Published: 08/09/2021 13:40:00 Updated: 08/09/2021
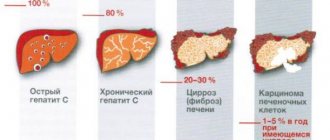
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic disease characterized by the irreversible replacement of the liver parenchyma with scar connective tissue with the gradual loss of the organ’s function, its thickening and wrinkling.
The pathology can be caused by a viral infection, intoxication of the body, hereditary and autoimmune disorders, and damage to other structures of the hepatobiliary system. Without the help of doctors, the disease progresses and after a few years leads to the death of the patient from developed complications.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis includes taking medications to relieve symptoms and correct associated disorders. The only radical treatment is surgical organ transplantation, but surgery is performed in extreme cases.
Causes of liver cirrhosis
One of the most common causes of liver cirrhosis, especially in men, is alcohol abuse.
Often organ fibrosis develops as a result of other diseases of the hepatobiliary system - viral and toxic hepatitis, obstruction or inflammation of the biliary tract, cholelithiasis. The following pathologies can also serve as an etiological factor:
- parasitic infestation;
- venous congestion in the vessels of the liver;
- portal hypertension;
- autoimmune diseases;
- severe right ventricular heart failure;
- secondary or tertiary syphilis, brucellosis;
- inherited metabolic disorders;
- long-term use of medications, for example, Iprazide, anabolic steroids, Isoniazid, androgens, Methyldopa, Inderal, Methotrexate;
- mushroom poisoning, ingestion of industrial poisons, heavy metal salts and other toxins.
Features of the occurrence of pathology
Dullness of the liver tissue and an increase in the parenchyma of the organ beyond the capsule on the section, a flabby structure, smoothness of the pattern and a clayey tint are the main indicators of the macroscopic picture of degeneration. Oxygen deficiency, or so-called circulatory hypoxia, is one of the factors in the development of fermentopathy and disruption of the synthesis of ATP - a universal source of energy, thanks to which all processes occur in the human body.
An insufficient amount of ATP causes a malfunction of the ion pump. This mechanism allows ions to be automatically removed along with water if the cell begins to swell. Due to a violation of ion exchange, intracellular accumulation of water occurs. Excess fluid inside the cell is the main reason for the increase in the size of mitochondria, which take on the shape of a grain.
As a result of insufficiency of the ATP system, the ability of cells to oxidize and reduce is lost, and membrane permeability increases. Sometimes the process is accompanied by cloudiness or foaminess of the cytoplasm. In this case, the boundaries of the cell become blurry, and the yard is almost invisible.
Classification
Depending on the cause of the development of liver cirrhosis, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- biliary, caused by damage to the biliary tract;
- toxic and toxic-allergic;
- infectious;
- circulatory, with venous stagnation;
- metabolic and nutritional;
- cryptogenic, when the etiology remains unspecified.
The severity level is set based on existing abnormalities in laboratory tests for liver cirrhosis and the severity of complications. Accordingly, it can be compensated, subcompensated, decompensated.
At what age does a child develop fatty liver disease?
May occur very early.
According to MRI data, the first signs were found in newborn children from mothers with obesity and diabetes.
Before reaching adulthood, a child can go through all phases of the disease from initial to severe.
One study that followed 66 children with fatty liver disease for 20 years found that they had a 14 times higher risk of severe liver disease and even death.
Even isolated cases of hepatocellular liver carcinoma in children have been described.
In adults, this is one of the most dangerous consequences of fatty liver disease.
Symptoms and stages of liver cirrhosis
As liver cirrhosis progresses, it goes through three stages:
- Initial. Moderate fibrosis is practically asymptomatic. The disease becomes an accidental discovery during periodic medical examinations, medical examinations, and when examining a patient with related pathology.
- Clinical. Severe fibrosis is accompanied by dysfunction of the organ. The first symptoms of liver cirrhosis are a bitter taste and a feeling of dry mouth, fatigue, irritability, weight loss, bloating, periodic bowel movements, pain in the right hypochondrium after exercise or an error in diet. Later, appetite decreases, nausea, vomiting, belching, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, and low-grade body temperature occur. The liver and spleen increase in size, dilated veins and spider veins appear on the abdomen.
- Terminal. The organ decreases in size. Jaundice, ascites, swelling of the extremities, bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus, stomach and intestines occur.
How to make a diagnosis?
Both recommendations clearly recommend not to forget about other liver diseases that can cause increased ALT or hepatic steatosis:
- viral hepatitis
- autoimmune hepatitis
- metabolic diseases
- Wilson's disease
- drug toxicity
The AASLD recommendations emphasize that if fatty disease develops very early or if its signs are detected in children without excess weight, it is imperative to exclude:
- inborn errors of fatty acid metabolism
- peroxisomal diseases.
