From the moment of registration and throughout pregnancy, a woman must undergo periodic examinations by various specialists, undergo tests and have ultrasound scans. Screening examinations are considered the most important.
The first screening is carried out at 11-14 weeks, but it is most informative if it is done at 12 weeks. How is the examination carried out? Why is it being done?
What examinations are included in the screening?
The first screening is included in the list of mandatory medical examinations of women during pregnancy. Screening includes 2 main procedures: ultrasound and venous blood donation.
During an ultrasound screening at 12 weeks, the doctor examines the woman’s reproductive organs, checks the condition of the fetus and takes its measurements, assesses the condition of the uterus and placenta.
Blood is taken to determine the level of hormones: human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and pregnancy-associated protein A (PAPP-A). The data obtained from the study is studied by a gynecologist and a genetics specialist. Women who are at risk or who have received questionable or negative results for certain indicators may be prescribed additional tests (amniocentesis, chorionic villus biopsy). Pregnant women at risk include:
- over 35 years old;
- with previous repeated miscarriages;
- having relatives or older children with genetic disorders;
- those who have had serious illnesses at an early stage;
- taking drugs during pregnancy that have an aggressive effect on the fetus.
Why is an ultrasound performed at 12 weeks?
The peculiarity of the first 12 weeks of pregnancy is that during this period all the main organs and systems of the baby are formed, but the fetus is not yet protected by the placenta from the influence of negative factors coming from outside.
An ultrasound at week 12 shows how the baby is developing and whether its parameters correspond to the gestational age. However, the main goal of the study is to identify developmental disorders. At this stage, genetic abnormalities can be detected.
Ultrasound also allows you to record:
- location of the fetus in the uterus;
- number of expected babies;
- condition of the placenta and reproductive organs of the mother;
- placenta attachment site;
- quantity and quality of amniotic fluid;
- successful pregnancy;
- expected date of birth.
If a woman does not know the exact date of her last menstruation (for example, with an irregular cycle), ultrasound can determine the gestational age with great certainty.
As already mentioned, the first screening makes it possible to see abnormalities in the development of the fetus, so that the mother can make a decision about the further fate of the pregnancy. If serious abnormalities are detected, doctors may interrupt the pregnancy process. Early diagnosis reveals the following fetal pathologies:
- disorders in the formation of the nervous system;
- Down's disease;
- Patau syndrome;
- Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome;
- Brahmann-Lange disease;
- Edwards disease.
Monitoring the condition of the placenta, uterus and intrauterine fluids is also important. If deviations are detected, treatment is prescribed to allow the woman to maintain the pregnancy and bear a healthy baby.
Screenings at a later date
The third screening is aimed primarily at fetometry and monitoring the condition of the placenta. The doctor determines the size and weight of the fetus, whether it is ready for birth, and what position it occupies in the uterus. In the later stages, it is important to monitor the amount of amniotic fluid, blood circulation and monitor pregnancy emergencies. Carrying out the procedure also helps to choose a birth scenario.
All ultrasound screenings are carried out using expert-class devices that accurately determine the characteristics. The examination is carried out by doctors who specialize in identifying certain abnormalities. Therefore, it is very important to choose the right medical center in which the procedures are performed.
The Zdorovye family clinic is equipped with the most modern ultrasound diagnostic equipment and conducts research at all stages of pregnancy. We will perform a complete screening and help you obtain complete information about the condition and development of your unborn child.
Preparing for an ultrasound

At 12 weeks, the fetus is still small, so it is necessary to exclude all factors that interfere with visualization of the uterine cavity during the study. Since during this period the uterus has not yet risen high enough, gases accumulated in the intestines may prevent its examination. To eliminate them, you must stop consuming the following for 2 days before the study:
- smoked, canned, fried and fatty foods;
- seafood;
- cabbage;
- legumes and soybeans;
- peas;
- flour;
- white bread;
- sweets.
If on the eve of the examination there is a feeling of gas accumulation in the abdomen, the woman can take Espumisan. This drug is harmless to the fetus and quickly eliminates gas formation in the intestines.
Ultrasound at 12 weeks is performed using 2 methods: transvaginal and transabdominal. The second method requires that the patient's bladder be full. To do this, half an hour before the procedure you need to drink 500 ml of water or not empty your bladder for 2-3 hours. You need to bring your own diaper to the ultrasound room. Some clinics also require disposable gloves.
