- What is a chest x-ray?
- In what areas is chest radiography used?
- How should you prepare for research?
- What does the diagnostic equipment look like?
- What is the basis for the research?
- How is the research conducted?
- What should you expect during and after the procedure?
- Who reviews the X-ray results and where can they be obtained?
- What are the benefits and risks of having a chest x-ray?
- Limitations of chest x-ray
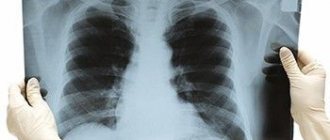
What is a chest x-ray?
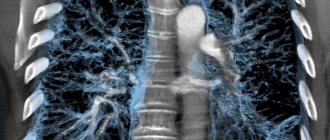
Among all x-ray examinations, chest x-ray is the most commonly used.
This procedure is used to take pictures of the lungs and airways, heart, blood vessels, and bones of the chest and spine. X-ray testing is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that helps doctors detect and treat various diseases. In this case, certain parts of the body are exposed to a small dose of ionizing radiation, which allows them to be photographed.
X-ray examination is the oldest imaging method and is most often used in diagnosis.
Up
When is it necessary to do a plain radiography of the spine?
X-ray of the spine: coccyx, cervical, thoracic, lumbosacral regions is used:
- For pain, impaired mobility, and a feeling of stiffness in the back.
- For inflammatory diseases such as arthritis or arthrosis.
- For curvature of the spine: scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis.
- For back injuries, vertebral displacements.
- For osteochondrosis and osteoporosis.
- Suspected tuberculosis, metastatic lesions and spinal tumors.
In what areas is chest radiography used?
Chest X-rays are used to evaluate the condition of the lungs, heart, and chest wall. As a rule, first of all, this study is prescribed to diagnose the following symptoms:
- Dyspnea
- Severe or long-lasting cough
- Chest pain
- Chest injury
- Fever
Chest X-ray is used to diagnose and monitor the following conditions:
- Pneumonia
- Heart failure and other heart diseases
- Emphysema
- Lungs' cancer
- Position of the central catheter or endotracheal tube
- Other diseases
Up
Result
After the examination, the specialist gives a transcript. There is no reason for concern if all structures are located correctly, are of normal size, there are no growths on them, and no foreign bodies are found in the chest cavity itself. The following signs are considered deviations:
- Changes in the size of blood vessels.
- The presence of infection or an increase in the size of organs.
- Fractures or deformations of the cavity bones.
X-rays can reveal the presence of swelling, tumors, and wounds. These signs are considered pathological.
How should you prepare for research?
In most cases, chest x-rays do not require any preparation.
During the examination, you will need to remove some or all of your clothing and wear a special hospital gown. In addition, you should remove all jewelry, glasses, dentures, and any metal or clothing that could interfere with the x-ray image.
Women should inform their doctor and radiologist of any possibility of pregnancy. As a rule, X-ray examinations are not performed during pregnancy to avoid exposure of the fetus to radiation. If x-rays are necessary, special precautions should be taken to protect the developing child.
Up
Information content
In some cases, the test result may be false negative. This may be due to projection layering from the shadow of the pathology focus onto the shadows of a healthy anatomical structure (for example, the mediastinum, diaphragm). Also, the lack of information is determined in some cases by the low intensity of the focus. This may be inflammation in the initial stage, especially against the background of agranulocytosis. A false negative conclusion may be a consequence of an inadequate projection of the study. This usually happens with a rib fracture or mediastinal pathology. If a chest x-ray turns out to be uninformative, a CT scan is prescribed, which is free of these shortcomings.
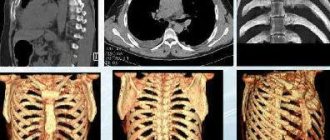
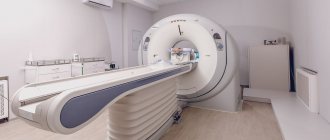
What does the diagnostic equipment look like?
Chest X-ray equipment typically includes a wall-mounted box-like machine that holds the X-ray film or matrix to take digital images, and an X-ray tube that is positioned 1.5 meters posteriorly.
