Not all couples are able to have a child right away. But thanks to the rapid development of reproductive medicine, this is not a problem. It is possible to perform artificial insemination and give life to a new person. It doesn’t matter under what conditions pregnancy occurs - naturally or with the help of IVF, the development process of the future fetus is identical. Today we will delve into this sacrament and tell you how conception occurs.
Fertilization process - stages
Many of us know how fertilization occurs in the traditional way. The male sperm merges with the female egg. This requires different amounts of time - from a few minutes to 5 days. It all depends on individual indicators.
The fusion of two cells, female and male, is a complex process. It is preceded by many processes: ejaculation in men, ovulation, penetration into the oocyte shell in women. In order for the egg to form into an embryo, it is important for a woman to monitor her health and plan pregnancy long before it occurs.
Let's consider the main stages of fertilization:
- Ovulation
Conceiving a child is impossible without ovulation. It falls in the middle of the cycle, represents the release of the egg from the follicle, and is regulated by hormones. Every month a woman releases one egg, sometimes several, which leads to the development of twins. For conception to occur, the female cell and the male sex gametes must meet in the fallopian tube. If this does not happen, it dies and comes out during menstruation.
- Fertilization
Future parents are interested to know how fertilization is progressing. Often the process takes place in the fallopian tube. But there are exceptions when this happens in the uterus.
- Sperm migration
Everyone knows in general terms how fertilization occurs in humans. This process is impossible without sperm. The most favorable process for pregnancy is 24 hours from the moment of ovulation. Male gametes are active for 2-5 days. If they managed to get to the fallopian tubes before the egg is released, they wait for it.
During sexual intercourse, about 3 million sperm enter the vagina. The more there are, the faster conception occurs. Many gametes die due to the acidic environment of the vagina and the mucus of the cervical canal. The most viable ones make their way to the fallopian tubes and uterus.
- Fertilization
The female reproductive cell is surrounded by a membrane that needs to be dissolved. The acrosome located on the head of the sperm is responsible for this.
How to determine the onset of ovulation?
Many women cannot objectively feel ovulation. And some, on the contrary, are able to independently determine the moment of release of a mature egg by sensations. What you should pay attention to:
- to increase vaginal discharge, change its character (before ovulation, the discharge becomes more abundant, viscous, stretchy, reminiscent of egg white in appearance);
- the appearance of cramping pain in the lower abdomen in the middle of the cycle;
- to a sharp jump in sexual desire (the female body itself adjusts to finding a partner and reproduction).
How long pain lasts during ovulation or how long discharge lasts during ovulation is completely individual. For most women, this process is not associated with pain at all.
The most accurate result is provided by a special ultrasound examination - folliculometry. If you have a regular cycle, you can use ovulation tests (sold in pharmacies) or a method for measuring basal temperature. Immediately before and during ovulation, the temperature drops slightly (the so-called ovulation recess occurs), and a day after ovulation it rises again. If you take measurements accurately and keep careful records, you can see from the temperature graph how long ovulation lasts.
Time of egg fertilization
Now that you know more about how fertilization occurs in humans, let's figure out how long it takes. On average, it takes male cells 3-5 hours to penetrate the fallopian tubes. However, these indicators are individual for each person.
Depends on the following factors:
- Ovulation and possible fertilization of the egg after it has left the ovary (12-24 hours).
- Sexual intercourse. The most favorable period is 1 day before ovulation and 4-5 days after.
Indicators depend on genetics and other factors. If the fertilized egg does not attach to the uterine cavity, it dies. It is believed that you can talk about pregnancy after 8 weeks. In the early stages there is a high risk of spontaneous miscarriage.
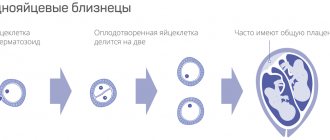
Can two embryos develop in a fertilized egg?
One fertilized egg and two embryos. Of course, two embryos can develop in a fertilized egg. Under this circumstance, monozygotic twins will be born. People call them identical. These babies are absolutely identical. They develop by fertilization of one egg by one sperm. The formed zygote begins to divide with a certain nuance. During the crushing process, not one embryo is formed, as usual, but two. These babies are copies of each other, having the same genetic material.
There are also not entirely successful development options for identical twins (buy donor eggs). Such a developmental anomaly as conjoined twins is the result of the development of monozygotic twins, which for certain reasons have grown together with different parts of the body.
