From this article you will learn: why and when an ECG is done during pregnancy, what disorders can be detected using this test, and how this examination is carried out.
Author of the article: Nivelichuk Taras, head of the department of anesthesiology and intensive care, work experience 8 years. Higher education in the specialty “General Medicine”.
Article publication date: 04/07/2017
Article updated date: 05/29/2019
Electrocardiography (ECG, cardiogram) is an examination method that can help detect problems with the electrical activity of the heart.
Electrocardiography is performed on a pregnant woman to assess the functioning of the heart under conditions of increasing stress on the body.
During pregnancy, an ECG is recorded for:
- checking the electrical activity of the heart;
- searching for the causes of symptoms of cardiovascular diseases in pregnant women;
- checking the condition of the heart if the expectant mother has other diseases and complications of pregnancy.
During the entire period of bearing a child, every pregnant woman undergoes this test at least once. It is mandatory to record a cardiogram in the third trimester. This is a completely safe examination with no contraindications. A pregnant woman who has any diseases affecting the cardiovascular system needs to undergo this test several times during the entire period of bearing a child - at least in each trimester, and more often if necessary.
Interpretation of examination results in pregnant women is carried out by therapists and cardiologists.
Changes in the cardiovascular system affecting ECG in pregnant women
Pregnancy is stressful for the heart and circulatory system. During pregnancy, the volume of blood in the vascular bed increases by 30–50%, this provides nutrients to the growing baby. The amount of blood pumped by the heart every minute also increases by 30–50%. In addition, the heart rate increases. All these changes make the heart work harder.
Pregnancy also affects the size of the heart and its position in the chest. The enlarged uterus puts pressure on the diaphragm, which moves upward and changes the position of the heart. Its size increases during pregnancy by approximately 12%.
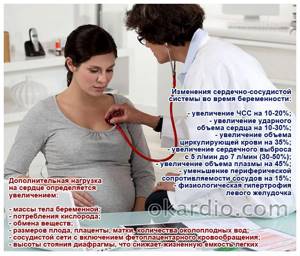
These changes in the size and position of the heart, and its harder work, can lead to the characteristic ECG appearance during pregnancy.
ECG during pregnancy - exercise test
For most pregnant women, it is important to check your heart rate not at rest, but with an exercise ECG. To do this, an exercise test is carried out, that is, a test that is carried out on a cycloergometer in a lying position, as well as on a cycloergometer in a sitting position or even on a treadmill. Using a stress test, you can evaluate physical performance, chronotropic response to pressure, and the presence of exercise-induced arrhythmia. Is an ECG in this form safe during pregnancy? Absolutely. There are no contraindications to its implementation, and the stress test is absolutely not a cause of miscarriage.
Preparing to take a cardiogram
In order for the test to pass as quickly and efficiently as possible, the following tips may be useful:
- Tell your doctor about all the medications you are taking, as many of them may affect the test results.
- Instead, wear clothes that are easy to take off or unbutton at the chest.
- On the day before the test, no creams should be applied to the skin, as they affect electrical conductivity.
- Remove all jewelry from your neck and arms in advance.
- Ask your doctor any questions you have about this test, its risks, and its results.
No special preparation is needed to record an ECG. Immediately before the test, you should avoid physical activity and do not drink cold water.

How is the examination carried out?
Typically, an ECG during pregnancy is carried out in a medical institution - a clinic, outpatient clinic, hospital. Since the machine itself that records the cardiogram is portable, this test can be performed almost anywhere.
During the examination:
- You will have to lie down on a couch or bed, exposing the chest, forearm and lower leg area.
- The healthcare professional applies a special gel to the skin of these areas that reduces electrical resistance.
- Electrodes are attached to the skin of the arms, legs and chest, which are connected to a machine that records the electrical activity of the heart on paper.
- During the test, you need to lie still and breathe normally. Sometimes your healthcare provider may ask you to take a deep breath and hold your breath. You cannot speak during the examination.
- You need to relax and not tremble, as any movement can affect the result.
- After recording is completed, the electrodes are removed from the skin and the gel is wiped off.
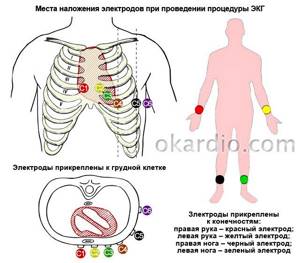
The duration of ECG recording rarely exceeds 10 minutes. After this, the electrodes are removed from the skin.
How is electrocardiography performed?
Some visitors to medical institutions do not know how electrocardiography is performed:
- 1. The office has a couch on which the study is performed.
- 2. The doctor attaches the electrodes to the chest and limbs.
