A fracture is a violation of the integrity of a bone. Depending on its nature, either two fragments or two or more fragments are formed. Of course, in this case the bone is temporarily unable to perform its functions - providing support and movement.
The body has a mechanism responsible for recovery: bone tissue can grow together. But in order for this to happen quickly and correctly, you need to correctly compare and fix the fragments.
The traumatologist is engaged in solving this problem.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a traumatologist-orthopedic specialist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Causes
For a bone to break, one of the following must be present:
- A strong blow from any object. In the place where it landed, the bone may break.
- A fall. Often it occurs from a height. But sometimes, in order to break something, it is enough to fall from your own height.
- Severe compression of the bone. For example, fragments of various collapsed massive structures.
- Excessive violent movement. For example, a helical fracture of the tibia often occurs when the leg turns, such as while skating.
How is the load reduced during x-rays?

All information about the radiation examinations performed, their number and radiation dose is entered into the medical record. If a critical dose accumulates over the course of a year, then prescribing another x-ray is highly undesirable.
To control the workload, the radiographer must have maximum information, so it is important to report all previous examinations and possible contraindications.
To protect the body, three main methods of protection are used:
- Protection by distance. The X-ray tube is placed in a special protective casing. It does not allow X-rays to pass through, which are directed at the patient through a special “window”. In addition, at the exit of the rays from the tube, an X-ray machine diaphragm is installed, with the help of which the irradiation field is increased or decreased.
- Time protection. The patient should be irradiated for as little time as possible (short shutter speeds when taking pictures), but not to the detriment of diagnostics. In this sense, images provide less radiation exposure than transillumination.
- Shielding protection. Parts of the body that are not to be photographed are covered with sheets and aprons-skirts made of leaded rubber. Particular attention is paid to the protection of the genital organs and thyroid gland, as they are the most sensitive to x-ray radiation.
Symptoms
All types of bone fractures have certain general symptoms:
- Pain. During the injury, it is strong and sharp, and after that it becomes dull. Increased pain with axial load.
- Deformation. If the fragments move relative to each other, then the leg or arm takes on an unnatural shape.
- Swelling. It begins to increase immediately after the injury.
- Subcutaneous hemorrhage - hematoma. Sharp bone fragments damage small blood vessels, and blood flows from them under the skin.
- Impaired function. If you ask the victim to move the injured leg or arm, this will not be possible due to severe pain, muscle strain and ligament damage.
The most dangerous are fractures of the skull, vertebrae, ribs, and pelvic bones. They can cause damage to internal organs and the nervous system. Multiple fractures are also dangerous; they can lead to shock.
Conditions for accurate diagnosis: where to get an x-ray
To obtain reliable information about the structures being studied, it is necessary to remain still. The doctor will tell you at what point to “freeze”. It takes a few seconds to take a photo. The lack of preparation required also simplifies the examination. However, it is important to remember that the study of the pelvic bones and hip joint can be complicated due to the accumulation of gases and/or feces in the intestines. In an emergency situation, such as in the case of injury, the doctor performs the test without thorough preparation.
There are many institutions in Moscow where you can get x-rays of your joints. When choosing a clinic, pay attention to the equipment. Modern X-ray machines have maximum resolution. This increases the diagnostic value of the procedure and eliminates the need to take a series of images.
Signs of a fracture
There are relative and absolute signs of a fracture. Among the relative ones are the following:
- Hematomas due to internal hemorrhage due to vascular injury. There is swelling and a large hematoma in the fracture area, touching which causes acute pain.
- Cutting and unbearable pain in the affected area. In rare cases, people lose consciousness from painful shock.
- Inability to move a limb (complete loss of motor function).
- Swelling of the soft tissues indicates a fracture or dislocation.
Absolute signs of a fracture:
- With open fractures, fragments are clearly visible, and with closed fractures, bone curvature and an unnatural position are detected (there is no rupture of soft tissues).
- The appearance of clicks and crunches, as well as excessive mobility in the affected area.
