Hysteroscopy: types, limitations, indications
Hysteroscopy in gynecology is one of the methods of endoscopic examination.
It allows the doctor, using a unique instrument, to penetrate the uterine cavity and obtain information about the condition of the organ and fallopian tubes.
Applicable in three directions:
- Diagnostics;
- Treatment;
- Biopsy.
More details below.
Kinds
Types of manipulation based on the goals of the doctor and the patient. They are:
- Diagnostic;
- Surgical;
- Test.
The main thing in diagnostic manipulation is examination of the internal system of the organ using special optics. Local anesthesia is often used here. Recovery is quick and does not require hospitalization.
In surgical manipulation, the main task is therapeutic. In fact, although this is a low-traumatic operation, it is still an operation, and therefore it is carried out in a hospital setting under anesthesia.
The control manipulation is designed to determine the condition of the organ after treatment.
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure during which a small telescopic instrument with light (hysteroscope) is used, which transmits an image of the cervical canal and uterine cavity, magnified 20 times, onto a monitor screen. Hysteroscopy allows you to visually examine the uterus and detect the cause of the disease. The procedure is performed under short-term intravenous anesthesia. The anesthesiologist examines the patient before administering anesthesia and selects the optimal anesthetic for the patient.
There are two types of hysteroscopy.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed to examine the uterus and determine whether there is any pathology in the uterus. Diagnostic hysteroscopy allows you to identify the presence of septa, adhesions, polyps, fibroids in the uterine cavity, and thus detect the cause of dysfunctional uterine bleeding, infertility, miscarriage, etc.
Operative hysteroscopy is performed to correct identified pathologies. During surgical hysteroscopy, additional instruments are inserted through the hysteroscope, allowing the doctor to perform various therapeutic manipulations. During surgical hysteroscopy, polyps can be removed, synechiae (adhesions) removed, and septums can be dissected. Endoscopic methods can also remove uterine fibroids. Diagnostic and operative hysteroscopy may be performed simultaneously or as two separate procedures, depending on the condition of the individual patient.
The timing of hysteroscopy depends on the indications for it. If organic pathology was suspected (uterine fibroids, endometriosis, etc.) in women of reproductive age, studies were carried out on the seventh, eighth, ninth day of the menstrual cycle. For the purpose of functional assessment of the endometrium, hysteroscopy was performed in the second phase of the cycle.
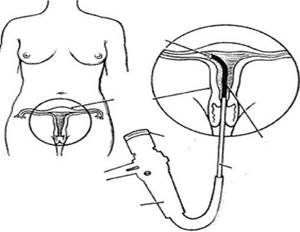
Indications for hysteroscopy:
- Infertility caused by adhesions (scar connective tissue) at the entrance to the fallopian tubes, or other reasons;
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding;
- Painful menstruation;
- Bleeding after the end of menstruation;
- Irregular or unusually light periods;
- Pathologies of the uterine cavity, including the uterine septum (a band of scar connective tissue in the uterus);
- Habitual miscarriage;
- Pain in the pelvic area;
- Removal of small submucous fibroids or polyps.
Hospitalization for hysteroscopy
If an endometrial biopsy is performed during hysteroscopy, the results of histological examination are usually ready within two weeks. After receiving the results of the histological examination, the patient must visit a doctor to receive recommendations.
Postoperative period after hysteroscopy
The patient usually experiences mild cramping and light spotting for one to two days after the hysteroscopy. Your doctor may prescribe a pain reliever to relieve any discomfort. Most patients can return to work the day after surgery.
To minimize the risk of infection or inflammation, you should avoid using tampons and douching for one to two days. After diagnostic hysteroscopy, patients are also advised to abstain from sexual intercourse for one to two days. After surgical hysteroscopy, the period of abstinence ranges from one to three weeks, depending on the extent of the intervention performed.
Hysteroscopy is performed after a clinical examination, including:
- General blood analysis.
- General urine analysis.
- Microscopic examination of genital tract discharge.
- Biochemical blood test (total protein, urea, bilirubin, glucose)
- Coagulogram.
- Blood test for CSR (RW).
- Blood for AIDS (HIV).
- Blood for hepatitis B, C.
- ECG
- Examination by a therapist
- Blood type and Rh factor.
- FG
The above studies are carried out on an outpatient basis before the patient is admitted to the hospital.