In some cases, the X-ray tube is suspended above the patient's table. A drawer under the table contains X-ray film or a photographic plate for obtaining digital images.
A portable (portable) X-ray machine is a compact device that allows you to examine a patient directly in the intensive care unit or in a hospital bed. In this case, the X-ray tube is attached to a flexible arm, which is placed above the patient's body, while the photographic plate or X-ray film holder is placed behind the patient's body.
Up
Children under 12 years old undergo the procedure accompanied by adults.
You can take a chest X-ray not only in public medical institutions, but also in private ones. The German clinic has at its disposal digital equipment for x-ray diagnostics, including devices that allow examinations of even infants. Thanks to such equipment, the radiation dose is significantly reduced, and the quality of the resulting images increases. The clinic employs specialists with extensive experience and high qualifications. They will help you correctly interpret the X-ray image and make an accurate diagnosis.
What is the basis for the research?
X-rays are similar to other forms of radiation such as light or radio waves. It has the ability to pass through most objects, including the human body. When used for diagnostic purposes, an X-ray machine produces a small beam of radiation that passes through the body and creates an image on photographic film or a special matrix for obtaining digital images.
X-rays are absorbed differently by different organs and parts of the body. Dense structures, such as bones, absorb radiation strongly, while soft tissue structures (muscles, fatty tissue and internal organs) transmit X-rays to a greater extent. As a result, on an x-ray, bone tissue appears white, air and air spaces appear black, and soft formations appear various shades of gray.
In a chest x-ray, most of the radiation is absorbed by the ribs, which appear white or light gray on the x-ray. Lung tissue absorbs X-rays weakly, and therefore the X-ray image appears dark in color.
Until recently, X-ray images were stored as copies on film, similar to photographic negatives. Nowadays, most images are available as digital files that are stored electronically. Such images are readily available and are used for comparison with the results of subsequent examinations to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
Up
Digital X-ray
In recent years, digital (computer) radiography has replaced the usual traditional X-ray examination. New technologies make it possible to obtain high-resolution images much faster, which speeds up the process of making a final diagnosis. The image is received immediately in digital format. This eliminates the possibility of image distortion. In conventional radiography, the conclusion is made from one x-ray image on film. This storage medium must be developed, which takes a lot of time.
Compared to the conventional research method, the radiation exposure to the patient is reduced by 40%, which prevents the development of complications.
How is a chest x-ray performed?
As a rule, it is necessary to obtain two images of the chest organs: in frontal and lateral projection. At this time, the patient is positioned opposite the photographic plate holder.
A radiologist (a doctor who specializes in X-ray examinations) or a nurse presses the patient's shoulders and pelvis against the surface of the device where the photographic plate is located. For the second image, the patient is positioned sideways with his arms up.
If the patient is unable to stand, he is placed on a special table. In this case, you should remain as still as possible, and during the photo itself, hold your breath for a few seconds, which reduces the likelihood of blurring the image. When the X-ray machine is operating, the doctor moves towards the wall or leaves the treatment room into an adjacent room.
After the examination is completed, the radiologist asks the patient to wait until the images are analyzed, as additional series of images may be required.
A chest x-ray generally takes about 15 minutes. Additional imaging may be needed to evaluate changes in the chest after a few days, weeks, or months.
Up
What should you expect during and after the study?
A chest x-ray itself is painless.
The cool temperature in the treatment room and the cold surface of the photographic plate may cause some discomfort to the patient. The inconvenience is caused by the need to stand still, especially if you have arthritis, injuries to the chest wall and upper or lower extremities. The doctor or physician's assistant helps the patient find the most comfortable position, which also ensures high-quality images.
Up
X-ray
Allows you to explore the internal structures of the body. The photo is usually life-size. The method can be survey or targeted, when a specific area of our body is studied. As a result, even small pathological changes can be seen. It is used only to clarify or make a correct diagnosis. It is not used for prophylactic purposes.
Examination helps to detect tuberculosis, pleurisy, cancer, fractures and other conditions. The image will allow you to form a clear picture regarding the size and contours of organs, the presence of cavities and foci of inflammation.