How to prepare for it
A referral for screening is given by the supervising doctor at the antenatal clinic, who will also tell you how to prepare for the procedure and how it will proceed. Here's what you need to know before your test:
- all studies must be carried out on the same day and in the same clinic;
- The examination should be done on an empty stomach in the first half of the day;
- before the procedure you should avoid intimacy;
- in a day or two you should exclude sweets, fatty foods, seafood, meat, fried, spicy and chocolate from your diet;
- to obtain reliable data, the break between the last meal and the blood test must be at least 8 hours;
- Before screening, you should weigh yourself and measure your height, as accurate data will be needed to interpret the results;
- Liquid intake should be reduced - no more than 100 ml.
The main condition for the reliability of the results is the calmness of the expectant mother. The doctor reports the results of the first screening of the pregnant woman.
Carrying out the procedure
The duration of the procedure is from 10 to 30 minutes. The speed of the procedure depends on the location of the fetus in the uterus, the need to examine the female genital organs, and abnormalities identified during the study.
Before the examination, the specialist fills out a special questionnaire, which includes general information about the mother, the presence of genetic diseases in the family, and the expected date of conception. This information is necessary for subsequent evaluation of the data obtained.
Transvaginal (internal) ultrasound involves examining the mother's genital organs and the uterine cavity by inserting a device sensor into the vagina. Before the procedure, the instrument is treated with an antiseptic and a condom is put on it. To conduct the study, a woman needs to lie on her back and bend her knees slightly.
Transabdominal (external) ultrasound is also performed in a lying position, but the device’s sensor is moved over the pregnant woman’s abdomen. In order to prevent air from penetrating between the skin and the instrument, a special gel is applied to the woman’s stomach. Regardless of the method of implementation, a correctly performed procedure should not cause discomfort to the patient.
The classic ultrasound method is transabdominal. The transvaginal research method is chosen in the following cases:
- If a woman is overweight, folds on the body prevent a high-quality examination through the skin.
- Suspicion of the development of pathologies of the genital organs. If a pregnant woman has signs of inflammation of the appendages, the formation of a cyst in the ovary or fibroids, examination through the skin will not give accurate results.
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency was diagnosed. Since the vaginal sensor is located closer to the cervical canal, it will allow a better assessment of the degree of development of the pathology.
In some cases, research is carried out in two ways. This is necessary when, during a transabdominal examination, difficulties arise in determining certain indicators. This is possible if:
- the child is positioned in such a way that it is not possible to assess the parameters of the collar zone;
- During the examination, the first method revealed formations in the uterus that were poorly visible;
- it turned out that the placenta or fetal membrane is attached low.
Ultrasound does not harm the baby or the mother, so performing the procedure in several ways is acceptable. After the examination, the woman is given a conclusion with which she must visit a doctor.
Decoding the results
The ultrasound protocol indicates the parameters of the child, the number of fetuses in the uterus, the quality of the amniotic fluid, the location of the baby in the womb, and the baby’s heart rate. The doctor also describes pathologies that are found in the uterus or other genital organs. Special medical abbreviations and specific abbreviations are used to describe the results.
When deciphering, specialists rely on norms corresponding to gestational age. The table describes the standards for the main indicators of pregnancy ultrasound at 12 weeks.
| Options for abbreviated indicator designation | Index | Norm, mm |
| BPR, BRGP, BPD | The distance between the parietal bones of the head or from temple to temple (biparietal size, size of the interparietal region) | 20-21 |
| KTL (KRL) | Length from the coccyx to the crown (coccyx-parietal size) | 51-73 |
| TVP, TVZ | Thickness or density of the nuchal region (skin fold at the back of the neck) | 1,6-2,7 |
| Height | Body length from head to toe | 80-82 |
| Dlb (FML) | Length of thigh, femur | 7-9 |
| NK | Nasal bone | more than 3 |
| Heart rate | Heart rate (the speed at which the baby's heart muscle contracts) | 140-174 beats/min |
| Weight | — | 17-19 g |
| YES | Physical activity | present |
| AC (coolant) | Abdominal circumference | 50-72 |
| OG | Head circumference | 58-84 |
| J (ABD) | Abdomen diameter | 15-23 |
| exhaust gas / coolant | Ratio of head size to abdominal volume | 1.1-1.3 units. |
When describing the location of the fetus, the following terms are used: longitudinal, transverse, diametrical. Any situation at this time is considered normal. It is normal to define the amount of amniotic fluid as “usual”.
