One of the diagnostic methods during pregnancy is ultrasound examination. How many times should the expectant mother undergo this examination, what information does ultrasound provide depending on the timing of its implementation, and in what cases does the number of examinations increase?
Almost all expectant mothers undergo ultrasound examinations, at least three times during the entire pregnancy - provided that the woman is registered with the antenatal clinic for a short period of time (up to 12 weeks) and follows all the recommendations of the obstetrician-gynecologist managing her pregnancy, which reflected in the relevant regulatory documents of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. However, for many women this test is performed more often.
It’s worth saying right away that obstetric ultrasound (a study performed during pregnancy) is a very important and informative diagnostic method that helps answer many questions and allows one to identify certain abnormalities in the intrauterine development of the fetus.
The examination itself is absolutely painless: the patient does not feel any discomfort, except for the sensor moving across her abdomen. Numerous scientific data indicate that ultrasound is almost completely harmless for the health of both the expectant mother and her baby. In particular, it was shown that the doses and intensity of ultrasound exposure during a standard obstetric examination did not have a negative effect on the embryos of laboratory animals and the chromosomes of living cells. Considering the safety and high informativeness of this study, the World Health Organization recommends ultrasound examinations during pregnancy at least 3 times.
However, expectant mothers should not abuse ultrasound examinations on their own initiative. For example, you should not run dozens of times for examination just to clarify the sex of the baby, estimate its weight and size. Agree, it is difficult to imagine that a pregnant woman would once again go to donate blood out of curiosity, without a doctor’s prescription; for an ultrasound examination, the timing and indications are also determined.
A little history
In the old days, our great-grandmothers not only did not know the concept of “pregnancy management,” but moreover, they considered it a bad omen to talk out loud about the unborn child. Like, childbirth will be difficult. But, as modern practice shows, in most cases, medical care not only does not aggravate, but helps ensure a successful resolution and often saves the lives of the mother and baby. Therefore, you should not be afraid to go to a consultation and have a frank conversation with your doctor. It is better, of course, if the doctor is an acquaintance, a friend, or simply recommended as a thoughtful and friendly specialist.
Here is a list of what you need to do in preparation for pregnancy:
- 1. Examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist. The doctor will examine you, talk to you, and take smears for flora and oncocytology. If during the consultation the doctor reveals any abnormalities, he will prescribe the necessary tests and ultrasound. Healthy women do not need to have a blood test for hormones.
- Definition of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). In preparation for pregnancy, the causative agent of gonorrhea, chlamydia and Micoplasma genitalium is determined by PCR in the discharge from the genital tract. The definition of ureaplasma is considered outdated.
- Fluorography.
- Testing for HIV, hepatitis B, C, syphilis. These tests are not mandatory, but women at risk may want to have them done before pregnancy.
- Folic acid in a dosage of 400 mcg per day for both partners. It is advisable to start taking folic acid at least 3 months before pregnancy and throughout the first trimester. Since you cannot know the exact date of conception, start taking this vitamin as soon as you decide to become pregnant.
- It is advisable to avoid alcohol, smoking, and drugs at least 3 months before pregnancy.
- For overweight, weight correction.
- If you have chronic diseases or take medications, consult your doctor. Perhaps even at the stage of preparation for pregnancy it is necessary to adjust the treatment or switch to other drugs.
The principle of ultrasound diagnostics
For those who still doubt whether to agree to a routine ultrasound during pregnancy , a little about the essence of the method.
The operation of the device is based on the properties of sound propagation in various media, in particular, on the division of the sound flow into refracted and reflected when passing from one medium to another. The reflected part of the flow returns to the sensor and its power determines the structure of the medium into which the sound penetrated. The result is shown on the monitor screen in the form of areas of greater or lesser brightness, which corresponds to the density of the bodies under study.
The method is considered absolutely harmless to humans.
