The photo shows a traditional closed-circuit MRI scanner. Magnetic resonance imaging is a high-tech diagnostic method that allows you to visualize bone structures and surrounding soft tissues of the body. The advantage of the procedure is the safety and information content of the images. There are several types of devices: open and closed MRI. The devices have their differences, pros and cons. A closed-type MRI device is considered classic, but the principle of operation of tomographs is identical.
The research is based on the use of magnetic induction. The field generated by the device interacts with hydrogen atoms, exciting them. Depending on the saturation of tissues with water, the intensity of the return signal will change. The device's sensors record the response, and the computer processes the information. The minimum imaging step is 1 mm, so pathological areas of even small size can be identified, for example, when examining the brain or oncology. Radiologists receive images, interpret the information and issue a report. The picture can be combined into a 3D model and video.
The difference between open and closed MRI is their design. A traditional tomograph is represented by a tube into which the subject is placed. The open-loop device looks like two “plates” between which the patient is positioned. The device is suitable for people with a fear of confined spaces, but the results are less informative. Some authors highlight the semi-open appearance of the devices, but this is incorrect.
The most important classification of tomographs is based on the strength of the magnetic field generated by the device. There are low-field devices (0.15-1 T), high-field (up to 3 T) and ultra-high-field (more than 3 T). High-field devices with a closed loop are used more often in clinical practice due to the reliability of the results, the speed of image acquisition and the absence of negative effects on the human body. The terms “half-open” and “half-closed” are not used in relation to MRI scanners, being a marketing ploy.
Open MRI
Photo of an open-ended MRI machine
An open-ended MRI device does not have a tube. Magnetic field sources and sensors are located under the table and above the table: from the sides the subject will have a view of what is happening in the room. The impact occurs only in one plane - perpendicular to the body. The structural features of this type of device lead to low power (from 0.15 to 1.0 Tesla) of the latter. The described technical characteristics lead to a longer scanning process and reduced image quality compared to closed-loop devices.
There is no such type of tomograph as a semi-open MR scanner. When you encounter this concept on the Internet, the tricks of marketers become available to your attention.
Many patients prefer to have an open-type MRI scanner because of the comfort. The device makes less loud sounds when operating. The patient sees the entire room, which opens up the possibility of performing an examination for claustrophobia.
Another significant difference between the described type of equipment is the availability of MRI for people weighing more than 120 kg. The scanner is not limited by the tunnel diameter and can expand. The maximum weight in this case is 200 kg.
Advantages of open MRI
The doctor will choose an examination due to the advantages:
- maintaining the relative accuracy of the result with minor movement during the procedure;
- performing diagnostics on young children without sedation or sedatives;
- lower noise level;
- fear of confined spaces does not limit the use of the method;
- easier tomography with reduced physical activity of the subject;
- MRI is allowed for body weight more than 120 kg.
Disadvantages of open MRI
There are serious drawbacks that may cause your doctor to recommend doing an MRI on a different scanner. These may include:
- less accurate images;
- It is impossible to evaluate moving organs (lungs, heart, etc.).
When studying the brain and searching for small defects, maximum resolution is required, so it is better to give preference to traditional equipment.
Which MRI machine should you prefer?
To conduct an MRI of the spine, heart and other organs, it is necessary to have sufficient experience of the specialists themselves, the availability of appropriate software, as well as the equipment itself, which is an example of high technology. This means that before the procedure you should understand which device should be preferred in a given situation.
The most important characteristic that should be taken into account when choosing an MRI is its power. Since this parameter directly affects the reliability and quality of the images obtained, which in turn affects the quality of the diagnosis. The most important thing in diagnosis will be the quality of the image, which determines the power of the magnet itself. Therefore, a low-field, open-type device gives worse image quality than a high-field, closed-type device.
All current MRI equipment is equipped with software necessary for clear interpretation of data and magnets of the required power.
As a result, the doctor has a lot of data needed to make the correct diagnosis. The devices currently used in diagnostic centers are much quieter than their predecessors in terms of noise levels. For this reason, the level of convenience during the examination increases significantly.
High-field MRI machine
With minor differences in image quality, one and a half Tesla devices make it possible to conduct research over a wider area. As a result, it is possible to diagnose different organs. This type of tomograph is a fairly informative device that is used to extract accurate information necessary for correct diagnosis. The latest versions of this equipment allow you to obtain all the data necessary for an error-free conclusion. The equipment of the latest models makes it possible to obtain all the necessary data for diagnostics within a short period of time.
