Vision defects can be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, surgery and laser correction. The last method of eliminating visual pathologies is the most effective. It provides excellent vision and is rarely accompanied by complications. Let's find out what the essence of this treatment method is, how the operation takes place and how long it lasts.
In this article
- When is laser vision correction prescribed?
- When does a person need to sign up for laser vision correction?
- Contraindications to laser vision correction
- How is laser vision restoration surgery performed?
- Are there complications after laser correction?
- How long does laser vision correction surgery take?
- Laser vision correction techniques
- Laser correction of vision pathologies: advantages
When is laser vision correction prescribed?
Laser vision correction today is a very popular technique for correcting refractive errors. Unlike surgery, laser treatment is absolutely painless and safe. With its help, it is possible to achieve almost one hundred percent vision. Laser correction allows many people to forget about glasses and contact lenses for many years or forever. This procedure is prescribed for the following visual pathologies:
- Myopia or myopia (from −1 diopter). With this disease, light rays are focused in front of the retina, as a result of which a person has difficulty seeing what is at a distance from him. The operation is performed when the reading is no higher than −1 diopter. Usually this degree of myopia is not corrected even with glasses and contact lenses.
- Farsightedness or hypermetropia (up to +6 diopters) is a refractive error caused by a decrease in the size of the eyeball. Light rays appear behind the mesh shell. The patient sees well into the distance, but objects close to the eyes appear blurry.
- Presbyopia (age-related farsightedness) is a pathology that occurs in people after 40 years of age. Almost every person who has reached the specified age encounters it. This happens due to the natural aging of the body and all its organs and structures, including the lens of the eye. Over the years, it becomes less elastic and it is difficult for it to change its shape when looking from distant objects to close ones and vice versa. The first symptom of presbyopia is difficulty viewing small objects (for example, the type in a book) at close range. If presbyopia develops against the background of myopia, a person will need several pairs of glasses - for distance and for near.
- Astigmatism (up to 4 diopters) is a visual pathology that results from curvature, change in the shape of the eyeball, cornea or lens. Light rays fall on several points of the retina and form a blurred image. A person has to constantly squint to see anything. Often, astigmatism is accompanied by myopia or hypermetropia.
Advantages of laparoscopy at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
- Innovative operating room equipment: infection-resistant seamless monolithic structures, 5 levels of sterility thanks to a sophisticated ventilation system.
- The use of surgical equipment from recognized global manufacturers of medical equipment - “Karl Storz”, “Covidien”, “Erbe”, etc.”
- The operation is carried out very carefully and is aimed at obtaining the maximum possible effectiveness of the intervention. Therefore, patients quickly recover and return to a full life.
The article was checked by obstetrician-gynecologist, prof. Kamoeva S.V. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
When does a person need to sign up for laser vision correction?
All of the above diseases can be corrected with glasses and contact lenses. However, if a person wants to get rid of the need to wear them, select them and systematically adjust their optical power, he agrees to laser surgery. In some cases, patients have to do this. This is due to a profession that does not allow you to wear contact lenses and glasses: we are talking about firefighters, military personnel. Laser vision correction as the only opportunity to play sports is becoming necessary for many athletes.
Wearing glasses during sports activities is dangerous and inconvenient, as they can break, fall off the face, fog up, and contact optics are not compatible, for example, with water sports. Laser correction is for such people a chance to work fully and do what they love.
Preparatory stage
Before undergoing surgery on the prostate gland, the patient must undergo consultations with a therapist and an anesthesiologist-resuscitator, and, if necessary, be examined by other specialized specialists. Before removing prostate cancer, the attending physician will give a detailed prescription, taking into account the chronic pathologies that the patient has. In this case, it is necessary to provide each patient with information about the medications they are taking, as well as medicinal herbs and dietary supplements.
The evening before the operation, the patient’s gastrointestinal tract should be cleansed using a special medication or enema. Then the area where the cuts (punctures) will be made is shaved. Night sleep is accompanied by taking sedatives. You must stop eating solid food 6 hours before surgery to remove the affected prostate, and liquids 2 hours before.