Is it possible to plan or predict the birth of twins? With the natural process of fertilization, it is impossible to plan a pregnancy with twins or triplets. The only option in which there is a possibility of planning the development of a multiple pregnancy is to carry out an in vitro fertilization procedure with the transfer of two or more embryos. However, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, currently during the in vitro fertilization procedure, no more than two blastocysts are planted due to the fact that such a pregnancy carries a high risk of perinatal losses, as well as premature birth.
However, when transferring two embryos during IVF, the resulting twins will be, as people say, fraternal. That is, there cannot be two embryos in a fertilized egg.
Is it possible to feel the fertilization of an egg?
Some women claim that they immediately feel the onset of pregnancy. At the same time, others claim that they did not notice a single symptom; moreover, they do not know exactly how the fertilization process occurs and when it happened.
It is worth noting that people who have been planning pregnancy for a long time or have encountered difficulties in conceiving a child are more attentive to their health and respond to the slightest changes.
According to vigilant women, after fertilization until the moment of implantation, the following symptoms can be noted:
- Increased breathing.
- Changes in basal temperature and metabolism.
- Increased levels of free amino acids (can be detected after testing).
Please note that these signs are objective and cannot be used to determine pregnancy. More obvious signs of fertilization occur after successful implantation of the embryo.
Among them:
- Lack of menstruation or scanty discharge;
- Mood swings;
- Irritability;
- Feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- Increase in the hormone hCG.
The surest sign of pregnancy is an increase in the specific hormone hCG in the first 3 months, and during an ultrasound, visualization of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity.
Symptoms of attachment
Most women do not feel any special signs of implantation of the fertilized egg. However, during this process, a pregnant woman may experience some special symptoms: drowsiness, severe irritability, mood swings, dizziness, and even a slight increase in body temperature (up to 37.5°). There may also be a slight tug in the lower abdomen and a slight tingling sensation in the chest.
Another sign of attachment is implantation bleeding (IB). About a third of women experience this. IR is similar to normal, but very scanty periods. The color of the discharge can be completely different: yellow, red, brown, pink. They must stop a maximum of 48 hours after they started. It is interesting to note that some women simply mistake implantation bleeding for normal menstruation, and therefore find out about their new status very late. But not all expectant mothers experience a similar phenomenon, so if you haven’t noticed similar discharge, then this is not a reason to sound the alarm or worry.
How many days does it take for a fertilized egg to enter the uterus?
Now you know how and when conception occurs. But many women are interested in the question of how long it takes for a fertilized egg to enter the uterus. After all, if you immediately go for an ultrasound, the specialist will not find anything. You need to wait at least 4 weeks.
The fertilized egg “searches” for a suitable place, then attaches to the hairs of the uterine wall within 3-7 days. During this period, a woman may notice slight pink or brown discharge. After successful implantation (attachment to the walls of the uterus), the fertilized egg is considered an embryo, has a chromosome set, and begins to grow and develop.
Immediately after ejaculation
In the vagina
After ejaculation, sperm enters the vagina.
The vagina has an acidic environment, unfavorable for sperm. At the same time, sperm has an alkaline reaction, and due to this, the acidity is slightly reduced for some time. Strong sperm survive in such an environment, and, having overcome this barrier, they continue to move. The next stage is the penetration of sperm into the cervix. Liquid sperm flows into the so-called “posterior vaginal fornix” - a small depression, and accumulates there. In the cervix (cervix) there is cervical (cervical) mucus with a slightly alkaline reaction. Usually thick, it becomes liquid during ovulation. All this facilitates the penetration of sperm further into the uterine cavity. But, nevertheless, only motile sperm can overcome this barrier: sedentary sperm are eliminated again.
In the uterus
The walls of the cervix move towards the uterus, as if pushing the contents inside; in the uterus there is also an active contraction of its mucous membrane towards the tubes where the egg is located. An alkaline environment awaits sperm in the uterus - favorable for activity and life. Here the sperm are activated - the so-called “capacitation” occurs: thanks to complex biochemical processes, they begin to move very actively. Now the most viable sperm must penetrate the egg.
Near the egg
After ovulation, the egg is located in the wide (ampullary) section of the fallopian tube, close to the ovary. Contractions of the fallopian tubes help sperm get there.
Before penetrating the egg, the sperm passes through its two membranes, which play a protective and nutritional role. This process is called penetration.
