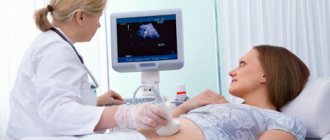
Ultrasound examination is one of the most convenient, accurate diagnostic methods and, importantly, absolutely harmless. In gynecology, ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women is an important diagnostic tool in identifying problems with these organs. Therefore, in order to monitor the state of health, it is recommended that every woman undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs 1-2 times a year in the absence of pathology. Using it, you can see and evaluate the condition of the uterus, cervix, ovaries, fallopian tubes (if they are pathological) and surrounding organs. During the procedure, the sizes of all organs available for examination are measured, their structure and compliance with the phase of the menstrual cycle are assessed.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women makes it possible to diagnose almost the entire range of possible gynecological problems:
- inflammatory disease of the genital organs
- endometrial pathologies, including endometritis, polyps, hyperplasia
- fibroids
- ovarian tumors and cysts
- track follicle growth when planning pregnancy.
In what cases does it need to be done urgently?
- Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen
- Cycle disruption
- Bleeding
On what day of the cycle is an ultrasound of the uterus and appendages performed?
Typically, an ultrasound of the female reproductive system is performed in the absence of menstruation. First of all, because it will be much more difficult for a diagnostician to examine the uterine cavity and assess the condition of the endometrium due to bloody clots. Various neoplasms are difficult to see during menstruation. Accordingly, the diagnosis may be incorrect.
An echography of the uterus and its adnexal structures is prescribed, as a rule, on days 5–10 of the menstrual cycle, when the vast majority of women have already had their periods. A new mucous membrane is formed in the uterus. At the time of the examination, it has not yet hardened, and therefore it can be examined qualitatively, pathological formations can be excluded or confirmed.
Another reason why it is advisable to postpone a planned examination of the organs of the reproductive system until the end of menstruation is psychological discomfort - it is unpleasant for a woman to see a doctor on “special” days.
Not least important is the issue of hygiene. In addition, during a transvaginal examination, the insertion of a special sensor may cause some pain, while on other days the manipulation does not provoke pain.
What is pelvic ultrasound
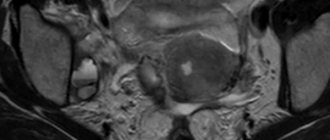
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is a diagnostic procedure aimed at visualizing the structure of organs, mainly the genitourinary system. Based on the properties of ultrasonic waves emitted by a special sensor, as well as on the basis of the reflectivity of body tissues, when conducting a study on the monitor screen, the doctor sees an image of the organs and tissues of the area being examined.
Provided the doctor has the required level of knowledge and practical skills, he can immediately interpret what he sees, suspecting or ruling out pathology of the pelvic organs.
Based on the ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, the doctor issues a conclusion, on the basis of which a final diagnosis will be made in the future and an appropriate treatment regimen will be prescribed.
Today, doctors use several options for ultrasound in this area: transabdominal, transvaginal and transrectal examination. Each method has its own characteristics, which we will discuss in more detail.
Exceptions to the general canons
They do not always wait until days 5–10 of the cycle to conduct an ultrasound examination. Moreover, when treating a number of gynecological ailments, ultrasound data obtained on other days is necessary. The examination cannot be delayed either in extreme situations when a woman’s life is in danger.
Indications for ultrasound during bleeding:
- uterine hemorrhage or heavy discharge during menstruation - may indicate dangerous pathologies of the endometrium;
- risk of miscarriage;
- acute inflammatory processes of the reproductive organs;
- suspected tubal pregnancy;
- complication after abortion;
- suspicion of uterine fibroids or hyperplasia, polyps, cysts (up to 10 mm in size) - ultrasound is indicated on days 1 - 3 of the cycle;
- injuries, burns of the pelvic organs;
- intense pain of unknown origin.
If a woman is carrying a child, the appearance of bloody discharge may indicate a threat of miscarriage, and therefore an ultrasound in this situation is performed urgently. Echography provides a complete assessment of the condition of the fertilized egg and the reliability of its implantation into the mucous membrane of the inner wall of the uterus.
An ultrasound is performed during menstruation if folliculogenesis needs to be examined. The procedure helps to record and evaluate all stages of follicle maturation and its migration from the ovary. The study is prescribed on days 1–4 of the cycle and continued until the 15th day. This data is necessary for the diagnosis and treatment of female infertility and cycle disorders.

