General information
Cancer of the digestive system is a malignant lesion of the digestive tube, as well as the glands involved in the process of digesting food. This type of oncology is dangerous because it may not manifest itself for a long time, damages a large volume of tissue and is capable of metastasis to neighboring and distant organs. Cancer tumors have different sizes and localization, histological type and shape, but lead to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and the formation of complications.
Compared to other types of cancer, the 5-year survival rate for gastrointestinal lesions is lower. If these are stomach tumors, it is up to 30%, for intestinal lesions - about 68%. With pancreatic cancer, only 9% of people live more than 5 years after diagnosis. The mortality rate from cancer of the digestive system is twice as high as the death rate from breast and prostate cancer combined. Source: E.M. Axel Statistics of malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract // Siberian Journal of Oncology, 2021, No. 16(3), pp. 5-11
The problem is also in the treatment of this type of cancer. Usually a combined approach is required with tumor removal, as well as radiation and chemotherapy. This is quite difficult for the body, so you need to select therapy individually and carefully, taking into account the stage and location of the cancer.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics is necessary to answer the following questions:
- Assessment of the size of a malignant tumor and its prevalence.
- Determination of process localization.
Diagnostics includes two types of studies: Detection of a tumor and assessment of the extent of spread of the tumor process to develop optimal treatment tactics.
Diagnostic methods
- X-ray of the stomach. It consists of an X-ray examination of the organ using a special contrast agent, which the patient drinks before the procedure. This is a painless and informative method of examination.
- FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy). A minimally invasive study during which a special flexible probe with a light source and a miniature camera is inserted into the patient's stomach. Allows you to visually assess the condition of the esophagus, stomach, and initial parts of the small intestine. In parallel with the study, biomaterial is collected.
- Biopsy. The essence of this study is to collect a section of tissue for histological analysis. It can be carried out both during FGDS and during the operation.
- CT scan. Makes it possible to obtain detailed images of the structures of the stomach. The procedure is absolutely painless and lasts no longer than 10-15 minutes.
- Endousy (endoscopic ultrasound). The procedure is similar in nature to FGDS, however, the apparatus for performing it has an additional sensor that allows a more detailed assessment of the depth of tumor growth into the layers of the stomach.
- Laparoscopy. A minimally invasive operation performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Its essence is the introduction of special instruments into the abdominal cavity through pinpoint incisions. It is performed under general anesthesia.
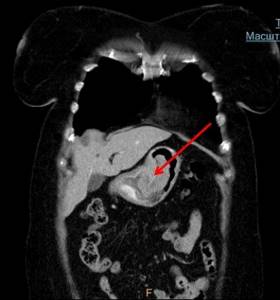
Assessment of the patient's general health.
- General blood analysis. It is carried out to estimate the amount of hemoglobin and blood cells (leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets). For accuracy, the test should be performed on an empty stomach.
- Biochemistry of blood. It is carried out to assess the amount of ALT, AST, bilirubin, amylase, bilirubin, glucose, albumin and other indicators.
- General urine analysis. It is carried out to assess the functioning of the human excretory system.
- FVD (function of external respiration). It is carried out to assess the condition of the lungs. The essence of the study is to determine the vital volume of the lungs.
- Electrocardiography. Prescribed to assess the functional state of the heart.
- EchoCG (echocardiography). Prescribed to assess the anatomy and functional state of the heart.
The diagnosis of stomach cancer is made only after a complete examination, including mandatory histological examination.
Causes of gastrointestinal cancer
Tumors of the digestive system are a fairly heterogeneous group of cancers. To date, no single specific reason has been identified that would provoke the growth of malignant oncological diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The influence of negative external factors in combination with a person’s genetic predisposition to the development of cancer is highlighted. These combinations provoke the transformation of healthy cells of the digestive system into neoplastic ones, which give rise to a cancerous tumor.
General risk factors for gastrointestinal cancer are relevant for most tumors. These include:
- bad habits – smoking, vaping and drinking alcohol in excessive doses;
- aging of the body;
- food high in fats, dyes, preservatives, chemical compounds, carcinogens;
- chronic inflammatory lesions of organs (colitis, pancreatitis, gastritis);
- overweight, obesity, metabolic syndrome;
- prolonged and irrational use of certain medications.
