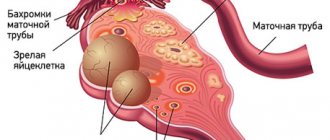
Ultrasound examination of the ovaries is the most important examination for women aimed at diagnosing complications, pathologies or diseases of the reproductive system of the female body. The ovaries themselves are small glands that are located in the pelvic area in women. The shape, size and presence of pathologies in the ovaries can be identified in different ways, but the most popular and effective is an ultrasound examination of the ovaries.
Indications for ultrasound of the ovaries
The content of the article
It is rarely performed as an independent procedure. As a rule, an ultrasound of the ovaries is performed in conjunction with an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. In some cases, the procedure is prescribed if it is necessary to assess the functional activity of the ovaries. This is mainly necessary when diagnosing the causes of female infertility.
In this case, an ovarian examination is performed to measure the dominant follicle when a woman has been unable to become pregnant for a long period. In this case, over a certain period, the doctor observes the follicle and records the occurrence or absence of ovulation. This examination of the ovaries is called folliculometry.
Also, indications for prescribing ultrasound of the ovaries are:
- irregular menstrual cycle, absence of menstruation (if not during pregnancy);
- regular nagging or sharp pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- too scanty or heavy menstrual bleeding;
- unusually severe menstrual pain;
- breast disease;
- suspicion of infertility;
- inflammation of the appendages;
- suspected pathology;
- preparation for pregnancy;
- preparation for IVF;
- preventive examination.
Restrictions
Ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus is a fairly fast and reliable method of examination. And yet, it is possible to make a diagnosis when it comes to tumor formation only by approaching diagnosis in a versatile and comprehensive manner. Unfortunately, it is impossible to accurately assess the tumor based on ultrasound results and distinguish its nature. To clarify whether this tumor is malignant or has a different nature, it is necessary to resort to histological examination or MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast.
| Ultrasound service of pelvic organs | Price, rub | Promotion Price |
| Ultrasound of the bladder with determination of residual urine | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis in women and men with an abdominal sensor | 1200 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis in women with a vaginal probe | 1300 rub. | |
| Comprehensive pelvic ultrasound with abdominal and vaginal probe | 1400 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of folliculogenesis | 750 rub. | |
| Ultrasound cervicometry | 1100 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland with a rectal probe | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum (testicles, appendages) | 1000 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the prostate and bladder with an abdominal probe | 1900 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the pelvis with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
What pathologies does ultrasound examination of the ovaries reveal?
Ultrasound of the ovaries is a fairly effective method in identifying pathologies, and with its help it is possible to detect some diseases even at the preclinical (before the onset of symptoms) stage, and those pathologies that cannot be detected using other research methods.
- An ovarian cyst
(functional and pathological) is a benign neoplasm characterized by the formation of a fluid-filled protrusion on the ovary (or both at once). The pathology is dangerous due to degeneration into a malignant tumor, provocation of infertility, peritonitis or disruption of the functioning of neighboring organs. - Polycystic ovary syndrome
is a hormonal disease in which the ovaries increase in size and accumulate many cysts. The disease provokes infertility because it prevents ovulation from occurring, i.e. release of eggs from the ovary. - Salpingo-oophoritis
is a joint infectious and inflammatory process in the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Independent inflammation of the ovary - oophoritis - is a fairly rare occurrence. The pathological process is caused by infection (streptococci, staphylococci, chlamydia, etc.). Most often it comes from the vagina and uterus along the ascending route. - Ovarian torsion
is a serious pathological condition in which the nutrition of the ovary is disrupted. Requires immediate medical attention. - Malignant tumors - cancer.
What can be seen with a gynecological ultrasound?
Ultrasound of the ovaries can reveal various pathologies:
- Anovulation as a probable cause of infertility.
- Volumetric formations of the gonads: cysts and tumors.
- Inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Anomalies of appendage development.
An ultrasound scan helps to find the cause of the pathological process and select the optimal treatment.
Gynecological ultrasound can also detect diseases of the uterus and fallopian tubes. The technique is actively used in the diagnosis of various conditions during pregnancy.
Question to the expert
Tell me, on what day of the menstrual cycle is an ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries performed? The doctor advised me to undergo an examination, but the date was not indicated in the direction.
Ultrasound of the uterus and ovary is done by default on the 5-7th day of the cycle, unless the doctor gives other instructions.