Who reviews the X-ray results and where can they be obtained?
The images are analyzed by a radiologist: a doctor who specializes in performing x-ray examinations and interpreting their results. After examining the images, the radiologist draws up and signs a report, which is sent to the attending physician. In some cases, the report can be collected from the radiology department itself. Chest x-ray results can be obtained fairly quickly.
A follow-up examination is often required, the exact reason for which will be explained to the patient by the attending physician. In some cases, additional examination is carried out when doubtful results are obtained that require clarification during repeated images or the use of special imaging techniques. Dynamic observation allows timely identification of any pathological abnormalities that arise over time. In some situations, repeated examination allows us to talk about the effectiveness of treatment or stabilization of tissue condition over time.
Up
When can an x-ray be prescribed?
A traumatologist or surgeon may prescribe digital radiography of bones and joints (skull, bones of the shoulder, forearm, foot, hand, femur, hip bone, etc.; temporomandibular, elbow, knee, wrist, hip joints, etc. ):
- If the patient experiences pain, crunching, movement blocking, or joint instability.
- In case of injury or suspected injury: dislocation, fracture, sprain.
- In order to make or exclude a diagnosis: longitudinal flatfoot.
- For the diagnosis of growths and calcified areas, metastatic lesions and tumors.
Benefits and Risks of Chest X-ray
Advantages:
- After completion of the examination, no radiation remains in the patient’s body.
- When used for diagnostic purposes, X-rays do not cause any side effects.
- X-ray equipment is relatively inexpensive and is available in most emergency departments, diagnostic centers, clinics and other institutions, making X-rays convenient for both patients and physicians.
- Since X-ray examination is quick and easy, it is particularly useful for the diagnosis and treatment of emergency conditions.
Risks:
- With excessive exposure to X-ray radiation on the body, there is always an extremely small risk of developing malignant tumors. However, the benefits of accurate diagnosis significantly outweigh this risk.
- The effective dose of radiation for bone x-rays varies.
- A woman should always tell her doctor or radiologist about the possibility of pregnancy.
A few words about reducing the effects of radiation on the body
During an x-ray examination, the doctor takes special measures to minimize radiation exposure to the body while trying to obtain the best quality image. Experts from international radiological safety councils regularly review radiology standards and produce new technical recommendations for radiologists.
State-of-the-art X-ray machines allow you to control the dose of X-ray radiation and provide filtration, which minimizes beam scattering. In this case, the patient’s organs and systems that are not examined receive a minimal dose of radiation.
Up
Clinical picture
Various factors may indicate pathology. For example, these may be missing or additional elements: clearing or darkening, increasing or decreasing the transparency of the background of the lungs, depleting or enriching the pulmonary pattern, etc. Each additional shadow element has its own characteristics: quantity, configuration, size, displacement, contours, structure, intensity. They are not only clinically important, but also greatly contribute to differential diagnosis. In addition, these features also have practical value in the process of planning surgical intervention, biopsy, and bronchoscopy.
What are the limitations of chest x-ray?
Chest X-ray is an extremely useful diagnostic tool but has some limitations.
Since routine x-ray examination does not reveal some conditions of internal organs, it does not always allow an accurate diagnosis. For example, chest x-rays do not always diagnose malignant tumors of small diameter. In addition, a blood clot in the lungs, which appears with pulmonary thromboembolism, cannot be seen on an x-ray.
Therefore, to clarify the results of chest x-ray, in some cases it is necessary to use other imaging methods.
Up
Fluorography and radiography: what is the difference?
Older patients often ask how fluorography differs from a chest x-ray. Today, fluorography is an outdated diagnostic method that allows you to obtain images from an X-ray machine onto film. Unlike radiography, it:
- Less accurate - the clarity of the resulting images is several times worse than with x-rays;
- Provides a higher dose of radiation: on average 3–5 times higher than with x-rays;
- Does not allow changes to be recorded as accurately;
- It will cost much less;
- Allows you to see the general condition of the lungs and heart muscle.