
How to behave after the study?
Immediately after the procedure, you can drink and eat. If the feeling of fullness of the abdomen with gases persists and the intestines are not emptied of remaining air naturally, you can take 8-10 tablets of finely crushed activated carbon, stirring it in 1/2 cup of warm boiled water. It is better to lie on your stomach for several hours after the examination.
Blood analysis:
— Morning hours are most suitable for blood testing.
— For most studies, blood is taken strictly on an empty stomach. Coffee, tea and juice are also food. You can drink water.
The following periods of time after the last meal are recommended:
— for a general blood test, at least 3 hours;
— for a biochemical blood test, it is advisable not to eat for 12-14 hours (but not less than 8 hours).
— 2 days before the examination, you must avoid fatty and fried foods.
— Before a blood test, you should reduce physical activity as much as possible. Avoid running and climbing stairs. Avoid emotional excitement. You need to rest, relax and calm down for 10-15 minutes to avoid an unmotivated release of hormones into the blood and an increase in their levels.
— You cannot donate blood immediately after physiotherapeutic procedures, ultrasound and x-ray examinations, massage and reflexology.
— Before donating blood, you need to calm down in order to avoid an unmotivated release of hormones into the blood and an increase in their levels.
— To donate blood for viral hepatitis, it is advisable to exclude citrus fruits, orange fruits and vegetables from the diet 2 days before the test.
— To correctly evaluate and compare the results of your laboratory tests, it is recommended to carry them out in the same laboratory, since different research methods and units of measurement of indicators may be used in different laboratories.
General clinical urine analysis:
- only morning urine taken in the middle of urination is collected;
- morning urine sample: collection is done immediately after getting out of bed, before drinking morning coffee or tea;
- previous urination was no later than 2 am;
— before collecting a urine test, a thorough toilet of the external genitalia is performed.
- 10 ml of urine is collected in a special container or test tube with a lid and provided with a label with the necessary data and direction. The collected urine is immediately sent to the laboratory.
Collection of daily urine:
- the patient collects urine for 24 hours with normal drinking regimen (about 1.5 liters per day);
- in the morning at 6-8 o'clock he empties the bladder and pours out this portion, then during the day he collects all the urine in a clean wide-necked dark glass vessel with a lid with a capacity of at least 2 liters;
- the last portion is taken at the same time when the collection began the day before, the start and end times of the collection are noted;
— at the end of urine collection, its volume is measured, the urine is thoroughly shaken and 50-100 ml is poured into a special container in which it will be delivered to the laboratory;
- Be sure to indicate the volume of daily urine.
Collecting urine for Nechiporenko research:
(detection of hidden inflammatory process)
- in the morning on an empty stomach, collect 10 ml of morning urine, taken in the middle of urination in a special laboratory container.
Collection of urine for research according to Zimnitsky:
(the patient takes into account the amount of fluid he drinks per day)
— after emptying the bladder at 6 o’clock in the morning, every 3 hours during the day, urine is collected in separate containers, which indicate the collection time or portion number, 8 portions in total.
1 serving - from 6-00 to 9-00, 2 serving - from 9-00 to 12-00, 3 serving - from 12-00 to 15-00, 4 serving from 15-00 to 18-00, 5 serving - from 18-00 to 21-00, 6 portion - from 21-00 to 24-00, 7 portion - from 24-00 to 3-00, 8 portion - from 3-00 to 6-00;
— the entire collected amount of urine in 8 special containers is delivered to the laboratory;
- be sure to indicate the volume of daily urine.
Collection of urine for microbiological examination (urine culture):
- morning urine is collected in a sterile laboratory container with a lid;
— the first 15 ml of urine are not used for analysis, the next 5-10 ml are taken;
- collected urine is delivered to the laboratory within 1.5 - 2 hours after collection;
- urine can be stored in the refrigerator, but not more than 3-4 hours;
— urine collection is carried out before the start of drug treatment;
— if you need to evaluate the effect of the therapy, then urine culture is performed at the end of the course of treatment.
Stool analysis:
- 2-3 days before the study, avoid taking medications that change the nature of stool and cause functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- you cannot examine stool after an enema, the use of rectal suppositories, taking laxatives or dyes, as well as pilocarpine, iron supplements, bismuth, barium, etc.;
— feces should not contain foreign impurities, such as urine, disinfectants, etc.;
— prepare a clean container for stool or purchase a container from the laboratory;
— the contents of morning stool from 3 points are collected in a container and delivered to the laboratory within 2 hours.
