- Laparoscopy of umbilical hernia in adults: features of the procedure
- Causes and factors contributing to the appearance of a hernia
- Symptoms and possible complications
- Diagnosis and treatment methods for pathology
- Umbilical hernia: laparoscopy or abdominal surgery
- Preparatory stage
- Tools and materials for repairing umbilical hernia
- Surgical technique
- Main contraindications to the technique
- Features of the recovery period
- Prevention of pathology
- Laparoscopic surgery for umbilical hernia in adults: price in Moscow
- Laparoscopic umbilical hernia surgery in adults: reviews
Causes and factors contributing to the appearance of a hernia
The main reason for the formation of an umbilical hernia is the expansion of the umbilical ring. This may be due to certain congenital characteristics, such as connective tissue dysplasia. The immediate cause of the development of a hernia is considered to be any situation that leads to an increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity, for example:
- chronic cough
- difficulty defecating (constipation)
- difficulty urinating (prostate adenoma)
- against the background of pregnancy and childbirth;
- lifting weights (loaders, athletes...)
Symptoms and possible complications
The main symptoms of an umbilical hernia:
- protrusion in the abdominal area, decreasing in size or disappearing when lying down;
- discomfort in the navel area (increased during physical activity and coughing);
- umbilical ring expansion
It is undesirable to start pathology. The abdominal wall defect does not disappear on its own; over time, the hernia can only increase in size. Lack of timely treatment can lead to the development of strangulation: compression of organs inside the hernial sac in the hernial orifice, which threatens organ necrosis, development of peritonitis and/or intestinal obstruction.
Superficial and deep infections
Occurs in the first month after endoprosthetics. Characterized by the development of inflammation in the soft tissues of the lower limb. The hip or knee joint itself remains intact, that is, it is not involved in the pathological process. The cause of the complication is most often the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms into the wound during surgery or in the postoperative period.
Superficial SSI:
- necrosis of the skin;
- ligature fistulas;
- divergence of wound edges;
- subcutaneous hematoma.
Deep infections:
- necrosis of paraprosthetic tissues;
- deep fistulas;
- infected subfascial hematoma.
Fact! Mild tenderness, local swelling, redness and hyperthermia of the skin in the scar area usually indicate a superficial infection, which can be treated. The appearance of fever, spontaneous dehiscence of sutures and severe pain in the leg suggest inflammation of deep tissues. In this case, the prognosis is less favorable.
Diagnosis and treatment methods for pathology
If you notice the symptoms described above, we do not recommend delaying your visit to the doctor. Diagnosis of an umbilical hernia is most often not difficult: the surgeon can make a diagnosis during an examination of the patient. Sometimes, to clarify and confirm the diagnosis in doubtful cases, determine the size of the tumor, the condition of the tissues of the anterior abdominal wall, and select the optimal treatment method in a particular situation, we use instrumental diagnostic methods:
- computed tomography
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- magnetic resonance imaging
Umbilical hernias, like other types of hernias, can only be eliminated through surgery. If the patient has contraindications to surgery (a rather rare situation with an umbilical hernia), it is recommended to wear a special bandage. It should be said that the bandage does not eliminate the hernia and does not reduce the risk of strangulation, but it does reduce the severity of pain in the hernia area. In case of congenital umbilical hernia, it is most often recommended to refrain from surgery for up to 3 years, relying on massage and physical therapy.
Types of paraprosthetic infection
In orthopedics and traumatology, several classifications of SSI are used. Systematization and assignment of infection to a specific type helps doctors assess the severity of the patient’s condition. The Coventry-Fitzgerald-Tsukayama classification is the most common.
Table 1. Types of deep paraprosthetic infection according to Coventry-Fitzgerald-Tsukayama.
| Type | Development time | Treatment tactics | |
| I | Acute postoperative | 1st month | Revision of the postoperative wound, removal of necrotic tissue, and, if necessary, replacement of some parts of the endoprosthesis while maintaining its main components. |
| II | Late chronic | From 1 month to 1 year | Mandatory revision endoprosthetics. |
| III | Acute hematogenous | After 1 year | It is entirely justified to try to preserve the installed prosthesis. |
| IV | Positive intraoperative cultures | Asymptomatic bacterial colonization of the implant surface | Conservative treatment consisting of parenteral antibiotic therapy for 6 weeks. |
In the classification created by the Novosibirsk Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics, SSIs are divided into early acute, late acute and chronic. The first develop within three months after endoprosthetics, the second - at 3-12 months, the third - after 1 year. Infectious complications can occur in a latent, fistulous, phlegmon-like or atypical form.
