Radiation therapy plays a vital role in the treatment of malignant neoplasms of various locations. It can be used as a completely independent method or in combination with surgical treatment and chemotherapy.
Ionizing radiation is energy that is released by atoms of substances in the form of elementary particles or electromagnetic waves. We encounter this phenomenon every day, since there is a natural background radiation, the sources of which are dozens of radioactive elements found in soil, water and air.
In addition to natural radiation, people periodically encounter artificial ones. An example of such an impact is fluorography, which must be performed annually. The damaging effect that radiation can have on biological tissues is used in radiotherapy of malignant neoplasms.
Rehabilitation after radiation therapy: tactics, drugs, diet
Oncology is absolutely deservedly called the plague of the 21st century. Despite the depth of the scientific community’s immersion in the problem of cancer, it is impossible to say unequivocally that humanity has defeated cancer. The rate of spread of the malignant process is frighteningly high; in the absence of competent treatment, the outcome is one – tragic.
A comprehensive approach to the problem can stop the development of a tumor. Current cancer treatments include medications and radiation therapy. Radiation methods mean dosed irradiation of the body in order to stop division and destroy “bad” cells. The main problem lies in the danger of the consequences of radiation. Rehabilitation after radiation is necessary for every patient, since the treatment itself is accompanied by serious consequences affecting health.
What happens in the body during irradiation?
Just like the human body, tumors are also made up of cells. Tumor growth is regulated by cell division. One of the main effects of irradiation is to disrupt or prevent fission. In particular, radiation affects the genetic material in the cell nucleus. The cell loses its ability to divide and, as a result, dies.
However, every cell has a regeneration system to repair such damage. The ability to regenerate is much more pronounced in healthy, normal cells than in tumor cells. Therefore, the effect of ionizing radiation affects the tumor much more strongly than healthy tissue. Radiation therapy benefits from this difference in regenerative ability.
Experience shows that in many cases daily exposure gives the best results. After successful irradiation, the tumor cells die, are broken down by the body's own cells and are eliminated from the body.
Each individual radiation therapy session lasts only a few minutes. During the session, the patient does not experience any significant pain. The procedure is carried out in a specially equipped room under the strict supervision of a doctor. To successfully treat cancer, multi-week treatment, 5 days a week, is often necessary. In this case, the weekend remains free.
Purpose of radiotherapy
The goal of radiotherapy is to destroy the cancer cells that make up the tumor. By destruction we mean the destruction of the DNA of such cells, which impairs their viability. This is achieved through the rupture of molecular bonds through the ionization of DNA, through the radiolysis of water included in the cytoplasm. The more active a cell’s ability to divide, the more effectively radiation affects it. Modern irradiation technologies have made it possible to focus on the source of the problem, so that healthy cells suffer less.
Consequences of radiation therapy
The main difficulty associated with radiotherapy is its consequences for the body, which manifest themselves through unwanted side effects. The intensity of side effects directly depends on the general condition of the patient, the type of radiation and its dose. For example, metastatic tumors require a sequential course of radiotherapy, which provokes tangible consequences that reduce the patient’s quality of life. The symptoms through which the consequences will be expressed are largely determined by the localization of the oncological process. The larger the area of radiation, the higher the risk of severe unwanted effects from radiotherapy. The least complications come from irradiation carried out using modern devices for targeted radiotherapy. The oncologist’s task is not only to calculate the radiation dose and duration of the course, but also to draw up a plan for leveling the consequences.
Gamma rays, which are used to destroy tumors, disrupt the functioning of healthy organs and systems and change normal metabolism. The most common symptoms are associated with nausea, vomiting and other disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Ion radiation drugs irritate the gastrointestinal tract, in particular the mucous membrane, which is why the primary response is nausea and vomiting. Irradiation often damages the surface of the skin, resulting in burns of varying degrees of intensity and extent. In addition, radiation changes the composition of the blood; most often, patients are faced with anemic conditions that require correction by replenishing deficiencies in microelements. Some effects from radiation therapy can be observed with local irradiation, for example, patients with laryngeal cancer may lose their voice, and with cervical or ovarian cancer, the pelvic organs may become inflamed.
In general, radiation therapy negatively affects the overall vitality of the body, slows down the normal course of metabolic processes, patients notice a lack of interest in food, lose weight, become pale and permanently tired.
Grodno Regional Children's Clinical Hospital
Details Published 01 February 2016
Kurpik A.V. Head of the office of the RKD UZ "GODKB"
The impact of radiation during X-ray CT studies on the human body.
