Ultrasound of the liver
– non-invasive examination of the organ using ultrasound waves. Allows you to obtain information about the size, shape and contours of the liver, the structure of the hepatic parenchyma and the state of local blood flow. Ultrasound of the liver makes it possible to detect pathological foci, assess their nature, location, shape, size and distribution. Prescribed for diffuse changes (cirrhosis, hepatitis, fatty hepatosis) and focal pathological processes (neoplasia, fluid formations). Liver ultrasound can be performed both on an outpatient basis and in an inpatient setting. Absolutely painless, does not cause discomfort, and does not pose any harm to the patient’s health. Requires special preparation to reduce gas formation in the intestines.
Ultrasound of the liver is a fairly new research method. Ultrasound was discovered in 1794, when the Italian scientist Spallanzani hypothesized the existence of invisible rays emitted by bats for orientation in space. Ultrasound waves have been used in medicine since the beginning of the twentieth century. Initially, ultrasound was used to treat certain diseases. Researchers then made a number of attempts to design diagnostic devices using ultrasound radiation.
The first ultrasound machine was created in 1949. When examining the liver and other abdominal organs using this machine, the patient had to sit motionless in a tank while a special scanner moved around him. In the mid-60s, the first devices for ultrasound of the liver, kidneys, male and female reproductive systems and other organs appeared, operating on the same principles as modern devices equipped with manual sensors. Currently, liver ultrasound has become a routine research method, widely used in gastroenterology and oncology.
What determines the quality of ultrasound?
For ultrasound diagnostics of the liver, sensors of different frequencies are used. Each of them penetrates to a different depth of the human body. Which sensor the doctor chooses will depend on the patient’s body volume and the condition of the abdominal fat layer. Typically 3.5-5 MHz sensors are used. They help to visualize formations with a diameter of 1-3 mm. A sensor with a frequency of 3.5 MHz allows you to obtain an image of tissues and organs located at a distance of 12-28 cm from the meter. Such sensors are used to study adult patients, especially overweight people. Sensors with a frequency of 5 MHz provide a good “picture” of structures that are located at a distance of 4-15 cm from the surface. They are used in the examination of children, adolescents and patients with asthenic body structure.
Ultrasound function during puncture
Using the device, the location of the needle insertion is determined. After the needle penetrates the node, the doctor watches for changes in the image. The disappearance of the formations suggests that these were hemangiomas and not malignant tumors.
The cost of the study and where it is carried out According to the medical direction, echography of the liver is carried out in state medical institutions. The price of the service is minimal or provided free of charge. In general centers and private clinics, the price of the study will range from 700-1200 rubles.
How is liver ultrasound performed?
The ultrasound procedure in medical institutions is carried out in a separate, specially equipped room, where the ultrasound machine itself is located with a monitor, keyboard and sensors and a couch for the patient. The patient will not have to undress completely during an ultrasound of the liver and abdominal organs. It will be enough to expose the abdominal area and lie down on a couch covered with a disposable sheet. The doctor will then indicate the position in which the examination will be performed. He will ask you to lie down either on your back or on your left side. After the patient has taken the desired position, the diagnostician applies a special gel to the sensor and the area of study for tighter contact and smooth sliding and begins to move it sequentially in different directions. During the ultrasound procedure, the diagnostician will give instructions to the patient for clearer visualization. He may ask the subject to inhale as hard as possible and hold his breath, exhale forcefully, or breathe normally. Different breathing intensities will help the doctor collect more information about the abdominal organs and the features of their anatomical structure. After the diagnostician has made all the necessary measurements, the liver examination is considered complete. The subject can slowly get up, remove the gel from the abdominal area with a disposable towel and get dressed.
Interpretation of results
Data obtained from liver ultrasound are interpreted taking into account normal indicators. During the interpretation process, the structure of the liver parenchyma, size, contours and echogenicity of the organ are assessed. If focal changes are detected, their localization is indicated taking into account the segment. In the absence of pathological changes according to ultrasound results, the liver is described as an organ with a homogeneous structure and smooth contours. The echogenicity of the liver is lower than that of the spleen and is approximately equal to the echogenicity of the pancreas.
