31.01.2020
Kolesnichenko Yu.Yu., ultrasound doctor, www.uzgraph.ru
According to a publication in the journal RadioGraphics for November 2015 - Normal and Abnormal US Findings in Early First-Trimester Pregnancy: Review of the Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound 2012 Consensus Panel Recommendations / Normal and abnormal ultrasound findings in early pregnancy in the first trimester: review of the 2012 Society of Radiology in Ultrasound Consensus Panel Recommendations - https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/rg.2015150092
Pelvic ultrasound and determination of beta-subunit human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG) levels in human serum are key to the diagnosis of early pregnancy and the management of associated complications. Ultrasound imaging in early pregnancy should be primarily endovaginal, with transabdominal imaging used for ovarian masses and documenting the amount of free fluid. These diagnostic tests differentiate between intrauterine (UI) and ectopic pregnancies (EPP), viable and nonviable MB, MB of uncertain viability, and pregnancy of unknown location—and have contributed to a marked decline in mortality from ectopic pregnancy since the 1980s. However, inappropriate use of these tests and misinterpretation of results can lead to unintended harm in potentially viable pregnancies, such as the administration of methotrexate when an ectopic pregnancy is suspected when in fact there is an undiagnosed MB, resulting in embryonic death or clinically significant birth defects. Given the large number of first-trimester pregnancies that are monitored by ultrasound, the danger of misdiagnosis, potentially causing harm to viable pregnancies, cannot be underestimated. In 2012, the Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound convened a multidisciplinary group of radiologists, obstetricians, and emergency medicine physicians and established conservative ultrasound criteria for the accurate diagnosis of miscarriage to minimize the potential for harm to potentially viable MBs.
This article reviews the normal development of early MB between 4 and 8 weeks of gestational age, as well as the diagnostic criteria for nonviable and MB of uncertain viability. Because of variations in the quality of ultrasound images obtained in early pregnancy, standard deviation of measurements, and variations in human development, the criteria are conservative and the concept of “watchful waiting” for potentially early ectopic pregnancies is emphasized. In addition, this article illustrates indicators of poor prognosis and reviews the management of pregnancy in an unknown location. The role of subsequent pelvic ultrasound and monitoring of beta-hCG levels is considered.
Objectives of ultrasound examination during pregnancy
The content of the article
Ultrasound examination is the most accurate and effective assessment of the condition of the pregnant woman and the fetus at different gestational stages. A woman undergoes it for the first time after learning about pregnancy, and then several more times during pregnancy.
A pregnant woman must undergo at least three routine screening ultrasounds without fail: during the period 10-14, 20-24, 32-34 weeks.
An ultrasound may also be required at an earlier stage or immediately before birth - an unscheduled examination is prescribed if the diagnosis is questionable or if there is an increased risk of pregnancy complications.
Observing the course of pregnancy week by week, the doctor pursues the following goals:
- confirmation of pregnancy;
- monitoring the development of the fetus, its size and weight;
- assessment of fetal viability;
- detection of pathologies at all stages of pregnancy;
- determining the sex of the child;
- assessment of maturity parameters, size and place of attachment of the placenta;
- calculation of amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) values.
Ultrasound by week of pregnancy is the most important examination during pregnancy.
Is ultrasound harmful?

Any ultrasound research methods, and in particular BP ultrasound, are absolutely safe and harmless to the body. It is these properties that make it possible to conduct ultrasound even in children and pregnant women.
The Andromed Center for Andrology and Diagnostics has modern ultrasound scanners that further improve the quality of diagnostics. Experienced doctors will conduct the study with comfort for you and provide a transcript of the results as soon as possible.
What a fetal ultrasound can and cannot reveal
1st trimester
: Ultrasound reveals the following pathologies:
- defects of the central nervous system (for example, anencephaly - absence of the brain);
- absence of the peritoneal wall (severe pathology - gastroschisis);
- spinal abnormalities - absence, hump, etc.;
- Down syndrome;
- umbilical hernia (diagnosis of omphalocele);
- absence of limbs.
2nd trimester
: all visible abnormalities can be identified, since all organs of the fetus are almost formed by this time.
3rd trimester
: defects previously identified by blood tests, chorionic villus biopsy and other methods are confirmed or refuted.
It is impossible to diagnose using ultrasound:
- blindness and deafness - ultrasound cannot show the quality of transmission of nerve impulses to visual and auditory receptors
- mental retardation, since these are properties of the brain, not its structure;
- minor disorders of organ development (for example, obstruction of the liver ducts or defects of the cardiac septum);
- some genetic diseases (for example, Duchenne myopathy, phenylketonuria, cystic fibrosis are not diagnosed);
- chromosomal abnormalities themselves (Edwards, Patau, Turner syndromes), the doctor can only observe the result of their development.
Having studied the list of problems that are not detected on fetal ultrasound, you should not worry - these pathologies will not go unnoticed. Many fetal malformations are detected by blood tests for fetal pathology and other special methods.
Ultrasound of the bladder, kidneys, adrenal glands and ureters
Ultrasound examination is considered one of the earliest and most informative ways to detect the disease in the early stages. Timely diagnosis allows you to prescribe treatment immediately, which contributes to complete recovery or rare relapses.
