This organic fat-like substance performs many important functions. Without it, the synthesis of hormones, the absorption of most vitamins, the formation of bile acids, and hematopoiesis are impossible. Most of the cholesterol is produced inside the body, about 20% comes from the outside, with food. An increase in the level of this compound is fraught with the development of atherosclerosis and other diseases. Excess cholesterol fills the lumen of blood vessels and settles in the gallbladder in the form of stones.
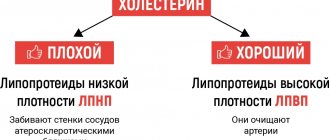
What is good and bad cholesterol
In tissues and blood, cholesterol forms special complexes with groups of lipoprotein proteins. They ensure its stable suspended state. Some of them have high density, others low. These properties of lipoproteins determine the types of cholesterol:
- “good”: HDL, protects cells from damage, ensures normal blood flow and vascular elasticity;
- “bad”: LDL, prone to precipitation, forming atherosclerotic plaques.
It is low-density cholesterol that is meant when they talk about its harm to health. This is true, since its excess is directly related to cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, poor circulation and the risk of strokes. LDL promotes the accumulation of triglycerides - simple fatty acids, overloads the liver, and contributes to the development of gallstones. High-density cholesterol inhibits these pathological processes and partially neutralizes the effect of the “bad”.
What to do if there are deviations from the norm
If a patient understands the indications of cholesterol levels in blood tests, they will be able to understand when treatment is needed. If deviations from normal values are small, it is enough to change your lifestyle and diet. The following measures will help normalize cholesterol levels:
- quit smoking and stop drinking alcoholic beverages;
- exclude fatty foods, sauces, fried foods, sweets, and confectionery from the diet;
- eat more vegetables and fruits;
- increase physical activity, walk, ride a bike, do gymnastics;
- Go to bed on time, avoid overtiredness.
These methods can reduce cholesterol levels by 10-15%. But if there is a serious deviation, they will not help. Therefore, it is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations and take prescribed medications. Statins are most often used in combination with fibrates. The doctor selects the necessary medications.
Sometimes you need to increase your cholesterol. At the same time, the amount of HDL increases, which helps prevent atherosclerosis. To do this, you also need to change your diet and lifestyle, and give up bad habits. It is recommended to consume more polyunsaturated fatty acids; they are found in vegetable oil and fatty fish. Medicines containing vitamin B3 are prescribed.
To prevent vascular disease, every adult needs to have blood tests for cholesterol every 3-5 years. In this case, it is advisable to know how it is indicated on the form. You won’t be able to fully decipher the results yourself, but you can find out whether there is a risk of cardiovascular disease. The work of many organs is associated with this substance. Therefore, any deviation from the norm indicates a serious violation of metabolic processes.
Measuring cholesterol levels: general norms
To determine the level of cholesterol in the blood, a special unit is used: millimoles (mmol). Calculate the number of mmol per 1 liter of biological fluid. The total cholesterol content is important, as is the concentration of HDL and LDL separately. The level of triglycerides in the blood is also important, which is used to judge the risk of atherosclerotic changes in the body, disorders of fat metabolism and liver function.
- Normal total cholesterol: 3–7.8 mmol/l. During life it fluctuates depending on age and hormonal status. This is the average rate throughout life, the same for men and women.
- Low-density cholesterol—“bad” LDL—ideally should range between 1.8–2.8 mmol/L. The upper limit for women is up to 4.5 mmol/l. For men - up to 4.8 mmol/l. Its limit level: 5.7 mmol/l.
- The level of high-density “good” HDL is normally half that of “bad”: 0.8–2.4 mmol/l for women and 0.7–1.7 mmol/l for men.
The higher the low-density cholesterol level, the more critical the health condition. Especially if the level of a good high-density connection does not reach the norm:
- A regular increase in LDL levels to 4 or more mmol/l is dangerous;
- a constant decrease in LPV to 0.7 mmol/l also signals problems in the body.
Triglycerides are measured in the same way as other cholesterol levels. Their normal level in the blood throughout life is up to 2.2 mmol/l. It is the same for the male and female halves of humanity.