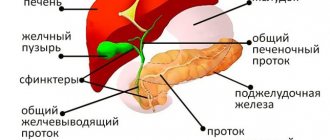
Normally, the length of the right lobe according to ultrasound of the liver ranges from 11-15 cm, the oblique vertical size is up to 15 cm. The height (craniocaudal size) of the left lobe is approximately 10 cm, thickness is no more than 7 cm. The total length of the organ according to ultrasound results liver is 14-18 cm, diameter – 20-22 cm, sagittal size – 9-12 cm. Diameter of the common bile duct – 6-8 mm, portal vein – 13 mm, vena cava – 15 mm, hepatic vein – 6-10 mm, portal vein – 4-7 mm. Fibrosis of the duct and vessels is absent. Ultrasound identifies the liver as a fine-grained organ. There are no volumetric formations in the liver tissue.
There are so-called ultrasound diagnoses - special terms that reflect the echo characteristics of pathological changes based on the results of liver ultrasound. Such terms may indicate several clinical diagnoses. For example, the term “spots on the liver” refers to areas of increased echogenicity, which may be evidence of giardiasis, or turn out to be neoplasia or nodes of incipient cirrhosis. To clarify clinical diagnoses, when these changes are detected, laboratory tests and additional clinical studies are prescribed.
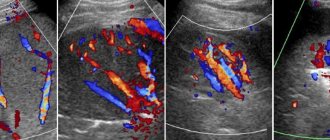
When performing an ultrasound of the liver, very dense areas (calcifications) and cavities filled with fluid (cysts, abscesses) can be detected. Malignant neoplasia of the organ on ultrasound of the liver appears as areas of unusual structure with uneven echogenicity, heterogeneous structure and unclear boundaries. The density of metastases can be either higher or lower than the density of liver tissue (depending on the density of the primary neoplasm); a characteristic sign of this pathology is a hypoechoic rim around the pathological focus. Hemangioma on liver ultrasound is a hyperechoic formation with clear boundaries and an acoustic track, located next to large vessels.
According to ultrasound of the liver in the acute period of hepatitis, an increase in the size and density of the organ in combination with the heterogeneity of the parenchyma structure is determined. In chronic hepatitis, liver ultrasound reveals enlargement of the organ, heterogeneity of the parenchyma and unclear vascular pattern. With cirrhosis, a mosaic and tuberous structure, rounded edges and widening of the angles of the organ are observed. With fatty hepatosis, an increase in echogenicity is detected (light liver). All of these diseases are diagnosed based on the results of a comprehensive examination, which, along with liver ultrasound, may include laboratory tests, CT, MRI and other diagnostic techniques.
Duration
In 10-20 minutes, the doctor examines in detail the condition of the liver and its lobes, adjacent tissue and vascular structures. The scanning time will depend on the type of installation, the qualifications of the diagnostician and the person’s body weight. In overweight patients, the fat layer is large, and the doctor will need 20 minutes to perform a high-quality liver scan. To examine people with a thin body structure, the research time will be required in half.
| Ultrasound service | Price according to Price, rub | Promotion price, rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, stomach) | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of one organ (liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, bladder, adrenal glands) | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys | 1700 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the bladder | 2000 rub. | |
| Kidney ultrasound | 800 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland) | 2400 rub. | 1999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidney + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + pelvic ultrasound with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
| Comprehensive body diagnostics (MRI of the thoracic spine, MRI of the lumbar spine, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist, consultation with a therapist) | 11700 rub. | 7000 rub. |
Benign and malignant tumors
Most often, liver cancer is diagnosed in men over 40 years of age and less often in women over 55 years of age. The most common is secondary liver cancer as a result of metastases in the organ. The risk of developing primary liver cancer increases in people who smoke and drink alcohol, as well as those who work in hazardous industries, suffer from diabetes and obesity.
Hemangioma is a tumor of a plexus of blood vessels that tends to increase in size without developing into a malignant neoplasm. It occurs in women 5 times more often than in men. It is believed that the formation of a tumor occurs during the intrauterine period of development, when the baby’s mother is adversely affected.
The trigger for tumor growth is hormonal changes associated with pregnancy, menopause, and taking contraceptive medications. The tumor develops asymptomatically and makes itself felt only when it reaches 4 cm, when the patient experiences pain in the right side. However, in most cases, hemangioma does not manifest itself in any way and is discovered by chance during a medical examination.
Biochemical and general blood tests do not reveal any abnormalities; only when the tumor is very large, bilirubin increases. Hemangioma itself is not dangerous, but as the tumor grows, the hepatic ducts become blocked, making it difficult to remove bile.