Preparation
There are risks in any procedure. To avoid them in ours, you need to:
- Take a blood and urine test prescribed by your doctor, including to determine your blood type and Rh factor;
- Take a smear test;
- Analysis for sexually transmitted infections;
- Pass a hematological test;
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- Tests for infectious diseases.
The hysteroscopy procedure itself should be done taking into account the menstrual cycle, preferably in the coming days after menstruation.
A few more tips you should know:
- Two days before the manipulation, we forget about sexual intimacy;
- Six hours before it, we stop eating;
- We take a shower;
- Before the procedure itself, we empty the bladder.
Yes, we forget to remove all jewelry from the body, get rid of contact lenses and dentures.
Indications for hysteroscopy
Indications for hysteroscopy are:
- infertility;
- miscarriage;
- menstrual irregularities;
- postmenopausal bleeding;
- suspicion of endometriosis based on ultrasound or hysterosalpingography results;
- suspicion of formations in the uterus;
- suspicion of malformations of the uterus (intrauterine septum);
- pain in the pelvic area;
- problems with the intrauterine device.
The diagnosis made by hysteroscopy is confirmed in more than 90% of cases. In almost half of the cases, hysteroscopy, carried out for the purpose of diagnosing some diseases, makes it possible to detect other, previously undetected pathologies, the signs of which were not recognized against the background of the symptoms of the underlying disease.
Carrying out
About an hour before the manipulation, the patient is given special medications, mainly to reduce anxiety.
She is then placed in a gynecological chair and anesthesia is administered. Its choice is discussed before the manipulation begins.
Then the procedure itself begins. Using unique instruments, the patient's cervical canal is dilated and either gas or sterile liquid is injected into it. This will allow the doctor to better see the organ cavity a little later.
At the second stage of the procedure, a hysteroscope with optics is inserted into the uterus. Through it, the doctor will see the cavity in an enlarged form.
If it is necessary to perform surgical manipulations, the hysteroscope has a channel necessary for introducing additional instruments.
After achieving the objectives of the manipulation, the instrument, gas or liquid is removed.
How long does the recovery period last?
It depends on the complexity of the operation and the procedures that were performed. If the patient has had an office hysteroscopy (examination using a thin endoscope), recovery will only take a few hours. Usually on the same day the woman is allowed to go home, and after two days she is allowed to lead her usual lifestyle.
A patient who has undergone hysteroscopy, during which extensive intervention was not required and the endometrium was not severely injured (removal of a small polyp, targeted biopsy), can leave the clinic in 1-3 days. It is necessary to stay under the supervision of doctors for at least a day to make sure that there are no complications after the manipulation. After an operation to remove large myomatous nodes or large-scale trauma to the endometrium, it is better to stay in the clinic for a week.
However, even after discharge, you need to monitor the condition of the body and help it recover. Experts advise for at least a month:
- take medications prescribed by a doctor;
- limit physical activity;
- walk more in the fresh air at a leisurely pace;
- do therapeutic exercises;
- eat only healthy foods (avoid fast food, fried, too spicy, salty foods, alcohol);
- do not swim in pools and ponds;
- do not neglect the rules of intimate hygiene.
Your doctor may also advise you to stop having sex. Deadlines are set individually. If you need hysteroscopy in Krasnodar, contact us.
After hysteroscopy, the polyp grew again
What to do if the polyp grows again after surgery? Polyps often appear due to hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body. Removing a polyp does not guarantee the cessation of their formation elsewhere in the uterine mucosa. Endometrial polyps are a disease characterized by the proliferation of the basal (inner) layer of the endometrium. The most common cause of the development of polyps is an excess of estrogen, a lack of progesterone; abortion, premature termination of pregnancy, and childbirth with incomplete delivery of the placenta can also cause the growth of polyps. It is possible to develop polyps after stress, with diseases: diabetes, thyroid disease, hypertension. Chronic inflammatory processes in the female genital area and a sharp drop in immunity play a negative role. If the polyp has grown again, you should be tested for sex hormone levels. When hormone levels are disrupted, polyps will reappear even after surgery. In this case, treatment with OCs (oral contraceptives) is prescribed, which will affect hormonal levels and stop the development of polyps. If hysteroscopy was used to remove a polyp, bloody discharge will persist for several days. You should monitor the condition of the discharge - it should not be abundant, change color, or have an unpleasant odor. If such symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately.