According to the prevalence, infections are epifascial (superficial) and subfascial (deep). May be accompanied by total, femoral or tibial instability.
Umbilical hernia: laparoscopy or abdominal surgery
In modern medicine, to eliminate an umbilical hernia, they resort to one of two surgical methods - traditional (when an incision is made in the navel area) or laparoscopy (a low-traumatic technique). Both operations have the same main stages - reduction of the hernial sac and/or its contents into the abdominal cavity and closure of the defect in the navel area. The difference is in the number and size of the incisions made and the method of eliminating the defect.
Both methods are characterized by low intensity of pain after surgery, reliability and high efficiency. Closing the defect with a mesh implant significantly (by several times) reduces the risk of recurrence of a hernia. The number of complications during these operations is very small, and those are the so-called “minor” ones, for example, the appearance of seroma (fluid accumulation) in the area of the former hernia.
The choice of surgical technique is individual in each case and depends on the size of the hernial sac and the degree of expansion of the umbilical ring, the condition of the skin in this area, the presence of concomitant diseases and a number of other criteria. We must not forget about the financial side of the issue - laparoscopic high-tech operations have a much higher cost.
If the size of the sac and the defect are large, and there are no contraindications to anesthesia, we most often recommend laparoscopic hernioplasty of the umbilical hernia. The technique has a number of advantages:
- low morbidity. Unlike traditional surgery, the surgeon does not need large incisions to repair the hernia. The operation is performed through mini-incisions (punctures) measuring 5 and 10 mm.
- excellent cosmetic effect
- short recovery period. The patient spends 1 day in the hospital after surgery. You can return to normal activities after 3-5 days. Full recovery, which involves intense physical activity, takes 6-12 weeks.
Relevance of the problem
According to various data, the incidence of early paraprosthetic infection after primary replacement of large joints is 0.3-0.5%, after revision - 9%. Inflammatory processes are detected during the first three weeks after surgery.
An example of a “quiet” seam.
If we talk about the incidence of late infectious complications, they most often occur in the first two years after endoprosthetics (1.63% of patients). Less commonly (in 0.59% of those operated on), deep paraprosthetic infections develop in the next 8 years after surgery.
The frequency of infectious complications has remained unchanged for several decades. However, the total number of arthroplasties has noticeably increased, and the total number of complications has also increased. Therefore, their prevention, early diagnosis and treatment are becoming increasingly important.
Fact! As scientific studies have shown, the risk of developing infectious complications depends on the type of endoprosthesis. It turned out that in total, implantation of domestic models leads to inflammation more often (3-10% of cases) than installation of imported ones (0.3-4.8%).
Preparatory stage
Elimination of hernia formation, like any surgical intervention, requires careful preparation. Typical pre-operative examinations include:
- Clinical blood test
- Biochemical blood test (total protein, urea, creatinine, bilirubin and its fractions, ALT, AST, potassium, sodium)
- Coagulogram (aPTT, prothrombin time, INR)
- Blood test for blood-borne infections (RW, HIV, HbS, HCV)
- Blood type, Rh factor*
- Clinical urine analysis
- ECG
- Chest X-ray (if done within six months, no need to repeat, the report is sufficient)
- Therapist's conclusion about the absence of contraindications to surgery
During the consultation, it may be necessary to perform additional studies to clarify the diagnosis and identify other diseases and conditions that may affect the choice of the optimal surgical procedure (MRI, CT, EchoCG, consultations with related specialists, etc.).
Before surgery, you should not eat for 6 hours before surgery; you are allowed to drink a small amount of water 2 hours before surgery.
Implant-sparing tactics
Its main goal is to eliminate the infectious process while preserving the endoprosthesis. The patient undergoes surgical treatment of the wound, during which pus and necrotic tissue are removed. If the joint itself is involved in the pathological process, arthroscopic debridement is performed. The patient is prescribed massive antibacterial therapy.
Curious! Scientific studies have proven the effectiveness of non-surgical treatment of early deep infections. As it turned out, a combination of antibiotics and enzyme preparations helps eliminate inflammation in 5-7 days.
Tools and materials for repairing umbilical hernia
During the operation, the surgeon works under the control of a special instrument - a laparoscope. This is an optical device with a diameter of 10 mm, connected to a light source and a high-resolution monitor. The laparoscope allows you to magnify the image several times, which allows you to clearly see the anatomical structures and operate almost bloodlessly. In addition, other tools are needed:
- trocars (for performing punctures);
- various clamps and instruments for cutting tissue
- mesh implant;
- herniosteppler for implant fixation;
- needle holder and suture material for suturing.
Surgical technique
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. A small skin incision is made on the left side of the abdomen, through which the first port for the laparoscope is installed. There is no free space in the abdominal cavity; sterile carbon dioxide is injected into it to create space for manipulation. Under direct visual control, two more ports for other instruments are installed. In principle, there are two ways to position the implant - inside the abdominal cavity and in the thickness of the anterior abdominal wall. The first is technically simpler, but requires the installation of a rather expensive implant with a special coating that prevents the formation of adhesions between the implant and internal organs. It is strictly forbidden to place an uncovered polypropylene implant in the abdominal cavity - this leads to serious complications, including the development of intestinal obstruction and fistulas. Such an implant can only be placed in the thickness of the abdominal wall, so that there is at least peritoneum between it and the intestinal loops. After isolating the hernial sac, the implant is fixed to the anterior abdominal wall using special staples.
The operation ends with the removal of carbon dioxide from the abdominal cavity and suturing the trocar wounds. We almost always use intradermal sutures with absorbable material, which do not require removal and lead to a good cosmetic effect.
Microbiological studies
Bacterioscopic and bacteriological studies make it possible to identify and identify the causative agent of infection, as well as determine its sensitivity to antibiotics. Quantitative studies make it possible to determine the number of microbial bodies in purulent discharge.
The following materials can be used for research:
- discharge from a wound;
- fabric samples;
- fluid from the joint cavity;
- prosthetic material.
In case of implant-associated infection, it is almost impossible to detect bacteria in biological fluids and tissues. Pathogenic microorganisms are found on the surfaces of endoprostheses themselves. They cover the implants in the form of an adhesive film.
Fact! In addition to bacteriological examination, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) can be used for diagnosis. The method has high sensitivity but low specificity. Because of this, it often gives false positive results.
Main contraindications to the technique
Despite all the advantages of laparoscopic hernioplasty, we choose the traditional option of surgery in the following cases.
- Large size of the hernial sac with stretched skin over the protrusion and the presence of trophic changes - such skin requires excision in any case
- Very small hernias that can be eliminated from one incision 15-20 mm long;
- In case of severe concomitant diseases (heart failure, liver cirrhosis, respiratory failure), when anesthesia is associated with a certain risk (traditional open surgery can be performed under local or spinal anesthesia).
- adhesions in the abdominal cavity after numerous previous operations.
Complications after abdominoplasty

Regardless of the complexity of the plastic surgery or the experience of the surgeon, there is a risk of complications. Abdominoplasty confidently occupies a leading position in the ranking of traumatism, so possible complications after abdominoplasty are very high.
The Plastic Surgery Center guarantees high quality service at all stages. The patient is in constant contact with the surgeon, any assistance is always immediately provided, and in case of any negative changes during rehabilitation, you should immediately consult with your doctor.
Important!
Possible complications after abdominoplasty are divided into general and local. Only a well-trained specialist from a plastic surgery clinic who performed the operation can determine how to deal with the difficulties that have arisen.
General complications
Conducted statistical studies show that 0.3-1.1 percent of patients after tummy tuck complain of complications affecting important systems of the body. If the reaction is untimely, general complications can not only cause an increase in the duration of the rehabilitation period, but also lead to death.
- When the pulmonary circulation is overloaded, pulmonary edema quickly develops, resulting in a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure. The root cause of a jump in intra-abdominal pressure may be wide suturing of the rectus abdominis muscles. This reduces the volume of the abdominal cavity, negatively affecting blood pressure. This complication is rare, but the specialist must take into account that excessive suturing of the muscle tissue in the anterior abdomen can lead to serious complications. For prevention, active training is prescribed for 2-4 weeks before surgery using a special tightening bandage.