In order to register you will undergo the following studies:
- Speculum examination, vaginal examination by your obstetrician-gynecologist. An inspection is required upon registration. During other visits to the residential complex, examinations are carried out if necessary.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). Fetal ultrasound is performed in the perinatal center from 11 to 14 weeks, then from 18 to 21 weeks, then from 32 to 35 weeks.
- An examination by an endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, dentist, therapist, and ENT specialist is carried out during the first visit to the residential complex. The endocrinologist will give you a referral for an analysis of thyroid hormones (TSH, T4, antibodies to the thyroid gland). Additional consultations with narrow specialists are prescribed according to indications, especially for women with chronic diseases.
- ECG. As a rule, electrocardiography is performed once, but can be repeated if necessary.
Laboratory research:

- General analysis of vaginal discharge, determination of antibiotic sensitivity.
- Testing for gonorrhea, chlamydia, and mycoplasma using PCR is carried out once in the first trimester, and for syphilis we additionally repeat it at 28-30 weeks.
- Determination of antibodies to HIV, hepatitis C and B viruses
- Determination of antibodies to toxoplasma and cytomegalovirus (CMV) upon registration, then if antibodies were not detected, the analysis is repeated in the second trimester from 18 to 20 weeks. After you have registered at the antenatal clinic, the results of your examinations will be entered into the exchange card. Depending on how you feel and how your pregnancy is going, your doctor may prescribe tests, ultrasound, or examination by specialists earlier than prescribed in the protocols.
Purpose of ultrasound during pregnancy
Ultrasound examination makes it possible to determine in utero the following parameters, deviations and malformations of the fetus:
- amount of amniotic fluid: in case of oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, appropriate therapy is prescribed
- condition of the placenta: including the possibility of independent pregnancy and natural childbirth
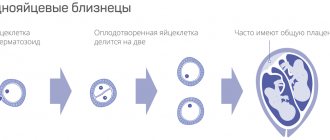
- number of embryos, their gender, degree of development, age correspondence
- the presence of developmental defects: defects of the skeleton, neural tube, heart, etc.
- identification of fetal defects incompatible with life
- determining the position of the fetus and the nature of future births
- determination of the position of the umbilical cord, the nature and intensity of blood flow.
Currently, medicine is capable of interfering even with intrauterine development and, in case of emergency, recommending abortion as the lesser of evils. In addition, ultrasound can reveal such nuances as oxygen deficiency of the fetus due to congestion in the placenta or umbilical cord overlap. Some of them are easily treated and the fetus subsequently develops absolutely normally. They can only be diagnosed through ultrasound.
Additional Research
It is very difficult to answer the question how many times during the entire period of bearing a child a woman will have to undergo an ultrasound procedure. It all depends on the health and age of the expectant mother, and on whether she had a bad experience in bearing a child. In addition, if a pregnant woman has complaints about her health, the doctor prescribes additional ultrasound examinations.
Each trimester has its own indications for prescribing an unscheduled ultrasound.
In the first three months of pregnancy, it can be caused by spotting and abdominal pain. The doctor sends for an ultrasound to find out the cause and understand whether there is a frozen or ectopic pregnancy.
In the second and third trimesters, ultrasound examination is indicated for multiple pregnancies, detection of abnormalities in the development and size of the fetus, impaired motor activity, the presence of an infectious disease or placenta previa in the mother, leakage of amniotic fluid, etc. In the later stages, a good reason may be the suspicion that the baby is breech. If it is confirmed, doctors will perform a caesarean section to reduce the risk of injury to the baby.
When is a routine ultrasound done during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, a woman is recommended to undergo ultrasound three times:
- 10-14 weeks: to clarify the timing of pregnancy, the presence of tumors in the uterus, the number of embryos
- 20-24 weeks: assessment of the condition of the placenta, rate of fetal development, sex determination, signs of chromosomal abnormalities
- 32-34 weeks: determination of readiness for childbirth, fetal presentation.
