Description
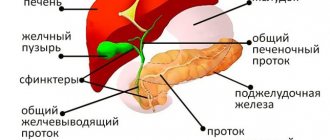
The largest internal organ in the human body is the liver.
Its weight varies from 1.2 to 1.5 kg. The location of the liver is the right corner of the abdominal cavity. The liver plays a vital role in maintaining a constant internal environment and ensuring protein synthesis. In addition, this organ synthesizes biologically active compounds, regulates fat, carbohydrate, and protein processes. The liver secretes bile, which breaks down fats. Another organ of the digestive system is the gallbladder. It acts as a kind of reservoir where bile accumulates. The liver constantly synthesizes bile, but it is not always necessary. Therefore, first of all, bile accumulates in the gallbladder, and then enters the duodenum.
When is an ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder necessary?
To diagnose various liver diseases that are accompanied by local and diffuse pathological changes, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound examination. This is a safe, painless and highly informative diagnostic method.
The main indications for the procedure are:
- Cyst, abscess.
- Benign liver tumor.
- Acute or chronic viral hepatitis.
- Non-viral hepatitis.
- Fatty hepatosis.
- Cirrhosis.
- Malignant formation in the liver.
- Vascular disease.
- The abdominal cavity is injured.
- Congenital developmental anomaly.
To diagnose pathology of the biliary system, the bile ducts and gallbladder are examined using an ultrasound machine. The disease can be functional or organic when the normal anatomy is changed.
A functional disease is a pathology when the regulation of the functioning of the sphincter and the tone of the biliary tract are disrupted. As a result, stagnation develops and the outflow of bile is disrupted. The main indications for gallstone ultrasound are:
- Presence of cholelithiasis.
- Acute cholecystitis.
- Inflammatory process in the bile ducts.
- Benign tumor in the biliary system.
- Malignant tumor in the biliary system.
- The presence of chronic cholecystitis.
- Stagnant processes in the organ.
- When the gallstone is bent.
- Biliary dyskinesia.
- Congenital anomaly of organ development. These include atresia and agenesis.
What is an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is located just below the liver, approximately at the level of the last rib, on the right side of the abdominal cavity. In normal condition, this organ cannot be palpated. Instrumental and laboratory methods (ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography) are used to diagnose it. The simplest and most accessible way to examine an organ is ultrasound.
Ultrasound, or echography, is a fast, informative and safe diagnostic method for the patient’s health. It is based on the ability of ultrasonic waves to penetrate the structures of our body and be reflected from them. The denser the tissue or organ is in the path of ultrasound, the more the characteristics of the reflected wave change. The ultrasound machine detects these changes, processes them and displays an image of the organ on the monitor.
Echography of the gallbladder allows you to determine the shape and location of the organ, its size, examine the ducts and identify stones and tumors. For ultrasound examination of the gallbladder, the transabdominal method is used, that is, scanning through the anterior wall of the abdomen. The procedure is carried out using ultrasound sensors with a frequency of 2.5-3.5 MHz. With this scanning mode, ultrasound waves can penetrate only to a depth of 23-25 cm. Therefore, for very obese people, ultrasound is a little informative method.
In addition to the standard procedure for ultrasound scanning of the gallbladder, echography is also prescribed to determine the function of the gallbladder (ultrasound with a choleretic breakfast). The essence of such an ultrasound is to monitor how much the organ contracts when eating food. During the study, the patient is asked to eat choleretic food (eggs or sour cream), then the release of bile is observed. Diagnosis of bladder function takes place in several stages. This ultrasound takes about an hour.
How to prepare for the procedure
To obtain the most accurate result of an ultrasound examination, the patient needs to adhere to simple rules for a short period of time. First, the stomach must be empty. If you eat food earlier than 12 hours before the appointed time of the ultrasound, the gallbladder may contract, causing accumulated bile to be released into the duodenum. And if the gallbladder is empty, the doctor is not able to carefully examine the organ. It is also not recommended to drink any liquid.
The main obstacle to a full-fledged ultrasound is excessive gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract. The presence of air does not allow ultrasound to pass through. For three days before the procedure, you must avoid foods that can cause gas formation. Such products include flour, sweets, spicy and salty foods, legumes, milk, white bread, and alcohol.
On the eve of the ultrasound examination, the patient is allowed to eat easily digestible food. This includes low-fat varieties of fish and meat, buckwheat or oatmeal, hard cheese, eggs, weak tea, and crackers. By following the above recommendations, the patient is guaranteed a successful and error-free diagnosis.
Ultrasound of gallbladder and biliary tract function
Ultrasound examination for biliary dyskinesia.
Impaired motor function of the gallbladder in children is one of the most long-standing problems of gastroenterology. A large number of techniques have been proposed, including duodenal intubation, X-ray, radioisotope, and ultrasound examination.