Fecal analysis to detect helminthic infestations:
- for two days the patient should not eat hard, poorly digestible food (“food waste”): seeds, nuts, raw vegetables and fruits with skins, as well as sorbents: activated carbon, etc., as well as mushrooms!
Functional diagnostics.
Functional methods for studying the heart:
Cardiac rhythmography (CRG) is an electrophysiological method that analyzes changes in the speed and rhythm of the heart, allowing one to judge the state of the autonomic nervous system.
— These types of procedures are carried out after a 15-20 minute rest.
— Before examinations, it is not recommended to eat a large meal, strong tea, coffee, as well as to carry out after taking medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, physical therapy and other examinations that contribute to the patient’s fatigue (X-ray, radioisotope).
Bicycle ergometry (ECG study with stress tests) - makes it possible to determine the reserve capacity of the myocardium and coronary vessels.
Conducting a bicycle ergometry study:
— On an empty stomach or 2-3 hours after eating
— A day or more before the study, in agreement with the attending physician, all medications (except nitroglycerin) are discontinued
Daily monitoring of ECG, blood pressure:
— When conducting Holter monitoring (HM) and 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM), patients are not recommended to be near powerful power lines, transformer boxes, or use a computer, mobile phone, etc.
— You cannot take general water procedures (bath, shower), or undergo prolonged, heavy physical activity, because Increased sweating can lead to the electrodes coming off.
— During the study, it is recommended to wear cotton underwear and try not to wear clothes made of electrifying synthetic and silk fabrics.
— Do not expose the device to shock, vibration, high or low temperatures.
Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart):
— The study is carried out after a 10-15 minute rest.
— Before examinations, it is not recommended to eat a large meal, strong tea, coffee, as well as to carry out after taking medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, physical therapy and other examinations that contribute to the patient’s fatigue (X-ray, radioisotope).
- Know the exact weight.
Studies of wall tone and vascular patency:
Rheocephalography (REG), rheovasography (RVG of the extremities), ultrasound Dopplerography of the vessels of the brachiocephalic region and lower extremities, USDG-BCA, transcranial Dopplerography.
— All these studies do not require special preparation. They are carried out before therapeutic exercises, physiotherapeutic procedures, or taking medications.
Neurophysiological research methods:
Electroencephalography (EEG) characterizes the state of bielectric activity of the brain.
— On the eve of the examination, wash your hair and do not use hair styling products (spray, mousse, gel).
— Be sure to get enough sleep before the study and have breakfast.
Electromyography (EMG) reflects the bielectric activity of muscles.
— On the eve of the study, the attending physician should conduct a psychotherapeutic conversation about the safety of the technique and cancel the prescribed therapy for one day (if necessary).
Echoencephalography (ECHO-EG) is an ultrasound location of the brain to identify intracranial pathologies.
— The study does not require special preparation. Conducted at any time.
Evoked cutaneous sympathetic potentials (ECSP) are a comprehensive method for studying the autonomic nervous system.
— The study does not require special preparation.
Spirometry (SP) is a method for studying external respiration
— Conducting research: in the morning from 8:00 to 10:00.
- On an empty stomach, no medical procedures (including morning exercises) or taking medications before the start of the study are allowed.
- Know your exact weight and height.
- Clothing that does not restrict breathing movements.
— Outpatient patients are examined no earlier than 10-20 minutes after arrival.
— The examination is carried out if the results of a fluorographic examination are available.
— Discontinuation of bronchodilators on the eve of the study.
Gas analyzer HELIKOBAKTER PYLORI:
— 5 days before the examination, the patient should exclude medications that affect HELIKOBAKTER PYLORI from use.
— The examination is carried out strictly on an empty stomach.
— It doesn’t work right after FGDS.
Peripheral gastroenterography (PEG) is a method based on recording the electrical activity of the gastrointestinal tract.
— On an empty stomach, no medical procedures (including morning exercises) or taking medications before the start of the study are allowed
pH-metry is a diagnostic procedure during which the acidity of the environment in the stomach, esophagus or duodenum is measured.
- It is carried out strictly on an empty stomach.
— Do not take food or medications 12 hours before the test.
— It doesn’t work right after FGDS.
— Availability of individual diapers and towels.
Plantovisor is a method of orthopedic diagnostics of anthropometric data, based on objective, reliable diagnostic and topographic indicators.
— Clothing (underwear) on the patient should be as open as possible (swimsuit, swimming trunks).