An ultrasound scan of the urinary system is indicated in the presence of the following complaints:
- elevated blood pressure numbers;
- suspicion of an aneurysm or neoplasm;
- pain and disturbance of the urination process;
- changes in urine (visual and laboratory confirmed);
- endocrine pathologies.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
Experts strongly recommend visiting an ultrasound diagnostic room if the following symptoms are noted:
- causeless increase in heart rate (tachycardia);
- constant feeling of a “lump” in the throat;
- swelling;
- sleep problems;
- weakness, fatigue;
- rapid mood swings, irritability.
Using ultrasound, you can easily determine the structure of the thyroid gland, its contours and size. Internal changes in the organ, the presence of lesions and how the gland affects nearby tissues are also clearly visible. Thanks to the use of this research method, it is possible to quickly and accurately diagnose diseases such as thyroid adenoma, thyroiditis, benign and malignant neoplasms.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland shows:
- production employees with hazardous working conditions;
- women planning pregnancy;
- patients taking hormonal medications for a long time;
- those people who have relatives with diabetes and thyroid diseases
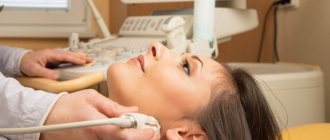
How is an ultrasound performed by week of pregnancy?
The doctor chooses from 2 methods:
- Transabdominal
– the examination is carried out using an external sensor through a small layer of a special gel applied to the woman’s abdomen. The main condition for the procedure is a full bladder. 30-60 minutes before the ultrasound, a woman should drink 1-1.5 liters of non-carbonated liquid and not urinate; - Transvaginal
– examination takes place using a vaginal sensor – transducer, inserted into the vagina. This type of ultrasound does not require special preparation. You just need to empty your bladder immediately before the procedure.
Basically, the examination is carried out using the abdominal method. It happens that in the early stages the fetus is poorly visualized, so they proceed to examination through the vagina. Read here which method to choose.
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound examination is suitable for patients of all ages; the procedure is painless and safe. In most cases, the patient does not need to adhere to a diet, discontinue medications, or undergo preparatory procedures.
High-frequency ultrasound waves pass through tissue and are reflected differently from internal organs and human structures. This is how the image on the screen is formed, with the help of which the presence of deviations is determined.
Ultrasound allows you to track the condition of patients with chronic diseases and determine the dynamics of changes. Ultrasound examination is also used to assess postoperative conditions: postoperative sutures and soft tissue scars, the structure of internal organs.
Ultrasound at 3 weeks of pregnancy
An ultrasound examination during this period is necessary to confirm pregnancy. Now the processes of embryogenesis are just beginning, but on ultrasound you can already see the fertilized egg attached to the wall of the uterus.
At week 3, a study may be prescribed in certain cases:
- diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy;
- Hydatidiform mole is a rare pathology of the ovum, characterized by the absence of an embryo in the presence of all the symptoms of pregnancy. The reason is that the structure necessary for the attachment of the fertilized egg in the uterus (trophoblast) degenerates into a huge number of small bubbles;
- doubts about pregnancy - signs of pregnancy are unclear.
Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound during pregnancy
3D ultrasound during pregnancy
– three-dimensional, volumetric image of the fetus. Future parents have already appreciated this type of ultrasound examination - often, instead of the first photograph of the baby, a 3D photograph is pasted into the family album.
However, from a medical point of view, the use of 3d
and even
4d ultrasound during pregnancy
, which is more like a film about the intrauterine life of a child, raises doubts.
According to medical indications, 3D ultrasound during pregnancy
is performed only if there is a suspicion of developmental anomalies of the face and limbs.
Ultrasound at 5 weeks of pregnancy
Often expectant mothers undergo their first examination at this time. A woman experiences a delay in menstruation (by about 3 weeks), so she, suspecting pregnancy, boldly goes to the gynecologist.
At the 5th week of gestation, it is still impossible to identify pathologies, assess the condition of the fetus, or determine the sex. However, during this period, ultrasound allows:
- hear the heartbeat of the embryo;
- diagnose normal and ectopic pregnancy;
- determine the duration of pregnancy;
- identify the cause of delayed menstruation if there is no pregnancy.
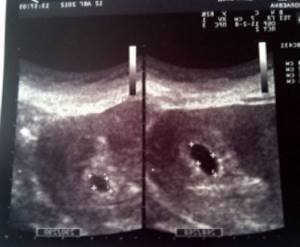
Interpretation of ultrasound during pregnancy
Very often, patients ask GUTA CLINIC gynecologists to decipher the results of ultrasound during pregnancy
.
Let's start with the fact that ultrasound images require direct visual assessment and, being sent by e-mail and then printed, lose a lot in quality, which significantly complicates diagnosis. Ultrasound during pregnancy
is a study performed in real time and requires assessment in real time.
Therefore, interpretation of ultrasound during pregnancy
should be carried out by the specialist who conducted this study for you.
Competent interpretation of ultrasound during pregnancy
requires highly qualified specialists and rich practical experience.
In order to correctly interpret the results of an ultrasound scan during pregnancy
, it is necessary to conduct a study using modern expert equipment by a highly qualified doctor who has undergone appropriate training.
These are the specialists who work at the GUTA CLINIC medical center. Our obstetrician-gynecologists are highly qualified and have extensive experience in performing ultrasound examinations during pregnancy.
.
We use high-quality European equipment, which allows us to perform not only standard ultrasound during pregnancy.
