Home / Articles / Fungal spores in a gynecological smear: causes and treatment
To identify an inflammatory process or a sexually transmitted disease (STD), a smear is taken from women for flora. A smear must be taken during a preventive examination, as well as in the presence of itching, burning and atypical discharge from the vagina.
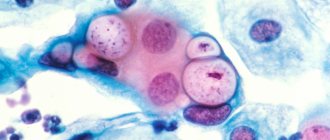
Normally, the fungus of the genus Candida is present in healthy women on the mucous membrane of the genital organs in small quantities. Under the influence of a number of factors, this indicator begins to increase, and the smear reveals pseudomycelium - a vegetative body formed by candida.
Causes of yeast in a smear
The immediate reason for detecting yeast in a smear is the yeast itself that is present there.
These are fungi of the genus Candida.
They are transmitted sexually.
In addition, the development of endogenous infection is possible.
The fact is that candida is part of the normal microflora.
These fungi have low immunogenicity.
Therefore, they exist on the skin, mucous membranes, in the genital and digestive organs.
However, there are no symptoms.
Problems only begin to arise when there is excessive growth of fungal flora.
Practical advice
Tip #1
In the presence of any inflammatory pathology, which is accompanied by heavy vaginal discharge, it is necessary to first carry out treatment and only after complete recovery take a smear for blastospores.
Tip #2
When choosing the timing for donating biomaterial, women must take into account the menstrual cycle. It is recommended to do this before the start of menstruation or a few days after it ends. Blood in the smear can distort laboratory test results.
Tip #3
At the same time, your sexual partner should also be treated for candidiasis, even if barrier types of contraception were used.
Why does yeast appear in the smear?
There are two reasons for detecting yeast cells:
- infection with candidiasis from a sexual partner;
- creating conditions in the body that are favorable for the growth of fungi.
Favorable conditions mean:
- decreased immunity;
- destruction of microflora competitive for candida with antibiotics (candidiasis often manifests against the background of antibiotic therapy for bacterial infections);
- insufficient hygiene of the reproductive organs, accumulation of gland secretion products and exfoliated cells on them;
- Fever – creates warm and humid conditions that are optimal for yeast growth.
In most cases, the disease is not dangerous.
It is fraught with only unpleasant sensations.
But complications do not usually develop in immunocompetent patients.
At risk are elderly, seriously ill and debilitated patients.
As well as persons with diabetes, immunodeficiency conditions or HIV.
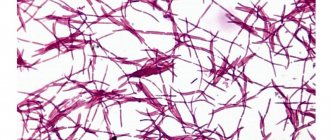
Are there transverse partitions in the mycelium threads?
The mycelium has septa.
But septa may be absent in pseudomycelium.
It differs from true mycelium in that during the budding process, the mother cells are not completely separated from the daughter cells.
They continue budding.
Therefore, structures appear that resemble mycelium in appearance.
It is called false.
It is unseptate, that is, not divided by partitions.
When pseudomycelium is detected, the doctor sees constrictions between the cells.
The terminal cells are smaller than those located in front of them.
Sometimes pseudomycelium consists of cells of the same type.
It is called vestigial.
In other cases, cells of different types develop in pseudomycelium.
It's called complex.
Long cells - pseudohyphae - are found.
They contain buds - one or more, round or wedge-shaped.
These buds are called blastospores.
Under what symptoms can yeast be detected in a smear?
Typically, women do not go to the doctor or laboratory just like that.
They are forced to seek medical help by the symptoms that arise.
Here is a list of clinical signs in which the probability of detecting yeast in a smear is quite high:
- redness of the genitals;
- severe itching;
- accumulation of white plaque;
- curdled vaginal discharge;
- swelling;
- sour smell;
- the appearance of erosions and cracks.
Elements of the rash are usually limited to red spots and papules.
In severe cases of candidiasis, erosions, ulcers and pustules occur.
The spots become larger.
In addition to the vagina and vulva, the surrounding skin may also become inflamed.
Candidiasis usually does not spread upward.
Culture of Candida spp./yeast-like fungi with selection of antimycotic drugs
This is a microbiological study that allows one to identify yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (C. spp.) in biomaterial and determine their sensitivity to antifungal (antimycotic) drugs.
Synonyms Russian
Sowing for fungi of the genus Candida (Candida, candidiasis) and determining sensitivity to antimycotic (antifungal, antifungal) drugs.
English synonyms
Yeast culture, fungus identification and susceptibility, Candida culture, fungus identification and susceptibility.