Print Email
- Back
- Forward
How is an X-ray of the lumbosacral spine done?
Before the patient enters the radiography room, he will be asked to remove all metal objects from himself. If there are metal implants in his body, it is necessary to inform the doctor about this, as they may distort the images. Pictures are taken in two projections:
- Straight - the patient assumes a supine position on the X-ray table;
- Lateral - the patient takes a position lying on his side.
In order for the image to be as clear as possible, the patient must lie absolutely still while it is being taken (and this is only a few seconds). The whole procedure will take no more than 15 minutes. This time is enough to take pictures in different projections.
You can find out the price of x-rays of the lumbar spine on our website or by calling us by phone. To make an appointment for an x-ray, use our simple online form or call us.
Protection against ionizing x-ray radiation
Protection from ionizing radiation during radiographic examination procedures is an important task for the physician, designed to protect both the patient and hospital staff from the adverse effects of electromagnetic radiation. Since such a procedure is quite complex and dangerous, it is carried out only by a qualified specialist with appropriate training.
There are several ways to protect yourself as much as possible from negative effects during x-ray examination:
- Taking into account the permissible frequency of radiography sessions. In other words, care must be taken to ensure that the radiation dose received over multiple procedures does not exceed the recommended maximum value. For this purpose, the radiologist maintains a special record sheet, with the help of which the patient’s radiation doses are monitored. This sheet is included in the outpatient card and is required to be studied before the next procedure.
- Highly qualified specialist conducting the examination and patient compliance with recommendations. If the examination is carried out in compliance with all rules and precautions, no complications will arise.
- Carrying out the procedure in modern medical x-ray rooms using new and high-quality equipment. Outdated X-ray equipment can cause more harm to the body.
- Complete immobility of the body during radiography. This is most often recommended when examining children. Due to the fact that it is quite difficult for them to remain in one place for a long time, the movement of the subject during the procedure can lead to damage to the image and, accordingly, the need to redo it. Repeated x-rays increase the dose of radiation the child receives.
- The use of special protective capes and aprons made of lead, which minimize the negative impact of electromagnetic radiation on human tissues and internal organs.
- The absence of unauthorized persons in the office, since when the device is turned on and without special protection worn on the body, radiation exposure poses a great danger to health.
It is impossible to completely get rid of the effects of electromagnetic waves during an x-ray examination. Therefore, it is recommended to carefully monitor the number of procedures performed and use protective equipment.
Trendelenburg study

A special feature is the examination of the stomach in the Trendelenburg position, which has long received the status of a classic of the fluoroscopy genre. Here, too, barium is used as a basis. But since any gastroenterologist knows how dangerous the substance presented in combination with radioactive exposure can be, experts prescribe an analysis only in exceptional cases.
If it was not possible to find a worthy alternative, then you cannot do without such testing to confirm a number of pathologies:
- esophageal stenosis;
- diverticula and tumors of the esophagus;
- erosion of the esophagus or other malformations;
- peptic ulcer of the duodenum, stomach;
- neoplasms of a malignant, benign nature;
- inflammatory process in the intestines;
- impaired intestinal motility.
By receiving a so-called “live” image of the stomach, the expert will be able to correctly make a diagnosis, as well as draw up a subsequent treatment program, including surgical intervention.
To obtain particularly clear visualization, 250 milliliters of barium are consumed per dose, which is drunk in one gulp. By monitoring the filling of organs in real time, the laboratory assistant manages to record how much the substance is required to complete the absolute filling phase.
When using a “tight” type of examination, it is possible to additionally establish a clear location of the ulcer, or confirm the presence of a neoplasm. If the presence of the latter is confirmed, then you will have to additionally go for other tests to determine the nature of the specific tumor.
All manipulations should be carried out with the patient in the Trendelenburg position. In practice, this means that in order to better view a person’s stomach, his pelvis is raised to a level of 45 degrees relative to the rest of the torso. Thanks to such a cunning trick, the laboratory technician can easily see a possible hernia characteristic of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm.
After checking in the indicated position, the victim will be asked to turn over on his side, which is especially important when trying to find some rare congenital or acquired pathologies.
How it works
There are several options for where this type of testing can be done. These are private clinics or public hospitals with an inpatient department. But private medical institutions are increasingly abandoning such studies of the stomach in favor of modern, safer analogues, so it is easier to find working devices in public hospitals. They use outdated technology that allows them to study the internal parts of the body based on the resulting black and white “photographs.” All bone structures, together with possible foreign objects, are painted in dark tones on visualization, while the soft tissues of the abdominal cavity have lighter shades.
