What tumor markers show and how to get tested correctly
Analysis for tumor markers allows you to:
• find out whether the patient is at risk; • roughly identify the affected organ; • suspect a relapse of oncology;
When receiving test results for tumor markers, special attention should be paid to:
• for increased performance; • appears to have elevated tumor markers.
Changes in indicators indicate that there are deviations from the norm in the human body, including progressive cancer cells. The main advantage of the analysis is that tumor markers show the presence of cancer in the early stages, which is very important for the effectiveness of treatment.
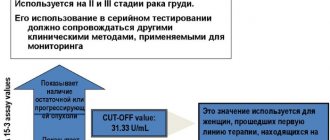
CA-125 decoding of indicators
To make a correct diagnosis, it is important to correctly interpret the results obtained. The assessment is carried out by an experienced doctor who knows the standard indicators and can accurately describe the processes occurring in the body. To ensure the reliability of the results obtained, it is necessary to record the values over time. That is, the analysis is carried out regularly at intervals of two, three, four weeks.
CA-125 values may be within the following limits:
- Up to 30 units/ml – risk factors are minimized, the patient is considered healthy.
- From 35 to 60 units/ml – changes have been detected in the ovaries, there are small cysts.
- Over 100 units/ml - an obvious cell mutation has been detected, a tumor has been identified in the ovaries.
Some points should be taken into account when the level of CA-125 may be overestimated, but without talking about the risk of developing pathology:
- a woman’s pregnancy in the first weeks, when she may not yet know about it;
- menstruation;
- inflammatory processes in the serous membranes, such as pleurisy, meningitis, peritonitis and pericarditis;
- growing metastases from cancer lesions.
A reduced level of Ca 125 in the blood during therapeutic treatment often indicates its positive effect. On the contrary, an increasing level of Ca 125 during therapy indicates that the tumor is unresponsive to the treatment. If therapy is completed and the Ca 125 level increases more and more, this indicates a relapse of the disease.
Rules for taking the analysis:
- blood is donated from a vein on an empty stomach, excluding food intake 8 hours before the procedure; — analysis is carried out until 11 a.m.; - three days before the test, stop drinking alcohol and junk food, reduce physical activity; - on the day of the analysis, smoking and taking medications are prohibited; - when taking a PSA test, abstain from sexual intercourse for seven days.
Tumor markers are found in the blood and urine of children, young, adults and elderly patients. In most cases, such an analysis shows the presence of cancer cells six months earlier than other diagnostic methods.
It is important that tumor markers show even the slightest changes and help solve the following problems:
1. Monitoring the effectiveness of therapy, which allows in some cases to change the treatment regimen or change medications. 2. Monitoring tumor recurrences, monitoring the appearance of new metastases. This will help you start re-treatment on time and not miss the disease. 3. The analysis will help decide which therapy methods should be used. 4. A tumor marker helps to assess the extent to which an organ is affected by cancer cells and the degree of progression, which helps to select a more adequate treatment regimen. 5. The analysis helps to assess how remission is progressing and make a prognosis for the patient’s life expectancy.
Patient preparation rules
Standard conditions:
In the morning before 11.00, on an empty stomach, after 8-12 hours of fasting.
Possible:
during the working day of the ML “DILA” branches.
A break of at least 6 hours after eating (fatty foods should be excluded). Attention:
if there is a diagnosis of a malignant disease, make a mark in the direction.
You can add this study to your cart on this page
Who needs analysis and when?
Screening tests should be carried out 1-2 times a year for those patients who have a genetic predisposition, benign neoplasms, suspicious papillomas and moles. Other people can be tested no more than once every two years, and also:
• after severe nervous strain; • when living in unfavorable environmental conditions; • under other circumstances that may cause cancer.
People are recommended to do screening tests more often:
• with a diagnosis; • with a treated malignant tumor; • upon initial detection of a neoplasm; • before and after surgery; • during a course of therapy.
Those who have recovered are recommended to check their tumor marker levels within 3 years after treatment is completed:
1. First year – every month. 2. Second year – once every two months. 3. Third year – once every three months. Subsequent years are analyzed every six months. Before screening, the patient must visit an oncologist, who will find out which markers need to be tested for.
REA

The CEA marker is secreted mainly by the digestive tract of the fetus. In adults, the substance is found in the blood in minimal quantities.
Normal: up to 6.3 ng/ml. A slight increase in CEA norms is determined in smokers. With high marker levels, there is a risk of neoplasms in the following organs:
- digestive tract; - mammary gland; - prostate; - liver; - lungs.
CEA analysis is recommended if:
• shortness of breath, causeless cough; • appearance of a visible tumor; • chronic fatigue; • unreasonable loss of strength; • sweating; • prolonged increase in body temperature; • weight loss; • appearance of new moles; • loss of appetite or complete reluctance to eat with attacks of nausea and vomiting; • disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract.