It should be noted that at present, X-ray studies - cholecystography and cholangiocholecystography in various modifications are not carried out in pediatric clinics, since they involve radiation exposure and due to their damaging effects on the body, and the lack of contrast agents, the industrial production of which has been discontinued.
Modern non-invasive methods for studying the condition of the biliary tract in children include ultrasound (ultrasound), which is harmless, physiological and has no contraindications.
Dynamic ultrasound examination of the function of the gallbladder to determine the presence of its motor disorders. Using ultrasound scanning on a monitor screen, the anatomical features of the gallbladder are studied, the size of the organ, its original volume, location, wall thickness and the nature of the contents are determined. Then the patient is offered to have breakfast and 15 - 20 minutes after taking the choleretic breakfast, the size of the bladder is measured - the greatest length and the greatest width. Similar measurements are carried out after another 15 - 20 minutes.
Unlike a classic ultrasound of the gallbladder, in this case the doctor takes readings not only from the supine position, but also from the side position.
According to numerous literary sources, according to ultrasound data, the contractile function of the gallbladder (CFG) is considered normal if the volume of the bladder by 30-40 minutes decreases by 1/2 from the original. If the volume of the bladder by 30-40 minutes has decreased by less than 50%, SFVP should be considered decreased, and if it decreases by more than 75%, it should be considered increased. Based on these indicators, corrective therapy should be prescribed.
The objective of the examination is to diagnose the nature of the motor-evacuation function of the gallbladder in children, allowing one to accurately differentiate between normal, hypomotor and hypermotor dyskinesia. Thus, this examination helps to establish the form of dyskinesia, reveals the presence of stones, allows you to determine the size of the organ and the thickness of its wall, the presence of peri-vesical infiltrate and the consistency of the contents of the gallbladder.
Accurate and timely diagnosis of the nature of violations of the motor-evacuation function of the gallbladder, taking into account the condition of the stomach and duodenum, allows us to develop adequate treatment tactics, prevent chronicization of the pathological process and associated associated disorders - irreversible changes in the liver, bile ducts, pancreas, and in in some cases, to avoid disability of the child.
Timely diagnosis and adequate treatment improve the quality of life, including psychological status, performance, etc.
The method is highly informative, objective and accurate, simple and accessible, it can be widely used in pediatric institutions of various types.
Indications:
- Biliary dyskinesia.
- Frequent pain in the right hypochondrium that is not relieved by medications.
- Impaired digestion of fats in the intestines - the presence of greasy stool.
- Recommended for patients who already have changes in blood tests, especially those related to liver enzymes (AST, ALT, total bilirubin, etc.).
- There were indications of abdominal trauma.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for diseases of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, etc. is required.
- Long-term use of medications for chronic pathologies.
- The presence of specific complaints (bitterness in the mouth, heaviness in the right hypochondrium).
- Abuse of spicy, fried, smoked foods, irregular nutrition.
- Having excess weight.
- Low-calorie diets.
- Suspicion of cholelithiasis.
- Study of the state of the biliary system in tumors.
There are no contraindications.
Preparation:
An ultrasound scan of the gallbladder should be performed strictly on an empty stomach, and you should also not drink water (it is recommended not to even brush your teeth so that you are not tempted to take a sip of water, even by accident).
During the consultation, discuss with your doctor the purpose of this study and whether it is possible to stop taking medications on the day of the ultrasound.
In order for an ultrasound to be informative, several conditions must be met:
- The last meal should be no later than 8 hours before the test, since normally, in the absence of food, bile accumulates in the bladder, and it increases slightly in size. If you drink even a little water, bile may be released and the bladder will shrink. This will also make diagnosis difficult.
- If you are planning to examine a child: it is recommended not to feed infants and children under 1 year of age 2.5 - 3 hours before the procedure (the best option is to sign up for an examination 20-25 minutes before feeding according to your schedule), children under 3 years of age - 4 hours, and for children under 8 years old – 6 hours. For a child over 8 years old, the same rules apply as for an adult.
- There should be no accumulation of gases in the intestines, as they interfere with visualization.
Deviation from the proposed recommendations is allowed for diseases that require regular use of medications and strict adherence to a diet (diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, hypertension, etc.). Regarding taking or stopping medications, consult your doctor!
As a choleretic breakfast in practice, to assess the contractile function of the gallbladder, use a sandwich with bread and 10 g of butter, or 200 ml of 10% cream, or two egg yolks, or 50 ml of vegetable oil, 200 g of yogurt with a fat content of at least 8% or milk chocolate (without additives).
What is the result of the study?
You receive a conclusion about the state of gallbladder function.
Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to determine:
- disturbances in gallbladder motility and determine the type of dyskinesia.