Closed-type MRI
MRI on a closed-type tomograph is a classic imaging method. The device looks like a short and wide pipe in which magnetic field sources are located. The latter affects the body from all sides in a circle. The structural features provide greater power compared to other equipment - up to 3 Tesla in clinical practice. The described difference makes diagnosis faster, and the images are of better quality and detail.
The subject is placed on a mobile table, fastened with belts and placed inside the tunnel. The work process is accompanied by loud sounds, crackling, knocking. It is important to remain still during the procedure. If the patient moves, the reliability of the image will decrease.
Doctors leave the room and monitor the process from a separate room. You can maintain constant communication using a radio device. During the diagnostic test, one of the parents is allowed to stay with the child during the MRI to calm the baby.
The limitation for using the apparatus of this design option is the presence of claustrophobia. Prolonged stay in a confined space accompanied by loud noises can trigger an attack. However, if you notify the specialists in advance, they will select a sedative for you, put on headphones with relaxing music, and the examination will take place without unnecessary stress. Another limitation is the patient’s weight is more than 120 kg. The structure may not withstand a large mass and break.
Advantages of closed-type MRI
There are a few differences that may make it better to choose the traditional option. These include:
- high accuracy of the result, regardless of the area of the body (suitable for examining the brain, determining the malignant potential of tumors, imaging the heart, etc.);
- difference in scanning duration - the average duration of native MRI is 15 minutes.
Disadvantages of closed-type MRI
There are the following disadvantages of using the device:
- limiting the weight of the subject to 120 kg;
- claustrophobia may be a contraindication to tomography;
- high noise level (you can use earplugs or headphones with pleasant music);
- complete stillness is required to obtain high-quality photographs.
Types of MRI studies
MRI of the head
- MRI of the sinuses
- MRI of the eye orbits
- MRI of the pituitary gland
- MRI of the brain
- MRI of the ear and auditory nerve
MRI of the spine
- MRI of the thoracic region
- MRI of the lumbosacral region
- MRI of the cervical spine
- MRI of 3 parts of the spine
Vascular MRI
- MRI of cerebral vessels
- MRI of neck vessels
- MRI of the head and cerebral vessels
- MRI of the aorta
MRI of joints
- MRI ankle
- MRI of the knee joint
- MRI of the elbow joint
- Shoulder MRI
- MRI of the hip joints
- MRI of the hand
- MRI of the foot
- MRI of the wrist joint
MRI of the pelvic organs
- MRI of the pelvis in women
- MRI of the pelvis in men
- Prostate MRI
- MRI of scrotum and penis
- MRI of the uterus and ovaries
- Bladder MRI
Abdominal MRI
- MRI of the spleen
- MRI of the gallbladder
- MRI of the liver
- MRI of the pancreas
- MRI of the kidneys and adrenal glands
- MRI of the biliary tract (MRCP)
Soft tissue MRI
- MRI of soft tissues of the face
- MRI of soft tissues of the neck
- MRI of soft tissues of the thigh
- MRI of the thyroid gland
- MRI of the mammary glands
MRI chest
- MRI of the heart and coronary vessels
- MRI of the lungs
- MRI of the larynx
- MRI of the thoracic aorta
Complexes and targeted programs
- MRI of the cervicothoracic spine
- MRI of the head and cervical spine
- MRI of the entire spine
How does a magnetic resonance imaging scanner work?
For diagnostic manipulation, power units called tomographs are used. There are several types of equipment: low-field, high-field, ultra-high-field.
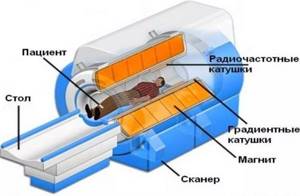
Scanners also differ in design, but they all work using the same protocol. Medical equipment generates a magnetic field that can temporarily change the arrangement of atoms at the cellular level. The particles affected by the vibrations are called hydrogen protons. These atoms are present in the cells of every living organism on the planet. Our body consists of 75% water, and it contains a similar element. Therefore, hydrogen is one of the most common in the body.
Under the influence of magnetic vibrations, protons resonate and release energy, which is captured by the scanner during examination. The information is transferred to a computer installation, where it is processed into three-dimensional images. Unique information comes from different parts of the body and characterizes the anatomical features of each person. When organs or nearby tissues are damaged, their signal structures change. These deformations are visible on tomographic screens.