Fragments of cytokeratin 19 CYFRA 21-1
Detection of soluble fragments of cytokeratin 19 (CYFRA 21-1) in blood serum, used for diagnosis, assessment of prognosis and monitoring of treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), as well as some other malignant neoplasms.
What is this analysis used for?
- For diagnosis, assessment of prognosis and monitoring of treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, as well as some other malignant neoplasms.
When is the test scheduled?
For symptoms:
- lung cancer;
- colon cancer;
- if you suspect breast cancer;
- when planning treatment tactics for metastatic thyroid cancer.
Synonyms Russian
Soluble fragments of cytokeratin 19, tumor marker CYFRA 21-1.
English synonyms
C-terminus of cytokeratin 19, CK19 soluble fragments, CYFRA 21-1, CYFRA, Cyfra 21.1.
Research method
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Units
ng/ml (nanograms per milliliter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
Do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood.
General information about the study
Cytokeratin 19 is one of the proteins of the cytoskeleton of epithelial cells, belonging to intermediate filaments (thread-like structures). Under the influence of the enzyme caspase-3 as a result of apoptosis, cytokeratin 19 and its soluble components (C-terminus of cytokeratin 19, CYFRA 21-1, CYFRA) enter the blood, where they can be measured using laboratory methods. An increase in the concentration of CYFRA 21-1 in the blood serum is observed in some malignant neoplasms of epithelial origin: cancer of the lung, colon, breast and thyroid gland and some others.
Detection of CYFRA 21-1 in blood serum is most typical for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and especially one of its varieties - squamous cell lung cancer. The CYFRA 21-1 assay can be used to differentiate small cell lung cancer (SCLC) from NSCLC. CYFRA 21-1 concentrations are increased in 57-59% of patients with NSCLC and less frequently in SCLC. The CYFRA 21-1 study has the greatest sensitivity for squamous cell lung cancer. The detection of an additional tumor marker, squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA), also supports the diagnosis of NSCLC.
There is a direct relationship between CYFRA 21-1 levels and tumor size. In this regard, the CYFRA 21-1 test is used to assess the prognosis of NSCLC. A high concentration of CYFRA 21-1 before the start of chemotherapy is an unfavorable sign. A significant (more than 27%) decrease in the concentration of CYFRA 21-1 during treatment reflects a good response to therapy.
Along with the determination of tumor markers such as CA 19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), the CYFRA 21-1 study can be used to diagnose, assess prognosis and monitor treatment of colon cancer. In colon adenocarcinoma, the level of this tumor marker is increased, with the highest levels characteristic of large tumors. At the same time, patients with a slight increase in the concentration of CYFRA 21-1 respond better to therapy with cytostatic drugs.
The CYFRA 21-1 study may also be used to guide the treatment of metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer. A high concentration of this tumor marker is characteristic of aggressive thyroid cancer that is resistant to radioactive iodine therapy. Elevated levels of CYFRA 21-1 are most commonly observed in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Increased concentrations of CYFRA 21-1 can be detected in 65% of women with metastatic breast cancer. The sensitivity of this tumor marker for breast cancer is superior to that of CEA or CA 15-3. The combination of analyzes using CYFRA 21-1, CEA and CA 15-3 allows achieving a sensitivity of about 90%. A high level of CYFRA 21-1 before treatment is an unfavorable prognostic sign.
It must be remembered that the presence of CYFRA 21-1 does not always indicate an existing malignant neoplasm. An increase in the level of this tumor marker can also be observed in various benign conditions (chronic renal failure, pulmonary fibrosis, diseases of the hepatobiliary system), so the result of the study should be assessed taking into account additional data.
What is the research used for?
- For diagnosis, assessment of prognosis and monitoring of treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, colon adenocarcinoma and breast adenocarcinoma.
- To determine treatment tactics for metastatic thyroid cancer.
When is the study scheduled?
- For symptoms of lung cancer: cough, hemoptysis, shortness of breath, signs of tumor compression of surrounding structures (hoarseness, difficulty swallowing), paraneoplastic syndromes (hypercalcemia, Cushingoid, Lambert-Eaton syndrome).
- For symptoms of colon cancer: iron deficiency anemia, rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea.
- If breast cancer is suspected.
- When planning treatment tactics for metastatic thyroid cancer.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 0 - 3.3 ng/ml.