Some types of cancer also have their own additional provoking factors. For example, stomach cancer is typically characterized by the presence of Helicobacter pylori, an acid-fast bacteria that damages cells, in the mucous membrane of the organ. For esophageal cancer, one of the provoking factors is reflux disease - the constant reflux of acid from the stomach leads to epithelial metaplasia and initiation of cancer. Long-term episodes of intoxication at work and at home are typical for intestinal cancer. Ulcerative colitis and intestinal polyposis, pernicious anemia can also be provocateurs of colon cancer.
Preparing for a blood test for cancer
To obtain reliable test results, patients should adhere to certain recommendations before taking blood:
- 2 weeks before the test, stop taking systemic medications;
- 2-3 days before the analysis, exclude fatty and fried foods and alcoholic beverages from the diet;
- stop smoking 2 hours before blood sampling;
- 30 minutes before the procedure, bring your emotional state back to normal, avoid mental and physical stress;
- In order to avoid obtaining distorted results, do not conduct analysis immediately after performing other types of examination (laboratory or instrumental).
You can eat food before a general blood test, but it is better not to eat eight hours before the test. To obtain a correct, undistorted result of a biochemical blood test, fasting is recommended before the test (8-12 hours). It is allowed to drink liquid in the form of purified still water.
First signs, clinical symptoms
For many types of gastrointestinal oncology, there are a number of specific signs reflecting dysfunction. The common characteristics of all types of cancer of the digestive organs are their long, asymptomatic course; in the early stages, patients have no complaints, or the complaints are general. Serious manifestations occur when tumors reach large sizes, destroy the intestinal wall, grow into neighboring tissues, and compress the ducts of the glands. Common signs include:
- feeling of pressure in the chest, abdominal cavity, back pain;
- disruption of the passage of food through the esophagus, disorder of bile secretion or excretion of pancreatic enzymes;
- digestive disorders with bloating, cramps, particles of undigested food in the stool;
- the appearance of blood in the stool or changes in its color.
Typically, symptoms of gastrointestinal cancer occur in the presence of large cancerous tumors, if they put pressure on the intestine, liver or neighboring abdominal organs. Occurs:
- nausea, lightheadedness, vomiting, sudden loss of appetite;
- pain in the affected area, especially after eating or exercising;
- a feeling of rapid satiety with food, severe hunger or anorexia;
- bloating, belching, flatulence, seething, constipation;
- palpation through the abdominal wall of a tumor-like formation. Source: Kentaro Murakami, Hisahiro Matsubara Chronology of Gastrointestinal Cancer // Surg Today. 2018 Apr;48(4):365-370. doi:10.1007/s00595-017-1574-y. Epub 2021 Aug 9
When the stomach is affected, bloody vomiting, anemia, and black stools are typical. If the liver is damaged - jaundice, itching, stool discoloration, alternating diarrhea and constipation, flatulence.
The first signs of stomach cancer: when should you be wary?
With stomach cancer, the first symptoms are in most cases local, caused by the resulting dysfunction of the organ affected by the tumor. But general nonspecific manifestations cannot be excluded. Moreover, in the initial stages of the disease they are associated not with cancer intoxication, as in advanced stages, but with anemia against the background of recurrent (repeated) gastric bleeding.
The first symptoms of stomach cancer may be:
- Discomfort in the stomach area soon after eating. The pain experienced is usually quite tolerable in intensity; many patients describe it as a feeling of fullness, unpleasant distension against the background of a small (habitual) amount of food eaten.
- The appearance of a tendency to belch, and it is usually sour in nature and is not associated with overeating.
- Increased acidity of gastric juice, which is why belching is often accompanied by a feeling of heartburn.
- Weakness, fatigue, discomfort and a tendency to random dizziness during physical activity. Typically, such complaints in case of initial stomach cancer are the first symptoms of chronic anemia that has gradually developed. Its appearance is caused by repeated small-scale bleeding from superficial vessels destroyed by the tumor. They may be accompanied by a change in the density and color of the stool, it becomes viscous and darkens. But many patients do not pay attention to this. But in many cases, such early bleeding in stomach cancer is detected only by examining stool for occult blood.
- Moderate changes in taste and food preferences, which can also be explained by the manifestation of anemia. But these symptoms are still more typical for later stages of cancer.
Some patients report slight weight loss. But in the early stages of the disease, this is not yet typical cancer cachexia (wasting), but rather a consequence of changes in appetite and a decrease in the amount of food eaten.