- The manifestation of hypostatic pneumonia or pulmonary embolism is possible if the operation took a long time. In addition, signs of pneumonia can be observed in the early stages of recovery after tummy tuck. Compression stockings worn by the patient before surgery help prevent possible negative consequences. Using hospital knitwear, dosed compression is created over the entire surface of the lower extremities. This precaution significantly improves venous outflow, reducing the risk of blood clots.
On a note!
Immediately before abdominoplasty, the patient is given subcutaneous anti-clotting medications to prevent the risk of blood clots. If there are problems with clotting, surgery is possible only after special therapy.
The attending physician monitors the patient's condition during the rehabilitation period. To reduce the risk of stagnation, early activation of the muscular system is used. It is required to begin moving around the ward as early as the next day after surgery. You need to walk slightly bent so as not to strain the stitches.
Local complications after abdominoplasty
Asymmetry
The reason for the asymmetry may be
- incorrect marking of the abdominal wall before surgery,
- excessive tension on one side of the upper flap during resection of the lower part,
- postoperative infection or necrosis, seroma, hematoma, lack of preoperative markings,
- navel asymmetry,
- excess residual fat on one side during preoperative liposuction and failure to adhere to marked incision lines or
- attempts to remove more skin after excision of the lower flap.
Marking before surgery should be done with the patient standing. If the patient is lying down, there will be tissue displacement on one side or the other, preventing symmetrical markings. The midline should be marked above the navel and in the pubic area.
The transverse incision line of the lower abdomen should be marked so that the distance from the midline is the same on each side. After applying the markings, you need to check the symmetry again. It would be helpful to take photographs at this time and transfer the results to the operating room, since the patient's shape will change as he lies on the operating table. Do not deviate from the marks when trying to take excess fabric.
The volume of excised skin is determined by applying strong tension to the skin flap at points equidistant on each side of the midline of the flap. This will prevent one side of the flap from being too tight on the other.
Care must be taken to center the navel to prevent asymmetry.
Asymmetry correction options
Excess fat or skin may be surgically removed to correct the asymmetry. Fat can also be subjected to liposuction in areas where there is excess fat. A hematoma or seroma may appear as an asymmetry or tumor. Typically, such asymmetry is corrected by aspiration of the fluid. Necrosis can lead to permanent deformation of the abdominal wall after the wound has healed and the scar has contracted.
Dog ears
Closure of the transverse wound in the lower abdomen begins with a midline suture to properly position the new umbilicus. The wound should then be closed starting from the sides on each side to give a flattened appearance to the most lateral portions of the wound.
If there is excessive fatty tissue in the area where dog ears typically form, this tissue should be excised before suturing. It is possible to remove dog ears during final closure by liposuctioning the excess fat and then excising the loose skin.
Often small dog ears will resolve within 3 months without treatment. If dog ears persist for more than 3 months, they can be removed under local anesthesia, usually in an elliptical shape. Very large dog ears and fullness in this area can be treated with either liposuction or excision.
Seroma
Lymph accumulating between the skin-fat flaps due to impaired outflow through the lymphatic tract leads to the formation of seroma.
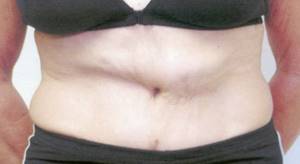
There are several reasons for this complication:
- Tightening the abdominal muscle tissue combined with liposuction creates a 30 percent chance of seroma due to the large volume of manipulations performed by the surgeon;
- extensive damage to the lymphatic ducts, as well as blood vessels, is the main risk factor;
- incorrectly selected size of compression garments, non-compliance with the rules and schedule for wearing them;
- activation of inflammatory processes in the body after abdominoplasty;
- a sharp increase in physical activity in the early period of rehabilitation.
After surgery, the wound surfaces do not touch tightly, so wound discharge begins to accumulate between them. Gradually, under the influence of gravity, excess fluid collects in the lower abdomen. By using compression garments, the patient minimizes the risk of seromas. With one-stage liposuction, the cannulas leave many long passages in the subcutaneous tissue, which increases the wound surface, increasing the risk of seroma formation. A signal that deviations have occurred is the formation of edema with pronounced fluctuations and sudden changes in temperature.
Preventive measures to prevent the development of seromas
- The use of innovative abdominoplasty techniques that guarantee gentle detachment of skin-fat flaps of the anterior abdominal walls.
- Used to increase the reliability of fixation of skin-fat flaps to the aponeurosis with additional sutures.
