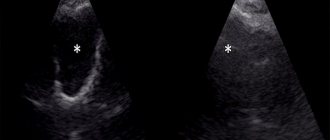
Ultrasound diagnostics (sonography) is a popular, painless and highly informative method of examining patients with a variety of problems. It is impossible to overestimate the importance of ultrasound in the early detection of tumors and other serious pathologies.
It is important to know: the collection and interpretation of diagnostic ultrasound data should be carried out by a specialist with deep theoretical knowledge and extensive practical experience. After all, the health, and sometimes the very life of the patient, depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis!
Our highly qualified ultrasound diagnostic doctors have excellent scientific and practical training and work on the best expert equipment - including the premium Voluson 10 scanner. Such medical equipment is available only in MedikCity and a few other clinics in the country!
1 ultrasound at the MEDICITY clinic

2 ultrasounds at the MEDICITY clinic
3 ultrasounds at the MEDICITY clinic
Uzi is...
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is a study of the condition of organs and tissues using ultrasonic waves. Ultrasound examination is based on the ability of ultrasound to be reflected from internal organs and tissues of varying densities, which appears as an image on the scanner screen. This method is used to examine those organs that do not contain air.
Ultrasound examination is one of the most common diagnostic methods due to its safety. Ultrasound used in equipment is completely harmless. It does not cause any side effects, much less damage. Ultrasound examination is much safer than x-ray and in many cases allows the most accurate diagnosis of the disease.
A little history
The early eighties of the 19th century made the Curie brothers the discoverers of the “piezoelectric effect”. The very concept of “ultrasound” means sound vibrations that lie beyond the threshold of our auditory perception.
The Curie brothers' effect, through which such oscillations can be achieved, came to fruition during the First World War. It was thanks to him that sonar was invented, which was used to navigate ships, search for submarines and calculate the exact distance to the target.
At the end of the 20s of the last century, ultrasound was used in industry, or more precisely, in metallurgy. It was used to evaluate the quality of the product. This type of analysis is called flaw detection.
It was only in 1937 that ultrasound firmly entered medicine, becoming an indispensable diagnostic method. This year was the year of the formation of echoencephalography.
The beginning of the fifties was marked by a real breakthrough in the use of ultrasound: it was finally possible to see the internal organs in the picture, their image. This was the impetus for the widespread use of ultrasound diagnostics to detect many diseases and organ damage, as well as the constant improvement of the method.
Types of ultrasound. Their goals. Preparation.
The following are the types of ultrasound examinations, the purposes of their use and preparation for them:
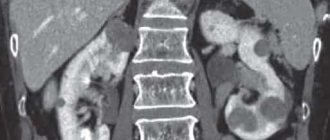
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen)
It is performed to assess the size and structure of these organs, allows to identify congenital developmental anomalies, diffuse and focal pathology of parenchymal organs (liver, pancreas, spleen), assess the condition of the walls of the gallbladder (the presence of inflammatory changes, changes associated with metabolic disorders, identify the presence volumetric formations (polyps and malignant formations), assess the condition of the gallbladder cavity (presence of stones, etc.), the condition of the biliary tract, abdominal vessels and retroperitoneal lymph nodes, motor function of the gallbladder, indirectly draw a conclusion about diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Preparation for an ultrasound of the abdominal organs: before examining the abdominal organs, you must refrain from eating, any liquid, nicotine, and also do not chew chewing gum 6-8 hours before the examination. Ideally, this ultrasound should be performed strictly on an empty stomach in the morning.
Ultrasound of the urinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder)
Allows you to assess the size of organs, the structure of the kidney parenchyma, the condition of the renal collecting system (urinary excretory system), the condition of the walls and cavity of the bladder, to identify diffuse and focal pathology of the kidneys, the presence of calculi (stones) in all parts of the urinary system and congenital developmental anomalies.
As preparation for an ultrasound of the urinary system, you should drink 600-700 ml of any liquid (non-carbonated) 1 hour before the ultrasound and do not urinate for 1 hour. You can eat and drink.
Ultrasound of the reproductive system in women
Allows you to assess the size and structure of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries, identify congenital developmental anomalies, cysts, focal, nodular and diffuse forms of diseases, identify hormonal disorders, observe the process of maturation and release of the egg (folliculogenesis), draw conclusions about the causes of infertility, diagnose pregnancy in early pregnancy, as well as pregnancy pathology, assess fetal development.