Research method
Microbiological method.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
A single portion of urine, urogenital swab, sputum, oropharyngeal swab, nasopharyngeal swab, ear discharge, nasal swab, conjunctival swab, nails, ejaculate.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Women are recommended to take a urogenital smear or urine before menstruation or 2-3 days after it ends.
- Men should not urinate for 3 hours before submitting a urogenital smear or urine test.
General information about the study
The simplest yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida, which numbers more than 170 species, are found in small quantities as part of the normal microflora of the oral cavity, vagina, gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract in healthy people. They are opportunistic organisms: under certain conditions that contribute to the rapid proliferation of these fungi (impaired immunity, HIV infection, taking broad-spectrum antibiotics, immunosuppressants, corticosteroids or oral contraceptives with a high content of estrogens, cancer, tuberculosis, blood diseases, diabetes diabetes, pregnancy, intrauterine device, tight synthetic clothing, hemodialysis, etc.), candidiasis develops.
Candida spp. enters the body through sexual contact, contact, and during pregnancy and childbirth. In 30-40% of cases, candidiasis develops as a result of sexual intercourse, but more often the disease is caused by an endogenous infection, when, under the influence of unfavorable factors leading to an imbalance in the natural microflora, rapid proliferation of these fungi occurs.
Candida usually affects the mucous membranes or skin. The most common candidiasis of the genitourinary tract mucosa, which is characterized by burning and itching in the genitals, cheesy white discharge (plaque), pain when urinating and sometimes the appearance of small blisters, erosions and cracks. Vulvovaginal candidiasis accounts for 75% of all cases of candidiasis; as a rule, this is an asymptomatic candidiasis. The development of candidal endocervicitis, urethritis or cystitis is possible. With oral candidiasis (pseudomembranous mucositis, thrush), a white coating appears on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, the back wall of the pharynx and the tongue. Most often it occurs in newborns. In adults, oral candidiasis is often an early sign of AIDS. Candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract usually develops after taking broad-spectrum antibiotics and is characterized by clinical signs of colitis and/or intestinal dysbiosis. With skin candidiasis, many small blisters appear, in place of which erosions with clear boundaries are formed. “Dropouts” may be observed on healthy skin in the form of small ulcers and pink spots that peel off in the center, paronychia, damage to the interdigital folds of the hands and feet, inguinal and axillary areas, and the anus. In some cases, generalization of the infection occurs with infection of various organs (usually the kidneys, liver, brain, heart, lungs and eyes), the formation of secondary metastatic foci and the appearance of symptoms of fever, damage to the central nervous system, dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and changes in peripheral blood . Sepsis, endocarditis, endophthalmitis, urinary tract infection, etc. may develop.
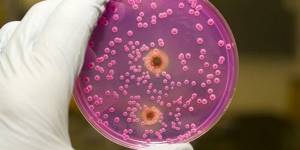
The gold standard for detecting Candida spp. is a microbiological method - cultivation on nutrient media (seeding on Sabouraud's medium). Determining the sensitivity of isolated microorganisms to antifungal (antimycotic) drugs is used mainly when treatment is insufficiently effective or when switching from parenteral antifungal drugs of one class to oral drugs of another class (for example, fluconazole) if long-term treatment of candidiasis is necessary (for example, with candidal meningitis, endocarditis or osteomyelitis).
What is the research used for?
- To detect candidiasis.
- For differential diagnosis (along with other studies) for diseases that occur with similar symptoms (bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, genital herpes, nonspecific vaginitis, etc.).
- To select rational antifungal therapy and evaluate its effectiveness.
When is the study scheduled?
- If a fungal infection is suspected, including after antibacterial therapy and with clinical signs of intestinal dysbiosis (bloating and pain in the abdomen, loose stools).
- For vaginal discharge accompanied by itching.
- During antifungal therapy (to assess the effectiveness of treatment).
What do the results mean?
Reference values: negative.
Detection of Candida spp. in biomaterial from normally sterile organs and tissues indicates the etiological role of these fungi in the development of the disease.
Negative result
- Candidiasis is unlikely.
Positive result
- Candidiasis.
- Combination of vaginal candidiasis with bacterial vaginosis.
What can influence the result?
Previous antifungal therapy contributes to a false-negative result.
Important Notes
With vulvovaginal candidiasis in a pregnant woman, the risk of oral candidiasis in a child in the future increases by 35 times. Therefore, in order to avoid thrush in the child, it is advisable to treat vulvovaginal candidiasis in the mother during pregnancy.
