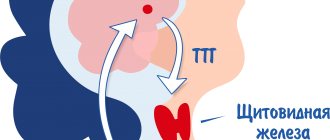
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is a biologically active substance that is synthesized in the endocrine organ adenohypophysis and is responsible for regulating the production of glucocorticosteroids. Disruption of the functional activity of the anterior part of the pituitary gland or the adrenal cortex can lead to the appearance of a number of pathologies, for the detection of which it becomes necessary to take a blood test for ACTH. This study can reliably confirm the diagnosis, as well as help the doctor correctly determine further treatment tactics.
Indications for testing ACTH levels in a blood test
A study of the content of adrenocorticotropic hormone may be necessary if the doctor finds symptoms in the patient that give reason to suspect that there is a decreased or increased level of ACTH in the body.
The following symptoms may indicate this:
- early appearance of secondary sexual characteristics in children and adolescents (advancement of the rate of puberty);
- persistent uncorrectable increase or decrease in blood pressure;
- the appearance of excess weight with unchanged diet and level of physical activity (in this case, fat deposits are distributed unevenly - they accumulate mainly on the torso and face);
- changes in the skin: the appearance of stretch marks, thinning, dryness;
- the appearance of an unusual bronze coloration of the skin (melasma);
- fatigue, causeless weight loss;
- decreased immunity, which can be manifested by frequent colds.
This indicator is also studied to assess the condition of the body after a long course of treatment with glucocorticoid hormones.
1.What is ACTH?
ACTH is a hormone that can be tested to test the condition of the pituitary and adrenal glands.
ACTH is produced by the pituitary gland.
The adrenal glands respond to ACTH levels in the blood and produce cortisol, which helps your body cope with stress. Cortisol is a vital hormone,
so its level in the blood should be monitored. When cortisol levels are elevated, ACTH levels fall and vice versa.
Cortisol and ACTH levels change throughout the day.
As a rule, the ACTH hormone is elevated in the morning (from 6 to 8 am) and decreases by 6 pm. If the doctor wants to check the ACTH level, then it is measured in the morning and evening. Cortisol levels are usually checked along with ACTH.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Preparing for the examination
First of all, it is necessary to choose a laboratory with a good reputation and a high level of trust, since if the research technology is incorrect, the indicators can be underestimated or overestimated, which can lead to serious diagnostic errors. You also need to take into account that the price in different laboratories for ACTH analysis may vary.
ACTH levels are largely dependent on external factors, such as:
- stress factors (excessive physical activity, intense sports);
- strong emotional states (fear, anger, prolonged experiences);
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- infectious diseases, extensive injuries;
- inadequate thermal effects (hypothermia or overheating);
- surgical interventions.
To obtain the most objective results, blood donation should be done only when the patient is fully confident that for the last 7-8 days his body has not been exposed to any factors that could affect the level of corticotropin. This is important to consider for further correct diagnosis. Therefore, the patient should be aware that it is necessary to begin preparing for the study in advance.
If the patient is constantly taking any medications, then healthcare workers must be notified about this, and the doctor can individually consider the issue of temporarily discontinuing them.
4. Risks of analysis and what can interfere with the test?
Risks of ACTH testing
If you take a blood test for ACTH, then possible risks may only be associated with taking blood from a vein. In particular, the appearance of bruises at the site of blood sampling and inflammation of the vein (phlebitis). Warm compresses several times a day will relieve phlebitis. If you are taking blood thinning medications, you may bleed at the puncture site.
What can interfere with the test?
Reasons why you may not be able to take a corticotropin test include:
- Taking corticosteroid drugs, estrogens, spironolactone. Also, the test results can be affected by amphetamines and insulin, after taking which the level of cortisol is increased.
- Alcohol or drug intoxication.
- Pregnancy or menstruation in women.
- Physical or emotional stress.
Blood collection procedure
The secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone changes cyclically throughout the day. In order to determine the peak daily concentration, the study is carried out in the early morning, and in order to determine the minimum concentration - in the evening (at 21-23 hours).