Pain after hysteroscopy
The pain occurs most often in the lower back and abdomen. Hysteroscopy is performed using a device whose diameter is no more than 3 mm. The insertion of the hysteroscope probe is almost painless, but after the manipulation, slight nagging pain will appear. If it hurts after hysteroscopy, which was performed for diagnostic purposes, then such pain goes away a few hours after the manipulation. Minor discomfort may be felt for several days. If the pain does not go away within several days, if severe pain occurs, this is a reason to consult a doctor for help. To avoid pain after this procedure, you should refrain from sexual intercourse for several days, do not lift anything heavy, do not take a hot shower, bath, or go to the sauna or bathhouse.
When is hysteroscopy used?
The manipulation is considered minimally invasive, that is, it does not violate the integrity of the tissues. Nevertheless, the uterine cavity is fundamentally closed and therefore each implantation, especially with a device, must be justified.
Hysteroscopy is not used for preventive examinations of the cavity, as is done with endoscopy of the gastrointestinal tract; manipulation is carried out if a pathological process is suspected, as shown by ultrasound and other types of tests.
The undeniable advantage of hysteroscopy is the possibility of carrying out a one-stage diagnostic and treatment measure: take a biopsy and remove the pathological focus - polyp, internal fibroid node, focus of hyperplasia, connective tissue adhesions - synechiae. This type of examination is called therapeutic. In case of tubal infertility, with endoscopy, the endometrial cavity restores the patency of the tubes along almost the entire length.
Diagnosis of pathology of the development of internal genital organs, elucidation of the causes of postmenopausal bleeding and infertility, even assessment of the effectiveness of hormonal therapy for uterine pathology is also included in the range of indications.
Review of the treatment of uterine fibroids and neurogenic bladder
The patient was admitted to the clinic with symptoms of uterine fibroids and multiple intramural nodes. Excision of the uterus and appendages was performed, as well as fixation of the vaginal stump in order to exclude a neurogenic bladder and prolapse of the vaginal walls. The surgical intervention and postoperative period passed without complications. The patient thanks her doctor for the treatment Read full review
Dysuric phenomena. Review of treatment
The patient complained of vaginal discomfort and dysuria. Surgical treatment was performed to restore the pelvic floor muscles, as well as levatoroplasty and strengthening of the bladder. The postoperative period proceeded smoothly. Today, the patient's problem has been solved. Read full review
Review of treatment 09.25.2020
For the past ten years, the patient had been experiencing problems with frequent urination. The examination showed the presence of residual urine. A surgical operation was performed. Today, urination is normalized. Read full review
Feedback on the treatment of vulvar kraurosis
The patient applied to the international clinic Medica24 for treatment of vulvar kraurosis. This disease is characterized by dystrophic, atrophic and sclerotic changes in the skin of the external genitalia, accompanied by itching and dryness, and narrowing of the vaginal opening. This condition is precancerous. In 20–50% of cases, kraurosis develops into vulvar cancer. The examination revealed insufficiency of the pelvic muscles. On the first… Read full review
Feedback on the treatment of vulvar dysplasia of the third degree
The patient was diagnosed with third-degree vulvar dysplasia. She was prescribed treatment in the form of radioablation and photodynamic therapy. Within two days a positive effect was achieved. The patient is satisfied with the results achieved and expresses gratitude to her attending physician Alimardonov Murad Bekmurotovich. Read full review
Review of surgery
The patient was admitted to the Medica24 international clinic in serious condition. A surgical operation was performed that saved her life. There is a course of rehabilitation and continued treatment ahead. Read full review
Even the “hopeless” have a chance
Many patients come to us after they were considered “hopeless” in other clinics. Such a case is before us. The patient was abandoned, saying that she would not survive the course of chemotherapy. She began to look for a way out and found it at the international clinic Medica24. Here her body was prepared and chemotherapy courses were successfully administered. After the tumor shrank, she underwent a complex operation. The patient has further developments ahead... Read full review
How to prepare for the examination?
Hysteroscopy is an intervention for which you need to prepare: take tests to rule out inflammation and infections; do an ECG and chest x-ray; Get your therapist's permission.
On the eve of the manipulation, the intestines are cleansed and the morning meal is abandoned. Hysteroscopy for emergency indications excludes the full range of tests, but the most important things are done: ECG, blood tests, ultrasound and x-rays.