Types of gastrointestinal cancer
Cancerous tumors of the gastrointestinal tract are differentiated depending on location. These include tumor lesions:
- tongue and pharynx;
- larynx;
- different types of stomach cancer;
- lesions of the pancreas;
- primary and metastatic lesions of the liver, bile ducts;
- small intestinal cancer;
- lesions of the large intestine;
- rectal and anal cancer;
- different localizations of gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
Based on the shape of the cancer tumor, taking into account its appearance, growth and cell composition, several types of lesions are distinguished:
- Ulcerative . The tumor grows into the lumen of the organs, gradually blocking it.
- Polypous . Nodes of different sizes are formed, protruding into the lumen of the organ and blocking it.
- Diffuse . The second name is infiltrative. It forms under the mucous membrane, affects all layers of the organ and grows away from the primary focus. Ulcers may form on the surface of the affected area. Source: Nathan M Krah, L Charles Murtaugh Differentiation and Inflammation: 'Best Enemies' in Gastrointestinal Carcinogenesis // Trends Cancer. 2016 Dec;2(12):723-735. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.11.005
Based on the structure of the cells that form cancerous tumors, there are several types of oncology. Based on these data, the doctor determines the aggressiveness of the course and prognosis of the disease.
- Highly differentiated tumor - cancer cells are very similar to healthy ones, tumor growth is slow, metastases are possible only in the terminal stages.
- Moderately differentiated tumor - cancer cells differ from healthy ones, the tumor grows relatively slowly, metastases are possible already at stage 3 of the process.
- Poorly differentiated tumor - cells differ significantly from normal ones, a typical rapid increase in cancer size, metastases affect neighboring tissues, lymph nodes and distant organs.
- Undifferentiated tumor – the cells are immature, appear from the mucosa, the course is aggressive with rapid growth of the tumor, metastases are possible in the early stages, the prognosis for life is unfavorable.
What is considered stomach cancer?
Stomach cancer is a malignant neoplasm that originates from the mucous membrane of any part of the stomach. Such a tumor does not have a clear demarcation from healthy cells; it easily grows into surrounding tissues, overcomes the outer serous membrane and spreads beyond the organ. Therefore, in the later stages, a conglomerate forms in the abdominal cavity, which can involve all adjacent anatomical formations.
In addition, stomach cancer quickly grows into the walls of blood vessels and begins to spread hematogenously and lymphogenously (through the blood and lymphatic channels). Its particles settle as metastases in the lymph nodes and organs; the favorite places for such cancer screenings are the liver, lungs, brain, and in women also the ovaries.
But at the first stage, gastric cancer is limited to the mucous membrane (stage 1A) or submucosal layer (stage 1B); there are no regional or even distant metastases yet. The tumor is small, its effect on the functioning of the organ and the entire body is still insignificant. Therefore, the first signs of stomach cancer that appear do not cause significant discomfort to the patient. In most cases, they are ignored or taken for manifestations of banal gastritis or even overeating. Therefore, people with the first symptoms of stomach cancer prefer self-medication, do not consult a doctor and do not see a reason for self-examination. This leads to late detection of this terrible disease.
Diagnostic methods
To detect cancer of the digestive tract, laboratory tests and instrumental diagnostics . In many ways, the examination plan depends on the location, size and type of cancer. Most gastrointestinal tumors do not have specific tumor markers that detect cancer at an early stage, so the doctor takes into account the first signs in adults, typical complaints and data obtained from imaging.
Typically, tumors are first discovered during endoscopic examination (fibrogastroscopy, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy), supplementing the study by taking a biopsy of a suspicious area with histological, genetic and histochemical tests.
Ultrasound diagnostics are also indicated to determine the size of the tumor, its location and boundaries, CT or MRI , and radiography . The general condition of the patient is determined based on blood and urine tests. Source: L.A. Mitina, V.M. Khomyakov, S. O. Stepanov General principles of ultrasound diagnosis of tumors of the esophagus, stomach and colon // Russian Journal of Oncology, 2012, No. 1, pp. 28-31
When to take blood tests
Oncology does not have any strictly specific initial symptoms. The development of a tumor in the body occurs individually and depends on many factors - the localization of the pathological process, stage, condition of the body, and so on. However, there are several signs of cancer that most often allow you to suspect the disease at an early stage:

periodic unmotivated increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels (37.5-38.5 degrees);- gradual, causeless weight loss;
- weakness, asthenia, fatigue;
- increased night sweats.