On the recommendation of a doctor, a woman may be prescribed ultrasound at other times. You should not refuse them - after all, this is the simplest and most harmless method of diagnosis.
Can an ultrasound be harmful?
Ultrasound is a procedure that can be performed repeatedly without danger to the health of the expectant mother and fetus and the course of pregnancy. Today, it is considered a highly accurate diagnostic method, incapable of harming the fetus and giving indicative results, subject to compliance with all modern principles and standards.
The study uses the ability of ultrasonic waves to reflect from various surfaces. The “echo” that returns to the ultrasound equipment from body tissue is transformed into an image of the area being examined. Moreover, such waves do not remain in the body, do not accumulate in it, and do not cause other harm. They provide accurate and detailed information that is of great diagnostic value.
It is important to understand that the ultrasound results themselves are not decisive in assessing the development of the fetus or the health of the mother. They are always complemented by other research methods if necessary.
During the study, the woman does not experience pain or any discomfort. When performing a transabdominal ultrasound, she needs to lie on the couch and free her stomach from clothing, after which the doctor applies a gel to the skin and begins the examination. It consists of conducting an ultrasound probe over the skin of the abdomen and transmitting the image to the equipment monitor. Transvaginal ultrasound uses a small transducer over which a disposable condom coated with gel is placed. The sensor is inserted into the vagina.
Today, in addition to standard ultrasound, there is also a Doppler study, which allows assessing the condition of the fetal vessels, and 3D/4D ultrasound, more modern methods that provide “high information content for visualizing individual facial structures in the fetus after 11 weeks of pregnancy, even with transabdominal examination . Taking into account three-dimensional anatomical images of individual anatomical structures will allow for a clear diagnosis of facial development anomalies in these periods. The use of 3D/4D images in archiving will allow us to objectively assess the anatomical picture and make an informed decision on pregnancy management.”
How often should a kidney ultrasound be done?
For the purpose of preventive health monitoring, healthy people are recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and abdominal cavity once a year. Persons suffering from chronic kidney disease need to monitor the disease process and have an ultrasound scan at least once every 3 months.
| Ultrasound service | Price according to Price, rub | Promotion price, rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, stomach) | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of one organ (liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, bladder, adrenal glands) | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys | 1700 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the bladder | 2000 rub. | |
| Kidney ultrasound | 800 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland) | 2400 rub. | 1999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidney + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + pelvic ultrasound with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
| Comprehensive body diagnostics (MRI of the thoracic spine, MRI of the lumbar spine, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist, consultation with a therapist) | 11700 rub. | 7000 rub. |
In the third trimester, closer to childbirth, pregnant women will have the following tests repeated:
- Smear on flora, tank. sowing is given at 34-36 weeks. Typically, women have more frequent smear tests during pregnancy. Remember, if you are concerned about discharge, it would be right to first take at least a smear for flora, and only then use medications based on its results.
- UAC.
We have a stereotype in our heads that all laboratory tests are carried out strictly on an empty stomach. And responsible pregnant women, having deprived themselves of breakfast, feel very bad in laboratories, even to the point of fainting.
Tests that need to be performed on an empty stomach:
- UAC
- HD blood test
- Coagulogram
- Blood glucose
- Glucose tolerance test
- Determining the level of hormones in the blood. When you go to donate blood for the tests listed above, take a snack with you so that you can eat immediately after the collection. But all other studies are performed after eating.
What tests should my husband undergo?
- 1. If your blood is negative, the Rhesus of the child’s father must be determined.
- 2. Fluorography. Fluorography performed within a year is also suitable.
- 3. Blood test for HIV, hepatitis B, C.
Don’t forget, if you are planning a partner birth, your husband needs a health certificate at the maternity hospital. This document is drawn up by a therapist at a local clinic or medical center.