Sonography technique
There are three ways to examine the ovaries using ultrasound. The doctor chooses a specific method taking into account the patient’s medical history.
- Transabdominal
- carried out using an external sensor through the abdominal wall. This method is the most comfortable, but the least informative; it can only be used to identify gross organ dysfunction. It is usually used during a general gynecological examination, for virgins and women with vaginal malformations. - Transvaginal
- performed using an intracavitary sensor (transducer), which is inserted into the vagina. The method is the most accurate and informative, since the sensor is located in close proximity to the internal organs. May be accompanied by minor discomfort during insertion of the sensor. This type of ultrasound is contraindicated for virgins and for vaginal malformations. - Transrectal
- carried out using an intracavitary sensor (thinner than for TVU), which is inserted into the rectum. The method is absolutely painless, but very uncomfortable for the woman. It is carried out in individual cases when TAU turned out to be insufficiently informative, and TVU cannot be performed for objective reasons (virginity, atresia (fusion), severe stenosis (narrowing) of the vaginal opening, etc.).
The duration of the procedure is about 15 – 20 minutes.
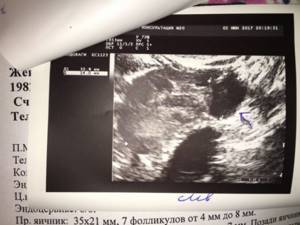
How to do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs
When performing ultrasound diagnostics in women, the following anatomical structures of the small pelvis are consistently “looked at”: the cervix and uterus, the ovaries with tubes, the periuterine space (vaults).
PREPARATION FOR THE STUDY.
Performing a pelvic ultrasound on a woman is quite simple - no complicated preparation is required. When performing diagnostics with a vaginal sensor, the bladder is emptied before starting. If an abdominal sensor is planned for the study, for example, in children and virgin girls, then, on the contrary, the bladder should be full. On the eve of the visit to the clinic, it is recommended to eat a diet that reduces gas formation in the intestines, as well as taking several tablets of activated carbon at night.
DIAGNOSTIC METHODS
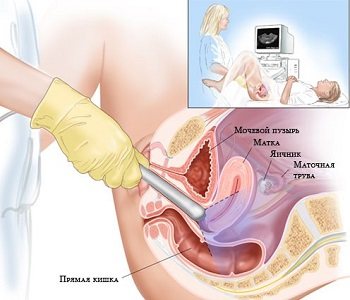
- Vaginal ultrasound of the pelvis. Vaginal ultrasound is the main method of echographic diagnosis in obstetric and gynecological practice. The medical term "vaginal ultrasound" means that it is performed through the vagina. The woman will need to either lie on her back or side, with her knees bent and pointed towards her chest. An ultrasound sensor with a condom on it is gently inserted into the vagina. By moving the tip of the sensor in different directions, the doctor transmits images of the pelvic organs to the monitor. The information transmitted by the vaginal sensor is displayed on the screen of the ultrasound machine in different projections, and scaling allows you to zoom in on the picture and examine the details of interest in more detail. Also, during the course of the study, the specialist periodically takes photos and videos of the scan results of the pelvic organs, which will later make it possible to better analyze the data obtained and/or write them to a disk or flash card. It should be borne in mind that vaginal ultrasound is performed only on women who have begun to be sexually active. For virgins, pelvic examination is not performed in this way. Therefore, when you come to the clinic to receive this service as a virgin, it would be reasonable to warn the diagnostician in advance about this circumstance. Ultrasound with a vaginal sensor is performed for a woman either as a separate ultrasound examination during the initial visit, or in combination with an abdominal one after a gynecological examination on the chair. If necessary and according to indications, two-dimensional echography is supplemented by ultrasound scanning of blood vessels.
- Abdominal pelvic ultrasound. This technique is a way to identify pathologies in children, teenage girls and patients who have not been sexually active. Also used in obstetric practice for pregnancy screenings and follow-up. Ultrasound is performed through abdominal access for virgins and other patients after mandatory preliminary filling of the bladder.
- Rectal ultrasound of the pelvis. Prescribed for men, virgin girls and women who have contraindications to vaginal examination. First of all, the rectal method for diagnosing the pelvic organs is used for patients who are not sexually active. The hymen makes it impossible to insert a sensor into the vagina without damaging it, so ultrasound through the anus is used. To do this, the patient lies on the couch in a side-lying position and pulls her knees towards her stomach. A condom is put on a sensor with a diameter of no more than 1.5 - 2.0 cm, lubricated with a special gel and inserted through the anus into the rectum, after which the image is displayed on the scanner screen.
