If there is something wrong with your digestion, the doctor will most likely prescribe not the most pleasant examination methods (in particular, gastro- and colonoscopy). But today these techniques have changed so much that you can no longer be afraid of them.
Our expert is an endoscopist at Moscow City Clinical Hospital No. 17 Igor Sadikov .
Gastro- and colonoscopy are two of the most important research methods used to assess the functioning of the digestive organs. Of course, they are not as comfortable as, say, ultrasound or CT and MRI, but they are very informative.
You'll have to be patient
Gastroscopy has virtually no alternative if you need to confirm or exclude diagnoses such as esophagitis, duodenitis, gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, tumors of the stomach and esophagus. Unfortunately, such diagnoses cannot be established non-invasively.
In addition, gastroscopy lasts a matter of minutes (a little longer if you need to take a biopsy - a piece of mucous membrane for examination). And in order to minimize discomfort, the doctor first administers local anesthesia - irrigates the patient’s mouth and throat with a 10% lidocaine solution. But sometimes this is not enough and the procedure is still difficult to bear, and even turns out to be ineffective. This happens if the patient prepared incorrectly for it or behaved incorrectly during the study.
Gastroscopy. 5 signs that you need this procedure Read more
For gastroscopy to go as quickly and smoothly as possible and give results, it is important:
- do not eat 10 hours, do not drink or smoke 2 hours before the examination (otherwise the production of gastric juice and mucus will interfere with the examination);
- If possible, refrain from taking medications before the procedure;
- warn the doctor about existing diseases (bronchial asthma, recent stroke, heart attack and other diseases are contraindications for gastroscopy);
- During the procedure, breathe only through your mouth, evenly and deeply. Such breathing in itself allows you to reduce the urge to vomit or even reduce it to zero. You need to fully concentrate on proper breathing and try not to think about anything else.
Contraindications
Circumstances that preclude gastroscopy are the presence of critical stenosis of the esophagus, which does not allow the insertion of an endoscope, chemical burns of the esophagus, phlegmonous esophagitis, mediastinitis, dissecting aortic aneurysm, hemorrhagic diathesis, acute periods of myocardial infarction or stroke requiring rest. Relative contraindications to gastroscopy include severe spinal deformity, large goiter, severe cardiopulmonary failure, mental disorders, and hemophilia.
For sissies
However, many people are simply unable to “swallow” the probe, even if they really need to. Most of them are people with a pronounced gag reflex. Another group is fearful patients, nervous and anxious. Fearing that swallowing the probe will deprive them of their ability to speak, they worry that they will not be able to control the progress of the study or interrupt it if suddenly necessary.
For such people there is an alternative - transnasal endoscopy. The examination is carried out not through the mouth, but through the nose. The device used - of a significantly smaller diameter compared to the traditional one - is inserted through the nostril, then passes along the back wall of the pharynx, but does not touch the root of the tongue. Accordingly, gagging does not occur (however, with a deviated nasal septum, there may be problems with the insertion of the device).
During a transnasal study, the patient is not given a mouthpiece, which is used in the traditional method to prevent the person from biting the device. Therefore, the patient can talk to the doctor and swallow saliva, which is highly not recommended during conventional gastroscopy, as this can provoke vomiting.
Both methods can be carried out free of charge, under compulsory medical insurance. But gentle transnasal endoscopy, in addition to its advantages, also has disadvantages. With her help:
- you cannot take a full biopsy (you can only pinch off very small pieces of tissue);
- it is impossible to see small details. This is due to the small size of the device and optics built into the gadget. Therefore, transnasal endoscopy is better suited not for detailed study, but for screening.

Not sparing your belly. Any pathology begins with problems in the stomach Read more
Interpretation of results
Normally, during gastroscopy, the gastric mucosa is visualized as pale pink or pink in color. The anterior wall has a shiny, smooth surface and contains a little mucus; the mucous membrane of the posterior wall has a folded structure. The gatekeeper is cone-shaped, freely passable. As the walls of the pylorus contract, the folds acquire a star-shaped appearance. With gastritis, swollen, hyperemic mucosa, submucosal hemorrhages, thickened folds, and an increased amount of mucus are visible. With atrophic gastritis, a pale color of the mucous membrane, smoothness and thinning of the folds are determined.
