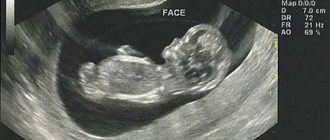
Friday, July 12, 2019
A very exciting moment is the onset of an expected pregnancy. Three days of delay, two lines on a test purchased at the nearest supermarket, and the woman is already sure that the desired conception has come true. However, to accurately confirm this fact, as well as to make sure that the fertilized egg from which the future baby will grow is located exactly where it should be, it is necessary to do an ultrasound of the uterus.
The woman turns to her gynecologist, who prescribes ultrasound diagnostics, but according to the results, the conclusion states that the result is negative: early pregnancy is not visible on ultrasound. Sometimes it happens that even a month or a little more after a positive test, an ultrasound will not show pregnancy. Why does this happen?
What to do if pregnancy is not visible on ultrasound?
There is no reason to worry. In such a situation, the doctor will certainly suggest taking a test for a specific hormone called hCG. In the first weeks of pregnancy, its concentration in a woman’s blood increases rapidly, doubling its levels every day. After blood tests and examination, the doctor will tell the woman how many days later the pregnancy will be visible on an ultrasound.
If both tests are positive - the one performed at home and the hCG test - and the ultrasound still does not show pregnancy, then it makes sense to undergo an examination in another medical institution with another specialist. Perhaps the problem really is that the device is not of an expert level enough.
Is ultrasound harmful in the early stages?
There are many different opinions about the dangers and benefits of ultrasound. But any pregnant woman should think: “What to expect after an ultrasound? Is this harmful for the baby? Is it harmless to undergo ultrasound in the early stages?
Opinion about early ultrasound of our and foreign doctors
European doctors are against frequent and unnecessary ultrasound examinations at the beginning of pregnancy. Ultrasound is permissible only in certain cases. But doctors in the post-Soviet space have nothing against early diagnosis. They don't think it's harmful.
Due to the wide range of errors that are allowed in early diagnosis, the myth created by girls about the highly reliable determination of any pathology on early ultrasound is dispelled.
So, to establish pregnancy and its normal progression, doctors use the level of hCG in the blood. It is known that the fertilized egg is visible only after this indicator rises above 1000-2000 mU/ml.
A fairly good reason for an ultrasound is elevated or insufficient hCG. A too high level of this indicator can be not only due to twins or triplets, but also due to hydatidiform mole. This is a very dangerous pathology; oncology can develop against its background.
It is now noted that doctors are speculating on ultrasound to determine the sex of the fetus. In some cases, this is commercially beneficial for them. It is because of this that they do not dissuade girls from doing an infinite number of early ultrasounds and assure them of the complete absence of harm. And every girl wants to know as soon as possible how many babies there will be, who to expect (a girl, a boy). They are eager to find out earlier than expected and do not think whether it is harmful and dangerous.
Is it possible to determine the gestational age by ultrasound?
It is possible, but approximately. The doctor determines the approximate period by ultrasound up to 12 weeks of pregnancy, measuring the size of the embryo:
| week of pregnancy | diameter of the fertilized egg, mm |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 6 |
| 5 | 8 |
| 6 | 14 |
| 7 | 20 |
| 8 | 27 |
| 9 | 34 |
| 10 | 40 |
| 11 | 47 |
| 12 | 53 |
| 13 | 60 |
From the fourth to fifth weeks of pregnancy, an additional indicator such as the coccygeal-parietal size is used. The values of this indicator are more accurate for determining the gestational age using ultrasound. Some of these values can be found in the table:
| CTE by ultrasound, cm | week/day of pregnancy |
| 0,3 | 4 |
| 0,4 | 5/2 |
| 0,5 | 6/1 |
| 0,6 | 6/3 |
| 1,0 | 7/2 |
| 1,2 | 7/5 |
| 1,4 | 8/1 |
| 2,0 | 9 |
| 2,7 | 10 |
| 3,6 | 11 |
| 4,7 | 12 |
| 5,9 | 13 |
| 7,3 | 14 |
| 7,6 | 14/2 |
| 8,0 | 14/4 |
| 8,7 | 15 |
And although the CTE indicator is more informative than the size of the ovum, both methods are insufficiently accurate and are only indicative. Especially in cases where a woman does not remember the exact dates of her last menstruation.
When will the ultrasound show the future baby?
At what time does an ultrasound show conception? - this question worries every woman, in case of expecting a long-awaited conception, a delay in menstruation, or simply because of symptoms indicating pregnancy. But first, you need to know how the fertilization period is determined :
- According to the woman’s calculations, starting from the last day of the delay;
- Based on the results of a gynecological examination;
- But the most effective and more accurate will be ultrasound diagnostics.