- The time for taking material for examination should be determined by the doctor, as this is of fundamental importance in the diagnosis of various pathologies. In most cases, blood drawing is scheduled for 7-8 am.
- The last meal should be 10-12 hours before the procedure.
- It is necessary to refrain from drinking alcohol and other stimulants for three days before the procedure.
- For the study, venous blood is taken from a peripheral vein. The laboratory does not examine whole blood, but only its plasma.
- If prescribed by a doctor, additional stress tests may be performed. In this case, in addition to taking blood, certain drugs will be administered according to a special regimen.
- When transporting the taken material, a certain temperature regime is observed, since the ACTH molecule quickly breaks down at high temperatures.
- Women need to consider the phase of the menstrual cycle when ordering a test. Typically, the material is collected 1-2 days after the end of menstruation.
Patient preparation rules
Standard conditions:
In the morning before 10-00, on an empty stomach, after 8-12 hours of fasting.
Before taking blood, complete physical and emotional rest is required (sit for at least 30 minutes). For women, indicate the day of the menstrual cycle. Attention:
In women, on the 6-7th day of the menstrual cycle, unless other dates are indicated by the attending physician.
You can add this study to your cart on this page
Symptoms of decreased ACTH
If the hormone is reduced due to dysfunction of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, this causes a decrease in the activity of the adrenal glands. The consequence of low ACTH is a slowdown in metabolic processes in the body. Signs that the indicator is reduced are less pronounced than when it increases. Symptoms of low ACTH hormone:
- Excessive pigmentation due to increased melanin production. The onset of pigmentation occurs in the area around the nipples, in the genital area, and inside the skin folds.
- Unexplained weight loss. The patient can lose from 3 to 10 kg.
- Loss of appetite.
- Constant constipation.
- Reduced production of female hormones progesterone and estrogen. This is expressed in the cessation of menstruation for more than six months, underdevelopment of the external and internal female genital organs.
- Decreased glucose levels. It makes itself felt by deteriorating well-being 2 to 3 hours after eating.
- Due to a failure of mineral metabolism in the body, pressure decreases. This is noticeable in the state of weakness, onset of nausea, and noticeable dizziness.
- Muscle weakness.
- Depression, apathy.
- Memory impairment.
- Poor mobility.
- Developing psychoses.
- Nausea and pain in the stomach area.

If the amount of hormone in the body is reduced for a short time, it does not have a negative effect on the body. A long-term low reading is a reason to consult a specialist. Tests for hormonal substances and further treatment are indicated. Taking medications to correct the situation without consulting a doctor can harm your health.
Indications for analysis
A test for hormone levels is prescribed for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases associated with dysfunction of the adrenal cortex. Monitoring indicators is also necessary to assess the effectiveness of therapy for oncological pathologies.
In women, ACTH is performed in case of menstrual irregularities, excessive hair growth, and infertility.
What symptoms and activities may be a reason for getting tested:
- abnormal pigmentation of the epidermis;
- acne in adults;
- early puberty in adolescents;
- Cushing's disease (fat deposition on the face, neck, abdomen, purple stretch marks on the abdomen, thinning limbs, increased blood sugar, high blood pressure);
- diseases of the skeletal system (osteoporosis), as well as muscle weakness and pain;
- causeless weight loss accompanied by high blood pressure;
- regular attacks of hypertension;
- severe fatigue, weakness and lethargy for a long time;
- deviation from the norm of cortisol in the blood;
- monitoring the patient’s rehabilitation after removal of corticotropinoma (tumor in the pituitary gland);
- long-term treatment with medications (for example, glucocorticoids);
- dysfunction of the adrenal cortex;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for cancer patients.
For a doctor, the reason for referring a patient to ACTH may be:
- test with corticotropin-releasing hormone;
- changes in cortisol levels;
- suspected ACTH-producing tumor.
The main tasks of the hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone regulates the functioning of the endocrine and reproductive systems. However, it has a direct impact on the functioning of other, no less important, organs.
One cannot but take into account its close interaction with other pituitary hormones - somatotropin, prolactin and vasopressin. But, despite the beneficial properties of the hormone, it also has a number of negative effects that you need to be aware of.