By the morning, the patient should have compression stockings ready, which should be put on without getting out of bed. Before cancer removal begins, the patient is given an antibiotic and a sedative by injection.
Contraindications to laser vision correction
Laser vision correction is a very safe and absolutely painless procedure. However, it is not available to everyone. There are a number of limitations that are revealed during a thorough examination of the patient. Contraindications can be relative or absolute. The first include:
- eye infectious diseases of the visual organs;
- dry eye syndrome in the initial and middle stages;

- severe lagophthalmos (failure to close the eyelids);
- viral keratitis. The laser can provoke the appearance of the herpes virus and cause an exacerbation of keratitis during the rehabilitation period;
- low sensitivity of the cornea. This is a symptom of neurotrophic diseases;
- glaucoma in one form or another;
- congenital cataract;
- mild corneal dystrophy;
- retinal detachment;
- autoimmune diseases during exacerbation;
- severe deterioration of vision over the past six months (it is necessary to find out the reason for the progression of the disease);

- young age. Until the age of 18, a person’s eyes are in the formative stage, so laser correction is inappropriate, since vision after 18 can improve without treatment;
- diabetes mellitus (depending on each specific case);
- pregnancy and lactation period.
Absolute contraindications
The above pathologies and conditions are temporary. Absolute forever exclude the possibility of prescribing the procedure:
- fourth degree glaucoma;
- severe corneal dystrophy;
- progressive cataract;

- last stage of diabetic retinopathy;
- keratoconus (thinning of the cornea and its taking on a cone-shaped shape);
- incurable blindness;
- chronic infectious diseases that greatly affect the functioning of the immune system (HIV);
- severe psychiatric pathologies.
Today, these contraindications are absolute, but the development of technology is expanding the possibilities for laser vision correction. Thus, some relative restrictions, for example, diabetes, were previously absolute.
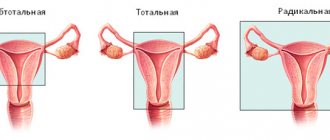
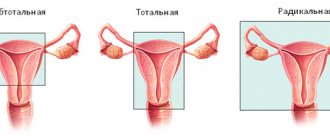
Indications for hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is a serious operation leading to complete loss of the organ being removed, which requires strict indications. The reasons for radical surgery may be:
- Adenomyosis is the growth of the endometrium into the muscular layer of the uterus, which can be accompanied by severe pain and bleeding.
- Malignant neoplasms of the endometrium. Hysterectomy is used as one of the options for solving the problem, but it is far from the only one. The selection of treatment is carried out individually based on the morphology of the tumor. Oncology today is the fastest growing industry, so they try to resort to radical operations as rarely as possible. However, there are situations when complete removal of the uterus cannot be done.
- Uterine fibroids. Multiple fibroids in combination with cervical pathology create a high risk of necrosis and hemorrhage.
- Endometriosis is the growth of the endometrium outside the uterus.
- Heavy bleeding
- Prolapse or prolapse of the uterus, which poses a threat of permanent infection.
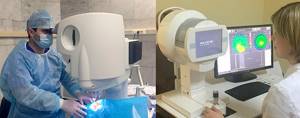
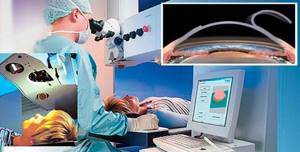
How is laser vision restoration surgery performed?
There are several laser techniques that differ from each other in a number of parameters. In general, the essence of any technique comes down to the following:
- the surgeon uses a scalpel or the laser itself to form a corneal flap from the epithelial layer of the cornea;
- then the doctor removes this corneal flap, as during PRK surgery (photorefractive keratectomy), or moves it to the side, as during LASIK (laser-assisted keratomileusis);
- the cornea is evaporated by a laser beam until it acquires the correct shape;
- the flap, if it was not removed, returns to its original place.