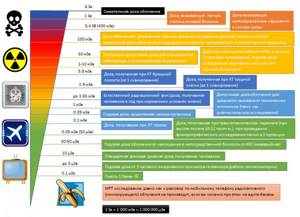
In this description we will talk about the effects of small and ultra-low doses of radiation on the body. Yes, that’s right, because contrary to popular belief that when conducting CT and X-ray examinations a person receives a HUGE dose of radiation, in reality this dose does not exceed an average of 1-1.5 mSv, and the maximum radiation exposure for the most complex, lengthy and expensive examinations is reaches 20 mSv. At the same time, in the definition of most scientific institutions and communities, low doses of radiation are considered to be 100 - 200 mSv, and some researchers classify doses below 10 mSv as ultra-low.
What is the essence of the impact of these very small doses, and the essence is that they do not have immediate (so-called “deterministic”) manifestations, such as redness on the skin, changes in blood composition, the appearance of malaise, etc. But they appear only in the form “stochastic” (probabilistic) changes. Among the stochastic effects:
- Increased probability and “rejuvenation” of oncological diseases (it has been proven that the probability of oncological diseases increases by 0.5% at doses of more than 100 mSv and in the future the probability grows in a progression close to geometric)
- Impact on heredity (it is for this reason that pregnancy, both current and planned, is a direct contraindication to any x-ray research methods; the effect of small doses of radiation manifests itself almost exclusively in the form of “small mutations” of genes, the probability of recovery after 3 months is 99.5- 99.9%)
- increasing the body's sensitivity to pathogens of infectious diseases
- metabolic and endocrine imbalance
- reduction in average life expectancy
- impaired mental function
- occurrence of cataracts
- temporary or permanent sterility
- other manifestations, such as: physiological disorders (dysfunction of the thyroid gland, etc.), cardiovascular diseases, allergies, chronic respiratory diseases (the likelihood of these changes is controversial and manifests itself at the level of statistical error).
*points 5.6 are reliable only for children who have not reached the age of puberty
The probability of all these changes, subject to compliance with radiation safety rules, is a maximum of thousandths of a percent. According to the same rules, in the Republic of Belarus there are maximum permissible doses of radiation to the population: for practically healthy people no more than 1 mSv/year; for people with diseases that do not pose an immediate threat to life, no more than 10 mSv/year; for cancer patients and patients with life-threatening conditions up to 100 mSv/year. For comparison, the background radiation (radiation from natural sources) received by each of us is up to 3.65 mSv/year, in some places on Earth where people live it exceeds 10 mSv/year (of course, I do not take into account Chernobyl and the top of Everest).
In conclusion, we can say that over more than 100 years of mankind’s acquaintance with ionizing radiation, most of the effects of AI have long been studied and calculated (although research on this topic is still carried out regularly and continues to bring new results), so it is either to be afraid or not to be afraid of radiation , this is an individual choice for everyone, but a properly prescribed and conducted study is much more likely to help save your life and health than to cause any harm.
Rehabilitation after radiation therapy
Competent rehabilitation under the guidance of the attending physician allows you to restore vitality. Restorative measures can be carried out in a hospital setting or at home, everything depends on the patient’s condition and his ability to fully function. If radiotherapy was carried out in a targeted manner and the side effects are vague, then staying at home is quite possible. General recommendations concern daily routine; speedy rehabilitation will occur with strict adherence to sleep, nutrition, and dosed activity in the fresh air.
Treatment of skin burn
Skin burns are a common consequence of radiation treatment. In most cases, signs of a burn cannot be observed immediately; they increase over several days. It is important to associate skin damage with radiation and differentiate it from other skin diseases. Signs may vary: redness, blisters, soreness, peeling, erosions, sores, swelling. These burns are different from those you get under the sun. The first thing to do is to ensure that the injured area is protected from the external environment and potentially dangerous factors. Superficial radiation burns can be treated with products such as Pantelol and Bepanten - provided that there are no papules with liquid inside. Blisters are treated with hydrogen peroxide or chlorhesidine and ointments such as Levomekol and Levosin are applied - they resist bacterial infection and accelerate healing. Deep tissue damage requires more serious measures, in particular, going to the hospital. In this case, treatment is prescribed by a doctor. As supportive remedies at home, for first and second degree burns, it is permissible to use such products as sea buckthorn oil, propolis ointments, and rosehip oil.
To prevent radiation burns, use Dieton ointment 5% and Lioxazone spray. The products provide protection from radiation, reduce the intensity and risk of radiation dermatitis, swelling and other related conditions.