Figure No. 1. “How a pelvic ultrasound is performed for women (abdominal and vaginal).”
|
|
| 1. Abdominal ultrasound | 2. Vaginal ultrasound |
After this study, the patient receives a description of the pelvic ultrasound result with a photo, transcript and specialist’s conclusion. If desired, the ultrasound doctor can order an additional service - recording the entire diagnostic process and its findings on a DVD. In the latter case, you should warn your doctor about this in advance. The table below shows several photographs of the results of such diagnostics carried out with vaginal and abdominal sensors.
PHOTO OF PELVIC ULTRASOUND
| Pregnancy 6 weeks. | Pregnancy 23 weeks. | Uterine fibroids |
| Intrauterine polyps | Ovarian cystadenomatosis | Follicular cyst |
On what day of the cycle should it be done?
The timing of a pelvic ultrasound should be determined, first of all, by your gynecologist. It is better to initially look at the small pelvis on an ultrasound in the first phase of the menstrual cycle, on the 5th - 7th day from the start of menstruation. The doctor may prescribe this diagnosis on other days of the cycle, for example, to monitor the maturation of the follicle in the ovary when planning pregnancy or to identify certain diseases. If there are complaints, for example, pain, uterine bleeding, etc., the phase of the cycle does not matter.
Which pelvic ultrasound is best?
A good ultrasound of the pelvic organs is one that is done on the right day of the menstrual cycle by a qualified specialist. We have already talked above about two types of this diagnosis - ultrasound with an abdominal sensor (i.e. external, along the abdomen) and vaginal ultrasound (i.e. internal, through the vagina). As an option, sometimes a pelvic ultrasound can be done with a vaginal probe through the rectum. If it is planned to carry out both types, then a transabdominal examination is first performed for a full bladder, and then, after urination, a transvaginal examination is done.
Which method of ultrasound diagnostics of organs should you choose? If there are no restrictions, preference should be given to conducting the study using the transvaginal method - visualization in this case is better, pelvic ultrasound in women will be more informative. This is explained by the fact that in this case, ultrasound immediately reaches the uterus and ovaries, bypassing other formations (intestines and bladder - as if done through the abdominal wall).
If you want to determine pregnancy in the early stages, identify small uterine fibroids, take a good look at the signs of chronic inflammation and adhesions in the area of the appendages, it is better to sign up and have an ultrasound scan with a vaginal sensor. In our clinic, all of the listed methods of ultrasound diagnostics are available, which are carried out on a modern, new ultrasound scanner equipped with Doppler and 3D/4D functions.
Ultrasound for virgins
For teenage girls and virgin girls, pelvic ultrasound is performed externally, abdominally, i.e. on the abdomen, or with a transrectal sensor. The bladder should be full before the examination. The fact that the organ is filled to the required level should be indicated by a moderate desire to visit the toilet. This condition will facilitate diagnosis - it will help the uterus take a place convenient for examination, and will displace the lower part of the gastrointestinal tract from view.
When should girls - virgins and girls who are not sexually active - undergo an ultrasound examination using this method? It is advisable to be examined on days 5–7 of the menstrual cycle. In some cases, a virgin undergoes a vaginal ultrasound of the pelvic organs (if the diameter of the hole in the hymen allows the instrument to be inserted into the vagina). As an option, an ultrasound of the uterus and appendages can be done with a rectal probe carefully inserted into the rectum.
Cost of services
| Pelvic ultrasound: | ! | Price |
| Vaginal sensor | 3 000 | |
| Abdominal sensor | 2 500 | |
| Rectal ultrasound of the pelvis | 3 000 | |
| Combined | 4 500 |
| Tubal patency (HSG ultrasound) | 9 000 |
| Determination of pregnancy (term and location) | 3 000 |
| Find out the gender of the child | 2 500 |
Where to go for a pelvic ultrasound in Moscow
Thus, diagnosing the pelvis by ultrasound is an informative and useful procedure for women of all ages. In our clinic it is carried out by competent, qualified specialists. A modern scanner, equipped with all options, including vaginal, abdominal, rectal and 3D/4D sensors, will allow you to conduct research with maximum accuracy. It is possible not only to perform an ultrasound, but also to video record the procedure on digital media (DVD or flash drive).