Signs of violations:
- elevated triglyceride levels: 2.3–5.6 mmol/l;
- dangerously high, signaling a disease: 5.7 mmol/l or more.
The risk of developing atherosclerosis is real at any age, but young people are more protected from it due to their high metabolic rate. Their cholesterol is quickly consumed by hormones and other physiological processes. Estrogen protects women from deposits of fatty plaques in blood vessels. However, with a sedentary lifestyle, a love of unhealthy foods, or the presence of systemic diseases, cholesterol also increases in young people. Over the years, its level grows even faster.
Explanation of meanings
When receiving a form with the test result, many patients do not understand what is written there. Deciphering a blood test for cholesterol is complex, since many factors and several indicators must be taken into account at once. For example, if Chol is elevated due to LDL and triglycerides, it will need to be lowered. But if this happened due to an increase in HDL, there is nothing to worry about, since this substance frees blood vessels from cholesterol plaques. Therefore, only a doctor can determine whether correction of cholesterol levels is necessary.
Chol or TS
The level of total cholesterol is designated in tests as Chol or TC. This indicator is necessarily included in any biochemical analysis. It is determined for preventive or diagnostic purposes. It shows how much of it is present in the blood. This allows us to draw a conclusion about the state of metabolic processes. The normal level for an adult should be no more than 5.2 mmol/l.
Cholesterol is synthesized in the liver and from there enters the blood. This substance is soluble only in fats, so it is not present in the blood in free form, but is part of lipoproteins - compounds of cholesterol molecules with proteins.
TRIG or TG
In women, the transcript of a blood test for cholesterol often contains indicators of the amount of triglycerides. They are designated by the letters TRIG or TG. It is a combination of fatty acids and glycerol. They come from fatty foods and are found in adipose tissue. If there are a lot of them, this threatens to block blood vessels. An increase in TG levels often occurs in diabetes mellitus. In healthy people, their amount should not exceed 1.7 mmol/l.
HDL
This designation determines the amount of high-density lipoprotein. Their main job is to bind LDL and transport it to the liver for disposal. Therefore, HDL cleanses blood vessels from cholesterol plaques. Therefore, their number should not be less than the norm. And in people with cardiovascular diseases, the higher it is, the better. To prevent the development of atherosclerosis, the HDL level should be at least 1.6 mmol/l.
VLDL
These letters indicate very low density lipoproteins. They contain a large number of cholesterol molecules, so they are often deposited on the walls of blood vessels. Low density lipoproteins are formed from them. It is a building material and a source of energy. The amount of VLDL should not be more than 1 mmol/l.
LDL
These letters indicate the level of low-density lipoprotein. This compound is called “bad” cholesterol. It should not be more than 3.5 mmol/l. A slight increase in the amount leads to its accumulation in the vessels. This happens when a lot of fat comes from food, because LDL is still produced in the liver. Narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels can lead to increased blood pressure and disruption of blood supply to tissues.
I.A.
To assess the risk of atherosclerosis, it is also necessary to determine the atherogenicity index. It is designated IA. Sometimes you can see the letters KA or CATR. This is the ratio of low and high density lipoproteins. The atherogenicity index is calculated based on the remaining results. You need to subtract the amount of HDL from the total Chol, and then divide the result by HDL. It should be less than 3. This means that the amount of high-density lipoproteins is such that they cope with the removal of “bad” cholesterol.
Changes in cholesterol standards by age in women
Differences in metabolism and the functioning of body systems at each stage of life also affect cholesterol levels. Over the years, due to a slowdown in metabolism, it inevitably increases. Changing total cholesterol averages for women:
- up to 5 years: from 2.90 to 5.18 mmol/l;
- 5-10 years: from 2.26 to 5.30 mmol/l;
- 10-15 years: from 3.21 to 5.20 mmol/l;
- 15-25 years: from 3.10-5.5 mmol/l;
- 25-35 years: from 3.37 to 5.96 mmol/l;
- 35-40 years: from 3.63 to 6.27 mmol/l;
- 40-50 years: from 3.81 to 6.53 mmol/l;
- 50-60 years: from 4.45 to 7.77 mmol/l;
- 60-70 years: from 4.45 to 7.69 mmol/l;
- 70 years or more: from 4.48 to 7.25 mmol/l.