- Loss of motor function (a person cannot move a limb and experiences severe pain). Often the symptoms resemble a severe bruise or dislocation, so differential diagnosis is required.
How can x-rays be dangerous?
X-rays are electromagnetic waves in the range between ultraviolet and gamma radiation.
Accordingly, an X-ray machine is a source of ionizing radiation, a serious overdose of which leads to the destruction of the integrity of DNA and RNA chains. They are not always restored, because the ability of the DNA molecule to withstand the negative effects of ionizing radiation is limited. Therefore, the annual effective dose approved by SanPin is determined based on the rapid restoration of DNA and RNA molecules, as well as the amount of radiation at which the damage will be insignificant.
Possible consequences of abuse of the procedure:
- cancer of any system or organ;
- radiation sickness;
- mutations;
- genetic changes, etc.
The consequences can be unpleasant and even scary, but all this becomes possible only with huge overdoses of ionizing radiation, which is simply impossible to obtain in modern digital X-ray machines. Especially if you are undergoing examination on the recommendation of a doctor.
The average annual dose of natural radiation is 2.4 mSv per person, and 1 hour on an airplane costs 0.003 mSv.
Now, for a better understanding, let’s look at the radiation doses that a patient receives during radiography:
- chest x-ray - 0.03 mSv;
- mammography - 0.05 mSv;
- intraoral radiography - 0.02 mSv;
- cervical spine - 0.03 mSv;
- fluorography - 0.03 mSv;
- X-ray of the skull - 0.04 mSv;
- X-ray of the intestines - 0.02 mSv.
It is obvious that X-ray examinations using modern digital devices are completely safe
and do not provide significant radiation exposure to the human body. This increases the chances of detecting a serious disease at an early stage and prescribing the most effective treatment.
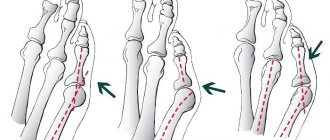
Types of fractures

Traumatic - appear due to bone damage, which leads to a change in shape, integrity and structure. Severe injuries can occur as a result of road accidents, falls, blows in contact martial arts or in professional sports.
Pathological – occur due to a violation of bone density. Often occur in diseases such as osteoporosis and osteomyelitis. Elderly people and children are at risk, as their bodies often lack calcium.
There is also a division into complete and incomplete fractures. With complete ones, displacement of the bones and penetration of fragments into soft tissues is observed, and with incomplete ones, partial destruction of bone tissue due to impacts (cracks form).
There are 6 types of fractures, which depend on the direction of bone damage:
- Helical - bones rotate.
- Splintered injuries are injuries that are accompanied by crushing of bones and penetration of fragments into soft tissues.
- Transverse - the fracture line is approximately perpendicular to the axis of the tubular bone.
- Wedge-shaped - bones are pressed into each other upon impact.
- Longitudinal - the fracture line is approximately parallel to the axis of the tubular bone.
- Oblique - the picture shows a right angle between the axis of the bone and the fracture line.
Etiology of radial fractures in a typical location.
In most cases, this is a fall supported by a straight arm; in the case of young patients, high-energy trauma, falls during sports, from bicycles or other rolling devices, and road traffic accidents are more common. In patients over 50 years of age, especially women, fractures of the distal radius are more often of a low-energy nature and occur due to osteoporosis. Low-energy fractures of the distal metaepiphysis of the radius are an indication for densitometry and subsequent consultation with an endocrinologist and significantly increase the risk of subsequent osteoporotic fractures.
First aid
If a fracture is suspected, the victim must be provided with complete rest, immobilization, and reliable fixation of the area of the suspected fracture. For example, a hand can be placed in a scarf, tied with bandages or scraps of clothing to the body, a thick board or a piece of reinforcement. The leg can be bandaged to the reinforcement, to the board, to the healthy leg.
If a spinal fracture is suspected, the person should be placed on a thick wooden board or any solid, flat surface. Depending on the severity of the injury, you must immediately either take the victim to the emergency room or call an ambulance. In the multidisciplinary CELT clinic, highly qualified traumatologists treat fractures.