Why is “calling a friend” important for MRI accuracy?
Each medical specialization, or more precisely, the disorders and pathologies that are in the area of responsibility of a doctor of a certain specialty, has its own characteristics. And identifying these specific manifestations in MRI images requires certain skills and experience from the radiologist who makes conclusions based on the images obtained during the tomography. The list of specializations with special requirements for MRI is quite wide. Most often these are oncology, neurosurgery, mammology, epileptology, etc. An error or inaccuracy in any examination can jeopardize not only the health, but also the life of the patient. But independently maintaining the level of qualifications in various branches of medicine is an almost impossible task for a radiologist who issues opinions on the obtained MRI images. What should a patient do when he entrusts an important stage of diagnosis?
In the structure of the Sergey Berezin Medical Institute (MIBS), which includes two MIBS MRI Centers in Moscow, the task of improving the qualifications of radiologists is of priority importance. In-person and distance learning courses, distribution of recommendations from manufacturers, results of new research, analysis of complex clinical cases from the practice of the international network of MIBS diagnostic centers - this is an integral part of the work of our radiologists. And thanks to a single information network for all representative offices, any radiologist who encounters ambiguous results from the images taken can quickly request a consultation with leading specialists of the MIBS network in this profile.
“I’m from Ivan Ivanovich...”
Without a doubt, the most important role in the informativeness of the examination is a clear statement of the task on the part of the attending physician. And here the patient has to make a difficult choice. On the one hand, an appointment issued to a specific MRI center is alarming. On the other hand, a competent doctor must be confident in the quality of the diagnosis performed and recommend the most experienced specialists. And in this case, the patient’s choice of an MRI center at his own discretion may mean an examination in a pretentious place, with columns and stucco, but with mediocre quality of the images and their descriptions. Making a choice is not easy. And the key to success is trust in your doctor.
Brain tomogram with contrast
A contrast enhancer improves the quality of the image, the visibility of the contours and structural elements of organs. The advantage of MRI is the possibility of early detection of the development of oncological processes and the detection of microscopic anomalies within the body. To add precision, a gadolinium saline solution is injected. The drug is safe, but has certain limitations. Contrast is used:
- Intravenously immediately before scanning;
- Partially when performing a dynamic MRI examination (the necessary intervals between the substances entering the blood are observed).
The tool helps create images with the most accurate dimensions of tumor formations. Diagnostics is informative after chemotherapy, the results of treatment are clearly visible. The main advantage of the method is the absence of the harmful effects of X-rays, so the examination can be repeated again without the risk of harm to health.
The magic of numbers in MRI - don't fall for the bait
In the previous paragraph, we figured out that “open” / “closed” tomograph actually means “high-field” and “low-field”, which have different image resolutions. But in addition to the “lack” of the field, there may also be “redundancy” for specific diagnostic tasks. This refers to a comparison of tension in numbers. Anyone who has had the need to undergo an MRI knows that in Moscow you can already find a tomograph with a field strength of 3 Tesla, an excellent diagnostic tool for a limited number of injuries and pathologies. But a 3T tomograph is not a new word in technology, but just a modification into a specialized solution. And the resolution of images taken on such devices is excessive for most diagnostic tasks. Although the costs of maintenance and service, reflected in the cost of the survey, are higher. Accordingly, the cost of MRI is higher. Whether it makes sense to pay a higher price is up to you...
Which tomograph is better, open or closed?
Open and closed MRI: which is better in terms of accuracy? These are definitely closed models. They are more powerful. The minimum magnetic field voltage in a closed device is 1.5 Tesla, while in open models it never reaches 1.0 Tesla (on average 0.5 or 0.4).
In the closed version, the study is carried out faster (about 35-45 minutes); according to subjective assessments, it brings less unpleasant sensations. Diagnosticians prefer such models because they are easier to analyze the results obtained.
Classification by magnetic field strength
Another sign of the classification of diagnostic MRI equipment is the magnetic field strength, measured in Tesla.
This parameter directly affects the resolution of the tomograph; the quality and information content of the examination depends on it.