Despite the fact that these symptoms can manifest themselves in various pathologies - from infectious to cardiac, when they appear, it is imperative to undergo a general blood test. And after receiving the results, the attending physician will refer you for in-depth diagnostic procedures, if necessary.
Treatment of gastrointestinal tumors
The leading method of therapy for gastrointestinal cancer is surgical removal of the tumor or part of it. If cancer is detected at a late stage, metastases to distant organs or growth into neighboring tissues are determined, the tumor is inoperable or the patient’s condition does not allow radical intervention, other methods are used, including palliative and symptomatic therapy.
During the operation, surgeons remove all cancerous tissue, including some healthy areas; if there are metastases, they also remove nearby lymph nodes. This is important to prevent relapses. After the operation, rehabilitation is carried out, and additional courses of therapy may be prescribed.
Radiation therapy can be an additional method, carried out before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor, or after it to suppress the growth of remaining cells. Source: V.Yu. Skoropad, B.A. Berdov, L.V. Evdokimov, L.N. Titova Intraoperative radiation therapy - an innovative technology in the combined treatment of tumors of the gastrointestinal tract // Volga Oncology Bulletin, 2013, No. 1, pp. 4-10
Chemotherapy may be used to destroy cancer cells before and after surgery, and for inoperable cancer as palliative treatment.
Laboratory diagnosis of cancer
Tests of biological fluid for cancer do not always provide a clear picture, and the doctor is forced to resort to instrumental diagnostic methods. The Yusupov Hospital is equipped with the latest equipment from European, Japanese, and American manufacturers, which makes it possible to detect a cancerous tumor of any location at an early stage of the cancer process.
CT scan
Using computed tomography scanners, doctors obtain layer-by-layer images of internal organs. Modern equipment makes it possible to perform tomography of the whole body or one or several organs, regardless of the patient’s weight.
Magnetic resonance imaging
With the help of magnetic resonance imaging, doctors obtain an accurate image of internal organs, bones, and soft tissues using pulses of electromagnetic radiation and a magnetic field. The advantage of this diagnostic method is its harmlessness. When using modern devices, patients do not receive radiation exposure. Doctors usually conduct magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, spine, muscles, and joints.
Mammography
Mammography is used to diagnose breast tumors. Modern expert-class devices installed at the Yusupov Hospital make it possible to detect volumetric formations with a diameter of several millimeters. The study is safe and does not cause discomfort in women. It is carried out regardless of breast size. The research results are presented in digital images or on film. Mammologists recommend that women over the age of 40 undergo preventive examinations annually. To rule out the presence of a malignant neoplasm, you should visit a doctor and have a mammogram or ultrasound examination of the mammary glands.
Make an appointment
Scintigraphy
This is a method of radionuclide diagnostics using gamma rays. With its help, doctors detect malignant tumors 6-12 months earlier than using other laboratory and instrumental methods. During the study, it is possible to visualize even the smallest volumetric formations, determine their nature and exact location. Scintigraphy is used to study the skeletal system, brain, mammary glands, lymphatic system, salivary glands, heart, liver and kidneys.
The device can operate in scintigraphy mode of the whole body or targeted projection of certain areas. Using scintigraphy, oncologists evaluate the effectiveness of chemical and radiation therapy and determine the viability of implants in bone tissue. The procedure is not performed on pregnant women and patients whose condition is assessed as serious.
Ultrasound
At the Yusupov Hospital, functional diagnostic doctors perform ultrasound examinations using the latest expert-class devices. They allow you to see a clear picture and get a high-quality image. Differential diagnosis of soft tissue tumors is carried out using elastography, a method based on visualization of soft tissues, determination of their elasticity and other characteristics. Oncologists prescribe ultrasound examination of the following anatomical areas:
- Thyroid gland;
- Lymph nodes;
- Mammary glands;
- Hearts;
- Abdominal and pelvic organs;
- Prostate;
- Kidney.
Biopsy
Used to determine the nature of the tumor process. Surgeons obtain pieces of tissue that are sent to the laboratory for histological examination using the following techniques:
- Stereotactic trephine biopsy - used in the diagnosis of microscopic neoplasms with a diameter of 1-2 mm, which are located in the mammary glands;
- Ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy – used primarily to extract the contents of breast cysts;
- Trephine biopsy using ultrasound – performed using a biopsy gun;
- Vacuum aspiration trephine biopsy – allows you to obtain large fragments from tissues;
- Core needle biopsy – used to remove a large tissue sample;
- Incisional biopsy - involves excision of a piece of tumor under local anesthesia;
- Excisional biopsy is a mini-surgery during which the surgeon removes the entire tumor or excises part of it.
