Women of childbearing age who are sexually active often complain of aching pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area. The cause of this symptom can be many pathological conditions of the pelvic organs and not only. It should also be remembered that due to anatomical and functional features and the development of the pelvic organs in the embryonic period, diseases can have similar manifestations. The final diagnosis, in most cases, is made after diagnostic procedures by exclusion.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy, of course, is not a disease, but a pleasant state in a woman’s life, which can sometimes manifest as unwanted pain symptoms in the presence of concomitant diseases. Confirmation or refutation of this condition is carried out after clarification of anamnestic data, physical examination, pregnancy tests, as well as additional instrumental methods. If, in the absence of menstruation, after an ultrasound, a neoplasm is discovered in the pelvis, then this is one of the indications for laparoscopy.
Recovery period after biopsy
After a diagnostic biopsy, the following is strictly contraindicated:
- engage in sports and heavy physical activity;
- go to the pool, swim in natural reservoirs;
- sunbathe, stay in direct sunlight for a long time;
- have sex.
To prevent bleeding after a cervical biopsy and other negative consequences, during the rehabilitation period a woman must follow these simple rules:
- Avoid thermal procedures, which activate blood circulation and can cause uncontrolled bleeding.
- Stop using medications that thin the blood.
- Avoid vaginal suppositories and douching.
- Do not use tampons, use sanitary pads instead.
If you strictly follow all the recommendations during the rehabilitation period, discharge and discomfort will cease to bother you after 5 to 7 days. The woman’s well-being will stabilize and she will be able to lead a normal life.
How much discharge will appear after a cervical biopsy depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and the type of procedure performed.
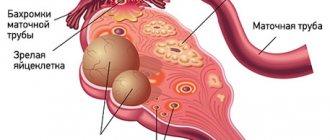
Ectopic pregnancy
This disease, despite modern developments in medicine, remains one of the main causes of maternal mortality. Diagnosing an early or uninterrupted pregnancy outside the uterus is somewhat difficult, and an accurate diagnosis can only be made after numerous examinations and a series of examinations.
Often, women complain of an irregular menstrual cycle with accompanying spotting discharge from the vagina, and consult a gynecologist one to two months after the last normal menstruation. Information about previous inflammatory processes in the reproductive system or about tubal ligation after laparoscopy, which was accompanied by menstruation, may lead the doctor to think about an ectopic pregnancy.
The pain can be either dull or acute, but unlike a miscarriage, in which the patient clearly notices pain in the middle of the abdomen, with an ectopic pregnancy it is one-sided.
Ultrasound examination in combination with the quantitative determination of human chorionic gonadotropin in blood plasma also has excellent diagnostic value. To determine the final diagnosis after a delay in menstruation and the presence of additional symptoms, laparoscopy or laparotomy is recommended.
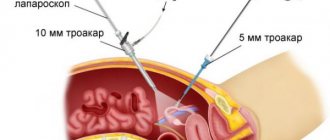
Laparoscopy in such cases is one of the only and low-traumatic methods of eliminating an ectopic pregnancy without the risk of developing serious complications.
Discharge after cervical biopsy
Light, bloody discharge after a cervical biopsy is considered normal and may bother you for 5 to 7 days after the procedure. Throughout this period, a woman should monitor her well-being, monitor symptoms and, if they worsen, immediately seek medical help. It is necessary to call an ambulance if the discharge becomes more intense and abundant, the body temperature rises, and an unpleasant odor develops, which indicates the progression of the infectious-inflammatory process.
Restoring menstruation after laparoscopy
Laparoscopy can affect the female body in different ways. For some, after laparoscopy, menstruation is restored, while for others, the cycle remains, as before, with disturbances. For example, if laparoscopic methods were used to remove an inflamed appendix, then menstruation after laparoscopy is delayed for a short time and such a violation should not be a reason for the patient to worry. The cause of this condition may be psycho-emotional experience or the effects of medications used during surgery.
But as for laparoscopy to restore the patency of the fallopian tubes, it is necessary to conceive a child as soon as possible in order to avoid the re-development of the adhesive process.
If menstruation after laparoscopy for ectopic pregnancy does not recover after a certain time, then gynecologists resort to conservative methods of treatment. Medicines are used to stimulate the ovulatory process.