First ultrasound: at 10-14 weeks (planned, screening)
Typically, 1 scheduled examination is scheduled for the 12th week of pregnancy. Already at this stage, the woman’s condition and how the pregnancy is progressing in general are easily assessed. Moreover, ultrasound reveals pathological changes in the fetus. This is important because if abnormalities are detected, termination of pregnancy may be necessary, and in the first trimester the doctor will prescribe a medical abortion, which is not dangerous to the woman’s health.
The main tasks of the first planned ultrasound:
- Determination of a special parameter - the thickness of the collar zone (the area between the soft tissues covering the spine and the inner surface of the skin, filled with fluid). Measuring this indicator allows us to identify the development of chromosomal pathologies - Down syndrome, etc.;
- Measuring the coccygeal-parietal size. The indicator determines the size of the fetus and the exact gestational age;
- Diagnosis of fetal cardiac activity is the main indicator of viability;
- Detection of multiple births;
- Assessment of the presence and development of the child’s organs;
- Determining the expected date of birth;
- Establishing the correspondence of fetal size to gestational age.
Also, the first examination allows you to assess the location of the placenta and determine the condition and tone of the uterus. Often, the first scheduled ultrasound is a significant event for a couple, since they can see their unborn child for the first time.
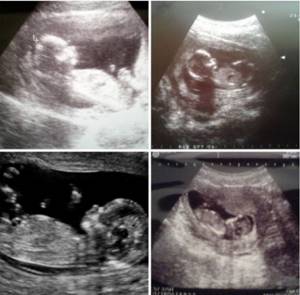
Normal development of early MB at 4 to 8 weeks of gestational age
Gestational age is calculated from the first day of a woman's last menstrual period; however, it is important to understand that conception occurs only after ovulation, approximately 2 weeks after the last menstrual period. This explains the 2-week discrepancy between clinical and histological gestational age. The gestational sac (*hereinafter referred to as the gestational sac or abbreviated PU) can be first visualized during endovaginal ultrasound at 4.5–5.0 weeks of gestational age in the form of round intrauterine fluid with a volume of 2-3 mm. The rate of growth of the average diameter of the PU (*SDPJ see) is 1.13 mm per day, but is often variable. Before visualizing the yolk sac or embryo, two signs can be used to confirm the visualized fluid structure as a true PO:
1) Intradecidual symptom, defined as an eccentrically located PU within the echogenic decidua with a relatively unchanged collapsed uterine cavity, visualized as a thin echogenic line;
2) Double sac sign, consisting of two concentric echogenic rings surrounding a fluid inclusion and separated by a thin crescent of endometrial fluid. The outer echogenic ring represents the decidua parietalis, and the inner ring represents the decidua capsularis and the chorion. The intradecidual symptom is visible at an earlier stage than the second sac. Ultrasound visualization of early POFs is variable, and although these two features are suggestive of early MB, they will be absent in at least 35% of POFs. Thus, the absence of these signs does not exclude MB. Visualization of a round collection of intrauterine fluid observed in a pregnant patient has a greater than 99.5% probability of the presence of a uterine ulcer.
Therefore, based on the much higher prevalence of MB compared with ectopic pregnancies and the fact that a minority of ectopic pregnancies have small intrauterine fluid collections, visualization of a round or oval intrauterine fluid collection represents MB until proven otherwise.
(*It just happens that MB is combined with VMB and in these cases the fact of the presence of MB does not exclude VMB).
The yolk sac is the earliest structure within the PU that can be visualized on ultrasound, which can fully confirm MB. It is the primary transport system between mother and fetus before the establishment of a fully developed placental circulation and can be visualized at approximately 5.5 weeks of gestational age as a round 3-5 mm structure, usually eccentrically located within the PU. In the PU after 5.0–5.5 weeks, the yolk sac may sometimes appear as two parallel lines representing the anterior edge and posterior wall, rather than as a discrete circle (*this is a question about the resolution/frequency of the sensor used and the size object).
The embryo is first visible at approximately 6 weeks of gestational age as a 1–2 mm structure at the periphery of the yolk sac. The length of the fetus/embryo is measured from the head to the coccyx, hence the term coccygeal-parietal size (CPR), which is the most accurate measurement of gestational age during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. The embryo should be visualized when the DPJ is at least 25 mm.
The embryo is located in the amniotic cavity, and the yolk sac is in the chorion cavity. The amniotic membrane is thinner than the yolk sac and although easier to see after 7 weeks, it can be seen as early as 6.5 weeks of gestational age. Between 6.5 and 10 weeks of pregnancy, there is a linear relationship between the diameter of the amniotic cavity and the CTE, with the average amnion diameter being 10% larger than the CTE. In a normal pregnancy, the chorionic cavity, amniotic cavity and CTE grow proportionally until the fetus begins to produce urine, after about 10 weeks. Fetal urine disproportionately enlarges the amniotic cavity, which then grows faster than the chorionic cavity, with possible fusion of the amnion and chorion after 14–16 weeks.