Also recommended
- Candida albicans, DNA [real-time PCR]
- Candida albicans, IgG, titer
- Microscopic examination of the discharge of the genitourinary organs of men (microflora)
- Microscopic examination of discharge from the genitourinary organs of women (microflora), 3 localizations
- Trichomonas vaginalis, DNA [real-time PCR]
- Herpes Simplex Virus 1/2, DNA [real-time PCR]
Who orders the study?
Gynecologist, urologist, general practitioner, pediatrician, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist.
Literature
- Encyclopedia of clinical laboratory tests / ed. WELL. Titsa. – M.: “Labinform”, 1997 – 942 p.
- Edwards JE Candida Species. In: Principles and practice of infectious disease / GL Mandell, Bennett JE, Dolin R (Eds) ; 6th ed. – Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia, PA 2005. – 2701 p.
- Genital candidiasis. In: Oxford handbook of genitourinary medicine, HIV, and Aids / R. Pattman (Eds) ; 1st edition. – USA: Oxford University Press, 2005 – 580 p.
- Prilepskaya V.N. Clinic, diagnosis and treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis (clinical lecture) / V.N. Prilepskaya // Gynecology. – 2002. – T. 3, No. 6. – P. 201-205.
- Tikhomirov A.L. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: a look at the problem / A.L. Tikhomirov, Ch.G. Oleinik // Gynecology. – 2005. – T. 7, No. 1. – P. 29-34.
- Yabluchansky N.I. Candidiasis / N.I. Yabluchansky // Medicus Amicus. Eletron. magazine – 2004. – No. 4.
- Kungurov N.V. Modern ideas about the treatment of urogenital candidiasis / N.V. Kungurov, N.M. Gerasimova, I.F. Vishnevskaya // Treatment. doctor. – 2004. – No. 6. – P. 76–78.
- Shevyakov M.A. Fungi of the genus Candida in the intestine: clinical aspects (review) / M.A. Shevyakov, E.B. Avalueva, N.V. Baryshnikova // Problems of medical mycology. – 2007. – T. 9, No. 4. – P. 4-11.
- Guidelines for treatment of candidiasis / PG Pappas [et al.] // Clinical Infection Diseases. – 2004. – Vol. 38, N 2. – P. 161–189.
What tests detect yeast?
A smear is just a way to take clinical material.
To find yeast in it, various laboratory tests are used.
Most often this is a microscopic examination.
Less commonly, fungal culture or PCR.
Microscopy
Discharge is taken from the genitals or plaque accumulated on the surface is collected.
A preparation is prepared from it, which is examined under microscope magnification.
Staining is usually done with potassium hydroxide.
It allows you to “clarify” the drug, making it more convenient for study.
In the field of view of the microscope, the doctor discovers:
- increased number of leukocytes - inflammatory cells;
- budding fungal cells;
- fungal elements (spores, pseudomycelium).
In combination with characteristic clinical signs, this is a sufficient basis for making a diagnosis.
This does not determine:
- type of fungus (there are many candida);
- number of fungi.
Regarding the quantity, only one thing can be said: if yeast begins to appear in the field of view, this indicates that its concentration is not less than 10 in 3 per ml.

As you can see, the test is not the most informative.
However, for most patients this is sufficient.
In the vast majority of cases:
- the type of fungus is candida albicans;
- the amount of yeast has no clinical significance and does not affect the choice of treatment regimen.
Therefore, compelling reasons are needed to prescribe additional tests.
They are usually required if:
- candidiasis is not treatable;
- the disease becomes chronic or recurrent.
Then it is necessary to determine the type of fungus, its quantity, as well as predisposing factors (concomitant diseases that provoke candidiasis).
Sowing
The biomaterial obtained as a result of the smear is sown on a nutrient medium.
After a few days, fungi grow.
The emerging colonies have a characteristic appearance.
In addition, different fungi differ in enzymatic, immunological and other properties.
Cultures provide the doctor with valuable information:
- determines the type of fungus;
- estimates the amount in colony-forming units;
- shows the sensitivity of yeast to antimycotics, allowing you to choose the best one for the treatment of candidiasis (the risk of treatment failure is reduced to a minimum).
PCR
The molecular biological method has both advantages and disadvantages.

Such diagnostics are cheaper and take less time.
It allows you to accurately determine the type of fungus and also gives quantitative indicators.
The examination is usually carried out simultaneously on 5-8 of the most common yeast species.
During PCR, a DNA fragment specific to a particular candida is detected.
On the other hand, sowing is still more preferable.