A sign of a stomach ulcer, determined by gastroscopy, is an ulcerative crater limited on the sides by a ridge. The bottom and edges of the crater are bright red in color, the surface is covered with a mucous, fibrinous or purulent coating. The ulcer after scarring has the appearance of a whitish spot. A malignant ulcer has uneven, nodular and tuberous edges. With stomach cancer, the folds are smoothed out, the mucous membrane acquires a grayish-white color. Gastroscopy may reveal a disintegrating or mushroom-shaped tumor of the stomach.
It was a dream?
The second option to avoid unpleasant sensations during endoscopy is to conduct it under the so-called medicinal sleep. Doctors call this intravenous anesthesia while maintaining spontaneous spontaneous breathing. This is not anesthesia, but sedation: a medicine is injected into a person’s vein, he calms down, falls asleep, feels nothing and, when he wakes up, does not remember what happened. This anesthesia is not enough to carry out serious abdominal surgery, but it is quite enough for many endoscopic interventions.
Some people come to their senses after a medicated sleep after 5 minutes; for the second, consciousness returns after half an hour; for the third, after an hour. But there is no reason to worry: the method does not cause complications. True, it can affect concentration and reaction. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend not to drive during the first 24 hours after the procedure.
Under such “sleep” you can perform not only a gastroscopic examination, but also a colonoscopy. True, such a service is already paid. However, many people prefer to endure the study “for profit” not out of savings, but because of the fear that during sleep the endoscope may damage the intestines, and the person himself will not feel it. In fact, such a risk is quite small (one hundredth of a percent), but it can still arise if the procedure is performed by an inexperienced doctor or if the patient has certain problems. For example, there is pronounced atrophy of the mucosa (this happens in very elderly people) or adhesions in the abdominal cavity, as well as large multiple diverticula in the colon (typical of Crohn's disease or severe ulcerative colitis). But an experienced endoscopist does not have such “punctures”.
Question answer
What are the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease?
Indications
Gastroenterology includes the presence of gastroesophageal reflux, dysphagia, retrosternal pain, nausea, dyspepsia, iron deficiency anemia, and weight loss in patients as planned diagnostic indications for gastroscopy. Gastroscopy is performed to clarify clinical or radiological symptoms suspicious for cancer. Dynamic gastroscopy is recommended for atrophic gastritis, peptic ulcer, after gastrectomy.
Emergency gastroscopy is indicated in emergency conditions: suspected foreign bodies of the esophagus or stomach, gastroduodenal bleeding, perforation of the esophageal tube or stomach wall. In addition to its diagnostic value, gastroscopy has a lot of therapeutic capabilities, allowing in some cases to perform endoscopic removal of foreign bodies of the esophagus and stomach, ligation and sclerosis of varicose veins, dissection of cicatricial strictures, clipping and coagulation of bleeding vessels during gastroduodenal bleeding, removal of polyps, and much more. etc.
Spy inside
Finally, there is a third option to avoid any discomfort during endoscopy. This opportunity is provided by a new generation device - a video capsule.
Preparation for the study is the same as for traditional endoscopy: you need to cleanse the intestines in a special way. Then - swallow a capsule slightly larger than a tablet, wash it down with water, put on a special belt or sensors, after which you can go about your business. And at this time, the capsule makes its journey through the gastrointestinal tract, simultaneously collecting a detailed video report about everything that comes across its path, and then, through a system of antennas, transmits information to a recording device, and from it to the doctor’s computer. The capsule itself comes out naturally after a few hours or days. It cannot be reused: the capsule is disposable.