Diagnosis of a radius fracture
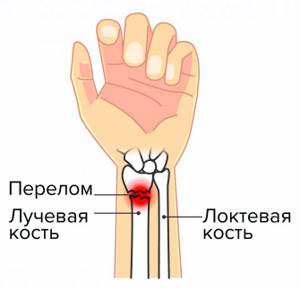
The first diagnosis occurs on the spot - upon injury. Usually, it's hard not to notice. A characteristic crunch and terrible pain arise immediately, the person himself realizes that he has broken his arm.
But for an accurate diagnosis, you need to consult a doctor. After all, wrist injuries are very different, and their treatment is also different.
Symptoms of a radial fracture:
- crunching sound caused by a fall or injury;
- immediately after a fracture of the radius, the hand does not bend, it is impossible to clench a fist and grasp an object;
- swelling after 30-120 minutes;
- if the joints are affected, then hemorrhage occurs and a hematoma is visible.
In some situations, the hand may only hurt during physical activity and show no other symptoms. This is dangerous because the bones may not heal properly. Then patients turn to Ladisten with a complaint: after a fracture of the radius, the arm is crooked.
X-ray confirms the diagnosis. It also determines the severity of the injury, the presence of displacements, fragments, and exact location. MRI and CT scans show whether joints and muscles are affected.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the fracture:
- For cracks and ordinary fractures without displacement, a plaster splint is applied. The duration of wearing it depends on which bone is damaged, on average - 2 - 4 weeks.
- For displaced fractures, closed reduction can be performed: under local or general anesthesia, the doctor compares the fragments and immediately applies a plaster splint.
- Sometimes skeletal traction can be performed: a knitting needle is passed through the bone fragment, from which a load is suspended.
- For complex displaced fractures, open reduction and osteosynthesis can be performed: the doctor makes an incision, compares the fragments and fastens them using various metal structures.
- Sometimes the application of an Ilizarov apparatus or similar devices is indicated: needles are inserted through a puncture of the skin and bone fragments, and then a metal apparatus is assembled on them, which ensures the correct configuration of the bone.
- Other types of osteosynthesis.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic employs experienced traumatologists and has modern equipment. Our specialists use the most advanced technologies to provide the most complete, effective and rapid treatment of various bone injuries. Our trauma department performs complex surgical interventions.
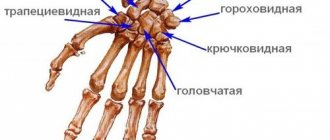
Metacarpal fractures
The long, thin metacarpal bones are often broken by a punch or direct trauma. Muscle traction and movements in the hand until the fracture is immobilized often lead to displacement of bone fragments. There are epiphyseal fractures, when the fracture line is localized in the area of the bone heads, and diaphyseal fractures, when the fracture line is located in the bone body.
First metacarpal fracture
The cause is a blow with a bent first finger, less often a direct blow to the first metacarpal bone.
Fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone . A typical injury for boxers and MMA fighters. A Bennett fracture is a separation of the base of the first metacarpal bone, which is held by ligaments, with simultaneous dislocation of most of it in the carpometacarpal joint. Rolando's fracture is a comminuted fracture-dislocation of the first metacarpal bone. Both injuries present with pain, deformation and swelling in the “anatomical snuffbox” area - the area under the base of the first finger - with increased pain when moving or trying to make a fist. Diagnosis is carried out taking into account complaints, trauma history, examination of the area of injury and x-ray of the hand. Bennett and Rolando fractures are treated surgically using osteosynthesis - restoring bone integrity by fixing fragments with metal knitting needles, pins or plates.
Fracture of the middle part of the first metacarpal bone . More often it occurs due to a direct blow to the bone. It manifests itself as pain, swelling and deformation in the area of the first metacarpal bone. The diagnosis is established taking into account the patient's complaints, information about the mechanism of injury, examination of the area of the first metacarpal bone and x-ray examination of the bones of the hand. Treatment is plaster immobilization for a period of 4-5 weeks; if the fragments are displaced, preliminary closed reposition is required. If conservative reduction is ineffective, an operation - pin osteosynthesis - is performed to compare the fragments.