Will strong alcohol help you cleanse yourself?
It is widely believed that alcohol destroys and removes radionuclides from the body. This statement is half true. Ethyl alcohol only helps to evenly distribute the radiation load across system organs, which reduces the amount of radiation received by a particular system.
However, strong alcohol is useless if consumed some time after the procedure. The harmful effects of vodka, on the contrary, will cause a noticeable blow to the body.

However, this clarification does not apply to all types of alcoholic beverages. For example, doctors recommend that people who work in x-ray laboratories drink “dry” red homemade wine. The product will not harm humans and will be an excellent means of preventing radiation sickness.
A single x-ray is not dangerous to human health, unlike forced or planned exposure to increased doses of radiation. Medicines and dietary supplements will help speed up the elimination of harmful components. The patient's nutrition is of no small importance.
Liver recovery after irradiation
The liver is one of the most radiation-sensitive organs. Even if the treatment was not aimed at eliminating the tumor localized in the liver tissue, it suffers quite seriously. Meanwhile, a normally functioning liver is one of the pillars of health and determines the quality of life of any person, especially a cancer patient. Taking drugs from the group of hepatoprotectors will help ensure regeneration of organ tissue. This category of products includes a large list of names; drugs can be divided according to the main active ingredient.
- Milk thistle flavonoid complex. The drugs Gepabene, Legalon, and Darsil are produced based on silymarin and other flavonoids. They effectively restore liver cell membranes and strengthen them. The performance of the organ improves, in particular, its ability to neutralize toxins and synthesize protein is activated.
- Extracts of medicinal plants and plant raw materials. This group includes LIV 52 (caper roots, chicory seeds, cassia seeds, arjuna bark, nightshade, etc.), Tykveol (pumpkin oil concentrate), Hofitol (field artichoke leaves). These drugs have an effect due to the plants they contain; they help regenerate hepatocytes, improve the flow of bile, etc.
- Components of animal origin. Hepatosan is produced from freeze-dried liver cells obtained from pigs. The drug has a complex effect: detoxification, protein synthetic, membrane stabilizing. Donor cells are related to human liver tissue, which determines the positive effect of using the drug.
- Essential phospholipids. The largest group of drugs, it includes Essentiale, Essliver, Fossfonziale, etc. Long-term, for several months, intake of phospholipids can achieve a positive effect on the condition of liver cell membranes. Thanks to the linoleic acid molecule, phospholipids are integrated into liver tissue, strengthening them.
- Low molecular weight sugars. The composition of the drug Geptrong includes low molecular weight sugars that have affinity for human hepatocytes. This is a natural and safe remedy that shows a whole range of liver-healthy effects: membrane stabilization, antioxidant effects, reducing the activity of liver enzymes, reducing inflammation. The injectable form is especially relevant for patients suffering from nausea.
- Ornithine. A high level of ammonia as a result of a violation of its neutralization in the liver has a toxic effect on the entire body. The drug Hepa-Merz based on the amino acid ornithine eliminates this problem.
Folk remedies for dealing with post-radiation symptoms
Traditional medicine offers alternative ways to restore the body after irradiation. It is recommended to use them after consultation with your doctor and only if they are compatible with the traditional treatment already prescribed.
Healing properties are attributed to pine needles - this plant material accumulates a huge amount of useful substances. Coniferous tree needles are used as a fortified food supplement, and drinks are prepared based on them.
Pectin, contained in large quantities in sour fruits and berries, is a recognized means of eliminating the effects of radiation. It is useful to include them in the daily menu.
Dietary recommendations during and after radiotherapy
The period of radiation therapy itself is associated with an increased load on the body in general and the gastrointestinal tract in particular. During and after the course, the patient must strictly monitor his diet; this will largely determine his well-being and influence the speed of rehabilitation. Key recommendations relate to the composition of products and their quality - you should avoid any food that contains synthetic additives such as dyes, flavor enhancers, and preservatives. Simple, low-fat home-cooked meals are the perfect solution. It would be optimal to give up everything that can serve as an irritant for the gastrointestinal tract: smoked meats, pickles, store-bought sweets, fatty meat, sausages, everything that provokes the formation of gases (legumes, cabbage). The preferred method of cooking is steaming, boiling, baking, stewing. Hot sauces, seasonings, excess salt and sugar - all this is prohibited. Alcohol does not benefit a healthy body, and it is completely dangerous for those that receive a serious load in the form of radiation. It is better to break up meals over time and limit portion sizes. Some time after completion of radiation therapy, the patient should continue to follow a restrictive diet for some time; as health improves, the excluded foods can be gradually introduced, it is important to do this in dosage.