Attention is also paid to internal organs. However, at 12 weeks they are still very small, so the specialist only notes their presence or absence. It can be seen that the hemispheres of the brain are formed, the heart has 4 chambers, there is a stomach, bladder, intestines, and abdominal walls. The doctor also counts the limbs: there should be 2 arms and 2 legs.

The greatest attention is paid to parameters indicating chromosomal abnormalities: the thickness of the collar space and the bones of the nose. In some cases, the exact length of the nasal bone cannot be measured. However, at this time it should stand out clearly.
They also look at where the placenta is attached to the uterus. Most often, the child's seat is attached to the back wall, but attachment to the front wall is also normal. The doctor also measures the length of the cervix (the norm is more than 30 mm) and the distance from the internal os to the placenta insertion. The thickness of the placenta should be 14.5-15.5 mm, and the degree of maturity should be 0.
External signs of pregnancy
Belly at the twelfth week of pregnancy.
This week, the size of the uterus increases to 10 centimeters in length and it is already crowded in the pelvic space. It rises into the abdominal cavity and begins to bulge. Now the tummy becomes more rounded and noticeable.
Breasts at the twelfth week of pregnancy.
During the first trimester, breasts increase by an average of two sizes. Now the glandular tissue stops growing and pain in the mammary glands decreases. The sensitivity of the nipples decreases, and the area around them darkens, and Montgomery tubercles appear.
Weight gain.
Not all pregnant women gain weight by this time. If a woman suffered from severe toxicosis for the entire twelve weeks, then most likely she will not gain, but lose kilograms. For this period, a weight gain of 2 to 4 kilograms is considered normal. Weight increases mainly due to the development of the placenta and additional blood volume. When you gain extra pounds, you need to adjust your diet and return to normal levels.
Colostrum release.
A characteristic phenomenon during this period is the release of colostrum. A yellowish viscous liquid may appear in small drops when you press on the nipple, or it may flow out spontaneously if this is not the first pregnancy.
Possible deviations
If abnormalities are detected, doctors recommend additional examinations and a repeat ultrasound scan after 10-14 days. In some cases, a woman is prescribed treatment. However, there are complications in which it is necessary to terminate the pregnancy.
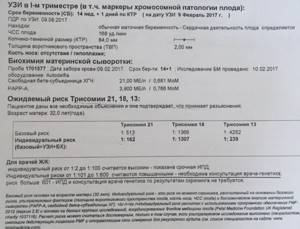
The table shows the most frequently detected deviations from the norm, the reasons that led to them, and options for what can be done in the future.
| Deviation | Cause | Possible actions |
| Small size from coccyx to crown | incorrect determination of gestational age; poor maternal nutrition; abnormal fetal development; hormonal deficiency in a pregnant woman; genetic predisposition | Carrying out additional diagnostics, repeat ultrasound after 2 weeks, comparing the indicator with other parameters |
| Missing nasal bone | chromosomal abnormality | Comparison with blood screening rates. Recommendations for termination of pregnancy if violations are confirmed. |
| Large deviation from the norm in the thickness of the collar zone | genetic disease (Patau, Down, Shershevsky-Turner, Edwards syndrome); intrauterine infection | Analysis of amniotic fluid and chorionic villi. Confirmation of the diagnosis by tests for hCG and PAPP-A. Moral preparation of a mother for the birth of a “special” baby or abortion for medical reasons. |
| Lack of physical activity and vital organs | abnormal fetal development; intrauterine death of a child | Abortion |
| Aging of the placenta, death of some parts of the placenta | hormonal deficiency; risk of miscarriage | Treatment in a hospital. Taking medications that maintain normal blood circulation in the placenta and hormone levels. |
| Uterine tone | lack of hormones; stress; poor nutrition; physical impact in the abdominal area | Therapy aimed at reducing uterine spasms. Taking hormonal drugs. Decreased physical activity. Development of a special diet. |
| Inconsistency of the amniotic fluid level with the norm | penetration of infection; genetic predisposition; poor kidney function; disorders of the central nervous system | Treatment in a hospital depending on the established diagnosis. |
| Central placenta previa | individual characteristics of a woman; lack of progesterone | Monitor the condition of the pregnant woman until the 3rd trimester. If the placenta does not rise, delivery is carried out by caesarean section. |
| The cervix is shortened | hormonal disbalance; mother's genetic trait | Maximum reduction in physical activity of the expectant mother. In case of serious deviations, a surgical operation is performed to suturing it or a special ring is inserted to hold the fetus in the uterus. |
How you feel
At the 12th week of pregnancy, you can feel a long-awaited improvement in your overall physical condition. The uterus continues to grow and already reaches 10 cm in width and up to 12 cm in length. The abdomen does not yet create discomfort, but your weight is gradually increasing: the normal indicator at this stage is an increase of up to 3.5 kg. But if you had severe toxicosis and didn’t manage to gain the treasured kilograms, don’t worry - very soon you’ll make up for everything.