Ultrasound diagnostics in the case of a vaginal examination (that is, a condom is put on the sensor of the device and inserted into the vagina), provided that the examination is performed by an experienced doctor using a modern device, allows you to record the fact of successful fertilization for a period of 14 days after conception.
This means that on the ultrasound monitor, a device in the uterus, you can see a fertilized egg measuring 0.4 cm after a week of missed period or a month later according to the obstetric period. If you go for an ultrasound a little later, at 1.5 months, then already in such a short time, the device will record the heartbeat of the unborn child.
At what day of delay will an ultrasound show pregnancy? In the case of an abdominal examination (that is, diagnosis is carried out through the abdominal wall), pregnancy will be visible no earlier than 4 weeks of embryonic age, or at least 14-21 days after the 1st day of delay.
29–32 weeks of pregnancy
It is believed that the best time for the third screening is 30–32 weeks of intrauterine development. The child is clearly visible , and he is still quite mobile. It was during this period that many parents decide to take not just a photo of their baby, but also record a video available during a 4D ultrasound. After 32 weeks, the baby will continue to grow, and he will no longer fit entirely on the monitor screen. Therefore, “photo and video shooting” for the family archive will become impossible.

33–36th week of pregnancy
During this period, many children already occupy their final position in the uterus. Ideally, the baby should lie head down. An ultrasound scan at this stage of pregnancy allows the doctor to find out the position of the baby and, if necessary, advise the mother on certain exercises that will help the fetus take the correct position. Also in the middle of the third trimester, so-called late developmental anomalies of the child can be detected - usually this concerns the development of the kidneys.
Advertising
Contraindications
Vaginal ultrasound examination has a small number of contraindications:
- It is never performed if the patient is a virgin, so as not to violate the integrity of the hymen. In this case, such a patient can undergo a transrectal examination, in which a sensor is inserted into the rectum
- The study is prohibited from being carried out in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, because it may provoke premature contractions or uterine contractions before the expected due date.
- This test is not used if the patient is allergic to latex
- If the patient has epilepsy, since the examination requires that she lie still
Scheduled diagnostics
After confirmation of successful conception, the expectant mother is registered with a gynecologist. At the antenatal clinic, she learns that during pregnancy, if the pregnancy progresses normally, she will have three scheduled ultrasounds. This procedure does not have any adverse reactions on the fetus or the expectant mother. There are times when, in order to more carefully monitor the course of pregnancy, the diagnosis is carried out 1–2 times more.
The dates for scheduled examinations are distributed by trimester, because each of them differs in the development and growth of the unborn baby:
During the first trimester (period from 10 to 14 weeks), diagnosis may show chromosomal abnormalities that can cause genetic diseases in the fetus. The features of anatomical development are also determined, and the estimated date of birth is calculated;
During the second trimester (period from 20 to 24 weeks), ultrasound shows the structure of the fetal organs, due to which there is a chance to detect deviations from the normal functioning of the heart, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, liver, as well as malfunctions in the nervous system. At this stage, very often, the sex of the child is determined, you can see the movements of his arms and legs. The length and estimated weight of the fetus are measured, and the placenta is characterized. In the same trimester, a Doppler ultrasound examination is performed to determine the blood flow in the fetal vessels;
The third trimester (the period from 31 to 36 weeks) is considered the final trimester. At this stage, the diagnosis of organ development disorders that could not be identified earlier is carried out. The position of the fetus is determined, which by this time should have taken a position upside down, and the probable entanglement of the umbilical cord around the neck. The child’s parameters are still measured and the date of the upcoming birth is specified. In the third trimester, the doctor gives an opinion - whether the woman will give birth naturally, or will have to resort to a cesarean section.
Along with routine examination procedures, after 12–13 weeks, biochemical screening of the fetus is carried out. A similar method is used to identify pathologies, as well as for early detection of Down syndrome. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
What does a pelvic ultrasound show? During a pelvic diagnosis, the doctor examines the uterus, appendages, ovaries, as well as the bladder and rectum. For a pregnant woman, this study is carried out to determine the condition of the reproductive organs and, of course, to examine the fetus, amniotic fluid, and placenta.
A feature of a pelvic examination can be considered the ability to detect pathologies such as:
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Abnormal development of the uterus during pregnancy;
- The process of inflammation of the ovaries, uterus, vagina;
- Malignant and benign tumors on the organs of the reproductive system.
What does the examination reveal?