In some cases, the surgeon installs a bandage lens on the eye - a hydrogel bandage that promotes rapid healing of the cornea and prevents bacteria from entering the eye. The patient does not need to prepare thoroughly and for a long time for the operation. Two weeks before vision correction, he stops wearing optics. This is necessary for the cornea to take its natural shape. Two days before the procedure you should not drink alcohol. It negatively affects the blood vessels of the eye.
On the day of the procedure, the patient needs to wash his hair and face. Make-up, cream and make-up are not allowed. Fragments of cosmetics can get into the eye and cause inflammation. The doctor will give all the necessary instructions that must be strictly followed. Any operation is associated with risk. If you do not follow your ophthalmologist's instructions, the risk of complications increases. In addition, the doctor may cancel the procedure.
Execution technique
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. Already in the operating room, antibiotics are administered to prevent surgical infection. The technique used depends on the chosen access and the extent of resection.
In general, the operation can be divided into several stages - preparation of the uterus, intersection of ligaments, vascular hemostasis, organ cutting and closure of the resulting defect.
Laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy, which combines the advantages of several approaches, is of some interest. During the operation, three trocars are used, which are inserted through small incisions on the anterior abdominal wall. A uterine manipulator is inserted through the vagina, with the help of which the surgeon coordinates the position of the uterus in the pelvis, which facilitates the intervention, reduces the duration and prevents complications. Then the round ligaments are crossed on the right and left, and the bladder is separated.
With a subtotal hysterectomy, the surgeon cuts the fallopian tubes and the ovarian ligaments without affecting the cervix, while a total resection involves the removal of all parts of the organ. The next stage is hemostasis. The uterus is abundantly supplied with arteries and veins that feed it. The vessels are coagulated at the level of the internal os, where after hemostasis the body of the uterus will be cut off from its cervix. The resulting defect is closed using peritoneal sheets during subtotal hysterectomy. This process is called peritonization. Whereas with total resection, sutures are placed on the vaginal wall. The uterus is removed using a morcellator, a device for grinding tissue. The organ is removed through the abdominal cavity or through the posterior vaginal fornix. At the end of the operation, the obstetrician-gynecologist carefully checks the pelvic cavity and monitors hemostasis.
For women at risk for developing prolapse, after removal of the uterus, the posterior vaginal vault is strengthened. This manipulation is called culdoplasty.
Are there complications after laser correction?
The likelihood of complications is very low. After PRK they occur in 2-5% of cases, and after LASIK - in 1-5% of cases. In the first days and weeks after the procedure, side effects may appear that do not affect visual acuity:

- blurred vision at night. Most often, the complication occurs in patients with pupils that are wider than the average norm;
- infection. May develop due to the patient’s failure to comply with hygiene in the postoperative period;
- painful sensations. Lasts until the cornea heals;
- lacrimation in the first three days after correction;
- dry eye syndrome associated with drying out of the cornea after laser evaporation. It is treated with eye drops;
- photophobia in the first 48 hours;
- Drooping of the upper eyelid (ptosis) is a very rare complication that goes away without treatment after a few days.
There are a number of complications that lead to decreased vision:

- poor-quality cut of the flap;
- ingrowth of epithelium under the flap;
- overcorrection or undercorrection (the doctor removed more or less tissue than planned);
- keratitis is an inflammatory disease of the cornea that leads to vision impairment.
Almost all of these complications, except keratitis, require repeated vision correction. They appear within a few months. There are even more severe side effects that occur extremely rarely and lead to a severe decrease in visual function:
- displacement, loss, damage to the corneal flap in the first month after the procedure as a result of mechanical trauma;
- diffuse lamellar keratitis. The reasons for its occurrence after laser correction are not exactly known, but treatment of the disease should begin as early as possible, as it leads to clouding of the cornea and serious vision loss.