Laparoscopic surgery - salpingo-ovariolysis
The purpose of the operation is to restore normal topographic relationships by cutting the adhesions around the fallopian tube and ovary, isolating them from each other. Salpingo-ovariolysis is performed either as an independent intervention or as a preparatory step for surgery on the fallopian tubes. The fallopian tube (ovary) is picked up with atraumatic forceps and moved upward if possible. The adhesions are cut with endoscissors after their preliminary coagulation. Rough adhesions are excised and removed from the abdominal cavity. Special precautions are necessary when working near the intestines, ureters, and large vessels. The risk of their damage can be reduced by observing the following conditions: the operation is performed under general anesthesia with sufficient relaxation, the absence of defects in the insulating braid of the instruments, short-term switching on of the electrosurgical unit. After complete release of the fallopian tube from adhesions along its entire length, ovariolysis is performed. In this case, it is imperative to lift the ovary and inspect its surface facing the broad uterine ligament, since adhesions can often be localized there.
Menstruation after treatment for endometriosis
Using laparoscopic methods, endometriosis is treated, and tumor processes are also diagnosed. In parallel, histological diagnosis of tissues is carried out, and, if necessary, complete removal of the tumor. After surgery, there is a possible risk of bleeding, which women often mistake for menstruation. Such symptoms require close attention, especially the appearance of aching pain in the lower abdomen and menstrual discharge from the vagina. Sometimes laparoscopic treatment is included in the complex of hormonal therapy, so menstruation may not occur before and after laparoscopy.
Reasons and features of a biopsy
A biopsy is an invasive diagnostic procedure, which is a gynecological operation that is performed in a hospital or outpatient setting. The essence of the procedure is to collect suspicious tissues for further histological and cytological examination.
The procedure is carried out at the beginning of the menstrual cycle, when the regeneration of uterine tissue occurs more intensively. A biopsy is performed to identify atypical cells that may be malignant or have a high risk of degenerating into an oncological tumor.
Indications for the procedure:
- cervical dysplasia or ectopia;
- neoplasm of malignant nature;
- precancerous tissue changes;
- human papillomavirus;
- polyposis and condylomas localized in the cervix;
- infertility.
The procedure has contraindications:
- exacerbation of a chronic process in the organs of the urinary and reproductive systems;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- pregnancy, lactation;
- foci of infection in the pelvic organs;
- hormonal and endocrine disorders;
- weakened immunity.
To exclude or confirm contraindications, before the biopsy, the doctor gives a referral for a comprehensive diagnosis. If everything is normal with the patient’s health, a date and time for the procedure are set.
The diagnostic operation itself lasts 25–30 minutes. Anesthesia is selected individually, after consultation with an anesthesiologist. After the procedure, the patient remains under the supervision of a gynecologist for 1.5 - 2 hours. If no complications arise during this time, the woman can return home and do her usual activities. If a large area is taken, then the patient remains in the hospital for 2–3 days for observation.
Depending on medical indications, the following types of biopsy may be prescribed:
- puncture;
- laser;
- conchotomous;
- radio wave;
- loop;
- wedge-shaped;
- circular.
Any of the above diagnostic techniques causes nagging pain in the abdomen and discharge of various types.
What could make the situation worse?
In order to quickly return to a normal lifestyle, and also not to provoke bleeding, a woman should temporarily give up:
- sex;
- heavy physical activity;
- using tampons;
- swimming in open springs;
- taking a bath (shower only);
- intravaginal drugs.
It must be remembered that in the period after surgery, especially the first month, the body is very vulnerable, therefore, with an incorrect lifestyle, other health problems may arise, and bleeding may also occur.
Features of normal secretion after surgery
Bloody discharge is considered normal after this type of surgery. Minor inclusions of blood may be present in the secretion for up to 20 days. But if the patient bled profusely for more than three days, then it is necessary to visit a doctor to rule out bleeding.
The appearance of clear, light discharge with a small amount of blood is considered normal. Pink ones are also allowed, but not bright scarlet ones.
Most often, they are not systematic and disappear immediately after all the damage has healed. There should be no unpleasant odor, and the consistency of the discharge should be uniform, except for minor blood clots. As for pain, some discomfort may be present, but acute pain may indicate various disorders.