ACTH performs the following important functions:
- Takes part in the synthesis of protein and nucleic acids. With prolonged exposure to hubbub on adrenal cells, they gradually grow. Since the paired organ produces sex hormonal substances (progesterone, estrogen, testosterone) and cortisol, with the active growth of its tissues, the concentration of these elements increases significantly.
- Short-term exposure of adrenal cells to ACTH stimulates the production of cortisol. Read more about the hormone here.
- It has a direct effect on the production of aldosterone and deoxycorticosterone. These are hormones that regulate mineral metabolism in the human body.
- Activates the production of hormonal substances that are precursors of androgen.
- Accelerates the process of cholesterol production.
- Promotes the production of melanocytes.
In addition, the hormone ACTH has a direct effect on the brain and stimulates the development of cognitive functions.
Negative effects of the substance
Adrenocorticotropin also has negative effects, manifested in:
- suppression of the immune system;
- decrease in muscle mass;
- slowing down the digestion process;
- deterioration of memory, thinking and other cognitive functions.
But such violations occur only in the case of excessively high ACTH levels. If they are normal, then no ailments should arise.
ACTH in women
ACTH hormone - what is it in women? By itself, this element has virtually no effect on the functioning of the ovaries. However, its close interaction with LT, FSH and prolactin cannot be denied.
Under the influence of corticotropin, the production of these hormones is accelerated or slowed down. Acting in close tandem, the hormones of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulate the functioning of the female reproductive system.
If we talk about what the ACTH hormone is responsible for in women of childbearing age, then the possibility of pregnancy and the stability of the menstrual cycle depend on its concentration in the blood. When the level of this substance in the blood increases, the production of female sex hormones is inhibited. Instead, the concentration of testosterone begins to steadily increase, which can lead to the appearance of acne on the skin, shifts in the menstrual cycle, and the appearance of hair on those parts of the body where the fairer sex should not have it (for example, on the face). At the same time, insufficient production of estrogen and progesterone, which occurs against the background of increased ACTH, can cause the development of infertility.
Corticotropin releasing hormone test
In rare cases, ACTH can be produced not only by the pituitary gland, but also by a malignant tumor in any organ. Tests show high levels of ACTH and cortisol. To diagnose the pathology, a test with corticotropin-releasing hormone is prescribed. After it, the ACTH level either increases (indicating Itsenko-Cushing's disease) or remains at the same level (ectopic production syndrome).
To carry out the test, venous blood is taken in the morning on an empty stomach and ACTH is measured. Then 100 mcg of corticotropin-releasing hormone is injected into a vein and blood is drawn after 30, 45 minutes and 1 hour, determining the ACTH level for each time.
Functions of ACTH
Generated by the pituitary gland and its eosinophilic cells, corticotropin enters the human kidneys and liver. Depending on its production, the adrenal glands work. The mechanism of action is as follows: if the production of the hormone is normal, the response ensures a rush of blood to the adrenal glands, and they actively function. With a lack of iron hormone, it can atrophy.
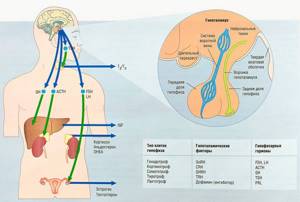
The production of corticotropin is influenced by active substances produced by the brain of the head; glucocorticosteroid produced by the adrenal glands; corticoliberin, generated by the hypothalamus part of the brain.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone affects the production of glucocorticoids, in particular, under its action, corticosterone, cortisone, and cortisol are formed. The functions of the hormone include stimulating the formation of adrenocorticosteroid. The mechanism is such that the substance indirectly affects the formation of adrenaline. All of these hormones influence how the body performs its functions at the cellular level. Under the influence of corticotropin, sex hormones are produced. Human hormones activate the work of the most important glands. In the female body, mood and well-being depend on the level of ACTH. In men, the substance affects sexual function and libido.

The mechanism of action of the adrenal glands is inversely related to the production of corticotropin. In each state of the body, the pituitary gland produces such an amount of corticotropin that will provide the required level of hormones produced by the adrenal glands.
