Absolutely all people develop their own special circulatory system in the womb. Being aware of your blood type is, of course, important, but not enough. Of particular importance is the Rh factor, which is vital to know. After all, various unpredictable situations can happen in life when a doctor may need this information during a blood transfusion. When a child is born, he receives from his parents not only genes, but also a blood type, which is created by combining antigens.
How does the Rh factor of parents affect the child?
It is known that if a woman has a Rh factor of “-” and a man has a Rh factor of “+,” then a serological conflict arises.
How does the Rh factor affect the unborn child?
Serological conflict is a disorder primarily affecting women with the Rh- blood type who have children with an Rh+ male. This phenomenon causes hemolytic disease of the fetus or newborn. The essence of the problem lies in the mother's production of antibodies that destroy the fetus's red blood cells. This leads to anemia and many other serious complications.
It should be noted that a serological conflict rarely occurs during the first pregnancy, since the mother's immune system does not yet produce antibodies to the Rh factor.
Rh conflict during pregnancy appears no earlier than 16 weeks after conception. If antibodies are not detected by 20 weeks of pregnancy, they are unlikely to appear.
Rhesus - conflict resembles a mechanism of defense against viruses, when resistance is formed by the immune system to destroy the “enemy”. While in the case of pathogenic microorganisms the phenomenon has a beneficial effect, in the case of a serological conflict the effect is completely opposite, since it causes pathological conditions in the child.
As a result of inheritance, the fetus receives antigenic characteristics from both the mother and the father. During pregnancy, due to the penetration of fetal blood cells into the mother's blood circulation with the antigenic characteristics of the father (which the mother does not have), the mother begins to produce antibodies directed against these antigens.
The most famous and important example of serological conflict is the difference in Rh cell antigens in the fetus and mother. The formation of antibodies in a woman's circulation occurs when the fetus inherits the father's "D" (Rh+) antigen and the mother has the "d" (Rh–) antigen.
The resulting antibodies to the Rh factor enter the baby's circulation and cause damage to blood cells, leading to hemolytic disease.
The mildest form of hemolytic disease is the destruction of a child's blood cells. The child is born with anemia, which is usually accompanied by an enlarged spleen and liver, but this does not pose a threat to his life. Over time, the blood picture improves significantly and the child develops correctly. However, it should be emphasized that in some cases anemia is severe and requires special treatment.
Neonatal jaundice is another form of hemolytic disease. The baby looks quite healthy, but on the first day after birth, a jaundiced color of the skin begins to appear. There is a very rapid increase in bilirubin, which has a toxic effect on the child’s brain and liver.
The final and most serious form of hemolytic disease of the newborn is generalized fetal edema. As a result of the destruction of the baby's blood cells by the mother's antibodies (still at the stage of intrauterine life), blood circulation is disrupted and vascular permeability increases. What does it mean? Fluid from the blood vessels leaks into nearby tissues, causing internal swelling to form in important organs, such as the peritoneum or the pericardial sac that surrounds the heart. Unfortunately, edema is such a serious pathological condition that it usually leads to the death of the child in the womb or immediately after birth.
Peculiarities
According to scientists, based on a person’s blood parameters, one can determine his predispositions and characteristics. Blood group 1 is considered the most ancient. Its owners were hunters and warriors. Ancient people were hardy, and their bodies fought well against various diseases. Scientists tend to explain these facts by the absence of antigens on the surface of red blood cells and their content in plasma.
It’s interesting, but doctors still only find it among the indigenous people of America. This is explained by the fact that Indians do not welcome mixed marriages, which means that blood is inherited without impurities.
The most common health problems they have are:
- Pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Poor blood clotting.
- Allergies.
- Ulcer.
- Pathologies of the respiratory system.
- Joint diseases.
Rhesus conflict: why does this happen?
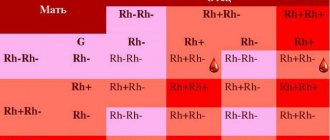
Each person has a blood type (O, A, B or AB), and also has a Rh factor (positive or negative), a protein that coats red blood cells. If the protein is on the cells, the person is Rh positive; if not, the person is Rh negative. In this case, the child may have the blood type and Rh factor of one of the parents or a combination of both.
The difference in blood type between a pregnant woman and her child causes Rh incompatibility. The condition occurs if a woman is Rh negative and her baby is Rh positive.
A serological conflict occurs when a small amount of the baby's blood enters the mother's bloodstream for the first time. This usually only occurs during childbirth, because the blood of the baby and mother do not mix during pregnancy due to the placental barrier between them; however, this can occur as a result of miscarriage, intrauterine surgery, bleeding, ectopic pregnancy, etc. When Rh (+) blood cells enter the mother's bloodstream, her body begins to produce antibodies (such as IgM and IgG) against the D-antigen present on the red blood cells of the fetus. These antibodies can cross the placenta and attack the baby's red blood cells, leading to the development of hemolytic anemia.
Once Rh antibodies have been formed, they remain forever in the woman’s body. As a result, all subsequent pregnancies with an Rh-positive child are at greater risk of developing hemolytic anemia and other pathologies.