Cardiac pulsations in the two paired endocardial heart tubes begin at approximately 6 weeks of gestation; thus, cardiac activity can be observed in embryos as small as 1–2 mm. However, the absence of cardiac activity in embryos smaller than 4 mm may also be normal. To account for measurement inaccuracies, different types of equipment, and other differences in ultrasound images, the Society of Radiological Ultrasound has established a measurement of 7 mm or more as the CTE at which cardiac activity must be present. Thus, a definitive diagnosis of a nonviable pregnancy can only be made if the embryo is at least 7 mm long and has no signs of cardiac activity. The fetal heart rate increases during the first 6–8 weeks of pregnancy, with the lower limit of normal being about 100 beats per minute at 6.2 weeks gestation and 120 beats per minute at 6.3–7.0 weeks gestation. Fetal tachycardia, defined as a heart rate of 135 beats per minute or higher before 6.3 weeks of gestation or 155 beats per minute or higher at 6.3 to 7.0 weeks of gestation, has shown a good prognosis with a high probability of a normal outcome.
Embryonic morphology is quite simple until 7–8 weeks, when the spine can be visualized. After about 8 weeks of pregnancy, it becomes possible to visualize the embryo's head and four limb buds. The rhombencephalon, which is the developing hindbrain, becomes prominent at 8–10 weeks of gestation and appears as an anechoic, rounded structure in the head. Movements of the embryo can be observed after 8.0–8.5 weeks.
Second planned ultrasound: at 20-24 weeks
Examination in the second trimester is an extremely important event. By the 22nd week of pregnancy, all the internal systems and organs of the child are practically formed and active motor activity is observed, so you can assess the child’s condition and examine it in detail from all sides. In addition, this is when future parents can find out the sex of the child.
The main objectives of the second study:
- carrying out fetometry - determination of biometric indicators (length of tubular bones, circumference of the head, abdomen, biparietal and fronto-occipital size). Based on the data obtained, the child’s weight is calculated;
- identification of possible pathologies of fetal development;
- assessment of the size, maturity, structure and location of the placenta;
- conducting Doppler measurements - studies of uteroplacental circulation and blood flow in the aorta and middle cerebral artery of the fetus;
- assessment of the umbilical cord - it is possible to detect entanglement around the fetal neck, but at this stage it is not dangerous, since the child is actively moving and the situation can resolve itself;
- cervical assessment. The normal size is at least 3 cm. As labor approaches, it shortens and smoothes out. The internal opening must be completely closed. Violation of these parameters indicates isthmic-cervical insufficiency, requiring suturing of the cervix or insertion of an obstetric pessary.
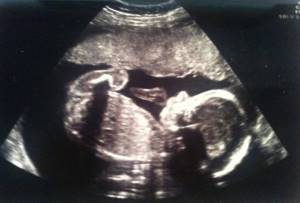
When is it better to perform 3D/4D ultrasound of the fetus?
The procedure does not harm the fetus at any stage of gestation - a three-dimensional ultrasound is performed in the same way as a regular one, the image is simply much clearer and more voluminous. You can do a 3D/4D ultrasound during screening or undergo a separate ultrasound examination at any stage of pregnancy:
3D/4D ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy:
In the first trimester of pregnancy, 3D/4D ultrasound is best performed at 11-14 weeks. In addition to the high efficiency of diagnostics using a 3D/4D device, the expectant mother gets the opportunity to see the baby as a whole, how he moves his small arms and legs, waves, crosses his legs, straightens his fists and sucks his thumb.
3D/4D ultrasound in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy:
In the second trimester of pregnancy, 3D/4D ultrasound is best done at 18-22 weeks. The fetus is becoming more and more like a newborn baby; its face is already formed. In the second trimester, the baby's facial expressions are actively developing - now you can see his first smile! The baby sucks his thumb and frowns. You can already recognize his ears, eyes and nose... for a short time you can still see the baby in full growth on a 3D/4D ultrasound machine.
3D/4D ultrasound in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy:
In the third trimester of pregnancy, 3D/4D ultrasound is most indicative at 30-35 weeks. This is the most favorable time for 3D/4D ultrasound examination; in addition to being informative, the image will be of greater interest to the mother. At this time, the baby has already formed all the vital systems. He already looks like a newborn baby, he even has eyelashes, nails, and sometimes hair on his head! He knows how to smile and open his eyes. In the third trimester, the baby develops all five senses - he sees light, tastes and smells amniotic fluid, hears sounds and feels touches through the mother's belly. Seeing your baby at this time is the greatest happiness for every mother!
Third planned ultrasound: at 32-34 weeks
An ultrasound in the third trimester is also extremely important, as the doctor determines how the delivery will proceed. In addition, it pursues the following goals:
- determination of the position and presentation of the fetus. The position in which the baby will be will not change until birth. The method of delivery will depend on it and on the presentation. So, with a longitudinal position and a normal cephalic presentation, this is a natural birth; with a transverse or oblique position and a pelvic presentation, this is a cesarean section;
- assessment of the size and weight of the fetus;
- assessment of the size, maturity and location of the placenta;
- assessment of the quantity and quality of amniotic fluid.