- 3. Next, you should lie in a calm position, as the device operates and records the readings of the heart muscle. The information is displayed on a computer monitor and then printed on paper.
Our clinic specialists interpret the results. The conclusion is given to the person examined - the process takes from 15 to 30 minutes. If necessary, you can get advice from an experienced cardiologist at the center.
Diseases that can be detected using an ECG
Registration of an ECG during pregnancy helps diagnose many heart diseases in expectant mothers. With this test, doctors can detect:
- fast or slow heartbeat;
- heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias);
- disturbances in the passage of electrical impulses in the heart (blockade);
- an increase in the size of the heart and thickening of its walls (hypertrophy);
- the cause of heart disease symptoms (eg, shortness of breath, heart pain, dizziness, fainting);
- signs of congenital heart defects in a pregnant woman;
- signs of electrolyte disturbances (increased or decreased levels of potassium, magnesium, calcium in the blood).
Electrocardiography during pregnancy: pros and cons
During pregnancy, a woman undergoes the procedure of taking an electrocardiogram at least twice, both for herself and for the fetus.
The cardiogram is recorded using electrodes located on the surface of the skin; with their help, the electrical activity of the heart is determined, the indicators of which are recorded on paper, among which the rhythm and frequency of the heartbeat are indicated.
In the absence of special medical indications, an electrocardiogram is taken for a pregnant woman twice: when registering for pregnancy and when going on maternity leave.
Carrying out this procedure is necessary to identify possible abnormalities in the functioning of the heart, and if there are any abnormalities, the pregnant woman is recommended to be observed by a cardiologist. Various forms of arrhythmias and blockade are the most common deviations.
Is it necessary to do an ECG during pregnancy?
An electrocardiogram study must be done to prematurely identify abnormal cardiac activity; in addition, with the help of an ECG it is possible to prevent gestosis, that is, a disorder of organs and systems in the body that can lead to a number of complications during pregnancy. If the pregnancy proceeds normally, then no significant changes in the cardiogram are observed. However, changes in the cardiogram during pregnancy do occur, and they are associated with displacement of the diaphragm and heart.
Indications for ECG examination
There are a number of indications based on which a pregnant woman is sent for an ECG. Firstly, this referral occurs during registration along with other tests to check the general health of the body and its readiness to bear a child.
During pregnancy, a woman may be referred for an unscheduled ECG examination in case of frequent pressure surges (sudden increases and decreases).
In addition, clear indications for unscheduled ECG examinations are pain in the heart, frequent dizziness and sudden fainting.
Also, additional reading of cardiograms is prescribed in case of complications during pregnancy, such as severe toxicosis, low blood pressure or polyhydramnios.
However, an unscheduled appointment of an ECG procedure does not indicate critical health problems, and it is necessary to clarify certain parameters of the body and is completely safe for both the woman and the child in the stomach.
The procedure for performing an ECG in pregnant women
The procedure for taking an ECG is carried out using a cardiograph and is absolutely painless; it is carried out in the same way as for any other population groups. Before taking a cardiogram, electrode plates are applied to the wrists and shins, and suction cups with electrodes are applied to the area of the heart. When recording an electrocardiogram, twelve graphs are printed on the cardiographic tape showing the directions of cardiac impulses.
There are a number of rules for the patient that must be followed to obtain an objective electrocardiogram: firstly, you must be moderately well-fed during this procedure (meal should be approximately two hours before the study). Secondly, you need to come rested, without climbing high stairs, since general or physical activity immediately before the examination can provoke a deterioration in the real picture of your health.
Is it harmful to have an ECG test during pregnancy?
Today, an ECG study is one of the safest diagnostic methods for all groups of the population, including pregnant women. Electrocardiography does not produce any negative effects, since this research method is passive and does not have any effect on the body, but only registers the human electric field emanating from the heart.
Electrocardiographic examination has no contraindications and can be performed a large number of times, regardless of time intervals. This study is carried out in pregnant women, young children, and seriously ill patients.
Interpretation of ECG results for a pregnant woman
Only a doctor can fully decipher cardiograms, but it is useful for everyone to know the general parameters.
The main point when decoding a cardiogram is to study the frequency and nature of the heartbeat; normal heart rate (heart rate) is considered to be a value in the range from 60 to 80 beats per minute. A heart rate of less than 60 beats is considered bradycardia, and a heart rate of more than 90 is considered tachycardia.
During pregnancy, excitation in the atria may occur, and if this phenomenon occurs frequently, additional examination is necessary.