How is blood of the first negative group obtained?

When a child is born, he receives from his parents not only genes, but also a blood type, which is created by combining antigens. So what is the chance that type 1 will be formed in the baby?
- Negative Rh factor during pregnancy consequences
Firstly, the appearance of the first blood group is 100% likely if it is present in two parents.
Secondly, there is a 50% chance if one parent has blood type two (three), and the other has blood type one.
Thirdly, there is a chance, about 25%, when both parents have the second blood type.
The formation of a negative Rh factor occurs in two cases:
- Provided that at least one parent is Rh negative.
- If both partners don’t have it, then most likely the child won’t have it either.
Important!
A child can be born with a negative Rh factor even if the parents are positive. But if at least one parent has the fourth blood type, a child with the first type will not be born.
What are the consequences for mother and child?
For a pregnant woman, the development of a serological conflict does not threaten her in any way and does not affect her health in any way, which cannot be said about a child. A serological conflict can cause severe hemolytic disease (erythroblastosis fetalis), brain damage, hypoxia, and damage the central nervous system, liver and kidneys. For this reason, such a pregnancy requires careful medical monitoring.
Does blood group compatibility affect conception and gender of a child?
When planning a child, parents need to know their own blood type and Rh factor. This is important information that can affect both the course of pregnancy and the health of the unborn child.
Is blood group and Rh factor compatibility so important? The blood type itself (if you do not take into account the Rh factor) does not in any way affect the process of conception, the course of pregnancy or the gender of the child. In the practice of any reproductive specialist, there is more than one case where parents with different blood groups became parents of a healthy child.
Ideally, the Rh factor of both parents should match, otherwise there is a high risk of developing a serological conflict, when the mother’s body rejects the fetus as a foreign body.
Daily regime
To avoid health problems, people of blood type 1 need to adhere to a lifestyle that suits them. Most often, women suffer from unorganized nutrition and work rhythm. Doctors prescribe:
- do not eat a lot at one time: it is better to divide the portion into 2 times;
- do not eat food at night;
- limit fatty foods in your diet;
- expose yourself to light physical activity at least twice a week.
In general, these rules apply to all people who strive to lead a healthy lifestyle. But for carriers of blood type 1, this is especially true, since they are prone to obesity.
The preferences and characteristics of these people:
- love meat products;
- have a strong digestive tract; but if the measure is not observed, poor nutrition combined with a predisposition to increased acidity of gastric juice can lead to gastrointestinal diseases;
- strong immunity, thanks to which such people get sick less;
- do not tolerate changes in diet, climate, or living conditions;
- require attention to their own menu.
What to do if there is a Rh conflict?
If the expectant mother and fetus are threatened by the consequences of Rh conflict, she should be under constant medical supervision.
In addition to regular blood tests to assess antibody levels (the more, the worse for the baby), a pregnant woman with a serological conflict should constantly undergo ultrasound examination for any signs of hemolytic disease of the fetus. Ultrasound examination allows you to measure blood flow in the artery of the child’s brain and assess the condition of the amniotic fluid and placenta. If anemia is suspected, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostic measures, most often cordocentesis. This is an accurate and commonly used test to obtain cord blood. Under ultrasound control, the umbilical vessels are dissected using a thin needle, after which about 0.5-1 ml of blood is taken. Such a blood test answers the question of what degree of anemia we are dealing with and what kind of blood the fetus has. This study allows you to plan further procedures.
Can incompatibility be cured?
Unfortunately, treatment of incompatibility is impossible, but, nevertheless, even with such a diagnosis there is a chance to carry and give birth to a healthy child.
The most important thing is the prevention of serological conflict and its early diagnosis. The expectant mother should be closely monitored by a doctor to undergo blood tests every few weeks, check antibody levels and check the intrauterine development of the fetus using ultrasound.
Most gynecologists, when identifying this phenomenon, prescribe the use of anti-D-immunoglobulin, which is administered by injection between 28 and 32 weeks of pregnancy, which increases the likelihood of avoiding the consequences of the conflict. A repeat dose is given 72 hours before the baby is born. After this time, the anti-D immunoglobulin vaccine will no longer serve its purpose. Administration of immunoglobulin during the first pregnancy often saves the life of the second child. The vaccine is also given after a miscarriage, abortion, amniocentesis, cesarean section, or bleeding during labor.
Types of blood
What blood groups does a person have, how many groups are there, and the very concept of them is under the jurisdiction of the International Society of Blood Transfusion. This organization has the most complete information on all these issues. For example, the types of blood here are divided into 33 classifications, and this is not the limit.

12 facts about blood: Tsuzmer A.M., Petrishina O.L. Biology. Man and his health. Textbook. 26th ed. - M.: Education, 2001. - 240 p.
The Karl Landsteiner blood groups remain the most widely used today. At the beginning of the twentieth century, a scientist experimented by mixing blood from different donors. In some cases it folded, in others it did not. Based on the data obtained, the following blood group designation was obtained: