Briefly about the diagnostic method
Echocardiography (EchoCG) is a test that uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to view the structure and study the function of the heart.
The common non-medical name for this test is cardiac ultrasound. The research is absolutely harmless to humans. Echocardiography uses reflected ultrasound waves to create images of the heart, its chambers, valves, walls and vessels (aorta, pulmonary arteries and veins). The sensor of the ultrasound machine is located on the chest and sends ultrasound waves that are reflected from the heart and again captured by the sensor, after which the signal is transmitted to the device, where it is converted into an image understandable to a specialist. If it is necessary to assess coronary reserve, stress echocardiography methods (stress echocardiography) are used.
Preparing for an ultrasound with Doppler
In most cases, Doppler ultrasound does not require any special preparation. The attending doctor who issued the referral must explain to the patient the features of this or that type of examination. If an ultrasound examination of the abdomen is performed, experts recommend not eating for twelve hours before the procedure, since the ultrasound waves may not penetrate intestinal gases and air in the lungs.
Before Doppler ultrasound, you must stop consuming tobacco products thirty minutes before the examination and two hours after it. You will have to give up nicotine-containing products due to the property of this substance to contract blood vessels, which may cause incorrect results.
Indications and contraindications for diagnosis
Echocardiography is prescribed to detect heart disease and evaluate its function. Most often, an echocardiogram is prescribed by a cardiologist; in preparation for major vascular operations, an ultrasound of the heart can be prescribed by the attending physician or an anesthesiologist-resuscitator.
Echocardiography can reveal:
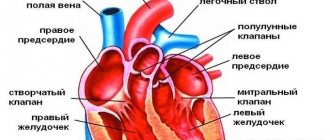
- The size and shape of your heart, the thickness and movement of the heart walls.
- Assess the pumping function of the heart - ejection fraction
- Check the condition of the heart valves, whether the valves are closed, whether there is a narrowing in the valve area.
- The presence of cardiac aneurysms, blood clots in the cavities of the heart.
- Abnormal openings between the atria or ventricles.
- Identify the presence of an infectious process on the valves.
- During echocardiography, you can evaluate the pressure in the pulmonary artery and its size
- Identify aneurysms of the ascending aorta.
- Fluid accumulation or disease in the outer lining of the heart (pericardium).
- Heart tumors.
Echocardiography is a safe study and has no contraindications.
General characteristics of the examination
A procedure such as Doppler ultrasound can be performed both to identify violations when indicated, and for preventive purposes. The whole point is the absence of radiation exposure to the patient’s body, as well as the fact that it will be possible to visualize areas that are inaccessible to other research methods.
Ultrasound scanning of the heart vessels is done using a special sensor that generates ultrasound signals and receives the echo reflected by the tissues. Special software is responsible for converting such signals into images.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
When performing an ultrasound of the heart, the patient is placed on his back or left side. During echocardiography, the sensor can be positioned in different planes for better visualization of the heart chambers. The sensor and the patient's skin are moistened with a special water-soluble gel, which ensures tight contact between the sensor plane and the body.
Our cardiac ultrasound machines allow us to perform various types of echocardiography. One-dimensional echocardiography in M-mode allows you to reproduce the movement of the heart walls and valves in the form of a graph, which allows you to evaluate the function of the ventricles.
Two-dimensional echocardiography shows a section of the heart in a certain projection and allows you to determine the size of the cavities of the ventricles and atria, the thickness of their walls, evaluate the movements of the valves and walls of the ventricles, and identify thrombosis of the cavities of the heart.
Using Doppler mapping, it is possible to identify the speed and direction of blood flow in the cavities of the heart, which makes it possible to determine valve insufficiency or stenosis, defects of the interatrial and interventricular septa.
The usual procedure for echocardiography involves first identifying the heart valves; heart septum. Next, the pattern of movement of the valve leaflets is revealed, the thickness of the walls and the size of the cavities of the heart are measured. Finally, Doppler echocardiography is performed to detect stenosis or insufficiency of the heart valves and pathological holes in the heart septa.
Echo CG with Dopplerography
Echocardiography (ECHO-CG) is a non-invasive ultrasound diagnostic method and is the leading method for diagnosing pathologies of the cardiovascular system. High information content, safety for humans and relatively low price of cardiac ultrasound (compared to other types of diagnostics) are the main parameters due to which the method has become widespread.
During the examination, the doctor evaluates in real time the activity, size and structure of all structures of the heart (heart muscles, chambers (atria and ventricles), valve apparatus, walls, great vessels).
Using an ultrasound examination of the heart, the doctor can confirm or exclude many pathologies of the heart and large vessels
- acquired congenital heart defects,
- post-infarction cardiosclerosis,
- atrial fibrillation,
- heart tumors,
- intracavitary thrombi,
- hypertension,
- ischemic disease,
- valve damage, etc.
This method allows you to accurately determine the speed of blood flow in any part of the heart or great vessel. Another advantage of Doppler ultrasound is its local nature: the results are not affected by blood flow in adjacent segments of the heart.
Indications for ECHO-CG
Diseases of the cardiovascular system often develop without symptoms. In order to notice in time and prevent the development of a minor pathology into a serious disease, it is recommended to undergo echocardiography once a year.
If the following symptoms occur, a study is required:
- acute pain in the heart and chest;
- feeling of lack of air and shortness of breath;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- swelling of the legs;
- frequent bluishness of the skin: ears, hands and fingers, around the lips;
- fast fatiguability;
- heart rhythm disturbances and detection of noise during listening;
- frequent headaches;
- hypertonic disease;
- atherosclerosis.