- Avoid massive liposuction through the walls of the main wounds.
- Carrying out optimal tissue immobilization after plastic surgery. For this you need to carry out several simple procedures.
- After completing the plastic surgeon’s work, put on compression garments. Wear it constantly for 1-1.5 months during the rehabilitation period.
- Do not get out of bed for the first day after plastic surgery.
- Reduce activity as much as possible during the first two weeks after abdominoplasty.
- During the first few weeks you should rest and sleep exclusively in a half-bent position. This will eliminate tissue overstrain at the site of fixation and speed up regeneration.
How is seroma treated?
When a seroma forms, the doctor performs a puncture, using a syringe to remove the serous fluid. If the volume of accumulated fluid is significant, permanent drainage is installed. In this case, a complex of medications is prescribed to accelerate the wound healing process. The appearance of a seroma is an unpleasant complication, however, timely intervention by the attending physician will prevent the result of plastic surgery from worsening. Proper therapy will relieve possible complications after abdominoplasty in 2-6 weeks.
Hematoma
After the work of a plastic surgeon, for reasons beyond his control, extensive accumulations of blood may form in the abdominal cavity. There are several signs that help determine the location of the hematoma, even if it is not visible.
- Sharp pain in one point that appears on palpation.
- Swelling at the site of hematoma formation, gradually increasing in size.
- The hematoma area always has a higher temperature compared to other parts of the body.
- A sharp decrease in the normal functioning of muscle tissue.
- Any exertion becomes painful.
- The skin at the site of the hematoma changes color.
The first signs of hematoma formation appear mainly immediately after abdominoplasty. Risks are correlated with the patient's weight. Internal bleeding is provoked by pressure surges, decreased coagulability due to anticoagulants taken before surgery, poorly fixed vessels, or other reasons. Possible complications after abdominoplasty often do not appear immediately, since adipose tissue easily absorbs a large volume of fluid. Constant supervision by the attending physician is required in order to quickly respond to the appearance of hematomas.
You can speed up the process of disappearance of minor hematomas by applying ice to them and applying pressure bandages. The attending physician prescribes physiotherapeutic procedures and analgesics to speed up tissue healing as much as possible. If the hematoma grows, the sutures are unraveled, the hematoma is removed, the cavity is disinfected, the bleeding vessels are cauterized, and active drainage is installed. By removing the hematoma in a timely manner, the doctor ensures an excellent plastic result.
Prevention of hematomas
- Careful treatment of blood vessels during surgery.
- Avoidance of cavities after wound suturing.
- Drainage of wound cavities.
- Maximum reduction of the risk of injury or bruises.
Important!
The attending physician carefully monitors the healing process and the disappearance of hematomas. If necessary, the cause of bleeding is eliminated by repeating the abdominal incision.
Infections
Infection of a wound is possible for two reasons.
- Failure by the surgeon to comply with antiseptic measures, which is completely excluded in our plastic surgery center.
- Failure to comply with the rules for caring for the wound surface by a patient discharged from the clinic.
It is not difficult to determine the development of infection yourself.
- The inflamed area always has a higher temperature in relation to other parts of the body.
- The inflammation gradually turns red.
- The appearance of pain at the site of inflammation.
- Sudden disruption of functioning.
In addition, sudden attacks of weakness begin, the temperature rises, and chills appear. You should not self-medicate; you should immediately contact your doctor for advice. The faster a specialist eliminates possible complications after abdominoplasty, the greater the chance of rapid rehabilitation. Since the wound surface occupies a large area, inflammation can easily spread to neighboring areas. Carefully following the instructions of the attending physician, strict adherence to the rules of asepsis and antisepsis when treating wounds will help avoid infection from entering the body.
Seam divergence
Suture dehiscence after abdominoplasty usually occurs in the area of the strongest tissue tension.
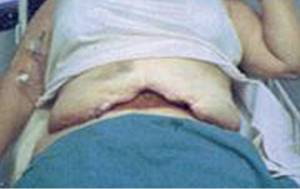
This point is the center of the flap at the site of attachment in the pubic area. The area darkens and necrosis occurs, followed by failure of closure, sometimes with dehiscence of the wound edges. Usually the edges of the wound do not spread far apart because the sutures located on the side of the separated edges of the wound hold it together.