Reasons for increased levels of cytokeratin CYFRA 21-1:
- non-small cell lung cancer;
- colon adenocarcinoma;
- breast cancer metastases;
- metastatic adenocarcinoma of the thyroid gland;
- small cell lung cancer;
- interstitial lung diseases;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- tuberculosis;
- peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis;
- diabetic nephropathy;
- chronic renal failure;
- liver cirrhosis and other diseases of the hepatobiliary system;
- pleurisy;
- pericarditis.
What can influence the result?
- The degree of increase in CYFRA 21-1 concentrations depends on tumor size in non-small cell lung cancer and colon cancer.
- Due to chemotherapy, the test result may be negative.
Important Notes
- A positive test result does not always indicate the presence of a malignant neoplasm.
- The test is not used to screen for malignant neoplasms.
- The result of the analysis should be interpreted taking into account additional clinical, laboratory and instrumental data.
Also recommended
- CA 15-3
- CA 19-9
- Squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA)
- Neuron-specific enolase (NSE)
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
- Fecal occult blood test
- Laboratory markers of lung cancer
- Laboratory markers of breast cancer
- Laboratory markers of colon cancer
- General laboratory screening (oncological)
- Thyroid profile (oncological)
- Cytological examination of material obtained during endoscopy (FGDS, bronchoscopy, laryngoscopy, cystoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy)
- Cytological examination of punctates, scrapings and discharge from the mammary gland
- Histological examination of surgical material
Who orders the study?
Oncologist, pulmonologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, surgeon, general practitioner.
Literature
- Edelman MJ, Hodgson L, Rosenblatt PY, Christenson RH, Vokes EE, Wang X, Kratzke R. CYFRA 21-1 as an aprognostic and predictive marker in advanced non-small cell cancer in a prospective trial: CALGB150304. J Thorac Oncol.2012 Apr;7(4):649-54.
- Giovanella L, Treglia G, Verburg FA, Salvatori M, Ceriani L. Serum Cytokeratin 19 Fragments: ADe-differentiation Marker in Advanced Thyroid Cancer. Eur J Endocrinol.2012 Sep 18.
- Holdenrieder S, Stieber P, Liska V, Treska V, Topolcan O, Dreslerova J, Matejka VM, Finek J, Holubec L. Cytokeratin serum biomarkers in patients with colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2012 May;32(5):1971-6.
- Bidard FC, Hajage D, Bachelot T, Delaloge S, Brain E, Campone M, Cottu P, Beuzeboc P, Rolland E, Mathiot C, Pierga JY. Assessment of circulating tumor cells and serum markers for progression-free survival prediction in metastatic breast cancer: a prospective observational study. Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Feb 13;14(1):R29.
- Trapé J, Filella X, Alsina-Donadeu M, Juan-Pereira L, Bosch-Ferrer Á, Rigo-Bonnin R; Oncology Section of the Catalan Association of Clinical Laboratory Science. Increased plasma concentrations of tumor markers in the absence of neoplasia. Clin Chem Lab Med.2011 Oct;49(10):1605-20. Epub 2011 Sep 6.
Elevated tumor marker (PSA)
PSA is a protein secreted by the prostate gland. A tumor marker will help identify a prostate tumor, adenoma. The analysis is used to monitor therapy.
Normal: up to 4.1 ng/l. If the norm is exceeded, then tumor markers indicate the presence of malignant pathology in the prostate. Experts recommend that men over 50 years of age be tested for prostate-specific antigen annually. This will help identify prostate diseases in the early stages, which will simplify therapy and make it as effective as possible.
To properly prepare for the analysis, you need to:
• stop eating food 10 hours in advance; clean, still water is recommended, other drinks are excluded; • you need to stick to a diet for two days; • you should not play sports and put as much stress on yourself as possible for several days. • seven days not to be sexually active.
Decoding the results of analysis for tumor markers
The CYFRA 21-1 tumor marker can only be deciphered by the doctor of the laboratory in which the examination was carried out.
If the norm changes, parallel testing is carried out to obtain the most accurate result. The unit of measurement for the normal tumor marker CYFRA 21-1 is “ng/ml”. The reference value is taken as a basis, which is 2.08 ng/ml and is a sign of the absence of pathologies.
If the result showed an increase in the normal level, this indicates the possible development of lung cancer, bladder cancer, cervical cancer, and malignant disease of the esophagus.
In some cases, a significant increase in 21-1 protein indicates renal failure, chronic hepatitis, pulmonary fibrosis and other types of benign neoplasms.
The level of the tumor marker CYFRA 21-1 is always slightly increased in people who smoke, which is associated with the risk of developing a malignant process in the lungs in this category of people.
High levels of cytokeratin 19 fragment do not define cancer. One test is not enough to make a diagnosis
The decrease in protein occurs quite quickly in case of successful treatment and returns to normal. If the decrease is too slow or the reference values are not reached, this may mean that the tumor has not been completely removed or the treatment has not been completed.