The procedure for echocardiography and ultrasound of the heart vessels (Dopplerography) is simple and does not require special preparation. During the examination, the patient is placed on the couch on his back or left side. The doctor, using a special sensor, scans the heart in various positions to obtain images of all its parts and surrounding vessels.
After the procedure, a conclusion is issued. Depending on what the ultrasound of the heart shows, the doctor may prescribe additional studies and tests.
What is ECHO-CG of the heart?
Echocardiography (ECHO-CG) is a non-invasive ultrasound diagnostic method and is the leading method for diagnosing pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
High information content, safety for humans and relatively low price of cardiac ultrasound (compared to other types of diagnostics) are the main parameters due to which the method has become widespread. During the examination, the doctor evaluates in real time the activity, size and structure of all structures of the heart (heart muscles, chambers (atria and ventricles), valve apparatus, walls, great vessels). Using an ultrasound examination of the heart, the doctor can confirm or exclude many pathologies of the heart and large vessels
- acquired congenital heart defects,
- post-infarction cardiosclerosis,
- atrial fibrillation,
- heart tumors,
- intracavitary thrombi,
- hypertension,
- ischemic disease,
- valve damage, etc.
In the photo, ultrasound doctor Tatyana Valentinovna Goryunova
Echocardiography with Doppler analysis
In our center, in addition to standard ECHO-CG, echocardiography with Doppler analysis is performed. Our equipment allows us to perform an advanced assessment of the functioning of the heart and great vessels using the following techniques:
- pulsed wave dopplerography. Serves to assess the pumping function of the heart. Allows you to record the clicks of opening and closing valves. Registers the speed of blood flow in the valves and great vessels;
- continuous wave Dopplerography. Allows you to measure high blood flow velocities. Also serves to calculate pressure in large vessels and cavities of the heart in different phases of the cardiac cycle;
- color dopplerography. Allows you to evaluate not only the speed, but also the direction of blood movement through the main vessels. Used to assess pathological blood flow through the heart valves.
Advantages of echocardiography with Doppler analysis
This method allows you to accurately determine the speed of blood flow in any part of the heart or great vessel. Another advantage of Doppler ultrasound is its local nature: the results are not affected by blood flow in adjacent segments of the heart.
Indications for ECHO-CG
Diseases of the cardiovascular system often develop without symptoms. In order to notice in time and prevent the development of a minor pathology into a serious disease, it is recommended to undergo echocardiography once a year. If the following symptoms occur, a study is required:
- acute pain in the heart and chest;
- feeling of lack of air and shortness of breath;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- swelling of the legs;
- frequent bluishness of the skin: ears, hands and fingers, around the lips;
- fast fatiguability;
- heart rhythm disturbances and detection of noise during listening;
- frequent headaches;
- hypertonic disease;
- atherosclerosis.
The procedure for echocardiography and ultrasound of the heart vessels (Dopplerography) is simple and does not require special preparation.
During the examination, the patient is placed on the couch on his back or left side. The doctor, using a special sensor, scans the heart in various positions to obtain images of all its parts and surrounding vessels. After the procedure, a conclusion is issued. Depending on what the ultrasound of the heart shows, the doctor may prescribe additional studies and tests.
How is research done?
The procedure does not involve surgical intervention, that is, it is non-invasive. There is also no radiation exposure, so the study can be carried out both for certain indications and for preventive purposes.
After the patient comes to see the doctor, he is asked to remove clothes that interfere with the examination and lie down on a special couch. After this, a special gel is applied to the sternum, which will help the sensor glide over the skin. Using a sensor, the doctor examines the organ and takes pictures, and also notes the condition and size of all structures. The data obtained will be compared with the norm of Doppler ultrasound of the heart, after which the doctor will draw up a conclusion and give it to the patient.
Diseases that can be detected using Doppler ultrasound
Doppler sonography plays an important role in identifying diseases of the cardiovascular system. These diseases are today considered one of the most dangerous and widespread in the world; they can lead not only to human disability, but also to death. Cardiac Dopplerography is prescribed to narrow the range of diagnostic alternatives; it allows one to identify abnormalities and make a decision on treatment, significantly increasing the chance of a positive outcome.
Congenital heart defect in a child
Heart defects can manifest themselves in both acute and latent forms. The cause of their occurrence is heredity, influenced by the age of the spouses, as well as external influences in the form of viral or infectious diseases. In this case, ultrasound examination of the heart vessels is extremely necessary, since the pathology can lead to tragic consequences.
Myocardial infarction (or pre-infarction condition)
Narrowing of the lumen of a blood vessel is a pre-infarction condition. Complete closure of the vessel and lack of oxygen supply to the heart muscle is a myocardial infarction. The cause may be a plaque or blood clot in the arteries. Such conditions are usually preceded by angina pectoris in an advanced form. Ultrasound of the heart and echocardiography
allow you to examine the organ and identify any abnormalities, make a conclusion about the condition of the blood vessels and determine whether conservative or surgical treatment is needed.
Pressure disorders - hypotension and hypertension
First of all, it is necessary to examine the heart in case of pressure disorders. It is not enough to select drugs that normalize blood pressure and intensity of blood flow; it is important to identify the cause of this phenomenon, since it may lie in heart pathology.
Acquired vices
Ultrasound scanning of the heart is often prescribed for suspected valve defects, otherwise known as “acquired” defects. They lie in the fact that due to infections, inflammatory processes, autoimmune reactions, dilatation and overload of the chambers of the heart, certain changes occur. They can be morphological or functional or combined.