For what diseases is abdominal ultrasound prescribed?
The need for an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity may arise if the presence of neoplasms is suspected, if there is pain in the abdominal area of unknown origin (origin), if there are already diagnosed pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, if there is unreasonably increased gas formation or a feeling of bitterness in the mouth.
The method is used both as preparation for subsequent surgical treatment, and for monitoring after it, and for abdominal injuries.
The doctors of the Andromed Center for Andrology and Diagnostics will help you determine the indications for performing an ultrasound of the PD based on your existing complaints and life history/illness. You will first be told about how an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity occurs and what recommendations for preparing for the procedure must be followed.
Ultrasound of other organs during menstruation
If there is a need to undergo a diagnostic examination of non-genital organs, the day of the menstrual cycle is not taken into account. You can undergo an examination and get a reliable result at any time, including during monthly bleeding, which will in no way interfere with the diagnosis or affect the result of the study.
Most often, using an ultrasound machine, the following structures of the body are viewed:
- heart, blood vessels;
- The lymph nodes;
- liver, gall bladder;
- kidneys;
- joints;
- thyroid gland.
For a routine examination of the mammary glands, which are considered part of the reproductive system, the doctor will suggest that the woman appear on days 8–12 of the cycle, when the breasts are not swollen and its lobules and ducts can be qualitatively examined. If an urgent reason arises, the date may also be adjusted.
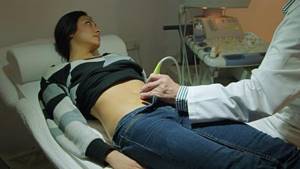
Decoding the results
The gynecologist analyzes the data obtained and makes a diagnosis. In conclusion, deviations from the norm and the presence of structural or tissue formations in the cervix that are different from others are recorded.
Examined on ultrasound
- Structure, shape and length of the cervix.
- Echogenicity (tissue density).
- The location of the cervical axis in relation to the uterine axis.
- Level of patency of the cervical canal.
Cervical cancer may look different on the ultrasound machine screen, but there are always common signs that indicate the presence of this disease:
- Increased size of regional lymph nodes.
- The shape of the uterus resembles a barrel.
- Uneven cervical walls.
- The density of the tumor tissue is normal or increased echogenicity.
- The Doppler method revealed the presence of anomalies in the development of blood vessels.
Examination of the cervix of a pregnant woman
This study cannot be excluded from the list of diagnostic procedures, since it can be used to determine the threat of miscarriage when the cervix becomes shorter and the cervical canal opens (isthmic-cervical insufficiency). The doctor diagnoses the threat if before 37 weeks of pregnancy the following is detected:
- Opening of the cervical canal.
- Shortening of the cervix to 25 mm or more.
- The shape of the expanded internal pharynx resembles a funnel.
Ultrasound determines readiness for childbirth (degree of maturity of the cervix). During a normal pregnancy, ripening should occur gradually.
Preparation for the procedure (ultrasound of the genital organs)
Ultrasound examination of the female reproductive apparatus is carried out in two main ways - transabdominal (through the abdominal wall) and transvaginally (through the vaginal wall). They are often combined.
If the doctor examines the reproductive organs through the abdominal wall, the woman will be asked to lie on her back and bend her legs at the knee joints. The lower abdomen is bare. The procedure requires preliminary preparation: the woman must appear in the ultrasound room with a full bladder (to be agreed with the doctor). A conductive gel-like agent is applied to the device’s sensor, the tip is moved over the abdomen and the necessary organs are examined.
The transvaginal method involves inserting a sensor into the vagina and examining the uterus and appendages. There is no need to drink water before the procedure, you cannot douche - hygienic washing is enough. The woman must have a bowel movement. A regular condom is put on the sensor, the gel is applied, and inserted into the vagina. The echo image is displayed on the device monitor.
So, to the very frequently asked question “Is it possible to do an ultrasound during menstruation?”, the answer can be given in the affirmative, if we are talking about the study of non-genital organs, as well as when studying folliculogenesis and in all the emergency situations listed above.
