X-ray (cystography) of the bladder is an X-ray, non-invasive diagnosis that is carried out to identify pathological changes in the genitourinary system. The procedure is prescribed for both adults and children. An X-ray examination is done using a contrast agent, which allows one to study the integrity, condition and structure of the organ being examined. As a result of the study, it is possible to identify serious diseases, make an accurate diagnosis and begin immediate treatment.
What will urography show?
X-ray examination of the kidneys and urinary tract or urography can detect the following pathologies and conditions:
- Urolithiasis is a disorder in endocrine metabolic processes that leads to the formation of stones of different sizes and composition.
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process in the kidneys.
- Polycystic disease is the formation of numerous cysts that replace kidney tissue.
- Dystrophy, nephroptosis - pathological mobility or location of the organ.
- Hydronephrosis (dropsy) of the kidneys is a violation of the outflow of urine from the kidneys due to the expansion of the renal pelvis and calyces.
- Kidney tuberculosis is an infectious and inflammatory process in the kidneys due to infection with tuberculosis pathogens.
- The presence of foreign bodies in the urinary system.
- Benign and malignant tumors.
From the photographs you can determine:
- Features of organs - structure, location, shape, size, integrity and homogeneity of structure.
- Features of the work - at what speed the substance is filtered and excreted, how the kidney is filled, what is the diameter and patency of the urinary tract.
- Features of tumors and foreign particles - the presence of calcifications, salt crystals and other deposits, the size of tumors, the presence of metastases and other details.
In addition to the kidneys, the images show neighboring organs - the gallbladder, pelvic bones, and lumbosacral spine.
Indications and contraindications
Indications include: ruptures and reflux, congenital pathologies, complications after infectious and inflammatory diseases, enuresis, sand and stones, tuberculosis of the internal organs of the genitourinary system, suspected tumor, trauma to internal organs, diseases of the bladder and kidneys.
Although the diagnosis is considered informative and reliable, it has contraindications. Cystography should not be performed on pregnant women; patients who have an inflammatory process in the bladder or ureters (the catheter tube can injure the urethra, which leads to aggravation of the inflammatory process); people who pass urine containing blood clots (clots can distort X-ray images and cause incorrect test results).
Types of urography
Depending on the method of implementation, there are:
- Plain radiography of the kidneys is an image that is used as a primary study to assess the anatomical features of the kidneys and other pelvic organs, identify tumors, inflammation, and stone deposits. The picture is taken in a direct projection without the introduction of a contrast agent.
- Excretory urography - x-ray with contrast (quickly excreted marking substances) to study the functionality of the kidneys, patency and integrity of the urinary tract. Pictures are taken in at least two projections, and the method has a greater degree of accuracy compared to survey x-rays.
- Infusion urography is an x-ray in which a contrast agent is injected intravenously.
- Direct pyelography - x-ray with contrast administered from the lower genitourinary tract through a catheter.
Each type of urography has different characteristics and has its own purposes and indications for use.
How is cystography performed?
The patient is placed on an X-ray table and a survey of the urinary system is taken.
The study must be carried out under the supervision of a urologist. He injects about 200-300 ml of water-soluble contrast material through a catheter into the bladder using a syringe or infusion set. After this, the radiologist takes a series of x-rays in direct, left and right oblique projections. The specialist evaluates the size, contours and uniformity of the bladder.
What does the radiologist pay attention to:
- the presence of kidney stones;
- condition of the spine and contours of the lumbar muscles;
- distribution of gas in the intestines.
If the procedure involves the use of a catheter (with ascending cystography or double contrast), then sedatives and analgesics are used.
To examine the bladder in as much detail as possible, the radiologist can perform double contrast. In this procedure, a certain amount of air is injected after contrast is administered. The method allows you to identify even the smallest defects on the mucous membrane, corresponding to tuberculosis, inflammation or erosion.
With descending cystography, contrast is administered intravenously rather than through a catheter. After administration of the contrast agent, the radiologist observes the dynamics of the removal of the contrast agent, assessing the excretory function of the kidneys, the functioning of the ureters and the filling of the bladder.
