It is best to begin proper preparation for pregnancy approximately six months before the expected conception. This time is enough to identify any adverse factors that may affect conception and fetal development. Before planning a pregnancy, a couple must undergo blood tests for hormones. With their help, you can determine hormonal levels and disturbances in the endocrine system.
Primary appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist from RUB 2,500.
Repeated appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist from 2,500 rubles.
All prices Make an appointment
In our International Hemostasis Clinic you can do the necessary blood tests and undergo other diagnostic measures when planning a pregnancy. We have our own laboratory with a scientific base, which allows us to perform any analyzes in the shortest possible time.
What is AMG for IVF
Anti-Mullerian hormone (abbreviated as AMH) is the most important hormone used to assess ovarian reserve and, accordingly, prospects for IVF (or natural conception, if we are talking about counseling when planning pregnancy).
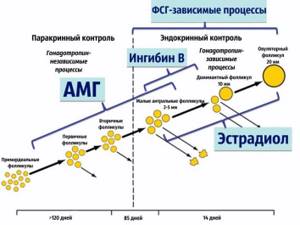
AMH as a diagnostic marker appeared and established itself in clinical practice relatively recently, and, together with ultrasound data, allows one to predict the ovarian response to stimulation, including the risk of developing hyperstimulation syndrome and, conversely, a poor (poor) response. In accordance with the assessment of the follicular reserve, reproductologists can select drugs, their doses and regimens (protocols). The hormone is named after the scientist Johann Muller, who identified a common channel-tube in male and female embryos - the Mullerian duct, from which the uterus, fallopian tubes and vagina develop in women and the prostatic “uterus” and epididymis in men. It is considered proven that there is a direct relationship between the level of the hormone and the number of eggs remaining in the ovaries (ovarian reserve). This explains the fact that the level of the hormone does not change significantly either depending on the day of the cycle, or as a result of taking medications or other related circumstances.
Usually, the need to take a blood test for AMH arises to decide on the choice of a treatment plan for infertility; although more and more often married couples, especially older (35+) age ones, are getting tested at the stage of pregnancy planning. AMH analysis for IVF is of utmost importance; it indicates how urgently the procedure needs to be started, what doses of gonadotropins should be prescribed, and finally, the need to use donor cells in the IVF procedure.
What is anti-Mullerian hormone?
Anti-Mullerian hormone (Mullerian inhibitory substance) performs very important functions in the body of men and women.
In boys during fetal development, AMH promotes the proper development of the genital organs and the movement of the testicles from the abdominal cavity to the scrotum.
In women, under the influence of AMH, the dominant follicle is selected (the same one from which a mature egg is released during ovulation) and its maturation.
The concentration of the hormone depends on the number of antral (“dormant”) follicles and reflects the reproductive potential of a woman. By assessing the level of AMH, it is possible to predict the number of eggs potentially capable of fertilization.
What is the hormone norm for IVF
In the classic version (using a standard diagnostic kit), the AMH norm ranges from 0.03 to 7.37 ng/ml for women aged 26 to 40 years. With the widespread use of the AMH test, diagnostic kits from different manufacturers have appeared, so the norms may be different: before interpreting the results, you should study the norm adopted in a given laboratory.
The interpretation of the obtained figures is not limited to assessing the level (above or below the norm). In the best case, a reproductive specialist should interpret the results obtained: he is the one who can compare the data from the patient’s medical history, ultrasound examination, and only after that give an assessment of reproductive function.
Preparing for the study
In preparation you should:
- the day before, give up serious physical activity, and also avoid emotional stress;
- do not eat for 8 hours before the test;
- do not smoke for at least an hour before the test.
If a dynamic assessment of the hormone level is required, a repeat analysis should be performed in the same laboratory as the first.
Many patients are interested in what day the study should be scheduled. Since the concentration of the hormone remains approximately the same throughout the cycle, this is not so significant. Usually, tests for FSH, LH and inhibin B are taken at the same time, so the study is carried out on days 2-3 of the menstrual cycle.
Deviations from the norm and pregnancy prognosis
The existing standards are based on many years of research and observations of physiologists and reproductive specialists around the world. The results obtained can be divided into three categories:
- AMH is above normal or close to/at the upper limit of normal. The prognosis for pregnancy naturally or by insemination is quite favorable; It must be taken into account that with such AMH indicators, hormonal disorders and anovulation are often detected, which can lead to infertility. In such cases, a detailed examination is necessary to clarify the diagnosis and draw up the correct treatment plan. At the same time, IVF requires especially careful actions from the reproductologist, because with high AMH, the development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is likely, and, often, even the most skilled doctor is not able to prevent the development of this syndrome with one hundred percent probability.