Complications after laser vision correction, as already noted, are rare. The entire procedure and its consequences are completely controlled by the doctor. The patient only needs to follow his instructions exactly.
Preoperative examination
Once a patient is suspected of having colon cancer and surgery is planned, there are several other important tests that need to be done before surgery.
This survey has two main objectives. First, by performing several studies, the stage of the tumor and its extent can be determined. Determining the stage of the tumor in the preoperative period will help you choose the right treatment tactics. Obviously, treatment for colon cancer that has metastasized to the liver will be very different from treatment for a small tumor that does not extend beyond the intestinal wall. Secondly, additional studies will help evaluate overall health and tolerability of surgery. Since surgery is extremely stressful for the body and can worsen existing problems with the lungs, heart, kidneys and other organs, special testing will help identify those patients who are at increased risk for complications in these organs during and after surgery.
Chest X-ray. The main purpose of this study is to evaluate the presence of cancer metastases to the lungs. This is a standard test that can determine with fairly high accuracy whether there are tumor nodes in the lungs. Chest X-rays can also look for signs of heart and lung disease. Therefore, this study is performed routinely in all patients before major operations.
Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and chest. Using this study, you can evaluate the condition of the liver and abdominal cavity for the presence of foci of tumor metastasis. If a chest CT scan is performed along with an abdominal examination, then a plain chest x-ray is not required.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pelvis. This study allows you to obtain clear images of the pelvic organs, assess the extent of spread of the rectal tumor, damage to the lymph nodes, and involvement of the anal canal muscles in the tumor. Unlike radiography and CT, MRI does not expose patients to ionizing radiation.
Positron emission tomography (PET). This type of examination uses a contrast agent containing a radioactive form of glucose, which helps determine the location in the human body where the tumor is located. Although this method can accurately identify “occult” tumor metastases that cannot be detected using CT or MRI, PET is currently not the method of choice for the preoperative evaluation of patients with colorectal cancer.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal cavity. Using this method, you can determine the condition of almost all abdominal organs and suspect the presence of tumor metastases in other organs, most often in the liver. You can also evaluate the condition of the kidneys, pancreas, and gallbladder. If it is not possible to perform a CT scan of the abdominal cavity, this study is the method of choice for assessing the presence or absence of distant metastases.
Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS). This study is performed using a special sensor, which is inserted into the rectum through the anal canal. This method allows you to identify the degree of tumor invasion of the rectal wall, assess the condition of nearby lymph nodes and rectal sphincters. If it is not possible to perform an MRI of the pelvic organs, it is the method of choice for assessing the spread of a rectal tumor.
Blood tests. A standard set of blood tests includes: a complete blood count, a biochemical blood test and a blood clotting test.
A complete blood count evaluates the total number of red blood cells (red blood cells), hemoglobin, leukocytes (white blood cells), and platelets. These cells play a crucial role in the functioning of the body. Red blood cells, with the help of the hemoglobin they contain, are an oxygen carrier and are responsible for supplying oxygen to all tissues and organs. In colorectal cancer, bleeding may occur from the tumor, so the number of red blood cells in such patients may be reduced. In severe cases, a blood transfusion may be required after surgery, and sometimes before surgery. Because platelets play an important role in normal blood clotting (blood clotting), counting these blood cells is a necessary test. If the patient has not had any episodes of abnormal bleeding in their lifetime, such as heavy nosebleeds or bleeding from the gums of teeth, there will likely be no abnormalities in this test. However, studying the platelet count is very important to determine the possible risks of bleeding during surgery.
As part of a biochemical blood test, plasma electrolytes, such as potassium and sodium ions, are assessed. Levels of these ions can be very low or high in patients taking medications for high blood pressure or other medications. Before surgery, it is necessary to restore the normal level of these ions in the blood plasma.
The blood clotting profile evaluates the effectiveness of clotting, which is important to know because blood clotting may be impaired in patients with hemophilia or other clotting factor disorders.