As before, at 12 weeks pregnant your breasts are still very sensitive. Due to the increase in the volume of circulating blood, you may experience increased heart rate. And because the hormone progesterone relaxes smooth muscles, constipation is possible. For the same reason, mild heartburn sometimes appears.
Abdominal pain is not uncommon for pregnant women. If discomfort occurs only from time to time, and the pain is localized on the sides of the abdomen, occasionally radiating to the lower back or groin, this is not dangerous. Such symptoms are explained by stretching of the uterus. A cause for concern during the 11th – 12th week of pregnancy should be aching, pulling or cramping pain in the lower abdomen. Especially when they are accompanied by brown or bloody spotting. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor, because such symptoms may be a sign of a threat of spontaneous abortion.
As for the emotional state at the 12th week of pregnancy, it is still subject to the action of hormones. Therefore, your mood is still very changeable: joy gives way to anxiety, and as soon as tears well up in your eyes. Learn to relax and think more about your baby.
Interpretation of blood test results during screening
To obtain the correct result of the first screening, it is necessary that blood be donated on the day of the ultrasound. When deciphering the analysis, doctors focus on absolute and average indicators (median). The median is the ratio of the average standard to the actual figures obtained in the study. For hCG and PAPP-A at week 12 it is 0.5-2 MoM.
The importance of these indicators lies in the fact that the hormones studied during screening are activated only during pregnancy. HCG is actively produced after fertilization, and protein A is secreted by the placenta. Their concentration varies depending on the duration of pregnancy.

The hCG norm for 12 weeks is 13.4-128.5 ng/ml. The standard for PAPP-A is 1.03-6.01 mIU/ml. Deviations from normal indicators make it possible to identify chromosomal abnormalities in the development of a child. When interpreting the results, specialists are guided by the totality of all screening indicators. The table shows possible reasons for deviations from normal levels of pregnancy hormones.
| HCG indicator | RARR-A | Reason for rejection |
| Above normal | Demoted | Development of Down syndrome in the fetus |
| Reduced | Short | The child develops Edwards disease |
| Below normal | Slight deviation from the norm, normal | Threat of miscarriage |
| Normal or slightly reduced | Below normal | Fetal pathologies: Patau syndrome, Shereshevsky-Turner disease, lack of vitamins and beneficial microelements in the mother’s body |
| High | High | Multiple pregnancy |
Proper preparation for analysis is no less important than meeting the deadlines for the study. 2 days before the test you need to stop eating fatty foods. The last meal should be taken 6 hours before visiting the laboratory.
Feelings of the expectant mother
At the twelfth obstetric week, most pregnant women stop suffering from sudden mood swings, nausea and vomiting. Hormonal levels stabilize. Now the placenta is responsible for producing the hormones necessary for bearing a child. Every day the load on the female body increases, so drowsiness and fatigue persist. An increase in blood volume forces the heart, liver, kidneys and lungs to work harder.
Increased appetite.
The high content of progesterone in the body of the expectant mother causes increased appetite. Many women have to show their will to keep their weight at a normal level and follow all nutritional recommendations. This may be a reason to develop new healthy eating habits.

Increased libido.
By the end of the first trimester, the woman's general condition improves. She has already become accustomed to the changes that have occurred. Under the influence of changed hormonal levels, desire increases in pregnant women. The growing volume of blood helps to increase its flow to the genitals and erogenous zones during moments of arousal, which allows you to experience new sensations.
Problems with stool.
Progesterone relaxes the uterine muscles to protect the fetus. Along with the uterus, the intestines relax, which leads to constipation, gas or diarrhea.
Nasal congestion.
Pregnancy hormones cause swelling of the mucous membranes, which is the cause of nasal congestion. In the second trimester, the swelling decreases and this sensation goes away.