It is advisable to plan a preventive examination of the reproductive system on days 5–10 of the cycle, when the uterus is sufficiently cleared of blood clots and remnants of exfoliated mucosa, and there will be no interference with a quality examination.
You should not interpret the result yourself, or self-medicate if you do not have a medical education. With the received conclusion of the ultrasound examination, you need to contact a specialized specialist - he will give a competent assessment of the data and prescribe therapy if necessary.
Preparatory activities
It all depends on the research method:
- There is no need to prepare for a transvaginal procedure or through the skin of the perineum.
- Before the transrectal examination, the intestines should be cleansed with an enema at least 6 hours before.
- 24 hours before performing an ultrasound through the walls of the abdomen, it is necessary to remove from the diet foods that cause gas formation and bloating (cabbage, brown bread, milk, legumes, fruits). 1 hour before the procedure, the patient should drink at least 1 liter of still water.
- Pregnant women do not need to prepare for the test. In the early stages it is carried out transvaginally, then through the walls of the abdomen.
Ultrasound results after cesarean section
After a birth performed by cesarean section, the restoration of the reproductive organs takes a long time due to the fact that the mass and overall size of the uterus, taking into account surgical intervention, expands and adds mass by about 40% when compared with natural childbirth. During ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor can see small hematomas, which are foci of hemorrhage in the area of the scar formed at the site of the operation. Such lesions are not dangerous, but they are quite capable of impairing the passage of ultrasound from the sensor to the organ and back. And if the scar swells, then this phenomenon may be a sign of the onset of inflammation in the uterine cavity and endometrium.
After delivery has been performed by cesarean section, the weight of the uterus decreases by approximately 200–250 g during the first postpartum week. The organ usually returns to its original weight values after two months. In terms of the shape of the organ: it acquires the appearance it had before birth no earlier than by the middle or end of the second week after the operation. Standard, basic measurement values (length, width, and anteroposterior dimension) are similarly delayed in parameters when compared with those for vaginal delivery. After the surgical delivery, the doctor will certainly conduct an extremely thorough ultrasound examination of the ovaries, veins and arteries of this area to be sure that their integrity has not been compromised.

Ultrasound results after natural childbirth
After the child is born through the natural birth canal, diagnostics of the pelvic condition by ultrasound is prescribed from the second to the fourth day. If the birth was complicated or there is concern that there is a rupture of the uterine wall, an ultrasound will be performed as an emergency. Visually, normally the uterus will have a certain shape, close to spherical. Immediately after childbirth, it will be located in the middle pelvic region. If a woman has had two or more children, or if she has one large baby, the uterus will move slightly toward the lower part of the pelvis.
If you conduct the study several times over a short period of time in the postpartum period, it is possible to monitor how the weight of the contracting uterus decreases and how it narrows. The reduction of the organ and its displacement to the location that was before the birth occurs little by little. The norm for changes is a shift of 1–2 cm every day. In terms of weight, the uterus loses approximately half (about 450–550 g) in the first few days (up to a week). Subsequently, weight loss becomes smoother and more gradual: about 100 g per week, to the standard 95-100 g that was before childbirth.
How an ultrasound examination is performed after childbirth
After labor ends, there is no more amniotic fluid left in the uterus. Therefore, before the ultrasound, which is performed in the maternity hospital, the doctor recommends filling the bladder properly in order to slightly elevate the uterus and improve visualization of the organ for a more accurate assessment by a specialist. To sufficiently fill the bladder, you need to drink about one and a half to two liters of warm water. If there is a reason for an urgent examination, and there is no way to wait, the bladder will be filled with fluid through a special catheter.
Ultrasound examination in the immediate postpartum period is carried out by installing a sensor on the abdominal wall: the uterus is still very large, transvaginal ultrasound (accessed through the vagina) will not show an objective and accurate picture.
The examination procedure takes about thirty minutes. The woman lies on her back.
What happens to the uterus?
During pregnancy, the uterus increases in volume and size many times – 500 times or more, gaining weight from 50 grams to a kilogram. Under pressure from the baby's body weight, as well as with the development of the placenta, the uterus changes its shape and stretches. And immediately after childbirth, it begins to contract back, most intensely in the first days.
Simultaneously with the change in shape, the uterus returns to its anatomically correct place in the woman’s pelvis, because in the last stages of pregnancy it occupied all the space in the abdominal cavity.