The radiologist examines the functioning of your urinary system, noting primarily the color and volume of urine. It also records whether you urinate on your own. An alarming symptom that a radiologist will definitely pay attention to is the presence of blood in the urine (in medicine - hematuria).
Indications
A survey x-ray of the kidneys is prescribed for:
- Examination of the structural features and location of the kidney.
- Detection of stones in the urinary system.
To clarify the nature and characteristics of already identified pathologies, excretory or intravenous urography is used. The study allows you to find out how passable the ureters are, how the kidneys work, features of neoplasms, foreign bodies, the exact structure of the organs of the urinary system (kidneys, bladder, ureters) and other features.
Main indications for excretory urography:
- Pathologies detected on a survey x-ray.
- Pain in the lower back or abdomen.
- Abnormalities in urine tests that persist for more than a month.
- Gross hematuria – noticeable traces of blood in the urine.
- High blood pressure without identified causes from the cardiovascular system.
- Low-grade body temperature without diseases of the respiratory organs or other systems.
- Anomalies and malformations of the external genitalia.
- Injuries to the lower back and abdomen.
- Urinary incontinence.
X-ray of the bladder (cystography) in Moscow
An X-ray of the bladder is performed with preliminary filling of it with a radiopaque substance. This type of radiation examination is called cystography, and it is done in a descending or ascending manner. Descending cystography serves as the final stage of excretory urography and is performed approximately half an hour after intravenous injection of a contrast agent. This time is usually sufficient for the radiocontrast agent to accumulate in the bladder. Ascending (retrograde) cystography is performed after filling the previously emptied bladder with a radiocontrast agent through a catheter. Sometimes, in order to improve image quality, gas is injected into the bladder in the same way (pneumocystography). To perform cystography, the patient is asked to lie on his back with his legs abducted and bent at the hip joints. To make an objective diagnosis, cystography is combined with cystoscopy or other instrumental studies.
Bladder X-ray is used in urological practice to recognize the following pathologies:
- anomalies and malformations;
- stones in the bladder;
- presence of foreign bodies;
- penetrating injuries and ruptures of the organ;
- tumor formations;
- tuberculous organ damage;
- diverticula;
- prostate adenomas;
- cystocele (downward displacement);
- stones in diverticula;
- vesicoureteral reflux (backflow of urine into the ureters);
- ureterocele.
To take an X-ray of the bladder, you must obtain a referral from a urologist, surgeon, traumatologist or oncologist. The results of the study are used by doctors to make a diagnosis, plan therapeutic measures, dynamically monitor the progress of treatment and rehabilitation.
The best way to find out where bladder x-rays are done in Moscow is to visit the Meds.ru portal. Using the simple and convenient menu of this online service, it is easy to find a medical institution suitable for location and other parameters where cystography is performed. Here you can also clarify information about the operating hours of the selected clinic, its distance from the nearest metro station, and find out the cost of an X-ray of the bladder. You can also use Meds.ru to sign up for a study at a time convenient for you. To do this, you need to fill out an online application on the website or contact its Call Center.
Text checked by a doctor:
Suleymanova Maria Miroslavovna
Radiologist, resident doctor
Contraindications for kidney x-rays
It is necessary to replace urography with other diagnostic methods (ultrasound, MRI and others) if:
- Pregnancy at any stage poses a risk to the developing fetus.
- Severe form of renal failure.
- Allergies to iodine for procedures with contrast.
- Severe health conditions of patients.
The attending physician will discuss possible contraindications when prescribing the examination and, if necessary, offer an alternative to x-rays. Before the examination, a blood test and a test to detect an allergic reaction to contrast are taken.
X-raying of the bladder for children
X-rays are performed on children from the age of five months. Parents are afraid of such an examination, since the child’s body is exposed to radiation and a special solution is injected. But if the attending physician insists on performing the procedure, you should prepare your child for the upcoming diagnosis.