The first shell is the radiant crown. Sperm literally crash into it, breaking through the layer of follicular cells. Yes, many sperm reach the corona radiata, and they all try to break through it. At this stage, sedentary sperm are again eliminated.
The second layer is the shiny shell. To break through it, in the front of the sperm head there is a vial with enzymes that can dissolve the cells of the zona pellucida. Those sperm that penetrate through it end up almost at their target - near the oolemma, the center of the egg, where conception will occur. One of the sperm will do this before the others, the penetration process will be instantly stopped, the other sperm will remain inside the uterus and tubes: their residues and enzymes will be needed to create an environment favorable for the movement of the fertilized egg to the site of attachment of the future fetus.
Where fertilization and embryo formation takes place
how a woman is fertilized day by day .
- 1st day. The seminal fluid merges with the egg. Sperm attack it and “pierce” the membrane. The most active one gets inside.
- On the 2nd and 3rd days, the zygote is formed. Cells are actively dividing, and their number doubles every 12 hours.
- On the 4th day, the number of cells is 16. The zygote emerges from the fallopian tube.
- 5th day - the fertilized egg moves along the mucous membrane, looking for a suitable place for implantation.
After the 12th day, cell division stops and the process of implantation of the embryo is completed.
Approximately 2 weeks after conception, “pregnancy hormones” are actively produced.
Now you have learned in more detail how quickly fertilization occurs. After 2-3 weeks from the moment of conception, the test may show a positive result.
Which fertilized egg produces an embryo?
When should an embryo appear in a fertilized egg? The processes that occur as a person develops in utero are called embryogenesis.
Embryogenesis is a set of successive stages of development of the embryo, and subsequently of the fetus, during which the main stages of its formation, growth and development occur.
The beginning of embryogenesis is considered to be the moment of fertilization of an egg by a sperm (there is no embryo in the fertilized egg). That is, it is from this moment that a new life is born (fertilization of the egg - embryo). For many years there has been a debate about when to consider an embryo a person and when not. Human life begins precisely with the formation of the zygote.
However, the zygote is only the beginning of life. The zygote goes through its stages of intrauterine development. From one cell two appear, from two - four, from four - eight, and so on. The cells that form a person during the four-day stage of initial development are called blastomeres.
The next day, a blastocyst is formed, which is a sac filled with liquid.
Where does the fetus grow and develop?
The fetus grows and develops in the uterus. Changes are observed every day. Over time, his limbs, organs, and facial features form. From 37 to 42 weeks, labor can begin and the baby is considered full-term. During pregnancy, a woman needs to lead a healthy lifestyle, take care of herself, get more rest, and visit the doctor on time. It is important to take care of yourself, because some infections and diseases pose a threat to the fetus.
Bearing and giving birth to a child is an incredibly complex process, so every woman needs to know how to conceive a child and how to do everything possible to ensure that he is born healthy.
What can stop him?
Factors that affect the movement of sperm in the woman’s genital tract can prevent sperm from entering the egg. This includes:
- Prostatitis.
- Changes in the biochemical parameters of sperm due to hormonal pathologies, malnutrition and other internal and external factors
- Excessively thick cervical mucus, which even during ovulation does not thin enough for sperm to overcome it. This is the so-called cervical factor of infertility.
- Insufficiency of contractile movements of the cervix and/or body associated with pathologies or hormonal disorders.
- Pathologies of spermatogenesis, in which the passage of sperm from the vagina to the tube is difficult, for example due to teratozoospermia, that is, an abnormality in the structure of sperm; asthenozoospermia - impaired motility and activity of sperm, etc.
- Violations of acid-base balance in the genital tract of both men and women, for example, due to infections.
- Ejaculation disorders.
The period of organogenesis and placentation - the laying of all organs and tissues of the fetus
This period lasts from the moment the fertilized egg is implanted into the uterine mucosa until 10-12 weeks of pregnancy, when all the organs and tissues of the fetus are fully formed, as well as the placenta (the baby’s place is the connecting link between the fetus and the maternal body, through which nutritional processes occur, metabolism and respiration of the fetus in the womb). This is a very important period of intrauterine life, because At this time, the formation of all organs and tissues of the fetus occurs. Already on the 7th day after fertilization of the egg, the mother’s body receives a signal of pregnancy thanks to the hormone chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which is secreted by the fertilized egg. HCG, in turn, supports the development of the corpus luteum in the ovary. The corpus luteum secretes progesterone and estrogens in quantities sufficient to maintain pregnancy. At the initial stage of pregnancy, before the formation of the placenta, the corpus luteum takes on the function of hormonal support of pregnancy, and if for one reason or another the corpus luteum does not work fully, then there may be a threat of miscarriage, miscarriage or a non-developing pregnancy.