The fact is that both studies are not routine.
They are prescribed strictly according to indications.
Namely, they are carried out when relapses occur or difficulties in treating a yeast infection occur.
But, unlike PCR, culture makes it possible to assess sensitivity to antimycotics.
Therefore, after this study, the likelihood of a cure is higher.
Blood analysis
Candidiasis is diagnosed by a blood test.
This test is not used for the primary diagnosis of infection.
It is used solely to assess the risk of complications.
Candida has low immunogenicity.
With superficial (uncomplicated) candidiasis, immunoglobulins in the blood are not detected.
They begin to appear only with deep (invasive) candidiasis.
It differs in that internal organs are involved in the pathological process.
This form of yeast infection develops only in patients with immunocompromised conditions.
The presence of IgG in the blood does not confirm invasive candidiasis.
But if IgG is not detected, this practically guarantees its absence.
Thus, this test has a high negative predictive value.
At the same time, its results only refute invasive candidiasis, but do not confirm it.
If antibodies are detected, additional tests are needed to assess the extent of the yeast infection.
What can mushroom mycelium threads be confused with?
Sometimes inexperienced laboratory technicians confuse mycelium threads with villi.
They can get into the vagina from tampons.
Then these are the lint of cotton fabric.
But they can be distinguished from threads of mycelium or pseudomycelium by certain parameters.
Firstly, in size.
The villi are always larger and thicker than the hyphae.
Secondly, due to the absence of kidneys.
Unlike mushrooms, cotton threads cannot reproduce by division.
Therefore, rudiments never form on their surface.
Increased yeast in the smear
If yeast is detected, it does not mean you are sick.
You need to pay attention to the following things:
- are there any symptoms of candidiasis;
- how the research was conducted.
Candida is a normal inhabitant of the human reproductive organs.
If there is a small amount of fungi on the skin and mucous membranes, it is not scary.
There is no point in treatment for:
- no symptoms of candidiasis;
- detection of this infection in an amount less than 10 to 3 degrees CFU or DNA copies per ml (depending on whether the diagnosis was carried out by culture or PCR).
At the same time, detection of yeast by microscopy is a clear indication for therapy.
Because mushrooms come into view only when their number is increased.
Features of threads for candidiasis
In candidiasis, the filaments are pseudomycelia rather than mycelium.
They do not have partitions.
But there are thickenings on the threads.
They appear in those areas where there are branches of pseudomycelium.
The fiber can have different lengths.
Sometimes the threads become twisted or intertwined.
Pseudohyphae can be detected in a native smear.
That is, not painted with anything.
But sometimes there are so many cells in the material that fungi are poorly visualized.
Then potassium hydroxide is added to the preparation.
The sample appears lighter when examined microscopically.
Elements of fungus become much more visible.
They are visible with a microscope magnification of 100 times.
A magnification of 400x is required to see the details.
This way the laboratory assistant can identify small and short filaments of pseudomycelium.
Budding cells and blastospores are also detected.
They are otherwise called blastoconidia.
They look like oval cells, corresponding in size to epithelial cells.
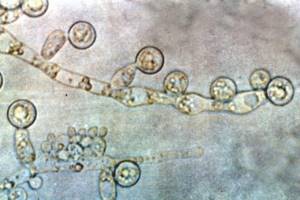
The appearance of budding forms is associated with the proliferation of fungi.
Their number may vary.
But it does not reflect the real quantitative indicators of the fungal process in the vagina.
It also does not correlate with the severity of symptoms.
Therefore, a smear on the flora cannot be used to assess the dynamic course of the disease.
This is an exceptionally high-quality test.
He gives a yes or no answer.
If mycelium threads are found, this indicates a fungal disease.
If they are not detected and the smear is clean, then the person is healthy.
Yeast in a smear of men
Male patients are much less likely to suffer from candidiasis.
However, such cases also happen to them.
There are two reasons:
- infection from a woman suffering from vulvovaginal candidiasis;
- creating favorable conditions for yeast growth (usually weakening the immune system or antibiotic therapy).
In men, the most common clinical form of the disease is candidiasis balanoposthitis.
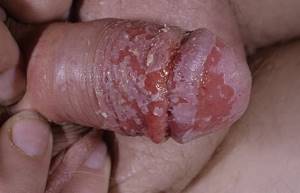
Urethritis is diagnosed much less frequently.
If present, it usually complicates inflammation of the head of the penis.
Symptoms are generally the same as in women:
- itching;
- redness;
- white thick deposits;
- papules, erosions, fissures, pustules, depending on the severity of the infection.