- the consistency of the contents and the condition of the tissues around the gallbladder - the treatment method will depend on this.
Contraindications
Ultrasound is a safe and accessible diagnostic method for various diseases. It does not require complex manipulations or special preparation. An ultrasound examination cannot negatively affect the patient’s health and well-being, and there will be no pain or discomfort during the procedure. Based on this, we can conclude that this method has no contraindications. Ultrasound is performed for both adults and children who have just been born, pregnant women, and seriously ill patients.
Who is prescribed an ultrasound of the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is examined in cases of liver dysfunction, as well as during ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs. In addition, the reasons for prescribing an ultrasound are:
- pain on the right side of the body,
- discomfort or heaviness in the liver area,
- icteric syndrome,
- injuries and damages,
- monitoring of the treatment performed,
- suspicion of stones or tumors formed.
The only contraindication for ultrasound is an open wound in the scanning area. Using an ultrasound sensor in such a situation can lead to infection in the wound.
Technique
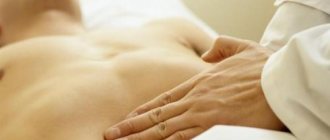
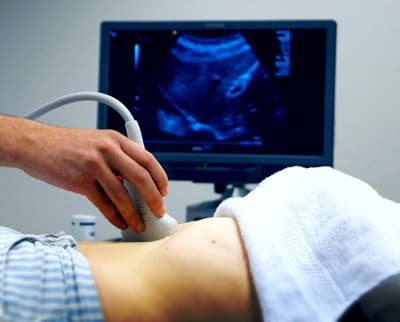
To begin the procedure, the patient is placed on a couch. You need to lie on your back. The doctor applies a special gel, which has good sound-conducting properties, to the abdomen, namely to the area of the right hypochondrium. Thanks to this gel, good contact between the sensor and the skin is ensured.
After this, the scanner is installed in the projection of the gallbladder or liver. First, the liver is examined, then the bile ducts and gallbladder. When the procedure is completed, the gel is removed from the patient's skin using a napkin.
How to decipher the results
Taking into account the physical basis of ultrasound examination, it is possible to decipher the results of ultrasound of the liver and gall bladder. How intensely ultrasound will be reflected depends on the organ’s density, structure, elasticity, and tissue resistance. In the presence of a pathological process in the organ being studied, the risk of changes in such indicators increases.
For example, if a person has a “porcelain” gallbladder, its walls will be saturated with calcium salts. Also, there will be an increase in tissue density.
When conducting an ultrasound examination of the liver, a lot of attention is paid to its size, shape, structure, and condition of the blood vessels. Normal liver size is 6-8 centimeters (left lobe), and 11-13 centimeters (right lobe). The edge of the organ is smooth, the structure should be uniform.
In addition, ultrasound examination determines the size of the gallbladder. It is considered normal if the gallbladder is from 6 to 10 cm long, 3 to 5 cm wide, the wall thickness is no more than 3 millimeters, the internal diameter of the lobar ducts is no more than three millimeters, and the common bile duct is from 6 to 8 millimeters.
What pathologies of the gallbladder can be detected on ultrasound?
Ultrasound can detect the following pathologies:
- cholecystitis (acute or chronic),
- organ dyskinesia,
- cholelithiasis (presence of stones),
- tumors
- congenital pathologies (absence or atypical position of the gallbladder, protrusion of its walls).
Cholecystitis is inflammation of an organ. Inflammation of the bladder can occur in chronic or acute form. The acute form is accompanied by intense pain in the right side, the chronic form is accompanied by nausea, heaviness, discomfort and dull pain in the area where the organ is located. Acute cholecystitis on an ultrasound image is determined by thickening of the walls and an increase in the size of the organ, while blood flow increases in the arteries of the bladder. In the chronic form, thickening and deformation of the walls, as well as a decrease in the size of the organ, are visualized.
Dyskinesia is a disorder of motor function in which there is insufficient contraction of the muscles of the organ. The ultrasound image shows an inflection of the neck of the organ and an increase in the tone of its muscles.
Cholelithiasis, or cholelithiasis, is the formation of calculi (stones) in the bile duct or its ducts. On echography, stones are displayed as areas with a dense echo structure, which can shift depending on the position of the body. Since stones reflect the signal well, an acoustic shadow from them can be seen on the echogram. In case of tumors, ultrasound shows formations on the walls of the organ that are larger than 2 cm in size. There is also a thickening of its walls and deformation of the contours.
The ultrasound procedure is sometimes not enough to make an accurate diagnosis, so patients are prescribed additional tests. Ultrasound allows you to quickly identify any abnormalities that have arisen, which makes it an indispensable method for diagnosing gallbladder diseases.