The entire period of organogenesis and placentation is also a critical period of intrauterine life of the fetus , because the fetus is highly sensitive to the damaging influences of the environment, especially in the first 3-6 weeks of organogenesis. This critical period of pregnancy is especially important because... under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors, the embryo may die or develop developmental abnormalities.
During these periods, the influence of environmental factors on the embryo is especially dangerous, including:
- physical (ionizing radiation, mechanical effects); this may be the effect of ionizing radiation, for example in the conditions of a man-made disaster at nuclear facilities, mechanical effects in the form of vibration, etc. in relevant industries or during sports training;
- chemical: phenols, nitric oxide, pesticides, heavy metals, etc. - these substances can also enter the body of a pregnant woman if she works in relevant industries or when carrying out repairs in a room where the woman stays for a long time. Chemicals include nicotine, alcohol, certain medications such as those used to treat cancer, etc.;
- biological (for example, herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, rubella virus, etc.).
It must be emphasized that during critical periods, harmful effects lead to the most severe consequences - the death of the embryo or the formation of gross malformations.
According to French researchers, if a pregnant woman for the first time in her life encounters cytomegalovirus , a pathogen that causes a disease that in adults can occur as a banal acute respiratory disease (acute respiratory disease) during pregnancy (as can be seen from blood tests for immunoglobulins to CMV), especially early stages, then in 1/3 of cases fetal malformations may occur. If she was already infected before pregnancy, the body turns on protective mechanisms to fight the virus in time, this probability is reduced to 1%. The same can be said about the herpes simplex virus.
The rubella virus is especially dangerous when infected in the early stages of pregnancy. In such cases, a woman is recommended to have an artificial termination of pregnancy, because there is a high risk of having a child with such developmental defects as microphthalmia - a malformation of the eyes, microcephaly - a serious malformation of the brain; deafness, congenital heart defects, etc.
Of the chemical compounds , lead, mercury, benzene, nicotine, carbon oxides and other substances that can cause developmental defects have a particularly adverse effect on the condition of the embryo.
Some medications are especially contraindicated during pregnancy (eg, antitumor antibiotics); if they were taken, early termination of pregnancy is recommended. When taking certain medications, it is necessary to consult a geneticist, carefully monitor the condition of the embryo and fetus during pregnancy (ultrasound, blood tests for human chorionic gonadotropin, alpha-fetoprotein, estriol, which allow one to suspect the presence of fetal malformations - the analysis is carried out at 16-20 weeks of pregnancy ).
Women working in chemical production during pregnancy must be transferred to other, less dangerous workshops. As for the influence of radiation, if it affects a woman before implantation of the embryo (during the preimplantation period), in 2/3 of cases the embryo dies. During the period of organogenesis and placentation, malformations often occur or intrauterine death of the embryo or fetus occurs.
At 7-8 weeks of pregnancy, the reverse development of the corpus luteum in the ovary usually begins: figuratively speaking, the ovaries transfer the function of hormonal support of pregnancy to the chorion (future placenta), and if the chorion is underdeveloped and inactive, then there is a threat of termination of pregnancy.
7-8 weeks is also a critical period for the development of pregnancy. Very often, a miscarriage, an undeveloped pregnancy, or a threatened miscarriage (bloody discharge from the genital tract, pain in the lower abdomen and lower back) appear precisely at this time. If this happens, the woman needs hospitalization. In the hospital, various medications are used that will help maintain pregnancy, if possible.
So, as we have seen, the 1st trimester of pregnancy consists almost entirely of critical periods, so at this time it is especially important:
- if possible, eliminate the negative impact of hazardous production;
- change the set of physical exercises during active training in the period before pregnancy, postpone extreme sports for the postpartum period;
- spend enough time outdoors;
- devote enough time (8-10 hours) to sleep;
- do not take an active part in the renovation of premises;
- give up bad habits, especially such as drinking alcohol, drugs, smoking.
Advertising