Similar tests are prescribed.
Yeast can be detected by microscopy.
To clarify the type of fungi, PCR or cultural testing is used.
Where does the smear come from?
A smear for yeast fungi in children is taken from the throat if there are characteristic signs of their increased activity. The doctor, using careful rotational movements, collects biomaterial from the surface of the tonsils, palate, and back wall of the throat. After taking a smear, he breaks off the end of the probe, and the swab places a test tube with transport medium and a ground-in stopper.
This procedure does not require special preparation; it is only forbidden to rinse your mouth 1-2 hours before. But it is needed before taking gynecological and urogenital smears in adults:
Enterococci in a smear
- do not use vaginal suppositories, tampons, ointments for 2-3 days;
- stop douching;
- abstain from sexual intercourse for one to two days;
- wash the genitals the evening before collecting biomaterial;
- Do not empty your bladder for 2 hours before taking a smear.
When collecting biomaterial from women from the vagina, cervix and external opening of the urethra, a special brush is used. To take a smear in men, a thin probe is inserted into the urethra. The biomaterial is distributed with a spatula evenly with a wide smear by the doctor onto a sterile glass slide and sent to the laboratory.
What to do if fungi are found in a smear?
Need treatment.
In most cases, therapy is quick and successful.
Often one tablet is enough to get rid of the disease.
If the disease is severe or constantly worsens, therapy takes longer and is carried out with several drugs.
In any case, it is not you, but your doctor, who will decide what to do next.
He is guided by the results of tests, including additional ones (for sexually transmitted infections and diseases that are predisposing factors).
Prevention
Prevention of intestinal candidiasis requires compliance with a number of requirements:
- rational nutrition, diet;
- increasing immunity;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- normalization of the daily routine, regular rest, creation of a calm environment;
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely treatment of genital candidiasis, diabetes mellitus, obesity, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, reproductive and urinary systems.
A. Ogulov - Cleansing the stomach from mushrooms
Yeast fungus in the stool of an adult and a child is no joke. The condition requires timely treatment and careful attention to yourself. Follow preventative measures and stay healthy!
Treatment of yeast in a smear
The easiest way to cure candidiasis is to take a fluconazole tablet.
It is taken once.
Dose – 150 mg.

Usually, after this, the symptoms of inflammation quickly disappear.
This scheme is used when:
- no complications;
- mild clinical course of candidiasis (and this is the majority of cases);
- form of the disease caused by Candida albicans rather than atypical Candida.
Itraconazole can be used as an alternative drug.
But they have to undergo treatment longer.
You can also treat yeast in a smear with local medications.
But most patients find them less comfortable.
Causes:
- the need for daily use;
- the course of treatment lasts 1 week, not 1 day;
- candles and creams stain linen: both underwear and bed linen;
- therapy may be more expensive.
On the other hand, local exposure has an obvious advantage.
Many antifungal medications are harmful to the liver.
When used locally, any health risks are eliminated and systemic side effects do not develop.
Treatment of mycelium threads
When threads appear, treatment includes the use of antifungal drugs.
Different diseases are treated differently.
For dermatophytosis of the skin, the use of local antifungal drugs is usually limited.
Ointments and creams are used.
They may contain:
- ketoconazole;
- miconazole;
- terbinafine;
- amorolfine;
- ciclopirox and other drugs.
In severe cases, oral medications are also used.
For candidiasis, clotrimazole is used externally.
Fluconazole can be prescribed orally.
In the recurrent form, treatment can be very long.
Yeast in a smear during pregnancy
During pregnancy, yeast is detected quite often.
This is due to the fact that due to hormonal changes, immunity decreases.
As we have already said, candida in this case begins to multiply quite quickly.
She's just waiting for her immune system to fail.
But treatment of yeast during this period cannot be carried out with systemic medications.
Because they can harm the fetus.
Preference is always given to local treatment.
Use creams, ointments or suppositories containing:
- clotrimazole;
- miconazole;
- Butoconazole
Of course, these drugs are not used simultaneously.
Only one of them is selected.
You need to put candles on at night, once a day.
The standard course of treatment lasts 7 days.
About the treatment of candidiasis
For mild or moderate infection, local medications are used in treatment - suppositories, antiseptic solutions, ointments, creams, gels. Taking antifungal tablets, capsules, dragees is required for severe mycoses.