- lysosomal diseases
In some cases, it is necessary to perform a biopsy - take a small piece of the liver and look under a microscope.
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/-/media/Images/Health-Information/Diagnostic-Tests/Liver_Biopsy.jpg
Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing fatty liver disease, but it is a technically challenging procedure that carries a small but risk of complications.
All children shouldn’t do it in a row...
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment of liver cirrhosis is carried out by a gastroenterologist.
During a conversation with the patient, he identifies predisposing factors to the development of pathology, such as taking alcohol or medications, poor diet, harmful working conditions, hereditary predisposition, and other chronic diseases. External examination and palpation of the right hypochondrium can detect objective signs of liver cirrhosis - yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes, enlargement of the liver, tuberosity of its edge and compaction.
To confirm the diagnosis and detect complications, laboratory and instrumental research methods are used:
- General clinical blood test. Assess signs of anemia and platelet count.
- General urine analysis. Deviations indicate hepatorenal syndrome.
- Blood chemistry. Pay attention to indicators such as AST, ALT, GGTP, alkaline phosphatase, total bilirubin and its fractions, albumin, serum iron, total cholesterol, creatinine, glucose, sodium, potassium, ferritin, ceruloplasmin.
- Blood test for coagulation - coagulogram.
- Level of antinuclear antibodies and alpha-fetoprotein in blood serum.
- Detection of markers of viral hepatitis - HBsAg, anti-HCV, anti-HDV, as well as HIV.
- Electrocardiography.
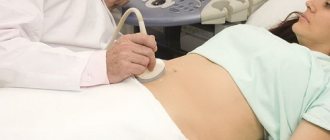
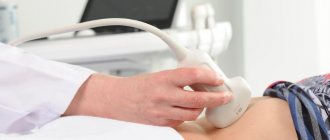
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
- Endoscopic examination of the stomach and duodenum, as well as examination of the vessels of the rectum using sigmoidoscopy for dilated veins.
- Determination of cognitive impairment using the number-linking test and other techniques.
Additional diagnostic tests include:
- determination of the average volume of erythrocytes in order to detect alcoholic liver damage;
- average hemoglobin content in a red blood cell;
- feces for occult blood;
- determination of gamma globulin;
- biochemical blood test for total protein, ammonia, urea levels;
- concentration of Α1-antitrypsin;
- antibodies to double-stranded DNA, smooth muscle, hepatorenal microsomes anti-LKM1;
- thyroid hormones – free T4, TSH, antibodies to thyroid peroxidase;
- study of the level of total estradiol in women, androgens in men;
- cryoglobulin content;
- CT or MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs if kidney damage is suspected;
- EchoCG;
- indirect elastography of the liver.
If hepatic encephalopathy is suspected, electrophysiological tests, CT and MRI of the brain are performed. Doppler examination of the vessels of the liver and spleen allows one to evaluate signs of acute or chronic thrombosis. To exclude oncology, including hepatocellular carcinoma, abdominal ultrasound, contrast-enhanced CT or MRI, and liver biopsy are recommended. In case of ascites, fluid is taken from the abdominal cavity and its composition is subsequently analyzed.
Why is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease dangerous?
The accumulation of fat droplets in liver cells can cause inflammation (steatohepatitis) and then fibrosis (scarring) of the liver.
First important fact: In children, everything can happen very quickly - literally in the first ten years of life, sometimes progression to fibrosis occurs, which is irreversible.
Second important fact: The earlier fatty liver disease occurs in a child, the higher the chance of life-threatening complications in adulthood.
That is why for fatty liver disease in obese and overweight children is extremely important
As evidence of the seriousness of the problem, I will cite the results of one of the latest large studies from California.
Incidence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: 2009–2018
The results were published in autumn 2021.
The authors analyzed data from a large number of children aged 5 to 17 years from 2009 to 2021.
What happened?
The rate of diagnosis of fatty liver disease has increased over the years from 36 to 58 per 100,000.
However, the authors mentioned that only 54% of obese children and 24% of overweight children were referred for additional examination.
So the actual incidence of fatty liver disease is likely even higher.
I will provide domestic statistics based on the text of the 2021 clinical recommendations “Diagnostics and treatment of obesity in children and adolescents” from the Russian Association of Endocrinologists
A 2017-2018 study conducted in Moscow as part of the COSI program, which included 2,166 children 7 years of age, revealed the presence of overweight in 27% of boys and 22% of girls, and obesity in 10% and 6% of children, respectively.
Taking into account the age of the subjects, it can be argued that global trends are also observed in our country - from the problem of obesity as a more common adolescent condition, we have come to the problem of excess body weight in children of preschool and primary school age.
In 2021, guidelines from the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) became available.
A little later, recommendations from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) came out.
The latter were mainly aimed at adult patients, but there was also a pediatric part.
Why are these recommendations so important?