Since adrenocorticotropic hormone is responsible for the synthesis of various biologically active substances in the body, it affects the following body functions:
- State of the immune system (disease resistance);
- Adaptability to changing external circumstances;
- Necessary reaction to stressful situations;
- Reduced allergic reactions;
- Increasing the pain threshold in a critical situation;
- Ensuring the possibility of childbearing.
All these functions are provided in both women and men. The amount of corticotropin in the body depends on the time of day. Its highest value is reached at 7 am, the lowest value is noted at 23 o'clock. This is the average time of the maximum and minimum. The exact figure depends on your sleep and wakefulness patterns.
In addition to the listed biological mechanisms, ACTH affects a person’s weight and muscle volume. It is involved in the process of burning fat and saturating the blood with amino acids and glucose.
ACTH norms in men and women
Having understood what the adrenocorticotropic hormone ACTH is responsible for, let’s consider an equally important topic - generally accepted indicators of the norm of this substance. The level of a hormonal element may be influenced by some external factors, but the possibility of developing a disease that affects the analysis data cannot be ruled out. In any case, the final decision remains with the endocrinologist.
The norm of ACTH in women can be as follows (unit of measurement - pmol/l of blood): from 2 to 11. If we consider the normal values of the hormone, taking into account the generally accepted units of measurement (pg/ml of blood), then they should range from 9 up to 52.
The ACTH norm in men ranges from 9 to 46 pg/ml of blood. If there is any suspicion of an increase or decrease in the concentration of corticotropin in the body, a clinical analysis is performed.
Important! Minor deviations from generally accepted norms are not a warning sign. However, if ACTH levels are 1.5 times or more higher than normal, this may indicate serious health problems!
ACTH is low
Insufficient production of the hormone is associated with the following processes:
- secondary hypocortisolism. If the functioning of the pituitary gland is disrupted (insufficient production of ACTH), atrophy of the adrenal cortex occurs (lack of cortisol synthesis). Functional failure of other glands of the endocrine system may also occur;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome. The level of adrenocorticotropic hormone falls in the presence of a malignant tumor in the adrenal glands. It differs from Cushing's disease in that there is excessive production of cortisol and, as a result, a reduction in the production of ACTH by the pituitary gland;
- benign formations in the adrenal glands. The tumors in this case perform the function of the organ and produce additional cortisol, which reduces ACTH levels;
- taking medications from the glucocorticoid group, cryptoheptadine.
ACTH is elevated
Pathology is indicated by a 1.5-fold increase in hormone levels:
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease. It occurs against the background of various pathologies (the most common is pituitary adenoma). Increased iron volume produces more hormone, which means it stimulates excess cortisol production - ACTH increases up to 2 times;
- Addison's disease (cortisol deficiency), as well as congenital adrenal hyperplasia. In these pathologies, the adrenal cortex does not produce cortisol, shifting the function to the pituitary gland. In this regard, the level of ACTH rises sharply; — 2-2.5 times (> 1000 pg/ml);
- paraneoplastic syndrome. It is a consequence of the reaction of the pituitary gland to an oncological formation in any organ;
- Nelson's syndrome. Develops in patients with Cushing's disease, in the presence of a pituitary tumor, after amputation of the adrenal glands. The patient experiences secondary adrenal insufficiency and ACTH levels increase;
- syndrome of ectopic production of adrenocorticotropic hormone - 1.5 times the norm. In rare cases, ACTH can be produced not only by the pituitary gland, but also by a malignant tumor in any organ. Tests show high levels of ACTH and cortisol. To diagnose the pathology, a test with corticotropin-releasing hormone is prescribed. After it, the ACTH level either increases (indicates Itsenko-Cushing's disease) or remains at the level (ectopic production syndrome);
- taking medications. Lithium-based drugs, insulin, ethanol, calcium gluconate, amphetamines, aminoglutethimide, levodopa, metoclopramide, metyrapone, pyrogens, vasopressin can artificially increase ACTH levels.