Detailed description of the study
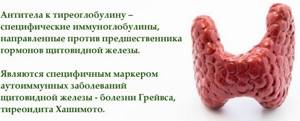
The thyroid gland is a small organ located in the neck. The hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are produced in the cells of the thyroid gland, which are involved in the body’s most important metabolic processes. They ensure the supply of oxygen and sufficient energy exchange in the cells and tissues of the body, the onset and healthy course of pregnancy. The production of T3 and T4 is carried out under the control of another gland - the pituitary gland, located among the structures of the brain through the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). An imbalance between the production of pituitary and thyroid hormones leads to changes in the endocrine function of these organs. This situation is observed in autoimmune thyroiditis - chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland caused by the body's immune aggression against this organ. The process is accompanied by the formation of antibodies to thyroid-stimulating hormone receptors in tissues (AT-TSH) and some substances produced by the gland. These substances include thyroglobulin. It is a precursor to the hormones T3 and T4, and is practically not released into the bloodstream normally. The destruction of pancreatic cells leads to an increase in the concentration of thyroglobulin in the blood and provokes the formation of antibodies to this protein (AT-TG). Other diseases of the thyroid gastric gland (diffuse toxic goiter, subacute thyroiditis) and autoimmune systemic diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's disease, type 1 diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis) also lead to the appearance of AT-TG. An increase in the production of thyroid hormones, observed in some cases with autoimmune damage, is called hyperthyroidism. It is manifested by the following symptoms: - Increased activity, excitability - Sleep disturbance - Feeling hot, increased sweating - Increased appetite - Unexplained weight loss - Tendency to diarrhea Prolonged inflammation of the thyroid gland reduces the ability of this organ to produce hormones, resulting in hypothyroidism. It can be manifested by the following symptoms: - Pathological fatigue, fatigue - Dry skin - Excess weight due to fluid retention in the body - Poor tolerance to cold - Depression - Drowsiness - Decreased memory - Tendency to constipation An endocrinologist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of thyroid diseases. If an autoimmune systemic disease or damage to only the thyroid gland is suspected, testing the titer of antibodies to thyroglobulin allows us to understand the cause of the disease and promptly prescribe treatment.
Factors influencing the result
The patient should be careful when preparing for the test and be completely honest with their doctor. For example, if a woman hides the fact of taking oral contraceptives (birth control) from a specialist and does not cancel them, then the AT-TG result may be false-positive (unreliable).
Changes in the structure of thyroid tissue can also distort the result.
The absence of antibodies in the biomaterial may also be due to other pathological processes:
- the body produces antibodies to other antigens;
- Specific thyroglobulin-antibody immune complexes appeared.
Antibody synthesis can be limited by lymphocytes, which will also give negative test results.
Important! The interpretation of the results is always carried out comprehensively. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on only one analysis.
Possible complications
In the absence of timely correction of the thyroid gland, the patient develops serious complications against the background of progressive pathological changes:
- depression develops;
- attacks of suffocation occur periodically;
- severe shortness of breath appears;
- body weight decreases;
- a person is worried about insomnia;
- patients complain of angina pectoris;
- heart failure is diagnosed.
A complication of a high level of antibodies to thyroglobulin (AT-TG) is also toxic hepatosis, atrial fibrillation, limb tremors, and hypothyroid coma. The greatest danger to human life is a malignant tumor. Delayed treatment in most cases leads to death.
The functioning of all internal organs and systems of the human body depends on the proper functioning of the thyroid gland. If AT-TG is very elevated, then you need to go to the hospital and undergo an examination. Identifying any disease at an early stage will allow timely treatment to begin and prevent serious consequences for a person.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Indicator table is normal
Normal levels of antibodies to thyroglobulin depend on many factors, but for men and women they range from 50-55 ng/mol.
| Name | Options |
| Thyroglobulin (TG) | < 56 ng/ml |
| AT to thyroglobulin | 04-17 U/ml |
| AT thyroid peroxidase | 5.5 U/ml |
AT-TG is highly elevated - this means that a serious disease is present in the human body. To determine the cause of the rise in the level of antibodies to thyroglobulin, it is necessary to undergo additional medical tests.
But to make an accurate diagnosis, the values must be really high. Minor deviations in antibody norms occur due to stress or after emotional stress. Fatigue and physical activity also affect AT-TG levels.