It was US doctors who were the first to face the problem of mass childhood obesity and have accumulated extensive experience.
Today we will compare the recommendations of these respected communities of experts.

https://unsplash.com/photos/YvvFRJgWShM
Who is a liver biopsy indicated for?
AASLD's opinion:
- unclear diagnosis
- several reasons are suggested
- high titer of autoantibodies + increased globulin levels (typical of autoimmune hepatitis)
- before starting treatment with a drug that is potentially toxic to the liver
- to confirm the diagnosis of steatohepatitis before starting its drug treatment
NASPGHAN's opinion:
High risk of steatohepatitis:
- ALT above 80
- enlarged spleen
- AST/ALT ratio above 1
Risk factors for progression:
- type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Panhypopituitarism is a rare but dangerous condition with a decrease in the level of all hormones of the anterior pituitary gland
Are there any drugs that will cure steatosis in a child?
NASPGHAN explicitly states that there are no such drugs or dietary supplements.
AASLD is less categorical - vitamin E can be used, but for each individual patient the benefits and risks must be weighed, since there are no long-term safety studies yet.
An important point made by the AASLD guidelines is that metformin 500 mg twice daily is not indicated for the treatment of steatohepatitis in children.
A few comments on drug treatment.
Insulin resistance plays an important role in the development of fatty liver disease.
Therefore, drugs that improve insulin sensitivity are interesting and promising.
One of them, pioglitazoline, has shown good results in adults, but due to side effects it is unlikely to be used in pediatrics.
Another drug in this group, metformin , is approved for children with diabetes.
But carried out in 2005-2010. The TONIC (Treatment of NAFLD in Children) trial found that metformin 500 mg twice daily had no effect on either ALT levels or biopsy results in children with fatty liver disease.
Perhaps higher doses will be more effective.
It is also logical to try treatment with metformin in children with concomitant prediabetes .
Results assessing the antioxidant effectiveness of vitamin E at 800 IU per day were taken from the same TONIC study.
Omega-3 fatty acids.
It is expected to be highly safe, but there are still very conflicting results from efficacy studies.
Probiotics.
The gut microbiota is hypothesized to play an important role in the development of obesity and its complications.
It makes sense that scientists are experimenting with strategies to control microflora.
There are several small but successful studies of the effectiveness of probiotics, particularly Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, in children. But additional data is needed to make specific recommendations.
Links for deeper self-study:
NASPGHAN Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children
Overview of Updated Practice Guidelines for Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
1, total, today
How to treat fatty liver disease?
Both guidelines emphasize:
Treatment should begin with lifestyle changes —correction of nutrition and level of physical activity.
At the same time, we understand that there are very few studies on the effectiveness of this approach in children; we have to rely on the results of studies in adults.
NASPGHAN specifically recommends avoiding sugar-sweetened beverages . It is precisely because of their high sugar content that doctors do not like Pepsi and Cola.
NASPGHAN also insists on increasing the level of physical activity to moderate and vigorous, limiting the time a child spends in front of a TV, smartphone or tablet
How is physical activity assessed?
Moderate-intensity physical activity is physical activity that results in increased heart rate, a feeling of warmth, and slight shortness of breath.
High-intensity physical activity - physical activity that causes increased sweating and rapid breathing.
I will again quote the Russian recommendations on obesity in children in 2021 .
The current trend in the dietology of childhood obesity is a normal calorie diet according to
age with a sufficient amount of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements and the necessary minimum of fats, compiled taking into account the child’s taste preferences.
All types of diets - hypocaloric, ketogenic, low-fat, with a reduced glycemic index, etc. are alternative treatment options, used according to indications and often in specialized departments.
This is due to several factors. First, current research has shown that long-term use of restrictive diets leads to nutritional status disorders, which is undesirable in children.
Secondly, the initial level of daily caloric intake in obese children and adolescents is quite high, and its sharp limitation is accompanied by an increased feeling of hunger, which leads to a breakdown in motivation, failure to follow these recommendations and loss of compliance.
There are also the necessary conditions for effective treatment:
- restriction of sweet drinks: prohibition (consumption of no more than 1 serving no more than 1 time per week) not only of carbonated sweet drinks, but also juices, compotes, fruit drinks) with permission to drink drinking water at the request of the child, limiting sweet fruits to 1 serving ( 100 g) per day
- at least 4 meals a day, mandatory breakfast
— prohibition of sweet dairy products, control of the size/number of portions. To visualize the desired portion size, “food plates” are now widely used. If a child wants to eat a second serving of lunch/dinner, allow it 20 minutes after the first, provided that it is eaten regularly (at least 4 times a day)
- enrichment of the diet with vegetables (for young children - 300 g, adolescents - 400 g per day, limiting the use of potatoes in such quantities as the only vegetable), dietary fiber, whole grain products
— teach children to eat slowly, without computer/television/mobile support