Despite the obvious advantages, this technology also has disadvantages: a high price and the doctor’s inability to stop and take a closer look at something and take a biopsy. So, if the video capsule detects a problem in the intestines, you will still have to perform a classic colonoscopy (at least to take fragments for a biopsy or remove polyps). But there is no longer any need to endure this unpleasant procedure unless there is an urgent need. Now scientists are working to make the capsule controllable. Then it will be able to completely replace traditional research options.

Get over it. The most common questions about the functioning of the stomach Read more
Preparation for gastroscopy
To increase the information content, it is advisable to carry out the procedure on an empty stomach, 8-12 hours after the last consumption of food and water. Before emergency gastroscopy, a tube emptying of the stomach is performed. After a radiocontrast examination of the gastrointestinal tract (radiography of the stomach, esophagus, passage of barium through the small intestine), the interval before performing gastroscopy should be 2-3 days.
Preparation for gastroscopy consists of the patient’s psychological mood (explaining the purpose of the study and rules of conduct), as well as medication (sedation, pain relief, prevention of pathological reflux). In addition, before gastroscopy, a consultation is scheduled with an endoscopist, who assesses the indications and risks of the study and explains to the patient the features of the procedure.
By the way
The German physician Adolf Kusmaul was the first to introduce gastroscopy into medical practice in 1868. The device that Kusmaul used was a metal tube with a flexible conductor.
Since the time of Kusmaul, gastroscopes have been constantly improved. In the middle of the 20th century. A new type of gastroscope has appeared - a fibrogastroscope, which helps study images through bundles of glass fibers, their thickness is the size of a human hair.
There are contraindications. Be sure to consult your doctor
How to prepare for the examination
Despite the fact that manipulation through the nose is minimally invasive, like any examination of internal organs, transnasal examination requires certain preparation. As a rule, the doctor explains to the patient how to prepare before the prescribed procedure.
As mentioned above, one of the contraindications to the use of this manipulation is the presence of acute respiratory viral diseases. To identify their presence in the body, the doctor prescribes a general blood and urine test for the patient. As a preventative measure, the heart is checked using an electrocardiogram.
The procedure through the nose is performed on an empty stomach. The patient is not recommended to eat food 8 hours before the scheduled procedure. For three days, it is necessary to exclude all unhealthy foods from the diet, such as foods that are too fatty, smoked, or salty. Do not drink alcohol under any circumstances. A few hours before gastroscopy you should not smoke. There are no restrictions on water consumption.
In general, the manipulation is completely safe and rarely leads to any complications.
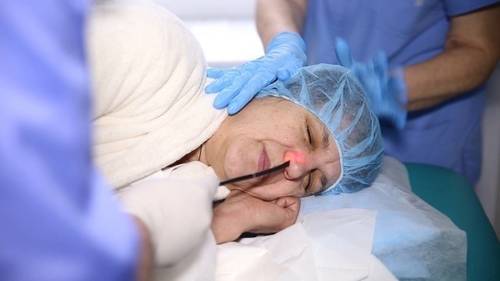
Diagnostic features
Transnasal manipulation has some features:
- Typically the procedure lasts about 15-30 minutes.
- The doctor asks the patient to lie on his side. The doctor must clarify that breathing during gastroscopy must be done through the mouth.
- Despite the fact that the manipulation is practically painless, an anesthetic is sprayed into the person’s nasal passage. In some cases they can do without it.
- In order for the probe to pass gently through the nasal passage without harming the nasal mucosa, the nasal passage is smeared with a special product - gel.
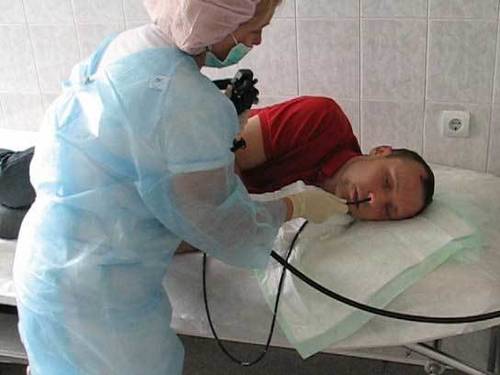
How to perform gastroscopy through the nose
The essence of this type of diagnosis is almost the same as fibrogastroduodenoscopy. The study is carried out to study the mucous membrane of the organ and detect any pathologies. The main device for this manipulation is a gastroscope, which is equipped with a camera of minimal size.