Causes that have led to this complication also include smoking, poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, underlying hematoma or seroma, and excessive patient activity.
Many surgeons close the wound with the patient tightly flexed: tilting the chest and legs towards each other. The surgeon then expects the patient to remain in this position for several weeks, even while walking. These recommendations are not always followed as it is difficult to maintain this position for a long time, especially if the patient has a history of back problems.
Treatment of wound dehiscence should be conservative. It may be possible to debride the wound and perform primary closure. This is usually not possible because the initial tension was the likely cause of necrosis and wound dehiscence.
The wound will be cleared of necrotic masses at appropriate intervals. In this case, the developing scar shrinks so much that it ultimately forms a slightly expanded scar, which can be corrected if necessary (if the patient is dissatisfied with the appearance).
Necrosis of the wound edge
Abdominoplasty is one of the most traumatic operations. Significant areas of skin and fat flaps peel off, which inevitably leads to disruption of the normal blood supply to the tissues. Crossing the main arteries increases the risk of necrosis of the wound edges.
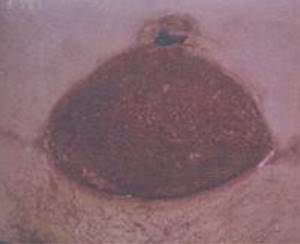
Among the root causes, it is necessary to highlight several:
- an overly large flap is formed on the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity with damage to the key arteries responsible for the blood supply;
- excessive tension on the edge of the flap when applying sutures reduces the supply of nutrients;
- additional scars on the anterior abdominal wall after old operations;
- poorly treated seroma or hematoma leads to tissue death at the edges of the wound.
At the first signs of necrosis, you should immediately consult your doctor. If the wound begins to look like a weeping abrasion, medical treatment is sufficient to help the body recover. If necrosis has spread to the deep layers and affected the subcutaneous tissue, treatment will require 3-6 months. Dead tissue is removed immediately, the wound is cleaned, and a new suture is applied. If emergency measures are not taken, healing is delayed, rough scars appear, and there is a great danger of infection of the body.
Complete or partial loss of sensation
Occurs when nerve endings are affected. Each organism is individual, so the restoration of normal sensitivity proceeds differently for each patient. Some patients feel any touch normally after a few days or weeks. Sometimes it will take several months for full sensitivity to be restored. In any case, any changes should be reported to the plastic surgeon who performed the operation.
Perforation of an intra-abdominal organ
It is possible to perform intestinal perforation during repair of an umbilical or ventral hernia simultaneously performed with abdominoplasty.
Liposuction before or after abdominoplasty may result in perforation of the cannula into the abdominal cavity. This in turn can lead to damage to blood vessels, intestines or bladder.
If perforation is diagnosed, immediate surgery is indicated. Preoperative antibiotic therapy should be started. The abdomen should be carefully examined for possible multiple perforations, and any observed bowel perforations should be sutured after thorough abdominal lavage. Early intervention can prevent severe infection.
Recurrence of fat deposits
Patients should be advised that weight gain after abdominoplasty may lead to recurrence of fat deposits, which may require repeat surgery.
Pregnancy after abdominoplasty is associated with the risk of sagging skin, stretching of the rectus abdominis muscles and the appearance of stretch marks. This may lead to the need for a repeat abdominoplasty.
Recurrent protrusion of the abdominal wall
In some patients the abdominal wall muscles are very weakened and there is a tendency for re-protrusion after apparently adequate restoration and strengthening of the muscular aponeurotic layer.
This may require revision abdominoplasty aimed at additional strengthening of the muscular aponeurotic layer.
Complications after anesthesia
Today, such problems appear very rarely. Modern types of pain relief do not produce side effects. The dosage is always selected individually by an experienced anesthesiologist after a comprehensive examination. However, if you suspect any possible complications after abdominoplasty, you should immediately consult with the doctor who performed the operation.
Scars (widened, thickened, hypertrophic, keloid)
Most often they appear in people who abuse tobacco or have circulatory problems. Poor supply of microelements necessary for regeneration to the wound increases the risk of tissue death at the edges of the wound. This leads to expansion of the scarring area.
Wide scars often occur after abdominoplasty, when the wound is sutured under strong tension. After 6 months, when the scar has matured and weakened, it can be excised to make it thinner.
Some people are prone to developing hypertrophic scars, although this is unpredictable.