- AMH is normal. The prognosis is favorable for both natural pregnancy and conception through IVF/IUI. Normal AMH is the most favorable prognostic indicator for IVF.
- AMH is below normal. The situation requires immediate measures to achieve pregnancy, since the ovarian reserve is depleted. IVF is preferable. The prospects for IVF are as follows: it may take more than one attempt, and here the optimization of the treatment plan directly depends on the skill of the doctor.
Let us repeat that it is incorrect to judge the prognosis separately only by the results of a blood test for AMH: firstly, all the circumstances taken into account when assessing the situation are important, and, secondly, any, even the most routine, analysis requires confirmation; in the case of AMH, this confirmatory indicator is the level of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone). They are the ones who “check” the obtained AMG result. The correlation is the opposite: with low AMH, FSH is increased (or closer to the upper limit of normal), and vice versa, high AMH is accompanied by low FSH.
However, among the predictive screening methods, the AMH test is the most important.
What can affect the final result of the analysis?
Diagnosis of anti-Mullerian hormone levels, like any other laboratory test, requires compliance with all prescribed rules and indications. Only in this case will the results obtained guarantee a high degree of objectivity and the prescription of further treatment in the right direction.
If the indicators raise suspicions of objectivity, then this means that there are some factors that prevented this work from being done efficiently at the time. These factors include the following:
- concomitant disease
- Unhealthy Lifestyle
- suffered stress
- increased loads
- consequences of body intoxication
- taking hormonal drugs and medications
- incorrectly performed analysis procedure as a result of erroneous actions of medical personnel.
It is advisable for every woman to understand the essence of conducting AMG and how to properly prepare for the study. Knowledge of the processes taking place in the ovaries gives them the opportunity to be more conscious about the preservation of their health.
Is it possible to increase AMH
The answer is clear - no! Small fluctuations in indicators with a clear general trend do not count. You need to understand that artificially increasing AMH (if such methods exist) is a rather pointless exercise and does not lead to an improvement in prognosis, because AMH only reflects ovarian reserve. The only reason why our patients’ attempts to achieve an increase in AMH is justified is to increase the chances of receiving a “quota” under compulsory medical insurance. But this in no way improves the prognosis and it is much more promising to contact the clinic where IVF is planned and receive some kind of “letter of guarantee”, which can help in obtaining a referral (“quota”). And, most importantly, discuss the treatment plan and, for example, the possibility of using donor material.
Is it possible to increase AMH levels?
There are no real methods to change AMH levels. Because, as I already said, the main reason for the decrease in AMH is a decrease in the level of preantral follicles, i.e. a decrease in the follicular reserve. There is no way to restore the follicular reserve. But in different laboratories the result of the analysis may be different, so there are cases when retaking the analysis gives a woman false hope, because the result turns out to be slightly higher than the previous values. But if AMH is less than 0.6, then there is no fundamental difference - 0.1 or 0.5 ng/ml. Both are extremely low indicators, which indicate a significant decrease in ovarian resource. Therefore, if the AMH result is less than 0.5 ng/ml, it does not need to be monitored.
Low AMH and conception
The most difficult situation is when low AMH numbers indicate a decrease in ovarian reserve and this is confirmed by ultrasound. In some cases, the ultrasound picture allows us to hope for spontaneous conception or successful IVF/IUI. But when the AMH level is confirmed by an ultrasound picture, it is important to correctly assess the overall situation, and if low ovarian reserve is detected in a woman under 35 years of age, and the husband’s spermogram is normal, it makes sense to try to achieve pregnancy using “programmed conception,” when attempts to become pregnant are made under Ultrasound monitoring of ovulation. On the contrary, if a meager supply of eggs is found in patients over 35, you need to think about IVF so as not to waste precious time (and not lose eggs).
Is AMH a reliable marker of pregnancy during IVF?
Partially. The number of oocytes is directly related to the woman's age. It is the woman’s age that is the main factor in reproductive success, including the frequency of pregnancy in the ART cycle. However, we must not forget about the quality of the eggs! If, against the background of a reduced level of AMH, a diagnosis of infertility is made, then you need to think not about increasing the amount of this hormone in the blood, but about how to stimulate the ovaries to produce healthy eggs.
IVF for low levels of anti-Mullerian hormone
IVF is the most effective method of treating infertility, which has been proving its effectiveness all over the world for 40 years.