At the same time, immunostimulants are included in therapeutic regimens to prevent relapses. The most commonly used drugs are shown in the table.
| Group of drugs | Names of medicines |
| Antimycotics | Clotrimazole, Isoconazole, Itraconazole, Ketoconazole, Fluconazole |
| Products with a combined composition | Terzhinan, Polygynax, Pimafucin |
| Immunostimulants | Immunal, echinacea tincture |
| Eubiotics | Lactobacterin, Linex, Acipol |
| Antiseptic solutions | Miramistin, Chlorhexidine |
Why is there no effect from treating yeast in a smear?
Insufficient effect of treatment means the following:
- symptoms do not disappear;
- there is no less yeast in the smear;
- the symptoms go away, but after a while a relapse occurs.
Such unfavorable situations may be due to the following reasons:
- the disease is caused by atypical candida (not albicans) - they are less susceptible to traditionally used drugs;
- the treatment was carried out incorrectly (perhaps you got a bad doctor);
- the person tried to treat himself;
- candida turned out to be resistant to the drug used;
- there are profound immunity disorders or other predisposing factors (diabetes, poor hygiene, local use of glucocorticoids, etc.).
If there is no effect of treatment or relapse, culture for candida or PCR is performed.
The patient is examined for HIV, diabetes, the state of immunity is assessed, and checked for concomitant sexually transmitted infections.
The treatment regimen usually changes.
Antimycotics of another pharmacological group are prescribed.
Using PCR, doctors monitor the dynamics.
They determine whether the concentration of yeast in the smear is decreasing.
In addition to the main treatment, enzymes, immunomodulators, local antiseptics and antifungal drugs are prescribed.
After a course of therapy, clinical and laboratory monitoring is required.
Reasons for appearance
Before starting to restore the natural flora of the vagina in women, it is important to establish the cause of the development of the pathology. The Candida fungus begins to actively multiply under the influence of the following factors:
- diabetes;
- weak immunity;
- use of antibiotics based on microorganisms;
- tuberculosis;
- hormonal imbalance (the level of estrogen in the body in women decreases);
- neglect of hygiene rules;
- synthetic underwear;
- inflammatory diseases caused by infection;
- use of oral contraceptives.
What causes thrush?
Thrush or fungus in women can occur for various reasons. Doctors call alkalization of the vagina one of the common reasons for the development of candidiasis - a change from the normal (acidic) environment of the vagina to an alkaline one due to hormonal disorders, infectious and gynecological diseases. The alkaline environment in the vagina becomes an impetus for the proliferation of fungi due to the death of microorganisms that make up the natural microflora of the vagina. The disease can be caused by taking corticosteroids or antibacterial drugs. Thrush can also develop:
- against the background of decreased immunity;
- due to wearing underwear made of synthetic materials;
- due to unprotected sexual intercourse, use of intrauterine contraceptives.
References
- Clinical recommendations. Russian Society of Dermatovenereologists and Cosmetologists. Urogenital candidiasis. -M. 2016;
- Russian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "Scientific Center of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Perinatology named after Academician V.I. KULAKOV" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation: Federal clinical recommendations. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases accompanied by pathological discharge from the female genital tract.
- Federal clinical guidelines for the management of patients with urogenital candidiasis. edited by Rakhmatulina M.R. 2015
- Clinical recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases accompanied by pathological discharge from the female genital tract. Russian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.2019
Vaginal smear - what infections does it show?
A vaginal smear allows you to identify pathogenic microflora in the vagina (bacteria, fungi). This is the simplest and most effective laboratory method for diagnosing the inflammatory process in the female genital organs. Based on the results of the analysis, the gynecologist makes a diagnosis (vaginal candidiasis, vaginitis or other gynecological disease).
A vaginal smear shows:
- number of leukocytes, lactobacilli, squamous epithelial cells;
- Is the ratio of “beneficial”, pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms, the number of which must be balanced, disturbed?
How to get rid of fungi in the body using folk remedies?
Fungal diseases of the female organs should be treated only as prescribed by a gynecologist. Self-medication can lead to the development of a chronic form of candidiasis, the appearance of concomitant diseases (cervical erosion, diseases of internal organs due to fungal infection of the kidneys, intestines or bladder).
If untimely or improperly treated, fungal infections can enter the bloodstream. This is called candidemia. According to the US Centers for Disease Prevention and Control, candidemia is one of the most common fungal infections in the United States. In addition, yeast infections can lead to other health problems, such as dermatological diseases, as the area around the vagina becomes inflamed due to yeast infections. Prolonged inflammation threatens skin infections and increases the chance of infection spreading to other parts of the body.