Examinations by doctors
| Specialists | Multiplicity | For what |
| Obstetrician-gynecologist | At least 7 times throughout pregnancy. | Examination with measurements, assessment of the course of pregnancy, assessment of the condition of the fetus and the health of the pregnant woman. |
| Therapist | The first time is during registration, the second time is in the 2nd or 3rd trimesters. | Determines the mother’s health status and the presence of chronic diseases. If necessary, prescribes treatment. |
| Dentist | The first time is when registering, the second time is in the 2nd or 3rd trimesters. | Examination, treatment of carious teeth and inflamed gums. |
| ENT | Once upon registration, then - as needed | Examination, treatment of diseases of the ENT organs. |
| Oculist | No later than 10 days after the first application to the housing complex. With good vision - once, with deviations - more often. | If there are changes in the eyes, the doctor may decide to perform a cesarean section. |
On a note:
* examination by an endocrinologist is optional, but recommended;
* genetic consultation - according to indications, more details - https://www.u-mama.ru/read/waiting/pregnancy/2055.html
* visiting other specialists - if necessary if there are health problems.
Unscheduled ultrasounds are prescribed as necessary and at the request of the patient
In some cases, a pregnant woman is prescribed an unscheduled ultrasound. It may be needed to assess the woman’s condition and prevent possible complications if pathologies or alarming symptoms occur:
- abnormal fetal development;
- discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the gestational age;
- abdominal pain;
- bloody issues;
- pathologies of placental maturation;
- absence of movements and other signs of the fetus;
- intrauterine developmental delay of the child.
Additional studies can be prescribed by a specialist at any period of gestation until birth.
Types of ultrasound at the effi clinic
We perform the following ultrasound examinations:
- Ankle joint - allows you to see the condition of tendons and ligaments, cartilage, detect fluid in the joint or bone osteophytes.
- Gallbladder - to determine the presence of polyps and stones, septations or deformation of shape, acute and chronic inflammatory processes, as well as evaluate the rheological properties of bile.
- Skin - examination allows you to detect inflammatory, tumor, degenerative and other pathologies.
- Knee and elbow joints – the examination reveals the cartilaginous surface of the joint, the bone surface, the membranes of the joint, ligaments, muscles and tendons.
- Uterus and appendages - determines the presence of inflammatory processes to control the treatment of uterine fibroids, as well as for any pathologies of the female reproductive system.
- Abdominal organs - the liver, spleen, gallbladder, pancreas are examined, the study ends with a survey scan to identify enlarged lymph nodes and other possible changes in the abdominal organs.
- Hip joints – allows free fluid in the cavity of the joint capsule, degenerative changes.
- Joints of the hands - used in the examination of inflammatory and degenerative lesions of joints and bones (arthritis and arthrosis), and surrounding tissues.
- Salivary glands - detects inflammatory diseases of the salivary glands (acute and chronic sialoadenitis), sialosis, salivary stone disease, adenomas and other tumor neoplasms.
- Prostate gland - allows you to determine the causes of problems such as impaired urination, pain in the lower abdomen during chronic and acute inflammatory processes in the prostate gland and seminal vesicles, prostate adenoma and other tumor formations.
- Kidneys and adrenal glands - allows you to determine the structure of the kidney tissue and its various changes, inflammatory processes, stones, simple and complicated cysts, as well as neoplasms. An obligatory stage of the study is to examine the adrenal glands for their enlargement and other structural changes.
- Thyroid gland - the method allows you to detect or suspect diffuse toxic goiter, nodular goiter, thyroiditis (inflammation), neoplasms and changes in the parathyroid glands.
- Soft tissues - the dermis, subcutaneous fat layer, tendons, muscles, blood vessels and lymph nodes are examined. Most often, doctors prescribe ultrasound scanning of soft tissues after operations, as well as to examine identified formations when examining various areas: abdomen, chest, back, neck and limbs and other areas.
- Bladder - allows you to study the features of the organ - the structure and condition of its walls, the position, shape and volume of the organ, the presence of stones, diverticula, ureterocele, as well as track the volume of residual urine.
- Breast organs is a scan of breast tissue. Ultrasound of the mammary glands can be performed on children, during pregnancy, during breastfeeding, on patients with implants installed, and on neoplasms. Reproductologists or gynecologists prescribe this study during pregnancy planning, IVF, and also for prevention. Ultrasound is done to identify life-threatening pathologies and timely treatment.
The norm of indicators determined by ultrasound. Tables by week of pregnancy
Fetal size by week of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Weight, g | Length, cm |
| 8 | 1 | 1,6 |
| 9 | 2 | 2,3 |
| 10 | 4 | 3,1 |
| 11 | 7 | 4,1 |
| 12 | 14 | 5,4 |
| 13 | 23 | 7,4 |
| 14 | 43 | 8,7 |
| 15 | 70 | 10,1 |
| 16 | 100 | 11,6 |
| 17 | 140 | 13 |
| 18 | 190 | 14,2 |
| 19 | 240 | 15,3 |
| 20 | 300 | 16,4 |
| 21 | 360 | 26,7 |
| 22 | 430 | 27,8 |
| 23 | 501 | 28,9 |
| 24 | 600 | 30 |
| 25 | 660 | 34,6 |
| 26 | 760 | 35,6 |
| 27 | 875 | 36,6 |
| 28 | 1005 | 37,6 |
| 29 | 1153 | 38,6 |
| 30 | 1319 | 39,9 |
| 31 | 1502 | 41,1 |
| 32 | 1702 | 42,4 |
| 33 | 1918 | 43,7 |
| 34 | 2146 | 45 |
| 35 | 2383 | 46,2 |
| 36 | 2622 | 47,4 |
| 37 | 2859 | 48,6 |
| 38 | 3083 | 49,8 |
| 39 | 3288 | 50,7 |
| 40 | 3462 | 51,2 |
| 41 | 3597 | 51,7 |
| 42 | 3685 | 51,5 |
Deviation of indicators in a smaller direction is a sign of intrauterine growth retardation; changes in a larger direction are a sign of a large fetus, which will complicate natural childbirth. In such cases, doctors prefer caesarean section.