The doctor watches what is happening on the screen. In addition to identifying pathology, a qualified specialist can determine the severity of the disease and the cause of its occurrence, even if the disease is caused by bacteria.
The difference between nasal gastroscopy is the insertion of a probe. With this type of diagnosis, the device is inserted through the nasal passage, which passes through the esophagus and enters the stomach. Another difference is the diameter of the probe, which is only 5 mm. Thanks to the thin instrument, the patient feels more comfortable during the examination and does not experience a gag reflex.
What does gastroscopy show?
The doctor will make the first conclusions about the presence or absence of pathologies at the stage of conducting a visual examination of the walls of hollow internal organs. Medical research makes it possible to fairly accurately establish a number of diseases and anatomical features of the structure of the gastrointestinal tract.
Doing an FGDS or undergoing other endoscopic diagnostic methods is required to promptly detect:
- hidden bleeding;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- ulcerative processes;
- oncological neoplasms;
- phlebeurysm;
- polyposis and other diseases.
Based on the results of the examination, the patient receives recommendations and referrals to specialists for further treatment. Early diagnosis in many cases allows you to prescribe effective conservative therapy and avoid surgical intervention. You can undergo a gastroscopy procedure in Moscow at an affordable cost in our clinic.
Possible consequences
Complications may also develop during transnasal gastroscopy. The most common of them are collected in the following table:
| Complication | First aid at home |
| Nausea | Refrain from eating for 2-3 hours after the procedure, take a sitting position, open the window, breathe deeply and slowly |
| Discomfort in the abdomen | Follow a diet, drug therapy (antacids, proton pump inhibitors) |
| Feeling of dryness in the nose | Water inhalations, use of sea water-based spray |
| Nasal congestion | Use vasoconstrictor drops (based on xylometazoline, oxymetazoline) |
| Nose bleed | Bend over the washbasin so that the blood can flow out, and place a handkerchief soaked in cold water or ice on top of your nose. If this does not help stop the bleeding, use a narrow piece of bandage to tamponade the nasal passage (close it completely and tightly) |
| Sharp cutting pain in the abdomen | Lie on your back, avoid excessive physical activity, call an ambulance or a doctor |
| Heart rhythm disturbances (the occurrence of atrial fibrillation or flutter) | Avoid excessive physical activity, take antiarrhythmic drugs (amiodarone, propafenone, flecainide), seek medical help |
| Feeling of irritation in the throat | Use tablets with local anesthetics and/or anti-inflammatory components, rinse with herbs (calendula, chamomile) |
| The appearance of a cough and a sharp increase in body temperature (signs of stomach contents entering the bronchi and lungs) | Seek medical help (you must undergo a chest x-ray and a course of antibiotic therapy) |
What is the best way to insert the probe?
Transnasal endoscopy is increasingly used as an alternative to the traditional FGDS technique. Their main advantages and disadvantages are summarized in the following table:
| Advantages | Flaws | |
| Transnasal gastroscopy | Less severe discomfort for the patient; · voice contact with the patient is maintained; · more free breathing; · Possibility of carrying out in case of narrowing of the esophagus or difficulty swallowing | · less accessibility (the necessary probe is not available in all clinics); Possibility of injury to the nasal mucosa |
| FGDS with insertion of a probe through the mouth | · greater availability; · opportunities for minimally invasive interventions (for example, stopping bleeding) after diagnosis | · more pronounced dyspeptic symptoms (abdominal discomfort, nausea); · lack of voice contact with the patient; · higher risk of injury to the throat mucosa ; Possible breathing difficulties (psycho-emotional in nature) |