An example of Dr. Valeev’s operation to restore after a fracture of the first metacarpal bone:
Before surgery:
After operation:
Fracture of II, III, IV, V metacarpal bones
The cause is a blow with a fist or a fall on fingers clenched into a fist. They can be single, but more often several metacarpal bones are broken, usually the fourth and fifth. It manifests itself as pain, swelling and deformation of the hand, and a hematoma often occurs. Diagnosed on the basis of complaints, history of injury, objective examination and X-ray results of the bones of the hand. To treat a non-displaced fracture, immobilization is performed for a period of 4-5 weeks. If fragments are displaced, closed reduction is indicated, and if it is ineffective, skeletal traction or pin osteosynthesis is indicated.
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| X-ray of bones and joints of the limbs | 2 200 |
| Gypsum bandage | 2 500 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Features of joint diagnostics
Foot.
The picture is taken in several projections. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor gets an accurate picture of all the bone and joint formations of the feet. The method allows you to detect injuries, degenerative changes, diagnose deformities, flat feet, heel spurs, synovitis, etc.
Ankle joint.
This joint experiences enormous loads and is therefore susceptible to disease. The most common pathologies are injuries, arthrosis, inflammatory diseases of the joint and joint capsule. To make a diagnosis, the image is taken in three projections.
Knee-joint.
A common reason for investigation is injuries: meniscus tear, dislocation, condyle fracture. Also, using an x-ray, a doctor can diagnose arthrosis, arthritis, hemorrhages in the joint and other diseases. This diagnosis makes it possible to examine both the joint and part of the fibula, tibia, and femur.
Elbow joint.
Injuries to this joint occur quite often, and they are especially common among athletes. Fractures of the shoulder, radius, processes of the ulna, and dislocations of the bones of the forearm may occur. Often there are cases of bursitis - inflammation of the synovial bursa.
Hip joint.
X-ray allows you to diagnose arthritis, necrosis of the femoral head, neck fracture, tumors, changes in tissue structure, coxarthrosis, etc. X-ray of joints is affordable. This is one of the few types of radiography that requires preparation: to increase the accuracy of the image and eliminate unnecessary shadows, you must have a bowel movement before the examination. This can be done naturally, using a laxative or an enema. When choosing a method, it is better to consult a doctor. Also, if possible, it is better to avoid foods that increase gas formation 2-3 days before the procedure. Such preparation measures will also be required when planning an x-ray of the pelvic bones.
Shoulder joint.
An X-ray may be required if glenohumeral periarthritis is suspected, as well as tumors, inflammatory and degenerative processes, fractures and dislocations. The image also allows you to visualize the collarbone and scapula.
Temporomandibular joint.
Radiography of this joint is often used in dental practice and maxillofacial surgery. It allows you to diagnose joint diseases and injuries. The data obtained is also used by the doctor to identify malocclusions. An image of the jaws allows one to draw conclusions about the volume and structure of bone tissue; this information is necessary when planning orthopedic treatment and dental implantation.
Treatment (conservative, surgical)
There are two treatment options:
Conservative. It is used for simple fractures, without fragments or displacements. The patient is given a plaster cast, and the arm heals under it on its own. Sometimes conservative treatment is used to restore fragments and displacement. The procedure may fail and the limb may become deformed over time. The entire treatment takes from 4 to 6 weeks plus a rehabilitation period.
Operational. It is carried out under anesthesia, cutting the arm and restoring the anatomical structure of the bone. The fragments are fixed with special titanium plates and screws. Transosseous osteosynthesis according to Ilizarov is also performed, and a special fixation apparatus is used to restore the arm. At the Laditsen Medical Center, the operation is performed using Dr. Veklich’s improved design, without the use of traumatic needles. After the operation, you do not need to wear a cast, just an elbow bandage. Recovery occurs faster, and the patient returns to his usual lifestyle.