Osteoscintigraphy, or bone scintigraphy, is a study of the osteoarticular system that allows us to identify foci of metastatic lesions, malignant tumors, inflammatory and degenerative processes. As a modern diagnostic method, bone scintigraphy allows us to identify a wide range of bone tissue pathologies even before the appearance of radiological signs of the disease.
- Indications for osteoscintigraphy of skeletal bones
- Methods
- Preparing for bone scintigraphy
- How is osteoscintigraphy performed?
- Side effects of osteoscintigraphy
- Contraindications
What does it show?
Using a scintigraphic examination, which is based on radiation diagnostics, doctors identify various pathologies that are inaccessible to other diagnostic methods, including in the early stages of development:
- Causes of unexplained bone pain;
- Hidden fracture that is not visible on an x-ray;
- Osteomyelitis;
- Bone cancer;
- Metastasis to bones in cancer of other organs.
If we are talking about scintigraphy in oncology, it is important to understand that this method allows us to identify the dynamics of treatment, and therefore confirms its effectiveness or indicates the need to change prescriptions.
Preparation for skeletal bone scintigraphy: not required.
Within an hour after the administration of the radiopharmaceutical, you will be asked to drink 1 liter of drinking water, as this is necessary to improve the accumulation of the drug in the skeletal bones and reduce radiation exposure. Immediately before the test, you must empty your bladder.
results
Photo: Pharm-sintez CJSC
The radiologist issues a conclusion the next day after the examination.
The photographs visualize the entire human skeleton. This is very important for identifying metastases, which are often located in the bones of the skull, ribs and spine.
Bone scintigraphy makes it possible to determine the exact location of the lesion (in bones or soft tissues), as well as to distinguish a malignant formation from a benign or other pathological process (inflammation, infection, mechanical damage).
Features of scintigraphy of skeletal bones:
The study is carried out 3 hours after administration of the radiopharmaceutical. Takes from 10 to 30 minutes. The conclusion is issued on the day of the study.
When patients come for the study, they must have with them extracts from their medical records or an outpatient card, conclusions (if available) based on the results of X-ray studies, CT, MRI, as well as the results of previous scintigraphic studies.
Radiopharmaceuticals (RPs) used: diagnosis of skeletal bone diseases is carried out with labeled phosphate complexes, which strongly bind to hydroxyapatite crystals and immature collagen. 99mTs is used as a tag, which has a short half-life - only 6 hours. Gamma quanta leave the body and are registered by the detectors of the device, resulting in an image after computer processing.
Normal scintigram of skeletal bones in anterior and posterior projection:
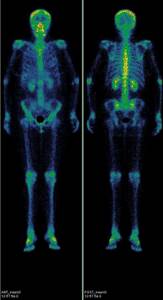
Metastases of various tumors to bone
Many tumors metastasize to the bones. First of all, suspicion of metastatic damage to the skeleton arises in breast and prostate cancer, lung cancer, kidney cancer and some others. Particular caution should be exercised when the level of tumor markers increases, for example: PSA (prostate-specific antigen), CA 15-3 and some others. After conservative treatment or surgical removal of the tumor, dynamic monitoring of the condition of the bone tissue is recommended. Scintigraphy should be performed the first 2 times with an interval of 6-8 months, then, if the study result is normal, after 1-2 years. You should clarify the need for repeat studies with a radiologist or your attending physician.
The advantages of radionuclide diagnostics include the ability to detect bone tissue pathology before the development of clinical and radiological signs of bone damage.
Sequencing
For confidence and peace of mind, the patient must know how the examination is carried out in order to be prepared for it. Diagnosis takes place in specialized medical centers and clinics. First, the patient signs a written consent to undergo a bone scan. Then they proceed in the following sequence:
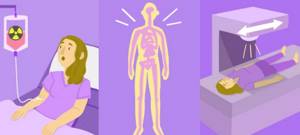
- A drug is administered intravenously - a radiotracer, which, spreading through the blood throughout the body, penetrates into the bone tissue. The body absorbs the contrast agent. The doctor conducting and monitoring the process must correctly calculate the amount of isotope. After three hours, the bone skeleton is saturated with liquid. While waiting for the process, it is recommended to drink plenty of clean water and bed rest. It is important to take a comfortable horizontal position and limit movements.
- Using a gamma camera, the musculoskeletal system is examined using an image. A radiopharmaceutical, a radiopharmaceutical, is used. The patient is placed on the treatment table. The examination process takes at least an hour, during which time the person must remain motionless. During hardware scanning, areas of damage are detected thanks to charged indicators that are concentrated in the damaged areas.
- After the procedure, it is recommended to drink a liter of clean, warm water. This will increase the rate of removal of the contrast agent from the body. A small number of them are dangerous for children under 14 years of age and pregnant women. After the procedure, radiation from a person occurs; contact with the child and pregnant woman should be limited.
The results of the examination should be given to the attending physician. Further interpretation of the results is carried out to establish an accurate diagnosis. It is strongly not recommended to read the indicators or diagnose the disease yourself, this is the job of a doctor! The type and regimen of therapeutic treatment is prescribed. Cooperation with the doctor and compliance with all recommendations contribute to effective treatment.