Content:
- How it works
- When you can't do without contrast
- Indications for use
- Trendelenburg study
- Contraindications for
The main advantage of the analysis is the ability to conduct assessments in real time, which guarantees the provision of fresh sections. This is relevant for situations when, during the examination, it turns out that the victim needs emergency surgery.
A popular method helps to determine not only the structure of the organ being studied, but also to understand in detail its distensibility, contractility, and displacement. When the patient is injected with barium sulfate, aimed at improving the final detail, it is possible to consider patency, as well as filling.
By controlling the flow of the contrast agent, it is possible to see even the localization of the changes occurring. This became possible thanks to rotation during direct manipulation.
Sometimes candling is a mandatory phase, which is typical of the preparatory stage if there is a need to carry out any instrumental procedure in the future. We are talking about:
- angioplasty;
- fistulography;
- catheter installation.

Initially, analog devices were used to obtain the necessary information, which required that the results be printed on film material. Today, the mechanism of how fluoroscopy is done is no different from the version ten years ago, but it displays the image directly on a computer screen. A digital installation can do this. It is believed that innovative analogues, while maintaining the same data collection algorithm, load the body with a lower percentage of radiation. Against the backdrop of this advantage and the ability to immediately see what is happening in the lungs, people prefer to use digital equipment. The visualization received from it can be stored on a disk or flash drive, or printed through a printer on paper.
The updated approach allowed diagnostics to get rid of several significant shortcomings, the main one of which was a reduction in radiation dosage by approximately 90% compared to previous machines.
Another difficulty was the low spatial resolution. Modernized units, which have a copy mode, are practically not inferior in clarity to the standard radiography mode. Previously, the problem was the inability to properly monitor the functional state of some internal organs that were dynamic. It was especially difficult to recognize heart parameters. Now, thanks to enhanced stabilization, it is possible to record the state of the organ during its active activity.
The final difficulty was the inability to properly document the information received. Thanks to digital detectors, doctors have learned to save examination results not only frame by frame, but also in short video format.
Despite the fact that survey diagnostics of this kind are a tool for studying soft tissues, they are occasionally used to evaluate the skeletal structure. The unusual direction of use is explained by the urgent need to consider the localization of complex traumatic injuries. And based on the data obtained, a decision is made on which area to conduct a classic X-ray, or even send the victim for an MRI.
But if the sternum area lends itself well to examination, then studying the characteristics of the duodenum, as well as other components of the peritoneum, is a real problem. Here you will have to use a special solution with barium, which will “illuminate” the organs of the retroperitoneal space. The effort will pay off in differentiation, as in the traditional black-and-white “photo” of a bone structure.
Indications for use
Since fluoroscopy is almost always an integral part of contrast, it is usually used to evaluate the gastrointestinal tract. The list of indications for examining the sternum is somewhat shorter than for the abdominal cavity.
The lungs are subjected to a similar load when it is necessary to monitor the process of puncture of the pleural area, which gives rise to two main reasons for issuing a referral for fluoroscopy:
- pleurisy;
- pericarditis.
In all other situations, it is easier to use computed tomography or the capabilities of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. But there are more indications for such an analysis of the gastrointestinal tract:
- diverticula;
- achalasia steal;
- hiatal hernia.
All of the above can be combined together, since in the three cases described, the contrast should be transported really simply.
Changing the patient's position in time will help to recognize the emerging shadow of a tumor. The patient is sometimes asked to simply stand or turn around.
Much less frequently than for gastroenterology and pulmonology, the method is used in:
- cardiology;
- urology;
- gynecology;
- traumatology.
The first group involves searching for areas of the heart valves that have received limescale deposits. Due to the good permeability of the solution, large vessels are tested for the same limescale inclusions. The secret of its effectiveness lies in the fact that lime belongs to the camp of contrast agents.
Women who have been prescribed hyperosalpingography must also go through the stage of introducing a special suspension. With its help, it is possible to detail the condition of the uterus with tubes. A similar algorithm uses contrast when it is necessary to monitor the process of urination. When monitoring the dynamics of urine passage, uterthrography is indispensable.
Traumatologists who prefer the results of standard radiography are sometimes still forced to use data with a barium suspension to align bone fragments. The quality of the image, together with the skills of a particular specialist, will determine how well the bone will assemble so that it can later heal without significant functional losses for the person.