✔ You can sign up for a pelvic ultrasound, including on weekends (Saturday and Sunday), by calling contact numbers or by clicking the “ONLINE REGISTRATION” button on the page below. It is also possible to see a gynecologist and undergo tests during one visit.
How to sign up for a pelvic ultrasound
- An appointment with a doctor for a pelvic ultrasound in women at the clinic is made by calling 8(495)749-4997 from 9-00 to 22-00 daily;
- You can also make an appointment around the clock on the website 24/7/365; for detailed information and the work schedule of a specialist in the ultrasound diagnostic room, see the link below. On Saturdays and Sundays, as well as on some holidays and weekends, studies are carried out on a shortened schedule, from 10-00 to 18-00.
| Address: Moscow, Kutuzovsky Prospekt, 35. Telephone from 10 to 21. near the metro station and the Kutuzovskaya MCC |
We are on Yandex map
How to prepare for the procedure
Each research method requires special preparation in order to obtain the most accurate and informative result.
Transabdominal ultrasound of the ovaries
This type of study requires careful preparation, including a slag-free diet and cleansing the intestines of gases. 2-3 days before the procedure, you must stop eating foods that cause flatulence (carbonated drinks, beans, fresh fruits and vegetables, yeast and dairy products, etc.). One day before, start taking adsorbent drugs (smecta, espumizan, activated carbon, etc.).
During the procedure, the bladder must be full, so the woman needs to drink 1 liter of liquid (non-carbonated and non-dairy) an hour before the procedure and not urinate.
Transvaginal ultrasound of the ovary
Special preparation for such an ultrasound is not needed, since the only condition for its implementation is an empty bladder. Immediately before the procedure, the woman simply needs to urinate. If there is a tendency to increased gas formation, two days a day, start taking medications that reduce flatulence (smecta, espumizan, activated carbon, etc.).
Transrectal ultrasound
Preparation for such an ultrasound is similar to preparation for a transvaginal examination. Additionally, 9–10 hours before, it is necessary to clear the intestines of feces using a cleansing enema (1–1.5 l), microenemas, glycerin suppository or laxative.
The timing of the study depends on its purpose. If the ultrasound is planned, then it is performed on the 5th – 6th day of the menstrual cycle and no later than a week after the end of menstruation. In severe situations, an ultrasound is performed on the day symptoms are detected. If it is necessary to evaluate the functioning of the ovaries, the procedure is prescribed three times (on days 8-9, on days 14-15 and on days 22-23 of the menstrual cycle).
Folliculometry
Folliculometry is an ultrasound examination that allows you to monitor the growth and development of follicles in the ovaries throughout the menstrual cycle. The purpose of the method is to choose the ideal day to conceive a child. Therefore, folliculometry is carried out several times in one cycle or several.
Overall, the study aims to track folliculogenesis (follicle maturation) and determine the date of ovulation. Ultrasound of the ovaries helps to find out whether there is a need for artificial stimulation of ovulation.
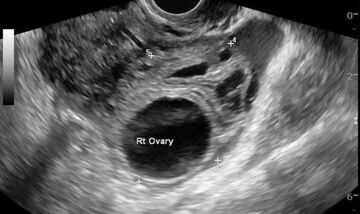
How is the procedure performed?
Transabdominal method.
The patient lies with her back on the couch and exposes her stomach. The doctor applies a special gel to the area of the abdomen projected to the ovaries to improve contact with the sensor, and then scans the ovaries by moving the device over this area.
Transvaginal method.
The patient exposes part of the body below the waist and lies with her back on the couch, bending her knees. The doctor carefully inserts a cavity sensor into the vagina, onto which he previously put a condom to prevent the entry of foreign microflora and lubricated it with lubricant. The transducer is inserted shallowly, approximately 5–8 cm.
Transrectal method.
The patient exposes the lower part of the body and lies sideways on the couch, bending her knees. The doctor slowly and carefully inserts a sensor into the anus, onto which a condom has previously been put on and a lubricant has been applied to reduce discomfort and unpleasant sensations for the woman to a minimum.
During the examination, the doctor evaluates the structure of the ovaries, their condition, size, location, confirms or denies the presence of pathological changes and inclusions. Upon completion of the procedure, he gives the patient an ultrasound report, with which the woman must contact the treating specialist to receive treatment.