Treatment of hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis
Overt hypothyroidism should always be treated. You will be prescribed thyroid hormone replacement therapy, levothyroxine, which you will need to take for life.
Subclinical hypothyroidism in most cases does not require treatment; tests must be repeated after 3–6 months. The exception is pregnancy, as well as a pronounced increase in cholesterol (> 7 mmol/l). In these cases, even with subclinical hypothyroidism, thyroxine replacement therapy is prescribed.
Manifest (overt) thyrotoxicosis almost always requires treatment. At first I wrote “always,” then, to be fair, I decided to add that there are rare forms that go away on their own. However, thyrotoxicosis always requires consultation with a doctor and observation.
Subclinical thyrotoxicosis does not require treatment, but tests must be repeated after 6 months, there is a possibility of transition to an expanded form.

Preparing and conducting analysis
Proper preparation for research will allow you to obtain the most accurate results and establish a diagnosis, as well as determine the cause of disorders in the thyroid gland.
To ensure the reliability of the data obtained, it is necessary to carefully prepare for the examination:
- Do not take medications before drawing blood. Active ingredients may affect results.
- It is not recommended to smoke before the test.
- During the week before the test, you should not drink alcohol or eat fried foods.
- Patients are also advised to avoid physical activity.
- 3 days before the test, you should not take medications that contain iodine.

The results of laboratory tests are also influenced by emotional outbursts, therefore, before taking the material, it is necessary to avoid stressful conditions and overexertion. If a person has suffered an infectious disease with a high fever, it is recommended to refuse diagnosis. Blood for research is taken from a vein on an empty stomach in the morning.
Symptoms of increase
The first signs of pathological changes may appear in the form of discomfort when swallowing. There is a feeling of a lump in the throat. In a supine position, the characteristic symptoms intensify.
Pathological symptoms with increased AT-TG values:
- lymph nodes enlarge;
- there is constant fatigue;
- body weight sharply decreases or increases;
- the mood is constantly changing, apathy towards the outside world appears;
- eyelids, arms, legs tremble;
- anxiety, aggression and depression appear;
- it is difficult for a person to withstand heat or cold;
- hair fall out;
- the skin becomes dry, nails break.
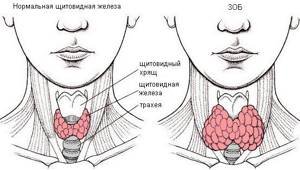
It is also recommended to be examined for women who cannot get pregnant for a long time or whose menstrual cycle is constantly disrupted. When a tumor forms, the doctor palpates a painful and immobile lump.
Prevention
There are no specific methods for preventing high or low TG levels. But in most cases, a change in the concentration of thyroid prohormone occurs due to iodine deficiency and damage to glandular tissue. To prevent endocrine pathologies, you should:
- eat a balanced diet;
- avoid stressful situations;
- replace regular salt with iodized salt;
- take vitamin and mineral complexes as prescribed by your doctor;
- treat foci of chronic infection;
- avoid contact with radioactive materials;
- do not abuse hormonal contraceptives.
Increased or decreased thyroglobulin (TG) is a specific marker of cancer, iodine deficiency and autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland. Quitting bad habits reduces the risk of organ dysfunction by 25%. If your family has relatives with endocrine, autoimmune or cancer diseases, you should be examined by an endocrinologist at least once a year.
How to get it back to normal
Treatment for highly elevated AT-TG is symptomatic. This means that patients are prescribed medications to restore the functioning of the thyroid gland. It is also necessary to adjust your lifestyle. In serious situations, surgery is performed.
Medications
Medicines are selected by an endocrinologist after a medical examination based on the results obtained. You should not take medications on your own, as this can cause serious consequences. Many drugs cause side effects.