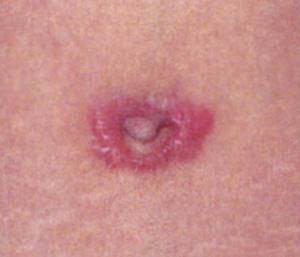
Hypertrophic scars may disappear without treatment.
Keloid scars affect up to 15% of blacks, Asians, and Hispanics. There are many treatments available, such as steroid injections, which can be used in combination with 5-fluorouracil or bleomycin. Silicone patches can reduce the height of the scar, but this takes several months. Recurrence of keloids is common.
Sometimes the transverse scar after abdominoplasty rises higher than planned due to suturing under strong skin tension. Another reason is that the surgeon makes the lower incision too high above the pubis, which leads to a high transverse scar.
Changes in the umbilical area
With abdominoplasty, the navel must be moved to a new place. Usually, after removing excess tissue, it is placed 1-2 centimeters above the old location. However, the individual characteristics of the body during regeneration can move it significantly further or seriously deviate from the white line of the abdomen to the right or left. The plastic surgeon will make the necessary correction six months after the recovery process is completed.
The main discomfort after tummy tuck is caused by injury to a large number of muscle tissues. The pain is localized in the upper abdomen, since the nerve endings here are not affected by surgery. The pain will intensify during the first ten days, so the attending physician prescribes analgesics. The pain will move towards the center of the abdomen as sensation is gradually restored. Minor spasms and tingling sensations will bother you for several months.
Features of the recovery period
After laparoscopic hernioplasty, the patient is transferred to the hospital ward. You can eat and get out of bed after 2-3 hours. The next day, the surgeon examines, bandages, and in the vast majority of cases the patient can be discharged (with a recommendation to immediately contact the surgeon if any symptoms appear.It is important to avoid strenuous activity for the first 2-3 days after surgery.
During the rehabilitation period, regular changes of bandages at puncture sites and treatment of sutures with an antiseptic solution are required. We do not recommend vigorous exercise for a month, but heavy lifting (>10 kg) for 12 weeks. You should follow a certain diet to prevent constipation. Your daily diet should contain foods rich in fiber (vegetables and fruits) and a sufficient amount of liquid.
Prevention of pathology
The goal of preventive measures is to reduce the impact of factors that contribute to the appearance of an umbilical hernia. As a preventative measure, experts recommend:
- maintain proper nutrition;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- wear a special bandage during pregnancy;
- maintain a drinking regime (drink at least 2 liters of water per day);
- promptly treat bronchopulmonary diseases;
- reduce weight (if obese);
- train the abdominal muscles (this will reduce the risk of a hernia, but cannot eliminate an existing one).
Laparoscopic surgery for umbilical hernia in adults: price in Moscow
Experienced specialists from the Clinical Center of Sechenov University perform umbilical hernia removal using laparoscopy, the price of the procedure is significantly lower than in private clinics in the city. In addition to the operation itself, the final cost includes a consultation with a surgeon, placement in an inpatient department in comfortable conditions, anesthesia, examination and dressing of wounds. Doctors are highly qualified and have extensive experience. You can find out more about prices on the official website.
In addition to the surgical procedure itself, you can undergo preoperative examination here. The Clinical Center of Sechenov University is equipped with modern equipment, which makes it possible to detect and cope with a number of other serious pathologies. To make an appointment with a specialist, you must call the numbers listed on the website or leave a request online, indicating your contact information.
Laparoscopic umbilical hernia surgery in adults: reviews
1. Olesya, 32 years old. Last month I had an umbilical hernia removed using laparoscopic hernioplasty. I carefully read the progress and reviews of this operation in advance. I concluded that this is a completely safe technique. The preparation, as well as the rehabilitation period, took me only 2 weeks. I am satisfied with the result, for which I thank the experienced doctors of the Clinical Center of Sechenov University.
2. Andrey, 44 years old. In the spring I began to experience abdominal pain during training and noticed a slight protrusion. At first I didn’t focus on the symptoms, but then the pain began to intensify. I went to the doctor, and after examining him, he immediately said that it looked like an umbilical hernia. An ultrasound confirmed the diagnosis. The doctor advised to perform laparoscopic hernioplasty to avoid complications. The operation was successful, recovery took a little time, and there were no complications. I feel good now.