Pregnancy management
When a long-awaited pregnancy occurs, you really need to find your doctor. This should be a person you can trust, with whom you can easily find mutual understanding, who respects privacy and confidentiality. These are the kind of obstetricians and gynecologists who work in Scandinavia to make pregnancy as easy as possible, and the birth of a baby remains a joyful memory.
You can find our pregnancy management programs here.
Department of Pregnancy Pathology
Despite the naturalness of the process, not every pregnancy goes smoothly, and you need to be prepared for this. Therefore, in Scandinavia, the pregnancy pathology department operates around the clock: you can come here if you have any symptoms or complications and count on timely and high-quality help.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the ovaries: norms
Normally, the ovaries are located on the sides of the uterus at a short distance from it, often asymmetrically. On the monitor they are visualized as oval, fairly defined, hypoechoic formations, while the ovaries are not identical to each other, the difference in their sizes is minimal. Their surface is considered normal to be lumpy due to the follicles maturing in them. The more time has passed since the beginning of the cycle, the larger these tubercles are.
Normally, the ovaries should be free of cystic, tumor-like and other formations, and the organ itself should not be enlarged. The interpretation of the results contains an indication of the sizes of the ovaries and follicles.
Standard indicators for ovarian size are presented in the table. Values may vary depending on the patient’s age, cycle phase, number of pregnancies, etc.
| Length | 2 – 3.7 cm |
| Width | 1.8 – 3 cm |
| Volume | : 4 – 10 cm 3 |
| Thickness | 1.4 – 2.2 cm |
After the onset of menopause, the ovaries decrease in size and volume by almost 2 times (on average to 2 cm3), their silhouette becomes uneven, wrinkled, and their echogenicity increases.
Normally, the ovaries consist of a capsule and follicles of varying degrees of maturity, the number of which on the left and right may differ. In healthy women, the following follicle indicators are visualized depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle:
| 5 – 7 day | 5 – 10 formations 0.2 – 0.6 cm each |
| 8 – 10 day | 5 – 9 formations up to 1 cm in size, dominant 1.2–1.5 cm |
| 11 – 14 days | dominant follicle size: 1.6–2 cm; Ovulation typically occurs at 1.8 cm |
| 15 – 18 days | corpus luteum (1.5–2 cm) at the site of the burst follicle |
| 19 – 23 days | the size of the corpus luteum is already 2.5–2.7 cm |
| 24 – 27 days | corpus luteum size: 1–1.5 cm |
Abnormal cystic formations
A dermoid cyst is considered a benign tumor and appears as a result of improper distribution of tissues in the body. The cavity of the cyst in this case consists of cells that should form the skin and other components, but end up in the ovaries. As a result, the cyst is filled with cells from hair, cartilage and nails. On an ultrasound machine it will look like a ball with very dense walls (up to 15 mm) and a high level of echogenicity. If this type of pathology is suspected, the doctor may prescribe an MRI or CT scan.
An endometrioid cyst is determined by ultrasound by the following signs:
• a round or oval formation is filled with liquid;
• located on one side, consists of one chamber;
• cystic walls are thin (up to 8 mm);
• the external structure is clear, the internal one is covered with irregularities;
• the ovary in the place where the cyst is found is not visible;
• the uterus is increased in size, but without changes in structure and shape;
• a healthy ovary contains many small follicles; up to 3 dominant follicles can mature in it;
• “honeycombs” are visible in the cavity - inclusions of an echo-positive nature of a linear, arc-shaped or ring-shaped shape, the thickness of which does not exceed 2 mm.
Polycystic disease can appear in girls and young women if their body produces too many male sex hormones. With this disease, the diameter of the ovaries reaches more than 10 cubic meters. cm with clearly visible cysts inside them with a diameter of up to 9 mm. The organ capsule becomes very thick
Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor that most often occurs in women during menopause, and in more rare cases - in young girls or girls who have not yet started menstruation. The doctor should be wary if an ultrasound showed the presence of a multi-chamber cyst with poorly defined contents, which began to develop on organs located close to it. A symptom of cancer can be the appearance of fluid in the peritoneum and pelvis.
In this case, the woman is prescribed a series of repeated examinations. If she has reached the age of 45 years older, or this is discovered in a girl before the start of her menstrual period, the doctor sends the patient for a biopsy.
Why are the ovaries not visible on ultrasound?