There is also a high probability of blocking the main feeding artery, which provokes a liver infarction and disruption of the functioning of neighboring organs. Complications of hemangioma occur in 15% of patients; if the tumor ruptures, internal bleeding occurs in 85%, leading to the death of the patient.
What will the transcript of the liver ultrasound show?
It will take the doctor 5-10 minutes to decipher the liver ultrasound and issue a report. The patient can wait in the clinic lobby or, if desired, receive a conclusion by email. The research protocol will necessarily indicate:
- the size of the liver as a whole and each of its lobes separately;
- the nature of the contours;
- features of fabric structure;
- bile duct parameters;
- condition of lymph nodes and large vessels.
The conclusion also notes the presence of any inclusions or neoplasms that are not typical for the norm.
What liver diseases are there?
The content of the article
Depending on the provoking factor, liver diseases are divided into 4 groups:
Caused by exposure to a foreign microorganism (viral, bacterial and parasitic).
Hepatitis is the most common viral liver disease. It has 6 varieties, each of which is characteristic of a specific region of the planet.
- Hepatitis A (Botkin's disease) occurs in 28% of cases. It is transmitted through unwashed hands, drinking or bathing in contaminated waters, and through blood. Most common in Latin America, Africa and Southeast Asia.
- Hepatitis B affects 18% of the total number of infected people, and this is the most common type of hepatitis in Russia. It is transmitted through blood, as well as during childbirth from mother to child.
- Hepatitis C is transmitted during unprotected sexual contact or during childbirth. It has the most severe consequences for the liver.
The other three varieties of the virus are concomitant with the three main ones. The most dangerous are hepatitis B and hepatitis C, they lead to liver destruction and death.
Caused by metabolic disorders:
Fatty hepatosis involves the death of functional liver cells of hepatocytes due to their damage by fat cells. This occurs due to metabolic disorders when dietary fat accumulates in the liver, causing inflammation and cell necrosis. As a result, they are replaced by connective tissue, disrupting the normal functioning of the organ.
Fatty hepatosis has a different nature: in people suffering from alcohol addiction, fat cells accumulate as a result of the death of liver cells under the influence of aldehydes.
Cholestatic hepatosis occurs as a result of excess “bad” cholesterol. Non-alcoholic hepatosis occurs in 65% of people who are overweight. Also, 1% of women expecting a child develop hepatosis during pregnancy.
Caused by an inflammatory process in the liver:
Liver cirrhosis is an inflammation of the organ in which the parenchyma (spongy tissue) is replaced by stroma (connective tissue). In 70% of cases, cirrhosis is a consequence of alcohol abuse, the rest is the result of damage by viruses, parasites or infections. Cirrhosis also occurs due to severe intoxication, for example, when consuming poisonous mushrooms. However, in 10% of cases it is impossible to determine the exact cause of liver cirrhosis.
Preparation
Ultrasound of the liver and abdominal organs requires preparation from both adults and children.
This scan should be performed on an empty stomach with a 6-hour fast. It is better to stop drinking 2 hours before the examination. If your body is prone to excessive gas formation and flatulence, you need to adhere to a special diet 2-3 days before the procedure, excluding flour and legume products, carbonated and alcoholic drinks. In the case where an ultrasound of the liver is planned to be performed on a child, the small patient should also be prepared. The first and rather difficult stage will be to limit food intake before the study. The minimum abstinence time for children is 3 hours (drinking is also excluded). Such preparation for a child can be difficult and is carried out only if the children tolerate restrictions on food and drinks relatively calmly. If such abstinence is difficult to achieve, you should stick to your regular eating schedule. Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Therapist with 25 years of experience
Prohibited foods and drinks
Preparation for an ultrasound diagnostic procedure does not cause any particular difficulties for people. As a rule, it begins 3-4 days before visiting the ultrasound room. Of course, no one forces a person to completely give up food and water. It is enough to follow a few general recommendations:
- minimize gas-forming foods - for example, legume dishes, raw vegetables, black cereal bread;
- give up carbonated drinks, coffee, alcohol;
- do not consume bakery and confectionery products - they often provoke putrefactive, stagnant processes in the intestines.
The diet recommends the presence of light, low-calorie dishes that do not require increased work from the digestive organs. It is imperative to monitor the timeliness of bowel movements. If difficulties arise with defecation, it is better to perform a cleansing enema.
If a person is prone to flatulence, the doctor will prescribe a short course of carminative medications. Motilium or Espumisan have proven themselves to be excellent.