Head sizes by week of pregnancy
| Gestation period, weeks. | Fronto-occipital size (LZR), mm | Biparietal size (BPR), mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 11 | 17 | 13-21 | ||
| 12 | 21 | 18-24 | ||
| 13 | 24 | 20-28 | ||
| 14 | 27 | 23-31 | ||
| 15 | 31 | 27-35 | ||
| 16 | 45 | 41-49 | 34 | 31-37 |
| 17 | 50 | 46-54 | 38 | 34-42 |
| 18 | 54 | 49-59 | 42 | 37-47 |
| 19 | 58 | 53-63 | 45 | 41-49 |
| 20 | 62 | 56-68 | 48 | 43-53 |
| 21 | 66 | 60-72 | 51 | 46-56 |
| 22 | 70 | 64-76 | 54 | 48-60 |
| 23 | 74 | 67-81 | 58 | 52-64 |
| 24 | 78 | 71-85 | 61 | 55-67 |
| 25 | 81 | 73-89 | 64 | 58-70 |
| 26 | 85 | 77-93 | 67 | 61-73 |
| 27 | 88 | 80-96 | 70 | 64-76 |
| 28 | 91 | 83-99 | 73 | 67-79 |
| 29 | 94 | 86-102 | 76 | 70-82 |
| 30 | 97 | 89-105 | 78 | 71-85 |
| 31 | 101 | 93-109 | 80 | 73-87 |
| 32 | 104 | 95-113 | 82 | 75-89 |
| 33 | 107 | 98-116 | 84 | 77-91 |
| 34 | 110 | 101-119 | 86 | 79-93 |
| 35 | 112 | 103-121 | 88 | 81-95 |
| 36 | 114 | 104-124 | 90 | 83-97 |
| 37 | 116 | 106-126 | 92 | 85-98 |
| 38 | 118 | 108-128 | 94 | 86-100 |
| 39 | 119 | 109-129 | 95 | 88-102 |
| 40 | 120 | 110-120 | 96 | 89-103 |
An increased size of the fetal head is a sign of hydrocephalus - an increase in the amount of fluid in the brain. To make such a diagnosis, the ventricles must also be enlarged. Sometimes the pathology is accompanied by other developmental disorders, so additional thorough research is necessary.
Abdominal circumference, fetal head
| Gestation period (weeks) | Abdominal circumference, mm | Head circumference, mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 11 | 51 | 40-62 | 63 | 53-73 |
| 12 | 61 | 50-72 | 71 | 58-84 |
| 13 | 69 | 58-80 | 84 | 73-96 |
| 14 | 78 | 66-90 | 97 | 84-110 |
| 15 | 90 | 110 | ||
| 16 | 102 | 88-116 | 124 | 112-136 |
| 17 | 112 | 93-131 | 135 | 121-149 |
| 18 | 124 | 104-144 | 146 | 131-161 |
| 19 | 134 | 114-154 | 158 | 142-174 |
| 20 | 144 | 124-164 | 170 | 154-186 |
| 21 | 157 | 137-177 | 183 | 166-200 |
| 22 | 169 | 148-190 | 195 | 178-212 |
| 23 | 181 | 160-202 | 207 | 190-224 |
| 24 | 193 | 172-224 | 219 | 201-237 |
| 25 | 206 | 183-229 | 232 | 214-250 |
| 26 | 217 | 194-217 | 243 | 224-262 |
| 27 | 229 | 205-229 | 254 | 235-273 |
| 28 | 241 | 217-241 | 265 | 245-285 |
| 29 | 253 | 228-278 | 275 | 255-295 |
| 30 | 264 | 238-290 | 285 | 265-305 |
| 31 | 274 | 247-301 | 294 | 273-315 |
| 32 | 286 | 258-314 | 304 | 283-325 |
| 33 | 296 | 267-325 | 311 | 289-333 |
| 34 | 306 | 276-336 | 317 | 295-339 |
| 35 | 315 | 285-345 | 322 | 299-345 |
| 36 | 323 | 292-354 | 326 | 303-349 |
| 37 | 330 | 299-361 | 330 | 307-353 |
| 38 | 336 | 304-368 | 333 | 309-357 |
| 39 | 342 | 310-374 | 335 | 311-359 |
| 40 | 347 | 313-347 | 337 | 312-362 |
Length of shin bones, femur femur
| Gestation period (weeks) | Abdominal circumference, mm | Head circumference, mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 11 | 5,6 | 3,4-7,8 | ||
| 12 | 7,3 | 4-10,8 | ||
| 13 | 9,4 | 7-11,8 | ||
| 14 | 12,4 | 9-15,8 | ||
| 15 | 16,2 | |||
| 16 | 18 | 15-21 | 20 | 17-23 |
| 17 | 21 | 17-25 | 24 | 20-28 |
| 18 | 24 | 20-28 | 27 | 23-31 |
| 19 | 27 | 23-31 | 30 | 26-34 |
| 20 | 30 | 26-34 | 33 | 29-37 |
| 21 | 33 | 29-37 | 36 | 32-40 |
| 22 | 35 | 31-39 | 39 | 35-43 |
| 23 | 38 | 34-42 | 41 | 37-45 |
| 24 | 40 | 36-44 | 44 | 40-48 |
| 25 | 42 | 38-46 | 46 | 42-50 |
| 26 | 45 | 41-49 | 49 | 45-53 |
| 27 | 47 | 43-51 | 51 | 47-55 |
| 28 | 49 | 45-53 | 53 | 49-57 |
| 29 | 51 | 48-55 | 55 | 50-60 |
| 30 | 53 | 49-57 | 57 | 52-62 |
| 31 | 55 | 50-60 | 59 | 54-64 |
| 32 | 56 | 51-61 | 61 | 56-66 |