For adult women, ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed both transabdominally (through the abdomen) and transvaginally (with an intracavitary sensor through the vagina). The combination of these two examination methods allows you to provide the most accurate information about the condition of the pelvic organs and does not require preparation.
preparation is required for a pelvic ultrasound in women.
Ultrasound of the reproductive system in men
It is performed to assess the size and structure of organs, identify diseases of an inflammatory nature, their complications (cysts, stones, urine outflow disorders, etc.) and space-occupying formations (adenomas and malignant formations).
To examine the prostate gland, two examination methods are used - through the abdomen (transabdominal) and through the rectum (transrectal ultrasound - TRUS).
To prepare for a transabdominal ultrasound (through the abdomen), you need to accumulate a bladder, i.e. 1 hour before the ultrasound, drink approximately 600-700 ml of non-carbonated liquid and do not urinate for 1 hour. Before transrectal ultrasound (TRUS), you need to do two cleansing enemas: in the evening before the examination and in the morning before the examination), there is no need to fill the bladder. You can eat before both types of examination.
Obstetric ultrasound (fetal ultrasound)
Produced at 10-14 weeks, 20-24 weeks and 30-34 weeks. The purpose of the examination is to assess the correct development of the fetus and exclude congenital malformations.
preparation is required for this test.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
Allows you to assess the size and structure of the gland, identify diffuse, focal and nodular pathology of the thyroid gland. Considering that our region is endemic for iodine deficiency in water, air and food, we have a lot of thyroid pathologies. The thyroid gland controls the level of metabolism, therefore it is a very important organ and requires attention.
preparation is required for a thyroid ultrasound.
Ultrasound of the mammary glands
Allows you to diagnose a predisposition to serious diseases of the mammary glands (dishormonal changes), as well as these diseases themselves (mastopathy, cysts and benign and malignant mass formations). The examination of the mammary glands includes examination of the axillary lymph nodes.
preparation is required for breast ultrasound.
Ultrasound of the salivary glands
It is performed to assess their size and structure for the diagnosis of inflammatory, diffuse and focal lesions of these organs, which are not uncommon.
preparation is required for an ultrasound of the salivary glands.
Ultrasound of peripheral lymph nodes
It is performed to verify that the palpable subcutaneous formation is lymph nodes, as well as to differentiate inflammatory and metastatic lymph nodes, although the most accurate method of differentiation is a puncture biopsy of palpable formations.
preparation is required for ultrasound of peripheral lymph nodes.
Ultrasound of subcutaneous formations
Often people find lumps or formations under their skin and do not know where to go or what to do. They come for an ultrasound and we find out the nature of the formation.
preparation is required for ultrasound examination of subcutaneous formations.
Ultrasound of postoperative sutures
In cases of prolonged non-healing of postoperative sutures, ultrasound plays a decisive role in diagnosing the cause of this condition.
preparation for this type of ultrasound .
Ultrasound of joints
Allows you to determine the cause of pain in the joint area. The fact is that it is not always the joint itself that hurts, but the surrounding soft tissues that hurt. Ultrasound allows you to evaluate the condition of the soft tissues of the joints and the contours of the bones that form the joint. X-ray examination determines the condition of the bone structures of the joint, and ultrasound determines the condition of the cartilage, articular surfaces, synovial membrane of the joint, ligaments and menisci, the presence of fluid in the joint cavity and surrounding bags, that is, ultrasound allows one to evaluate inflammatory, traumatic, degenerative and destructive changes in the joints and soft tissue surrounding the joints.
preparation is required for joint ultrasound.
For children: Ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography)
It is carried out to assess the correct development of the brain structures of children, the presence of intracranial hypertension, and the consequences of birth injuries.
Ultrasound of the hip joints
It is carried out to assess the correct development of the hip joint. There is also no preparation required for these studies.
Safety of Ultrasound Diagnostics
Diagnostic ultrasound has been widely used in clinical practice for many years and has no proven harmful effects. However, if used carelessly, it can cause damaging effects. The clinical applications of ultrasound are expanding, the number of patients undergoing it is increasing, and new technologies are being introduced with higher acoustic power of ultrasound, so this test should only be carried out by competent personnel who are trained and aware of its safety. It is also important to maintain ultrasonic equipment in proper technical condition.