We also note that the female body’s ability to recover and compliance with doctors’ recommendations plays an important role.
Doctor's comment
Pain, debilitating prolonged bleeding, infertility, miscarriage - all these signs may indicate a serious disease - uterine fibroids. This pathology is dangerous due to its complications, therefore, if you have been diagnosed with fibroids, you must undergo a course of treatment. In our clinic, the emphasis is on organ-preserving operations. By seeking help in a timely manner, you can count on maintaining your reproductive function. As for complications during the operation, our clinic successfully uses the most advanced techniques, modern instruments and equipment are used, so the likelihood of adverse consequences is minimized. If you are experiencing any ailment related to the reproductive organs, then just make an appointment and we will discuss all the problems together. However, it is better to undergo preventive examinations regularly; in this case, any violation can be detected on time, and in the initial stages, most diseases can be treated conservatively. Our clinic carries out all types of diagnostics; here you can undergo a comprehensive examination - all in one building and without tiring queues. Make an appointment, because even the slightest deviation may indicate a serious problem. Don't give diseases a single chance!
Head of the surgical service at SwissClinic Konstantin Viktorovich Puchkov
Prevention of diseases of the genitourinary organs in women
Some rules of behavior to prevent new episodes of leukorrhea:
- Avoid douching, for example, during menstruation or after sex.
- Carefully observe personal hygiene, which should not be too frequent.
- Use special and delicate personal hygiene products.
- After using the toilet, wash in one direction from the vagina to the anus, and never vice versa, so as not to promote the passage of intestinal pathogens into the vulva.
- Use only cotton underwear.
- Avoid clothing that is too tight.
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse to prevent possible sexually transmitted diseases.
- Treat any metabolic disorders, such as diabetes, promptly.
- If you have intimate disorders, consult a gynecologist and avoid self-treatment.
Have regular gynecological examinations at least once a year, even if you have no complaints.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Why is it better to have myomectomy done at the Swiss University Hospital?
- Surgeons at our clinic were the first in the country to perform SILS surgery and laparoscopic myomectomy. The clinic also performs operations using transvaginal access (NOTES surgery).
- The specialists of our Center have impressive experience in performing myomectomies; our surgeons have performed several thousand successfully performed operations; more than 1,500 unique surgical interventions are performed annually. Moreover, our leading specialists act as experts in many professional organizations.
- The clinic’s surgeons strive to use organ-preserving and minimally invasive techniques that are as gentle as possible during surgical treatment of reproductive organs. Thanks to this approach, our patients can have children in the future.
- If necessary, we perform simultaneous operations; during one intervention, you can get rid of not only fibroids, but also concomitant diseases of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- Simultaneously with myomectomy, we can perform reconstructive surgeries on the vagina and rectum for widespread endometriosis.
- We successfully use our own patented laparoscopy technique with temporary occlusion of the uterine arteries, so we are able to remove complex, large myomatous nodes without blood loss.
- Due to excellent visualization of the operation site and the absence of bleeding during the intervention, we are able to reliably suture the myometrium, which affects the formation of a healthy scar. We also use anti-adhesion barriers to prevent the occurrence of adhesions, which is especially important if a woman plans to give birth in the future.
Pathological secretion after laparoscopy
Some types of vaginal discharge should alert a woman and cause a quick visit to the attending physician:
Yellow secretion
Dark green, yellow-green discharge indicates infection in the body. This could happen during the procedure or unprotected sexual intercourse, which, by the way, is prohibited in the first month after the operation. Additional symptoms of infection are considered to be general weakness, malaise, high body temperature, systematic headaches, and pain in the lumbar region.

White curds
Such secretion can appear while taking antibiotics, which create optimal conditions for the proliferation of fungi. Also, this discharge may be bloody and accompanied by itching and burning.
Brown discharge
Let us immediately note that they may be normal (indicate residual bleeding), but there should not be a lot of them, and an unpleasant pungent odor should not be allowed. In other cases, secretion of a similar color may be associated with infection or a complication after surgery.
In all these cases, it is better to undergo additional diagnostics (ultrasound of the fallopian tubes, various smears, routine gynecological examination).