Registration of fetal ECG during pregnancy
Electrocardiography of the fetus during pregnancy is called cardiotocography (CTG). Basically, such a study is carried out in the last months of pregnancy and immediately before childbirth. CTG is used to measure the baby's heart rate and, during labor, the frequency of contractions. Also, this procedure can be performed, if necessary, at earlier stages of pregnancy to study the condition of the fetus.
This procedure is absolutely safe for both the mother and her unborn child.
Processing ECG results
Interpretation of a cardiogram recording requires quite a lot of experience from the doctor. The results of the examination will be known on the day of its conduct; decoding usually takes no more than 10–15 minutes.
In his conclusion, the doctor indicates the nature of the heart rhythm, the frequency of heart contractions, the electrical axis of the heart (characteristics of the position of the heart), and describes existing disturbances in electrical conductivity (if any). Diagnosis is not made solely on the basis of a cardiogram; symptoms and signs of the disease are also taken into account.
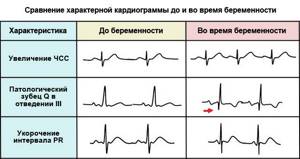
Features of a cardiogram in pregnant women
Changes in the cardiovascular system characteristic of pregnancy change the character of the cardiogram, especially in the later stages.
ECG of pregnant women is characterized by:
- Increased heart rate.
- Shift of the electrical axis to the left.
- Shortening the PR interval.
- Negative T wave in leads III, V
- Pathological Q wave in leads III, aVF.
It should be remembered that all these characteristic features of the ECG during pregnancy are not observed in all women.
Fetal ECG - features
When asked whether it is possible to perform an ECG during pregnancy, everyone unanimously gives a positive answer. The procedure is safe for the child. Sensors are attached to the woman's abdomen; they will record the baby's heartbeat, as well as the number of uterine contractions. It is recommended to conduct the study in the morning or after seven o'clock in the evening.
Interesting! To increase the baby's activity, it is recommended to eat a small amount of chocolate a few hours before the procedure.
The baby's respiratory activity and full rest cycles are formed by the 29th week, which is why this is the time when the procedure is performed. If abnormalities are detected, treatment is prescribed, and an ECG is repeated ten days later. If fetal hypoxia has been detected, the procedure is performed once a day.
A specialist deciphers the analyzes
The test results are reflected in a 10-point system, it looks like this:
- 5 points – hospitalization is required;
- 6-7 points - additional examination is necessary to identify the cause of the deviation;
- 8-10 points – the child is healthy, nothing threatens his development.
In this case, the attending physician also deciphers the tests.
Contraindications
An ECG is one of the few studies that has no contraindications. Moreover, during the period of gestation, doctors strongly recommend carrying out the procedure, because this is the only way to understand whether there are any deviations.
The procedure can be carried out up to several times a day, no harm will be caused to the body or the child.
Thus, we can conclude that an ECG during pregnancy is not only not prohibited, but also useful. You need to take responsibility for your health and the health of your unborn child, because this is the only way to avoid many complications.
Limitations of ECG
Like many diagnostic methods, ECG has certain disadvantages and limitations:
- This is a static method and may not reflect existing heart problems if there are no symptoms at the time of recording.
- Many pathological changes on the cardiogram can be nonspecific, that is, observed in various diseases. To clarify the diagnosis in such cases, additional examinations are carried out.
- In some heart diseases, the cardiogram may be completely normal.
CTG during pregnancy
A good cardiotocogram during pregnancy includes signs such as a basal rhythm of 120-160 beats per minute, absent deceleration, present acceleration (5 or more - for 45-60 minutes during the recording itself), as well as variability of 5-25 beats. min.
But such an ideal picture is quite rare, which is why variants of the norm are allowed for the following indicators: basal rhythm with a lower limit of 110 beats per minute, as well as the presence of single short-term decelerations lasting no more than 10 seconds. in amplitude no more than 20 beats (and after them the heart rhythm should fully recover).
Pathological CTG is considered if:
- there is a lack of acceleration or a slowdown in the rhythm, but the basal one is normal - this is a silent CTG;
- a so-called sinusoidal cardiotocogram is observed, but with a small amplitude - from 6 to 10 beats per minute. (this may indicate fetal hypoxia);
- there is an alternation of accelerations coming after decelerations - this is the Lambda rhythm and in 95% it indicates the presence of compression of the umbilical cord.
In addition, cardiotocography indicators do not always reflect the correct reality regarding the condition of the fetus at the current moment. Even if the nature of the recorded recording seems somewhat alarming due to a short-term disruption of blood flow (due to compression of the umbilical cord vessels by the fetal head), the child himself in the womb will not suffer. Sometimes a different picture is observed when, during prolonged hypoxia, the cardiotocogram displays quite acceptable indicators. As a result, additional studies are prescribed to clarify the parameters of the performed cardiotocography.