Pathological examination
Morphologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a pathological examination of pieces of pathologically altered tissue using special equipment.
Dermatoscopy
Using dermatoscopy, the nature of skin formations is determined. The study is necessary if there are a large number of pigmented moles on the skin, changes in their shape and color. It allows you to detect skin cancer and melanoma at an early stage.
Prognosis for gastrointestinal cancer
In many ways, the prognosis for life and health depends on the type of tumor cells, the stage of detection and treatment features, the age of the patient and the concomitant pathologies he has.
The most unfavorable prognosis is for pancreatic cancer, the most optimistic is for neuroendocrine tumors of the intestinal wall. The 5-year survival rate ranges from 5 to 90% depending on the type of cancer. In the initial stages, when there are no metastases, the chances of success reach 80-90%, in the terminal stages they do not exceed 10%.
Sources:
- EAT. Axel. Statistics of malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract // Siberian Journal of Oncology, 2017, No. 16(3), pp. 5-11.
- L.A. Mitina, V.M. Khomyakov, S. O. Stepanov. General principles of ultrasound diagnosis of tumors of the esophagus, stomach and colon // Russian Journal of Oncology, 2012, No. 1, pp. 28-31.
- V.Yu. Skoropad, B.A. Berdov, L.V. Evdokimov, L.N. Titova. Intraoperative radiation therapy is an innovative technology in the combined treatment of gastrointestinal tumors // Volga Oncology Bulletin, 2013, No. 1, pp. 4-10.
- Kentaro Murakami, Hisahiro Matsubara. Chronology of Gastrointestinal Cancer // Surg Today. 2021 Apr;48(4):365-370. doi:10.1007/s00595-017-1574-y. Epub 2021 Aug 9.
- Nathan M Krah, L Charles Murtaugh. Differentiation and Inflammation: 'Best Enemies' in Gastrointestinal Carcinogenesis // Trends Cancer. 2021 Dec;2(12):723-735. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2016.11.005.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
FAQ
When deciphering blood tests, patients often ask questions about how this or that indicator can change with cancer and what this can mean. Let's look at the most common of them.
Can a good blood test be detected in cancer patients?
Yes, it can if the disease is detected in the initial stages or at the compensation stage. In addition, do not forget that there are a huge number of types of blood tests and a situation may arise that there are no changes in the general analysis, and tumor markers were not detected.
However, the situation when a general blood test for cancer does not have any abnormalities does not occur so often
Is it possible to determine the stage of cancer using a blood test?
Oncology is staged based on many criteria, and most of them are purely clinical - the spread of the primary tumor, the presence of metastases in the lymph nodes and nearby organs, and so on. Therefore, if it is possible to draw a parallel with the stage using a blood test, then it is very approximately, and such an analysis should be highly specific, such as genetic tests or determination of tumor markers.
Is there a specific test to detect stomach cancer?
Stomach tumors cannot be detected by analyzing general blood tests. However, today there are innovative molecular tests that make it possible to determine gastric cancer and its antigenic set. This is the detection of PEA-1 tumor markers and the Foundation One genetic test, which completely determines the antigenic profile of a cancer cell. This test will show the cancer itself and determine its aggressiveness.
These tests are not carried out in all clinics in the world and are expensive. At the First Tel Aviv Medical Center, the patient has the opportunity to order all the latest genetic and molecular tests.
Can a blood test detect cancer?
Most often, even general and biochemical blood tests will show changes in indicators in the presence of cancer. However, this does not always happen and these changes may be associated with other reasons - infections, stress, and so on.
Identification of specific tumor markers is a more specific criterion, but they can also be elevated in related pathologies. But innovative genetic tests will always give an answer - what type of tumor led to the changes, whether it is treatable and show the degree of aggressiveness of atypical cells.
However, such tests are not performed in the CIS countries, so the answer to the question is no, there is no general test that determines cancer in the blood.
What tests should I take for blood cancer?
For hemoblastoses, the most effective will be a general blood test with a formula of cellular elements and a detailed biochemical analysis with the identification of tumor markers NSE and CEA-5
Deciphering a blood test for bone marrow cancer
In this situation, the general analysis will include immature cells and progenitor cells that are not normally found in the blood. During a tumor process in the bone marrow, they do not have time to develop to mature forms, enter the bloodstream and cease to perform their function