In some cases, the doctor cannot recognize the ovary on an ultrasound. This may happen for the following reasons:
- congenital absence of ovaries;
- removal during surgery;
- premature organ depletion;
- severe bloating;
- high density of the abdominal wall with pelvioperitonitis;
- severe adhesive disease of the pelvis;
- dense fatty layer or scars on the anterior abdominal wall.
In this case, a repeat study is usually carried out, in preparation for which an obligatory emphasis is placed on getting rid of flatulence with the help of medications.
Can an ultrasound detect signs of an impending miscarriage?
During a miscarriage, the fertilized egg separates from the inner wall of the uterus and, as a result of contraction of the myometrium, it is expelled from the uterine cavity. This process is divided into phases: a threatened miscarriage, one that has begun, one that is “in progress,” and one that has occurred. Excessive tension (hypertonicity) of the uterine muscles is determined by ultrasound.
ONLINE CONSULTATIONS We treat where it is convenient for you MORE DETAILS

Ovarian pathologies and their signs on ultrasound
Some conditions, such as luteal cyst (corpus luteum cyst) and follicular cyst, are considered “normal” and do not require treatment because they usually heal spontaneously as soon as hormonal levels change. Other cysts and diseases are pathological and require mandatory treatment.
On ultrasound, the cyst looks like a formation of 2.5 cm with liquid inside, having a different structure and degree of staining.
| Ovarian damage | The ovaries have the appearance of oval hypoechoic formations with an uneven intermittent contour; fluid (blood) or echogenic signals of various sizes and shapes (blood clots) may be detected along the lateral uterine wall or in the uterine space |
| Salpingo-oophoritis, oophoritis (acute form) | Increased ovarian size; clear, defined contour; reduced sound conductivity due to swelling; hypoechoic areas can be detected - foci of necrosis (small abscesses) |
| Salpingo-oophoritis, oophoritis (chronic form) | Normal or slightly enlarged ovarian size; fuzzy, blurred outline; increased echogenicity of the organ; heterogeneous tissue structure |
| Dermoid cyst | Visible round neoplasm with thickened walls from 0.7 to 1.5 cm, which contains various hyperechoic inclusions inside |
| Endometrioid cyst | The formation is relatively small in size (up to 7 cm in diameter) with a double contour; unilateral localization - behind or to the side of the uterus; medium and increased echogenicity of non-displaceable fine suspension |
| Polycystic ovary syndrome | Increased size of the ovaries (volume more than 7 cm3); cysts are found in both ovaries (from 10 pieces in each of them) with a diameter of 2 to 8 mm; location of cysts along the periphery of the ovarian structure |
| Malignant tumor | A cyst that has several chambers and spreads to neighboring organs; unclear contents of the cyst; accumulation of fluid in the pelvis or abdominal cavity |
Any pathology detected on ultrasound of the ovaries must be confirmed by other research methods, only after which an accurate final diagnosis can be made.
The following ultrasound diagnostic indicators are considered normal:
In women 16-40 years old, the sizes of both ovaries should not differ (length 30-41 mm, thickness - 14-22 mm, width - 20-31 mm). The normal volume of each of them is 12 cubic meters. ml. The outer surface of the ovary is lumpy and consists of many follicles. The degree of echogenicity of the stroma resembles the uterus. The total number of follicles must be at least 12; if there are less than 5, then we are talking about abnormal functioning of the follicular apparatus.
In the middle of the menstrual period, one dominant follicle of larger size should appear. Subsequently, an egg is released from it, and after 2 weeks a corpus luteum is formed in this area.
Research Alternative
There are many alternative methods for examining the ovaries, among which the most commonly prescribed are:
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging;
- puncture of the pouch of Douglas followed by cytological analysis of the washout;
- diagnostic laparoscopy (laparotomy) with express biopsy and taking smears.
Ultrasound of the ovaries is the most universal method of examination and stands out among the rest.
Its advantages are as follows:
- non-invasive (without tissue trauma) research method;
- painless;
- much cheaper and more accessible than other methods;
- absolutely harmless to the body - no ionizing radiation is used, so it can be carried out repeatedly;
- perfectly visualizes soft tissues, unlike x-rays;
- ideal for monitoring intrauterine development of the fetus;
- shows the state of the body in “real time”, thanks to which it is possible to diagnose even an acute disease without resorting to puncture of the posterior vaginal vault and biopsy.