Also, mandatory tests that are performed on all patients before surgery are the determination of blood type and Rh factor, since these data may be required for blood transfusion, and the determination of markers of infectious diseases - viral hepatitis (B and C), syphilis, HIV infection. In the absence of all these tests, the operation is impossible.
Electrocardiography (ECG). This is a simple screening test that can determine heart function. It can help identify signs of atherosclerotic heart disease (narrowing of the arteries of the heart), which is a serious risk during surgery. ECG signs of a previous myocardial infarction or cardiac ischemia (lack of blood supply to certain areas of the heart due to insufficient blood flow) are signs of atherosclerotic damage to the coronary arteries (arteries of the heart). If you receive an abnormal ECG picture, you may need to perform additional tests, which will be prescribed by your doctor or cardiologist.
How long does laser vision correction surgery take?
15 minutes before the procedure, a local anesthetic is instilled into the patient’s eyes. During these 15 minutes, the doctor tells the patient about how the operation will proceed and what needs to be done. The laser action takes about 20-60 seconds depending on the damage. In total, the procedure lasts from 10 to 30 minutes on one eye.
The duration of the operation depends, among other things, on the technique. LASIK is done in 5-7 minutes. Usually, laser vision correction is performed on both organs of vision on the same day. PRK takes about 10-15 minutes on one eye.
After the operation, the person operated on remains in the clinic for 1-3 hours and is sent home. The doctor instructs him on what can and cannot be done after the correction, and sets the time for the next examination. The duration of the operation may depend not only on the degree of pathology that needs to be corrected, but also on the methods used by the doctor.
What to take with you to the hospital?
You should be prepared to stay in the clinic for several days. Be practical and use common sense. Do not take valuables, fashionable clothes or large amounts of money with you. Bring a small bag with the essentials. You will need leg compression stockings, which help reduce the risk of blood clots during long surgery. This can include elastic bandages or special compression stockings. Immediately after the operation, to protect the sutures of the anterior abdominal wall, you will need to constantly wear a bandage - this is a special wide elastic belt that helps support the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall at times when there is strong pressure on it - when you stand up, cough, sit down or bend over. You will only be in bed for one or two days after surgery, after which you will be encouraged to get up and walk around. You may want to wear a robe or comfortable pajamas and slippers with non-slip soles. After surgery, for some time, a small amount of wound discharge may be released from the sutures, which, even through a sterile dressing, can stain clothing. Therefore, prepare two sets of clothes and do not take expensive or favorite things, as they may get damaged in the hospital.
Don't forget toiletries such as a toothbrush, toothpaste, comb, deodorant, perfume or cologne, they will help you feel more “human” after surgery. During surgery, patients should not wear contact lenses, so do not wear them on the day of surgery; instead, it is better to wear glasses and leave contact lenses for the period after surgery. Before the operation, give valuables and wallet to your family members, leave a small amount of money to pay for television or telephone. You may also benefit from a good book, some magazines or a craft kit to help pass the time during your final days in the clinic when you feel better.
If you regularly take any medications (for example, for high blood pressure or diabetes), be sure to take them with you. It is very important that you continue to take these medications until the day of surgery, unless your doctor prescribes something else.
Laser vision correction techniques
There are two main types of laser vision correction surgery: PRK and LASIK. The second technique is constantly being improved, newer methods are appearing that are even safer and faster. LASIK modifications:
- Super LASIK (Super LASIK) is a procedure performed according to the individual characteristics of each individual patient. This operation gives very high results, since it uses a topographic examination of the cornea. Using a topographer, the eye is scanned and the resulting map is transferred to an excimer laser installation for correction. The operation is almost completely automated. It lasts 7-10 minutes on one eye. The laser takes 1-1.5 minutes to operate.
- Femto Lasik (FemtoLASIK). In this procedure, a corneal flap is created using a femtosecond laser. This allows surgery to be performed on very thin corneas. The doctor performs correction of one eye in about 10 minutes.