Inflammatory and traumatic changes in bone tissue
One of the indications for radionuclide studies of the skeletal system (bone scintigraphy) is inflammatory changes in bone tissue. The method allows you to determine the prevalence of the process by identifying foci of inflammation in the bones and joints throughout the skeleton, even in the early stages of the disease. Radiographs of osteomyelitis usually reveal a less widespread process than it actually is. Scintigraphy shows the true size of the inflammatory focus.
In addition, this method can detect fractures and assess how well they are healing. Bone fractures are often an incidental finding, such as rib fractures in patients with advanced osteoporosis. In some cases, it is possible to detect a violation of the integrity of bones in the early stages, when x-ray examination does not allow this, for example, fractures of the scaphoid bone, ribs.
Possible complications
If the procedure is carried out with contraindications, complications are possible. Diagnostic scintigraphy is a safe type of bone examination that does not entail serious complications. But in some cases side effects are observed:
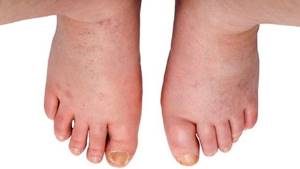
- Allergic reactions: swelling of the limbs, body parts. Severe itching, hives, redness and peeling of the skin.
- Dizziness, state of weakness, instability.
- Headache.
- Nausea, digestive tract disorders, discomfort in the stomach and intestines.
- Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath.
- Rapid heartbeat, tachycardia, arrhythmia.
- Deterioration of the general condition of the body, feeling of weakness, lethargy.
The type of complication and well-being depends on the characteristics of the body, the severity of the disease and the health of the patient. In the advanced stage of a serious disease, if contraindications are ignored, the complications are deplorable. It is important to cooperate with your doctor, follow his recommendations and consultations. Then the examination procedure will be painless and without consequences.
Osteoscintigraphy in orthopedics and vertebrology
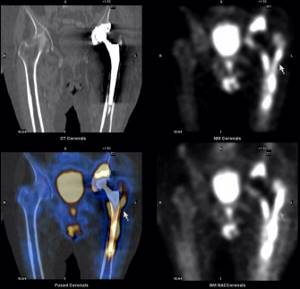
When replacing joints or installing metal structures in the spine, scintigraphy of the skeleton bones allows us to detect mechanical instability of the prosthesis components (looseness) or an inflammatory process around the prosthesis or metal structure. Unlike other research methods (X-ray, CT, MRI), scintigraphy of skeletal bones makes it possible to determine the intensity of the inflammatory process in various parts of the bone.
Additional SPECT/CT with the possibility of slice-by-slice image analysis allows you to more accurately localize the area of damage, which makes it possible to carry out the necessary treatment in a timely manner. Advantages of SPECT/CT over planar scintigraphy: lack of summation (sectional analysis of radiopharmaceutical accumulation), and precise localization due to the combination of radionuclide and CT images.
Survey reliability
Patients doubt how much they can trust the scan and the results obtained. The scintigraphy procedure is imperfect, like all examination methods. In some cases, diagnostic results may turn out to be false and may not correspond to the actual condition. But among other imaging methods, the error statistics for scintigraphy is 1%. The reason for a false reading sometimes lies in the uneven introduction and distribution of a specific contrast agent. In this case, the indicators signal a pathological accumulation of fluid in the skeletal localization, the spread of metastases, or the development of pathologies. In fact, the reason is the unprofessional technique of distributing the excipient and the doctor’s insufficiently professional approach.
Also, signs of malignant, pathological tissue damage can be diagnosed in those places of the skeleton where injuries, bruises or fractures previously occurred. Therefore, before the examination, it is worth telling the doctor about all injuries to the musculoskeletal system of the body. This will help avoid unnecessary worries and false diagnoses. The doctor conducting the skeletal scanning process must filter the information received to focus on areas that indicate actual diseases and pathologies.
Scintigraphy is a reliable and accurate bone examination method. The negative impact on humans is minimal, and the results obtained about the health of the body are characterized by increased accuracy and reliability.
In isolated cases, unreliable images occur due to insufficient experience of the attending physician or equipment malfunction. False indicators may also be influenced by non-compliance with preparation for the examination and recommendations of medical personnel.
How is recovery after the procedure?
The examination is carried out in a gamma camera, which illuminates the human body with radioactive rays, detecting radiopharmaceuticals in the bones and joints. Despite the apparent complexity, the procedure does not produce any harmful consequences and immediately after diagnosis the patient can return to their normal lifestyle. Recommendations for the rehabilitation period include monitoring sufficient fluid intake on the first day (the more, the better), as well as observing good personal hygiene measures - thorough bathing, washing all things.
Contraindications
Before starting the procedure, patients who suffer from cardiovascular diseases and are taking any medications to treat them should inform the doctor about this. This is not an obstacle to undergoing osteoscintigraphy, but requires more careful monitoring of the patient's condition during the procedure.
The procedure is contraindicated for pregnant women. Women who are breastfeeding should feed their baby immediately before the test. After the procedure, they should express and discard breast milk once, after which they can resume breastfeeding.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78