Basic principles for the safe use of ultrasound:
- Ultrasound should only be used for the purpose of making a medical diagnosis.
- Ultrasound equipment should only be used by personnel who are fully familiar with its safe and proper use.
- The examination time should be as short as necessary to establish a diagnosis
- Ultrasound output power should be kept as low as possible to obtain useful diagnostic information.
- Ultrasound scans during pregnancy should not be performed for the sole purpose of obtaining photographs or videos.
Currently, there is very little information regarding the possible hidden biological effects of diagnostic power ultrasound on the development of the human embryo or fetus, so the possibility of its influence on brain development cannot be excluded. There is evidence that ultrasound diagnostic power can influence the development of the brain of small animals, but at the same time it is not possible to extrapolate these results to humans. In any case, it is necessary to maintain a balance between diagnostic benefit and risk to the patient.
Ultrasound diagnostics has long been firmly established in our lives, and today it is one of the most popular medical procedures. This method is simple and accessible, and has virtually no contraindications. Ultrasound is considered a highly safe procedure, so there is no need to worry if you are scheduled for an ultrasound examination, even during pregnancy. But it should be remembered that not a single medical intervention, even the most harmless, should be performed unnecessarily. Therefore, before undergoing an ultrasound diagnostic procedure, consult your doctor.
Ultrasound methods
There are several types of ultrasound examinations, among which the most commonly used is scanning (what is traditionally called ultrasound). Recently, Dopplerography has been added to it. Dopplerography is based on the Doppler effect (this is a change in the wavelength reflected from moving objects). This effect makes it possible to study blood flow and the state of patency of blood vessels.
In recent years, intracavity studies have been widely used as a research technique using ultrasonic waves. Special sensors have been developed for them. Gynecological transvaginal and urological transrectal examinations are also performed. These diagnostic methods are the most accurate and modern and allow you to obtain information about almost every millimeter of tissue of the female internal genital organs and the prostate gland in men, therefore in modern medicine they are recommended for widespread use. When conducting intracavity studies, much attention is paid to their sterility, for which special attachments for ultrasonic sensors and sensor processing technologies are used. Intracavitary examinations are also painless and do not cause any significant inconvenience for the patient, although preparation for these examinations is of great importance.
Ultrasound diagnostics is a fast, painless and safe method of obtaining reliable information about your health. Ultrasound helps to make an accurate diagnosis in the shortest possible time and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Carrying out
Special preparation for the procedure is not required, but if we are talking about specific organs, there are recommendations that must be followed so that the result of the study is as accurate as possible.
For example, if we are talking about an ultrasound of the genitourinary system, then several glasses of water are needed to fill the bladder. This is important to ensure a better overview.
Examination of the mammary glands should be carried out between the fifth and fourteenth day of the menstrual cycle.
The procedure itself lasts 15-45 minutes.
The patient assumes the position necessary to ensure the best visualization of the organ being examined.
The specialist applies a special gel to the skin and places an ultrasound sensor that can be moved during the procedure.
At the end of the procedure, the specialist issues the result of the study.
What ultrasound examinations should women undergo at the age of 40-50?
In addition to everything described above, in addition, women over 40 years of age must regularly undergo the following types of studies:
- Ultrasound of the heart (once a year).
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity (every year).
The main thing that can be diagnosed during this procedure is oncological diseases, but there are other problems in the vital functions of the body that can be detected using intestinal ultrasound: accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, infection, inflammatory processes, incorrect location of organs, discrepancy between the sizes of organs and standard values (for example, enlarged lymph nodes).
The intestine is examined in one of three ways: transabdominal (organs are poorly visible through the abdominal wall due to their location, so this method is rarely used), endorectally (by inserting a sensor into the rectum, and it is possible to use a special solution to improve the quality of the picture) , transvaginally (additional method, used if data from other sources is insufficient).
- Mammography (every 2 years).
- Checking the amount of hormones.
- Intraocular pressure (severe changes may indicate serious health problems).
- Gastroscopy (if problems with digestion occur).
If you carry out all the research on time, you can avoid many diseases:
- Cancer (development of cancer in the uterus, intestines, mammary glands).
- Coronary heart disease (and other problems associated with the activity of the cardiovascular system).