| 33 | 58 | 53-63 | 63 | 58-68 |
| 34 | 60 | 55-65 | 65 | 60-70 |
| 35 | 61 | 56-66 | 67 | 62-72 |
| 36 | 62 | 57-67 | 69 | 64-74 |
| 37 | 64 | 59-69 | 71 | 66-76 |
| 38 | 65 | 60-70 | 73 | 68-78 |
| 39 | 66 | 61-71 | 74 | 69-80 |
| 40 | 67 | 62-72 | 75 | 70-80 |
Length of the humerus, fetal forearm bones
| Gestation period (weeks) | Abdominal circumference, mm | Head circumference, mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 16 | 15 | 12-18 | 18 | 15-21 |
| 17 | 18 | 15-21 | 21 | 17-25 |
| 18 | 20 | 17-23 | 24 | 20-28 |
| 19 | 23 | 20-26 | 27 | 23-31 |
| 20 | 26 | 22-29 | 30 | 26-34 |
| 21 | 28 | 24-32 | 33 | 29-37 |
| 22 | 30 | 26-34 | 35 | 31-39 |
| 23 | 33 | 29-37 | 38 | 34-42 |
| 24 | 35 | 31-39 | 40 | 36-44 |
| 25 | 37 | 33-41 | 43 | 39-47 |
| 26 | 39 | 35-43 | 45 | 41-49 |
| 27 | 41 | 37-45 | 47 | 43-51 |
| 28 | 43 | 39-47 | 49 | 45-53 |
| 29 | 44 | 40-48 | 51 | 47-55 |
| 30 | 46 | 42-50 | 53 | 49-57 |
| 31 | 48 | 44-52 | 55 | 51-59 |
| 32 | 49 | 45-53 | 55 | 52-59 |
| 33 | 50 | 46-54 | 58 | 54-62 |
| 34 | 52 | 48-56 | 59 | 55-63 |
| 35 | 53 | 49-57 | 61 | 57-65 |
| 36 | 54 | 50-58 | 62 | 58-66 |
| 37 | 55 | 51-59 | 63 | 59-67 |
| 38 | 56 | 52-60 | 64 | 60-68 |
| 39 | 57 | 53-61 | 65 | 60-70 |
| 40 | 58 | 54-62 | 66 | 61-71 |
Nuchal translucency (NVP) values in the first trimester of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Thickness of collar space, mm | |
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 10 weeks 0 days – 10 weeks 6 days | 1,5 | 0,8-2,2 |
| 11 weeks 0 days – 11 weeks 6 days | 1,6 | 0,8-2,2 |
| 12 weeks 0 days – 12 weeks 6 days | 1,6 | 0,7-2,5 |
| 13 weeks 0 days – 13 weeks 6 days | 1,7 | 0,7-2,7 |
If the nuchal translucency indicators are too high, the woman should consult a geneticist and undergo additional examinations as prescribed by a specialist:
- blood test for alpha fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin;
- amniocentesis - study of amniotic fluid;
- placentocentesis - study of placental cells;
- cordocentesis is the study of blood taken from the fetal umbilical cord.
Coccygeal-parietal size values 1st trimester of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Coccyx-parietal size, mm | |
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 10 weeks | 31 | 24-38 |
| 10 weeks 1 days | 33 | 25-41 |
| 10 weeks 2 days | 34 | 26-42 |
| 10 weeks 3 days | 35 | 27-43 |
| 10 weeks 4 days | 37 | 29-45 |
| 10 weeks 5 days | 39 | 31-47 |
| 10 weeks 6 days | 41 | 33-49 |
| 11 weeks | 42 | 34-50 |
| 11 weeks 1 days | 43 | 35-51 |
| 11 weeks 2 days | 44 | 36-52 |
| 11 weeks 3 days | 45 | 37-54 |
| 11 weeks 4 days | 47 | 38-56 |
| 11 weeks 5 days | 48 | 39-57 |
| 11 weeks 6 days | 49 | 40-58 |
| 12 weeks | 51 | 42-59 |
| 12 weeks 1 days | 53 | 44-62 |
| 12 weeks 2 days | 55 | 45-65 |
| 12 weeks 3 days | 57 | 47-67 |
| 12 weeks 4 days | 59 | 49-69 |
| 12 weeks 5 days | 61 | 50-72 |
| 12 weeks 6 days | 62 | 51-73 |
| 13 weeks | 63 | 51-75 |
| 13 weeks 1 days | 65 | 53-77 |
| 13 weeks 2 days | 66 | 54-78 |
| 13 weeks 3 days | 68 | 56-80 |
| 13 weeks 4 days | 70 | 58-82 |
| 13 weeks 5 days | 72 | 59-85 |
| 13 weeks 6 days | 74 | 61-87 |
| 14 weeks | 76 | 63-89 |
Normal heart rate by stage of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Heart rate, beats. |
| 10 | 161-179 |
| 11 | 153-177 |
| 12 | 150-174 |
| 13 | 147-171 |
| 14 | 146-168 |
A child's normal heartbeat is rhythmic, occurring at regular intervals, clear and distinct. Irregular heartbeats may indicate a congenital heart defect or fetal hypoxia, and a dull sound may indicate intrauterine oxygen deficiency.