- Epi LASIK (Epi LASIK). This technique involves creating a flap along the natural interface between the layers of the cornea. The correction lasts as long as the standard LASIK procedure, but the recovery period after Epi LASIK is longer.
- Presby LASIK (PresbyLASIK) - laser correction of presbyopia. During the procedure, the surgeon uses a laser to create a shape of the cornea that is similar to the design of multifocal lenses. Thanks to this, after treatment the person sees well at close and long distances.
In terms of the time it takes the doctor to perform the operation, the techniques practically do not differ from each other. The doctor prescribes a particular procedure depending on the indications and financial capabilities of the patient.
Indications and contraindications
Excision of the prostate gland for cancer is carried out if the tumor is localized inside the prostate and on the tissue around it, but has not affected neighboring organs. This type of tumor is called locally advanced.
It is unacceptable to perform the operation in the following conditions:
- violation of the blood clotting process;
- severe insufficiency of the respiratory or cardiovascular system;
- spreading infectious process;
- purulent-inflammatory lesions in the area of the abdominal wall.
Also, surgery to remove the affected prostate gland for cancer is not recommended in the following situations:
- the predicted result of prostate removal is worse than that which will be obtained from conservative therapy (it is assumed that the patient’s life expectancy with tumor preservation will be at least 10 years);
- the likelihood of a complete cure for cancer is low (often this applies to situations where tumors extend beyond the prostate, touching the seminal vesicles and metastasizing into the lymphatic system).
There are also limitations for endoscopic surgery. Basically, these are cases when access to the tumor is difficult in some way:
- obesity;
- prostate size is too small or large (optimal volume is 20-80 ml);
- radiation therapy previously used in the fight against cancer (brachytherapy);
- previous operations on the prostate gland, for example, transurethral resection.
If a patient, having a prostate tumor, wants to have a child, then his genetic material (sperm) must be donated and frozen until the time of surgery, because after that, fertility will be lost.
Laser correction of vision pathologies: advantages
Now you know how the correction works, what the indications are for it, how long the operation lasts and whether there are complications. Despite the presence of the last point, this method of correcting refractive errors has a number of undeniable advantages:
- correction of any vision pathology;
- safety and painlessness;
- a small number of contraindications;
- short recovery period compared to surgery;
- speed of implementation;
- performed on an outpatient basis. You don’t have to stay in the hospital; it’s enough to take a day off or a few days off from work;
- stability of results.

The shape that the cornea takes on during laser vision correction lasts for life. In some cases, if there is no progressive myopia, the person will never need to wear glasses again.
Recovery period
Rehabilitation after laser intervention is considered the shortest compared to other operations for the treatment of the organ of vision. During the first day, you should not touch the operated eyes; it is important to strictly limit the possibility of foreign bodies entering to prevent inflammatory complications. The initial recovery period lasts about a week and involves more stringent restrictions on the usual lifestyle - careful behavior during hygiene procedures, minimizing the load with its gradual increase.
For the next three weeks, it is important to avoid exposure to bright light, temperature changes, the use of decorative cosmetics, and excessive physical activity. The general recovery period is approximately 1 month, after which the person can return to their normal routine.
Progress of the operation
Regardless of the chosen method of performing RP surgery for cancer, it is implemented according to the same scheme.
- Inserting a catheter into the bladder.
- Penetration through incisions (punctures) into the body of the prostate for its subsequent separation from surrounding tissues.
- Crossing the urethra.
- Cutting off the prostate along with the seminal vesicles.
- The urethra is sutured to the bladder on a catheter without removing the device.
- A drainage system is installed in the surgical area to ensure outflow.
Based on the results of preliminary studies carried out before removal of prostate cancer, lymph nodes in the pelvic area may be additionally removed or preserved. If it is necessary to preserve erectile function when removing the prostate, the surgeon collects the neurovascular bundles surrounding the cavernous nerve. A functioning nerve, even after cancer removal, allows you to have an active sex life.