Sonography during pregnancy has advantages over other examination methods:
- speed of implementation in two-dimensional (black and white) mode - up to 15 minutes. 3d and 4d ultrasound during pregnancy takes longer - at least 40-50 minutes;
- determination of pathological markers. Their detection is not a 100% sign of pathology, but they are an indication for an in-depth examination, including expert ultrasound;
- highly accurate determination of gestational age;
- no discomfort or pain during the procedure;
- the ability to monitor (up to 4 times a day) if problems arise during pregnancy;
- early detection of genetic abnormalities, deformities, defects incompatible with life, when the timing allows for a medical or other type of abortion;
- timely diagnosis of developmental disorders, when therapeutic correction will allow you to maintain pregnancy, carry and give birth to a healthy baby;
- identifying abnormalities in the second and third trimesters, which allows you to determine the tactics of postpartum treatment of the child or draw up a plan for surgical intervention.
- Ultrasound is the most quickly accessible method that can be used in the event of unforeseen changes in a woman’s condition, if something went wrong with the pregnancy as it should be for a specific period.
Preparation
There is no need to prepare specially for the procedure. It is recommended to reduce the consumption of gas-forming products within 2-4 days. On the day of the ultrasound, you need to cleanse the intestines. If you have a tendency to constipation and cannot have a natural bowel movement, then doing an enema or taking a laxative is best discussed with a gynecologist. With the transvaginal method, you need to completely empty the bladder; with the transabdominal method, this is not necessary.
Ultrasound to determine pregnancy is performed predominantly transvaginally. To a public medical institution for a free examination, you need to take with you shoe covers, a diaper to cover the couch, paper towels to remove the gel from the skin, two condoms to put on the sensor to maintain sterility, a bandage or gauze. If an ultrasound is performed with an abdominal probe, then contraceptives are not needed.
Documentation must include a passport, medical card, medical referral, insurance policy (if any). You should not take anything other than a package of documentation to a paid clinic. The woman must urinate and perform hygiene procedures.
22–24 weeks of pregnancy
The time has come to conduct the second mandatory screening . Indeed, at this stage it is possible not only to distinguish individual parts of the fetal body, but also to “see” its smaller structures: details of the structure of the vertebrae, brain, heart. The data obtained will allow the doctor to draw conclusions about whether the child is developing normally. Starting from the 22–24th week of pregnancy, 3D ultrasound . Three-dimensional reconstruction will allow you to form an idea of the baby’s appearance, look for the first similarities with mom or dad, and help the doctor get a complete picture of the development of the fetus.
Ultrasound of the cervix
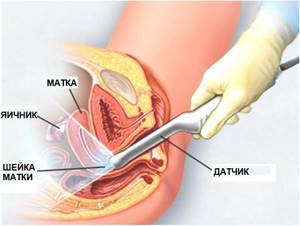
Ultrasound examination of the cervix during pregnancy is prescribed as an auxiliary precaution during a routine examination by a gynecologist.
A timely examination makes it possible to detect and exclude various types of pathologies that can harm the health of the fetus and mother.
Throughout pregnancy, the uterine canal tends to change. This is considered the norm, since the physiological process of preparation for the upcoming childbirth is in full swing. Therefore, the slightest deviations in this process may be considered a threat to the normal course of pregnancy, which means you should not postpone visiting a specialist for a long time. The sooner the examination occurs, the greater the chances of a positive birth.
Containment of the fetus is the most important function of the cervix in a pregnant woman. Because, during most of the pregnancy, its closed position protects the unborn child and prevents various types of infections from entering. But after 36 weeks, the cervix becomes deformed, becomes shorter, softer and moves towards the center, thereby starting the process of its opening. Afterwards, a single canal is formed connecting the cervix with the external os. Its full opening reaches dimensions of 12 cm.
If you look at it from an anatomical point of view, the cervix is the entrance to the body of the uterus itself. The organ also includes: internal and external pharynx, which is covered with muscle connective tissue. As a result, a cervical canal is formed, smoothly connecting to the vagina. The muscle holding the unborn child in the form of a ring is located in the internal pharynx.
If the muscle loses tone, the cervix loses the ability to contain the child inside itself.
During pregnancy, the length of the cervix plays an important role. It determines the possible risk of premature birth. It happens that it may have a shortened state, which indicates isthmic-cervical insufficiency (premature pathological dilatation of the cervix due to strong internal pressure of the fetus and amniotic fluid).
For this reason, unfortunately, a miscarriage occurs. But in our time of modern technologies, timely treatment helps prevent premature initiation of the birth process and miscarriage.