If the heart rate exceeds the norm, a diagnosis of tachycardia is possible; if it decreases to 120 or less, a diagnosis of bradycardia is possible. A heart rate that goes beyond normal limits often occurs as a result of a reaction to a decrease in oxygen in the blood - fetal hypoxia. In this case, the woman is prescribed inpatient treatment aimed at improving uteroplacental blood flow and intracellular metabolism.
Normal values for placental thickness per week
| Gestation period (weeks) | Average, mm | Allowable fluctuations, mm |
| 20 | 21,96 | 16,7-28,6 |
| 21 | 22,81 | 17,4-29,7 |
| 22 | 23,66 | 18,1-30,7 |
| 23 | 24,55 | 18,8-31,8 |
| 24 | 25,37 | 19,6-32,9 |
| 25 | 26,22 | 20,3-34 |
| 26 | 27,07 | 21-35,1 |
| 27 | 27,92 | 21,7-36,2 |
| 28 | 28,78 | 22,4-37,3 |
| 29 | 29,63 | 23,2-38,4 |
| 30 | 30,48 | 23,9-39,5 |
| 31 | 31,33 | 24,6-40,6 |
| 32 | 32,18 | 25,3-41,6 |
| 33 | 33,04 | 24,6-40,6 |
| 34 | 33,89 | 25,3-41,6 |
| 35 | 34,74 | 26-42,7 |
| 36 | 35,59 | 28,2-46 |
| 37 | 34,35 | 27,8-45,8 |
| 38 | 34,07 | 27,5-45,5 |
| 39 | 33,78 | 27,1-45,3 |
| 40 | 33,5 | 26,7-45 |
If the thickness of the placenta exceeds the permissible normal values, this may indicate inflammation of the placenta (placentitis).
Normally, the placenta should be attached to the posterior wall of the uterus (rarely to the anterior or fundus). It should be 6 cm or more from the internal os of the cervix. Low attachment, marginal or central presentation with overlap of the internal os is a dangerous pathology that threatens the life and health of both mother and child. It often occurs in women who have given birth repeatedly, terminated pregnancies, or have inflammation or uterine fibroids. In this case, the woman needs careful hospital monitoring or at home with complete rest. With complete placenta previa, the birth of a child is possible only by caesarean section. If it is low, natural birth is possible, but there is a high risk of bleeding.
Degree of maturity of the placenta
| Gestation period (weeks) | Maturity level |
| up to 30 | 0 |
| 30-34 | 1 |
| 35-39 | 2 |
| after 39 | 3 |
The reason for late maturation of the placenta may be smoking by a pregnant woman or the presence of chronic diseases, and premature maturation may be due to gestosis, intrauterine infections, endocrine pathologies, termination of a previous pregnancy, and also smoking.
If such a deviation is detected in a woman, she needs to undergo a Doppler ultrasound and be tested for infections. After which a course of therapy is prescribed aimed at treating fetal hypoxia, vitamin supplementation, reducing uterine tone and getting rid of infection (if necessary).
Amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) index
| Gestation period (weeks) | Average, mm | Allowable fluctuations, mm |
| 16 | 121 | 73-201 |
| 17 | 127 | 77-211 |
| 18 | 133 | 80-220 |
| 19 | 137 | 83-225 |
| 20 | 141 | 86-230 |
| 21 | 143 | 88-233 |
| 22 | 145 | 89-235 |
| 23 | 146 | 90-237 |
| 24 | 147 | 90-238 |
| 25 | 147 | 89-240 |
| 26 | 147 | 89-242 |
| 27 | 146 | 85-245 |
| 28 | 146 | 86-249 |
| 29 | 145 | 84-254 |
| 30 | 145 | 82-258 |
| 31 | 144 | 79-263 |
| 32 | 144 | 77-269 |
| 33 | 143 | 74-274 |
| 34 | 142 | 72-278 |
| 35 | 140 | 70-279 |
| 36 | 138 | 68-279 |
| 37 | 135 | 66-275 |
| 38 | 132 | 65-269 |
| 39 | 127 | 64-255 |
| 40 | 123 | 63-240 |
Deviation of indicators towards a smaller or larger direction indicates oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, respectively. In case of polyhydramnios, a woman is prescribed mandatory treatment with antibiotics and drugs to improve uteroplacental blood flow. Oligohydramnios indicates a severe fetal malformation - the complete absence of kidneys. In this case, appropriate therapy is carried out to support the child.
An important indicator is the quality of the amniotic fluid. Normally, it should be transparent, without turbidity, mucus, or flakes. Otherwise, this may be a sign of the development of an infectious process.