Experts distinguish the following classes of equipment:
- Low floor installations. The magnetic field strength does not exceed 0.5 Tesla. The information content of scanning on such devices is low, the resolution makes it possible to see only objects no smaller than 5–7 mm, and allows you to record only gross, pronounced pathology. A qualitative study of the pathology of the heart, brain or dynamic MR angiography is impossible here;
- Mid-field devices with 0.5 - 1 Tesla are distinguished by their information content, which is not much higher than that of the first group, and therefore are not popular;
- High-field installations show a field strength of 1 - 1.5 Tesla and are the most common type of devices offering optimal quality for relatively little money. Such tomographs distinguish pathologies up to 1 mm in size;
- Ultra-high-field equipment with a voltage level of 3 Tesla makes it possible to conduct high-quality studies of the brain, cerebral circulation, carry out spectroscopy and tractography, and obtain information not only about the anatomy of organs, but also about the functional indicators of the body.
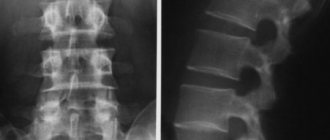
How to do an MRI of the spine: photo
The photo shows the results of an MRI examination of the spinal column. A large number of sections are shown, allowing for detailed examination.
Advantages of magnetic scanning:
- High level of accuracy and information content;
- The method is non-invasive (there is no introduction of instruments and devices into the body);
- The appearance of pain is impossible;
- Checking your back makes it possible to detect pathology in the early stages of development, and there is a chance of quickly eliminating the disease.
The technique allows you to obtain complete information about the state of the departments of the area under study:
- The spinal canal, its nerve fibers;
- Intervertebral discs;
- Vascular channels.
With the help of MRI diagnostics, it is possible to determine the speed parameters of the movement of cerebrospinal fluid and examine the cranium (required procedures for dangerous injuries).
A nuclear magnetic resonance session is in great demand among specialists involved in the treatment of spinal diseases, oncologists, and neurologists.
The study must be completed:
- Preoperative examination;
- If the structure of areas of the spinal column is disrupted;
- If there are anomalies of a degenerative-dystrophic nature (damage to articular cartilage, hernia, vertebral deformity);
- Determination of sources of chronic pain syndromes;
- In case of abnormal phenomena;
- After surgical interventions (to track recovery processes).
Spinal cord tomography is done:
- For post-traumatic consequences;
- There is an assumption of the presence of cancerous formations, secondary tumors;
- Study of cerebrospinal fluid, detection of cystic inclusions.
During diseases accompanied by destruction of the myelin sheath of neurons:
- Acute polyradiculoneuritis;
- Multiple sclerosis.
The picture shows scanning with verticalization. The method helps to visualize the displacement of the vertebrae under axial loads.
Equipment Manufacturers
The main manufacturers of tomographs are Siemens and Philips corporations.
Siemens is a German concern founded in 1841, operating in the electronics, energy equipment, transport, medical equipment and lighting industries. The corporation sells ten types of MRI machines, characterized by high efficiency, quality, safety and ease of maintenance. The corporation's solutions are used in clinics almost all over the world.
The second leading manufacturer of tomographs is Philips. It is a Dutch corporation operating since 1891 and focusing its efforts on the healthcare, lighting solutions and consumer goods industries. The holding occupies a leading position in the production of equipment for cardiology, home health care, emergency care and comprehensive diagnostics.
Philips devices are no less popular among doctors all over the world due to their gradient characteristics and Sence technologies.

Open tomograph: advantages and disadvantages, examinations
Magnetic resonance imaging on an open machine is suitable for:
- patients with limited physical abilities;
- patients with fractures and other painful injuries;
- mobile children;
- people who are overweight (more than 100 kg);
- patients with an acute form of fear of closed spaces.
Advantages:
- scanning is available for a wide range of patients without restrictions (weight, age, physical capacity, fears, etc.);
- medical personnel are located next to the person being examined, and not in the next room;
- low noise level.
Flaws:
- It is not always possible to diagnose complex cases due to insufficient image quality;
- The images do not show blood vessels, small parts of organs, or organs that are in constant motion (for example, the heart).
More is not better
The desire to do the maximum to maintain your health is understandable. But, from the point of view of the optimal cost of an MRI examination, it is important to accurately formulate (best in collaboration with the attending physician) the task at hand - which organ (or part of it) needs to be studied. For example, MRI of the spine. If the study is of a preventive nature, it would be advisable to conduct a tomography of all parts of the spine (MIBS-Moscow offers discounts for such comprehensive programs). If we are talking about diagnostics for injury or localized pain, then an MRI of one part of the spine will be similar in cost, but more effective, but with contrast, which increases the information content of the images. Likewise, a balanced approach to the volume of MRI of other parts of the body (MRI of the pelvis, MRI of the brain, etc.) will save both your money and your health.