A decrease in ovarian reserve, confirmed by a low AMH level, is an indication for IVF in most couples over 35 years of age. The difficulty of IVF in such situations is that stimulation of the ovaries with gonadotropins is less effective than with normal ovarian reserve. In other words, the number of eggs that can be obtained during the stimulation process is small, which means that the likelihood of getting pregnant as a result of one stimulation is reduced. In order to increase efficiency, an increase in doses of gonadotropins for stimulation and, in the absence of effect, “accumulation of eggs/embryos” has been adopted. In the latter case, several IVF protocols are carried out with stimulation or in a natural cycle, the transfer is not performed, and the embryos are “accumulated” - frozen in order to be transferred later.
Often, the accumulation of embryos is necessary for PGD (preimplantation genetic diagnosis) in order to select “healthy” embryos; this dramatically increases the likelihood of pregnancy. If it is not possible to obtain eggs, the question of using donor eggs is raised.
IVF and high AMH
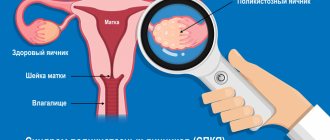
A high level of anti-Mullerian hormone indicates the presence of pathologies in a woman’s body. More often it is polycystic ovaries or granulosa formations in them, lack of ovulation, delays in sexual development. Smoking, alcohol abuse, exacerbation of chronic diseases, and psychoemotional stress can also provoke an increase in AMH. The most common cause of high AMH is PCOS - polycystic ovary syndrome.
The indicator is considered high if the hormone concentration exceeds 6.8 ng/ml. This is not an obstacle to IVF, but there are certain risks. During the stimulation process, there is a possibility of complications in the form of OHS (ovarian hyperstimulation), which is characterized by severe swelling and deterioration of blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
In isolated cases, HOS leads to death. To eliminate the slightest risks, in case of high levels of anti-Mullerian hormone, in vitro fertilization is carried out with one’s own eggs, without stimulation. If there are indications, minimal hormonal stimulation can be performed, during which the patient is under the supervision of a reproductologist.
Features of the compulsory medical insurance procedure
The procedure for obtaining a “Referral for IVF under Compulsory Medical Insurance” is standard and varies slightly depending on the region. Most importantly, in some regions, patient selection criteria are applied depending on AMH numbers. This is explained as follows:
It is well known that with age, the ovarian reserve decreases due to its consumption during the reproductive period. The age at which the decline becomes critical depends on many circumstances: the initial reserve, ovarian surgery, and hereditary factors. And, when a critical decrease in ovarian reserve is achieved, pregnancy using one’s own egg becomes problematic for a woman. This (not age) is what the restrictions set in some regions are based on. In other words, patients are selected based not on age, but on AMH numbers. And an effective way to “get” a referral for IVF under compulsory medical insurance is to undergo a consultation with a fertility specialist at the clinic where IVF was planned and develop a treatment plan. Clinics can confirm consent to accept a patient with some kind of “letter of guarantee” (it is not required as a standard).
Preparing and conducting a test for anti-Mullerian hormone levels
Preparing for the extended Efort test must be approached responsibly, since only in this case can you obtain accurate, and therefore informative, data. Follow these guidelines:
- Get tested on the third day of your cycle.
- A few days before the procedure, avoid strenuous training and other activities. You should also try to avoid stress.
- You should not eat or smoke before the test. Ideally, 8 to 12 hours should pass between the analysis and the last meal.
- You can drink, but only water. Sweet tea, juice, coffee are prohibited.
For analysis, laboratory assistants take blood from a vein.
Normal and abnormal levels of anti-Mullerian hormone
The following norms for the concentration of AMH in the blood of patients will help you interpret the data yourself:
- The norm for women reaches 1.0–2.5 ng/ml.
- The normal range for men is 0.49–5.98 ng/ml.
However, you should entrust the interpretation of the results to an endocrinologist. For example, a woman’s anti-Mullerian hormone concentration is less than 1.1 ng/ml, indicating a reduced ovulatory reserve. But it may also indicate the following conditions:
- Early puberty.
- Menopause.
- Obesity and other metabolic disorders.
- Gonadal dysgenesis (congenital disorders of the female and male reproductive system).
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (a pathology that is provoked by reduced production of sex hormones and is characterized by underdevelopment of the genital organs).
Concentrations above normal may be caused by the following reasons:
- Delayed sexual development.
- Granulosa cell tumors of the ovaries.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Congenital mutations of specific receptors.
- Anovulatory infertility, etc.