For 1-2 weeks, the child should not eat food that can cause excessive gas formation and flatulence. In the morning, before cystography, it is recommended to give the child a cleansing enema. To avoid an allergic reaction to the medications that will be administered, it is advisable to conduct an allergy test.
Features of bladder cystography of a child:
- a catheter tube will be inserted through the urethra through which contrast is injected;
- the drug can be prescribed before and after urination;
- small children are given anesthesia to make the procedure painless;
- you should not eat or drink 4-6 hours before the test;
- the examination takes no more than 10-15 minutes;
- after the x-ray, the child is under the supervision of medical staff for 2 hours (during this time the bladder should empty).
After the procedure, the baby should take a furagin tablet to prevent the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system. Adverse reactions occur rarely. The child needs to drink a lot of fluids throughout the day so that the medication is eliminated faster.
Preparation
For good visualization of all internal organs, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the intestines, the accumulation of gases in which can cause darkening of the images. To do this, 3-4 days before the x-ray, the patient is advised to follow a diet without certain foods (cabbage, legumes, black bread and others).
The day before the examination, you can take activated charcoal to reduce flatulence, and before the procedure, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines. X-ray of the kidneys is done on an empty stomach; a light dinner is possible the night before.
How is urography performed?
Before entering the X-ray room, the patient must take off his clothes, putting on a special robe and metal jewelry. Pictures are taken in a lying or standing position, as determined by the doctor. The examination time depends on the method, the use of contrast agents and the characteristics of the kidneys. The procedure is completely painless, and the main thing that is required of the patient is not to move for several seconds while the image is being taken.
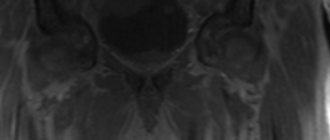
The result of an x-ray is one or a series of images of the examination area. The images are saved on a disk (or other storage medium), and based on the images, radiologists will draw up a conclusion. It describes in detail the structure and condition of the kidneys, bladder and ureters, detected pathologies and their features.
How is cystography performed on adult patients?

You should prepare in advance for x-rays. 4-5 days before the test, you must stop eating foods that cause gas and flatulence. It is forbidden to drink strong coffee and tea, sparkling water. You should refrain from consuming fermented milk products, whole milk, corn, cabbage, grapes and legumes. Before the procedure, you need to do a cleansing enema.
With the ascending diagnostic method, the patient takes a horizontal position, then the x-ray technician injects 200 milliliters of a special solution into his bladder. After the substance is completely injected, the doctor clamps the catheter so that the injected liquid does not flow back out. Next, you need to listen to the specialist’s commands so that the pictures are detailed and accurate.
Images are taken in different positions: lying on your back, on your side, during and after urination. When the bladder is empty, comparison pictures will be taken. A diagnosis will be made based on the x-ray images.
Descending diagnosis is carried out 30-60 minutes after administration of the drug into a vein. During this time, the contrast fills the bladder and provides detailed visualization of the contours of the internal organ. Next, photographs are taken.
The medical staff warns the patient in advance that the examination may be accompanied by pain and unpleasant discomfort. If the patient has a high pain threshold, for example a child, the examination will be carried out with simultaneous anesthesia. Before cystography, it is recommended to consult with a nephrologist, urologist and radiologist. They will be able to give recommendations on how to carry out the manipulation.
To protect yourself from side effects, after the x-ray, the patient should remain in bed for 24 hours and drink plenty of fluids.
X-ray of the kidneys and urinary tract in Moscow
We invite you to urography and other examinations at our clinic. Our priorities in work:
- Caring for the patient and his health.
- The quality of services provided.
- High diagnostic accuracy thanks to advanced equipment.
We are confident in the professionalism of our doctors - each of them has extensive work experience, regular advanced training in courses and trainings, and specialized training in the use of the clinic’s diagnostic equipment.
All this allows you to quickly and accurately make a diagnosis and determine the optimal treatment method for a wide variety of pathologies.
Want to learn more about kidney x-rays? We are ready to answer your questions and make an appointment at a convenient time by phone: +7(495) 478-10-03.