A significant increase in the upper limit of indicators in women over 60 years of age is explained by the decline of ovarian function. During this period, the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and osteoporosis increases.
Why do you need a blood test?
The state of human health greatly depends on the composition of the blood. Therefore, tests help the doctor make a diagnosis or prevent serious pathologies. To do this, a general analysis is performed to evaluate the cellular composition of the blood that is taken from the finger. Biochemical analysis provides detailed information about the presence of hormones, enzymes and other substances. It definitely includes cholesterol.
This substance belongs to lipids. It is used to build cell membranes, participates in the synthesis of hormones, digestion and removal of toxins. Therefore, the body needs cholesterol for normal functioning. But it is beneficial only when the amount is within the normal range. If this level rises, the excess accumulates in the vessels. Because of this, coronary heart disease develops, blood pressure rises, and cerebral circulation is impaired.
To avoid dangerous consequences, every adult is recommended to regularly check their cholesterol levels. A doctor may also prescribe a blood test in the following cases:
- people with a hereditary predisposition to cardiovascular diseases;
- when diagnosing atherosclerosis or the causes of high blood pressure;
- for liver diseases;
- diabetes mellitus;
- for diagnosing diseases of the endocrine system;
- in case of metabolic disorders;
- to assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
A person himself can ask for a referral for such a blood test if he experiences frequent malaise, decreased performance, or worsened mood. Increased cholesterol levels may be indicated by memory impairment, heaviness in the legs, and the appearance of yellow spots under the skin. In addition, it is recommended to donate blood annually even if you feel normal in the following cases:
- smoking;
- being overweight;
- frequent increases in blood pressure;
- people who move little;
- those who are over 40 years old.
Changes in cholesterol levels over the years in men
Men are naturally protected from atherosclerosis less than women. They do not have a high level of estrogen in the body, but they have a higher craving for bad habits that increase the risk of dangerous diseases.
Norms of total cholesterol in men:
- up to 5 years: from 2.95-5.25 mmol/l;
- 5-10 years: from 3.13 to 5.25 mmol/l;
- 10-15 years: from 3.08 to 5.23 mmol/l;
- 15-25 years: from 2.93 to 5.59 mmol/l;
- 25-35 years: from 3.44-6.58 mmol/l;
- 35-40 years: from 3.78-6.99 mmol/l;
- 40-50 years: from 3.91 to 7.15 mmol/l;
- 50-60 years: from 4.09 to 7.17 mmol/l;
- 60-70 years: from 4.12 to 7.15 mmol/l
- 70 years or more: from 3.73 to 7.86 mmol/l.
The closer the cholesterol level is to the lower limit of normal, the safer it is for blood vessels and the heart. Regular levels exceeding 5–6 mmol/l signal the need to prevent atherosclerosis. It is especially important to monitor indicators for men over 50 years of age. From this age their growth accelerates.
Ways to Maintain Normal Cholesterol Levels
High levels are recorded in a biochemical blood test. If the numbers regularly exceed the norm, it is important to undergo a medical examination of the thyroid, pancreas, liver, and take a hormonal profile test. To normalize fat metabolism, courses of antilipid drugs are prescribed.
A therapeutic diet low in meat and dairy products also helps lower total cholesterol. It is useful to include sea fish containing Omega-3 complex, olive, flaxseed, sunflower oils, fresh vegetables, and herbs in your food.
Preparing for a cholesterol test
No preparatory measures are provided, however, the physical and psychological state of the patient may affect the results of the study. To avoid errors, try to fulfill the following conditions:
- limit sports and other physical activities (can cause a false jump in HDL levels;
- exclude alcohol-containing drinks and medications (at least 3 days before);
- make sure that your last meal is 8-12 hours before the test; follow your normal diet, but avoid fatty foods;
- postpone physical procedures and hardware examinations (preferably after taking blood);
- stop taking medications (if this is not possible, notify your doctor).
The test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach. You can drink a glass of clean water first