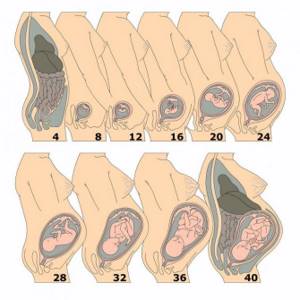
And on a pelvic ultrasound immediately after childbirth, it is necessary to evaluate the weight of the uterus: it is decreasing. The shape gradually changes from round to pear-shaped, as it was before pregnancy and the birth process itself.
Good days for diagnosing ovaries
Often such an examination is done for preventive purposes, during an annual medical examination. A woman can find out which day of her cycle is best to undergo this procedure directly from her doctor.
As a general rule, an ultrasound examination of the ovary is performed on the same day as the diagnosis of the uterus. This is the period between the 5th and 7th day of the monthly cycle.
However, the doctor sometimes needs to evaluate the functioning of the gonads on different days of the cycle. In this case, he prescribes additional examinations for the woman.
The appointment of additional examinations on different days of the monthly cycle is due to the fact that the follicles function differently. The doctor needs to monitor how the corpus luteum is formed, whether there are any pathologies in this process, the dynamics of which can be used to judge the probable causes of infertility.
The most likely timing of an ovarian ultrasound will therefore be as follows:
- from 5 to 7 days of the monthly cycle;
- from 8 to 10 days;
- on days 14–16 (after ovulation);
- in the interval between 22 and 24 days of the cycle, that is, on the eve of the next menstruation.
Sometimes a woman may have a delay in her menstrual cycle even though pregnancy tests are negative. This is an indication for additional ultrasound examination to exclude a possible ovarian cyst.
Why should an ultrasound scan of the ovary be done in the first half of the menstrual cycle, that is, before ovulation occurs? The fact is that at the specified time it is possible to study the condition of the organ under study in more detail. At the same time, cysts and other formations in the ovary can be examined in more detail to determine their degree of malignancy.
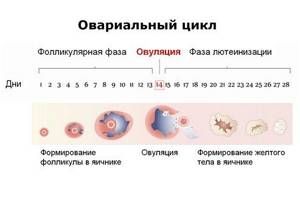
Ovulation is the process by which a mature egg is released from the ovary. This phenomenon occurs approximately 14 days before the onset of menstruation.
It often happens that in the second half of the cycle, the doctor cannot definitely say what type of cyst a woman has, since it is difficult to see.
Due to the fact that the functioning of the ovaries is not the same on different days of the cycle, the doctor periodically needs to repeat the studies.
In particular, additional examinations of the ovaries are essential when determining the cause of female infertility and further determining treatment methods.
So, the effectiveness of an ultrasound examination directly depends on what day of the cycle an ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries is performed. And if such a diagnosis is carried out in the most favorable time frame, then the likelihood of establishing an accurate diagnosis increases significantly.
In some cases, examinations may be required on other days. In any case, your doctor will tell you which day of the cycle is best to do an ultrasound.
Of course, there is no need to be afraid of such an examination. Ultrasound is not dangerous to humans, and it can be used to diagnose internal organs as often as required.
What are the complications?
Conducting a pelvic ultrasound almost immediately after childbirth ensures the detection of some possible problems, which, if not eliminated in time, are quite capable of developing into serious complications requiring treatment. The most common abnormalities that a specialist can see during an ultrasound procedure include:
- the presence of residual blood clots that have coagulated in the uterine cavity, or fragments of the placenta. If enough such fragments have accumulated, they interfere with the outflow of normal postpartum secretions, which leads to inflammatory diseases or even bleeding from the uterus. In order to remove debris from the uterus, the doctor will usually prescribe vacuum aspiration (that is, removal) of the contents of the cavity;
- insufficient activity of uterine muscle contractions. The doctor will suspect this condition when the organ measurements do not correspond to standard values. Prescribing certain medications will help correct the situation;
- inflammatory phenomena of the mucous layer of the uterine cavity (so-called endometritis). The basis for the development of the disease, as a rule, is the addition of a bacterial infection. Pathological microorganisms enter the organ cavity from the genitals if shortly before birth the vaginal microflora was disturbed or its sanitation (cleansing) was not carried out.