Timely access to medical care, strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations, well-chosen drug therapy with the support of a balanced diet will allow you to count not only on a positive result of radiation treatment, but also maintain the patient’s quality of life and neutralize the side effects of radiation.
Cleansing the body from radiation
What to do after repeated x-rays? Depending on the radiation dose received, one or several methods are used to cleanse the body of radiation.
Medicines and dietary supplements to help
| Medicine/dietary supplement | Characteristic |
| Potassium iodide | Prevents the concentration of iodine and reduces the dose of its absorption by the thyroid gland, protects the endocrine system from radiation; |
| Revalid | Strengthens the immune system, contains vitamins and elements the body lacks, balances the process of material metabolism, reduces the level of intoxication; |
| Polyphepan | Reduces the impact of radiation. Suitable for children and pregnant and lactating women; |
| Methandrostenolone | Indicated in case of severe exhaustion of the body. Belongs to a group of steroids that activate the process of cellular, tissue and muscle regeneration. Stimulates the synthesis of RNA and DNA, prevents oxygen starvation of the body; |
| Iodine | Dietary supplements that include a component reduce the adverse effects of radiation accumulated in the thyroid gland; |
| Clay with zeolites | Helps bind and remove radiation waste from the body; |
| Calcium | Dietary supplements with calcium destroy radiation strontium by more than 85%. |
In addition to medications and dietary supplements, diet helps in removing radiation from the body.

Nutritional Features
What can and cannot be eaten after an x-ray? After taking a dose of X-ray radiation, experts advise adhering to the following dietary recommendations:
- Before eating vegetables or fruits, they need to be peeled. It is recommended to remove the first three leaves of white cabbage, since the bulk of pesticides accumulate in the peel;
- meat products should be limited. It is not recommended to eat a lot of beef: it contains the most radionuclides;
- It is necessary to enrich the body with fluid: it helps eliminate harmful substances. An excellent option for daily use would be a decoction of flax and prunes. Natural juices with pulp lead to the absorption and removal of heavy metals.
Before eating, it is recommended to eat activated carbon, after mixing it with water. The tablets are crushed and sifted through a sieve. The total amount of substance consumed should be within 400 g.
Products that help in removing radiation
The table below shows what to drink and eat after fluoroscopy or radiography to stimulate the process of removing radiation particles from the body. We will focus on the key components of the products:
| Substance | Products containing the component |
| Selenium (absorbed with vitamins C, E) | Wheat bran, pine nuts, beans, raisins, almonds, dried apricots; |
| Cellulose | Pasta, fresh vegetables, grapefruit, beets, herbs, plums; |
| Potassium (component in excess is harmful to health) | Rabbit meat, tuna, sardine, dried apricots, nuts, raisins; |
| Pectin | Carrots, beets, peaches, plums, pears, jelly, apples; |
| Antioxidants | Fresh vegetables and fruits (strawberries, blackberries, blueberries), fruit juices with pulp, green tea, cocoa; |
| Carotene (yellow-orange pigments) | Carrots, rose hips, leaves of all representatives of the flora |
| Caffeic acid | All plants |
| Calcium | Fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese, etc.), sesame seeds, beans, parsley, basil; |
| Methionine | Chicken and quail eggs, dairy products, legumes, almonds, cheese, seafood |
| Vitamin P | Garlic, tomatoes, black currants; |
| Vitamin A | Dill, carrots, rose hips, spinach; |
| B vitamins | Flaxseed, poultry meat, liver, nuts, cereals; |
| Ascorbic acid | Sea kale, sorrel, currants; |
| Vitamin E | Oils (olive, vegetable), bananas. |
A specialist will advise what you can drink or eat to remove radiation from the body. By following the doctor’s recommendations when planning a diet, the patient will quickly cleanse himself and will not provoke an exacerbation of other chronic diseases (if any).
Along with useful products, there are also useless ones. During the period after irradiation, experts advise excluding the following foods from the diet:
- sugar;
- coffee;
- yeast;
- whole grain products.

The properties of these products prevent the removal of harmful components from the body. Concluding the topic of nutrition in the period after exposure to X-ray radiation, it is worth saying a few words about fasting. According to practice, periodic refusal to eat helps eliminate radionuclides.
At the moment of fasting, the process of cell division is slowed down, nucleic acid is actively restored - damaged cells begin the recovery process. Therapeutic fasting is recommended for people living in radiation-contaminated areas.