Decoding
The diagnostic doctor will give the results recorded in the protocol to the patient upon completion of the diagnosis. The conclusion reflects all important parameters indicating deviations from the norm. In normal condition, the buds should be bean-shaped with smooth, clearly defined edges. The diagnostician must indicate the size of the organ and the thickness of the capsule. The pelvis system, as well as the calyces, should not be visualized. The most difficult thing to visualize with this examination method is small vessels.
Renal ultrasound protocol
Right kidney
10.39 x 4.88 cm, position and shape are typical, the contours are smooth, clear, the parenchyma is 1.32 cm thick, homogeneous, uniformly hypoechoic, the jaw is not expanded.
The vascular pedicle is not changed.
Pathological formations in the area of the adrenal gland are not visualized.
Left kidney
10.9 x 5.6 cm, position and shape are typical, the contours are smooth, clear, the parenchyma is 1.3 cm thick, homogeneous, uniformly hypoechoic, the jaw is not expanded.
The vascular pedicle is not changed.
Pathological formations in the area of the adrenal gland are not visualized.
Conclusion:
Ultrasound signs of mineral metabolism disorders.
Renal ultrasound protocol
Right kidney
10.17 x 3.99 cm, position and shape are typical, the contours are smooth, clear, the parenchyma is 1.2 cm thick, homogeneous, uniformly hypoechoic, the jaw is not expanded. Weak hyperechoic signals (crystals) are detected in the abdominal system. Concrete 0.4 cm
The vascular pedicle is not changed.
Pathological formations in the area of the adrenal gland are not visualized.
Left kidney
10.07 x 4.53 cm, position and shape are typical, the contours are smooth, clear, the parenchyma is 1.2 cm thick, homogeneous, uniformly hypoechoic, the jaw is not expanded. Weak hyperechoic signals (crystals) are detected in the abdominal system.
The vascular pedicle is not changed.
Pathological formations in the area of the adrenal gland are not visualized.
Conclusion:
Ultrasound signs of mineral metabolism disorders. Right kidney stone.
Second week
In the middle of the cycle, the egg fully matures and leaves the ovary. It enters the abdominal cavity. This process is called ovulation. With a regular cycle lasting 30 days, ovulation occurs on the fifteenth. The egg is not capable of moving on its own. When it leaves the follicle, the fimbriae of the fallopian tube ensure its penetration inside. The fallopian tubes are characterized by longitudinal folding and are filled with mucus. The muscular movements of the tubes have a wave-like character, which, with a significant number of cilia, creates optimal conditions for transporting the egg.
Through the tubes, the egg enters their widest part, which is called the ampullary. It is in this place that fertilization occurs. If the meeting with the sperm does not occur, the egg dies, and the female body receives the appropriate signal about the need to start a new cycle. There is a rejection of the mucous membrane that was created by the uterus. A manifestation of such rejection is bloody discharge, which is called menstruation.
The waiting period for fertilization of an egg is short. On average it takes no more than a day. Fertilization is likely on the day of ovulation and at most the next. Sperm have a longer lifespan, on average three to five days, in some cases seven. Accordingly, if a sperm enters the female genital tract before ovulation, there is a possibility that it will be able to wait for the egg to appear.
When an egg is waiting for fertilization, certain substances are released that are designed to detect it. If sperm find an egg, they begin to secrete special enzymes that can loosen its shell. As soon as one of the sperm penetrates the egg, the others cannot do this due to the restoration of the density of its shell. Thus, one egg can be fertilized by only one sperm.
After fertilization, the chromosomal sets of the parents merge - 23 chromosomes from each. As a result, two different cells form one, which is called a zygote. The sex of the unborn child depends on which chromosome, X or Y, the sperm had. Eggs contain only X chromosomes. When XX is combined, girls are born. If the sperm contains the Y chromosome, that is, with the XY combination, boys are born. As soon as a zygote is formed in the body, a mechanism is launched in it aimed at maintaining pregnancy. Changes occur in hormonal levels, biochemical reactions, immune mechanisms, and the receipt of nerve signals. The female body creates all the necessary conditions for the safe development of the fetus.