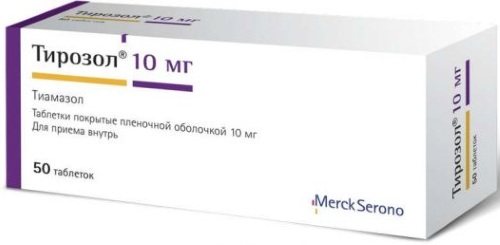
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Indomethacin, Almiral | The medicine is taken orally, without chewing, with a sufficient amount of water. The adult dosage is 25 mg 2-3 times a day. If necessary, the amount of medication is increased to 100 mg, divided into 4 doses. |
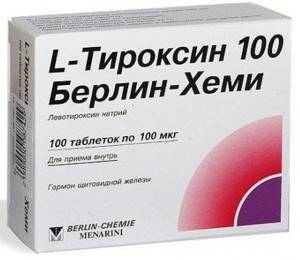
| Hormonal drugs | Levothyroxine, Euthyrox | The drug is taken in the morning on an empty stomach 30 minutes before meals. The daily dosage for an adult is 1.6-1.8 mcg/kg. The course of therapy is selected individually in each case. |
| Decreased synthesis of T3 and T4 | Metizol, Tyrozol | The medicine is taken with or after meals. Depending on the patient’s condition, an adult patient is prescribed 10-40 mg per day. |
Additionally, the endocrinologist recommends that patients take vitamin complexes. Hormonal drugs improve blood supply to the brain and mental abilities.
Traditional methods
Recipes from witch doctors and healers are used in the absence of serious inflammatory and degenerative processes. It is recommended to discuss alternative treatment with your doctor to prevent negative consequences.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Herbal collection | Mix valerian roots, lemon balm, yarrow and adonis in equal parts. Pour 2 tbsp. herbal mixture with hot water (1 tbsp.). Leave for 30 minutes and strain. | The prepared solution is taken orally 100-150 ml 2-3 times every day. |
| Wormwood compress | Pour dry grass (200 g) with pork lard (200 g). Mix all ingredients well. | The finished product is used for a compress. Apply warm to the neck before bedtime. The course of therapy lasts 2 weeks. The compress relieves discomfort well and eliminates pain. |
| Sea kale tincture | Mix 50 g of seaweed, 25 g of pine buds, 2-3 plantain leaves, honey and lemon. Place the resulting mass in a water bath and heat for 30 minutes. | It is recommended to take 1 tbsp of seaweed tincture. 3 times a day before meals 30 minutes. The minimum course of treatment lasts 30 days. |
Folk remedies can restore hormonal balance and eliminate mental and emotional disorders. Therapy is carried out comprehensively, together with medications.
Other methods
AT-TG is greatly elevated - this means it’s time to take a closer look at your health. Patients with changes in the level of antibodies to thyroglobulin are advised to adhere to a healthy lifestyle. This is, first of all, giving up bad habits (alcohol, cigarettes, drugs), eliminating stress and eating healthy.

| Recommended Products | Prohibited Products |
|
|
The drinking regime involves drinking at least 3 liters of liquid every day.
In cases where drug therapy does not produce positive dynamics, the person’s condition worsens due to the progression of pathological processes, the patient undergoes surgical intervention.
Main indications for surgery:
- malignant tumor in the tissues of the thyroid gland;
- increase in diffuse goiter;
- development of adenoma;
- benign neoplasm.
After surgical treatment, the patient is prescribed hormonal drugs (Thyroxine) so that the body receives hormones.
Thyroid diseases: 5 tips
Since we're talking about the thyroid gland, I'll take this opportunity to give a few more important recommendations.
Ultrasound does not provide insight into how the thyroid gland works
- Most regions of Russia are in the zone of iodine deficiency. Buy only iodized salt and use it instead of regular salt.
- Sea kale does not contain as much iodine as is commonly believed. You can use seaweed to make salads if you like, but this does not mean at all that you can abandon traditional methods of iodine prophylaxis (iodized salt or pharmacological doses of iodine for pregnant women).
- You cannot use an alcohol solution of iodine for “prevention and treatment of the thyroid gland,” as is sometimes recommended in TV shows and pseudoscientific books about health. “Iodine nets,” a solution of iodine in sugar or milk, can quickly lead to the accumulation of toxic doses of iodine in the thyroid gland and the development of thyrotoxicosis.
- There is no need to do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland just in case. If the function of the thyroid gland is not impaired, and the gland itself is not enlarged and no formations are palpable in it, then an ultrasound “just in case” will do more harm than good. Detection of small nodular formations, fear of detecting cancer, unjustified repeated punctures, repeated ultrasounds - this is what awaits a person who has set foot on this slippery path of multiple unnecessary examinations.
- A healthy adult needs to have their TSH level determined once every 5 years. If you have previously been diagnosed with subclinical hypothyroidism, subclinical thyrotoxicosis, or if you are taking the antiarrhythmic drug amiodarone, then take a TSH blood test once every 6 months.