HIV tests
HIV is a virus of the retrovirus family that attacks the human immune system. It is the only cause of the development of AIDS.
There are 2 types of virus:
- HIV-1 is the most common type among the population. Found in Russia, USA, Europe, Japan, Australia.
- HIV-2 is a rarer type that is widespread in West Africa.
Today, modern test systems are used to diagnose the disease, capable of detecting the presence of a pathogen within 2 weeks after entering the body. Until recently, the only way to diagnose the disease was first-generation test systems, with which it was possible to detect viral cells only 6-12 weeks after entering the body.
Modern combined HIV analysis has a number of advantages. The main thing is that this test can detect the virus within 1-4 weeks from the moment of infection, before seroconversion. This significantly reduces the “window period” and allows you to provide the necessary medical care in a timely manner.
This test is also capable of detecting antibodies to HIV-1 and HIV-2 in the blood, which are produced in sufficient quantities to be detected by the test system within 2-8 weeks from the moment of infection. This helps identify which type of virus a person is infected with.
It is noteworthy that at the terminal stage the AIDS test for HIV antibodies may give a negative result. This is due to a disruption in the mechanism of antibody production.
Main stages of HIV infection
The incubation period of HIV infection is also called the “seronegative window period.” This is the name given to the period from the moment of infection to the development of protective antibodies to the virus in the blood. At this time, tests for antibodies to HIV will give a negative result, but the person is already a spreader of the infection. This period can last from 2 weeks to 6 months, depending on the individual characteristics of the body.
The period of acute HIV infection begins 2-4 weeks after the pathogen enters the body and lasts approximately 2-3 weeks. At this point, some patients experience mild symptoms of the disease, similar to flu-like symptoms, which actually indicates active replication of the virus. However, in the vast majority of cases, the latent stage of the disease occurs without any symptoms. During this period, immunity steadily decreases, and the number of viral cells in the blood increases significantly. AIDS is the final stage of development of HIV infection. Human acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is characterized by severe suppression of the immune system, as well as the occurrence of concomitant pathologies, including encephalopathy and cancer.
There is currently no cure for HIV infection; the disease is incurable. However, effective antiretroviral therapy has been developed, which significantly improves the quality of life of the infected patient.
Purpose of the test
This type of study is of great diagnostic value if the infection occurred shortly before the time of testing. With early diagnosis, further spread of the disease can be controlled. This will also help you start taking special medications on time that can stop the progression of HIV infection.
Indications for the study
There are a number of situations in which a patient is required to undergo an HIV test:
- Persistent symptoms of unknown origin: low fever, diarrhea, night sweats, sudden weight loss, swollen lymph nodes.
- Constantly recurrent herpes infection, pneumonia, viral hepatitis, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis.
- If the patient is diagnosed with one or more sexually transmitted diseases - syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, genital herpes, bacterial vaginosis or others.
- If a person had unprotected sexual contact with a new partner whose HIV status was not sure.
- After undergoing a blood transfusion procedure (in fact, infection is practically excluded in this way, because the biological material is carefully tested for a huge number of different infections, and is also subjected to special heat treatment).
- If we are talking about drug addiction using unsterile instruments.
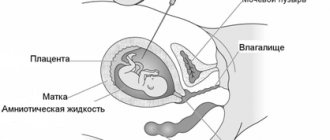
- During pregnancy or when planning it. Today, doctors have developed tactics that can help reduce the risk of a child becoming infected by an HIV-positive mother to almost zero - taking azidothymidine during pregnancy, prescribing a cesarean section to avoid transmitting the virus to the child during passage through the birth canal, and refusing to breastfeed.
- Accidental injection with a syringe or other sharp object containing infected blood. However, the likelihood of infection in this way is extremely low.
Decoding the HIV test
The greatest likelihood of an informative diagnosis of HIV occurs 12 weeks after infection. During this period, the concentration of antibodies is sufficient to detect them in 95% of cases. For example, a month after infection, the probability of their detection is only 60-65%.
If a person receives a positive HIV test result, it is recommended that the test be repeated - preferably several times. It is highly recommended that it be carried out in other ways in order to accurately confirm or refute the presence of the disease, because often the results of the study are false positive.
The result is considered positive if two tests performed on different equipment using different methods detect antibodies to HIV in the blood.
There are several different tests, based on the results of which you can accurately understand whether there is a virus in the body or not. But why are there different tests? How are HIV tests evolving? And why is it better to take several different types of testing? Questions about testing are probably the most pressing not only for HIV-positive people, but also for those who take tests for the sake of prevention.
We should probably start with how HIV tests evolved. HIV tests were first introduced in 1985. At that time, the main purpose of testing was to detect infection in donated blood. Since there was no cure for HIV at that time, there was also no incentive to do this test. Subsequently, antiretroviral drugs were developed, which became a big step in the treatment of HIV infection. Therefore, not only doctors, but also people who care about their health began to pay much more attention to testing. Over the history of the development of HIV tests, several generations have been developed. Tests from the first to the third generation can only find antibodies in the blood. They are released in the blood by the immune system in response to the appearance of a foreign microorganism, in this case a virus. Most of these tests work using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. Such tests are also called "indirect testing". The first test detected antibodies using sonicated virus and was called a lysate test. This is the first test that could detect HIV in the body. However, it could only detect HIV1. Also, the first generation test was not very sensitive and specific, so it required improvement.
The next round of development in the study of HIV occurred in the second half of the 20th century, more precisely in the 80s. Second generation tests were developed at this time. They could already detect antibodies to HIV1 and HIV2. Recombinant and/or peptide methods were used to determine the presence of antibodies. The recombinant method used genetically modified proteins that were similar to the protein antigens of the virus. The peptide method used protein fragments that were synthesized artificially and chemically.
In the 90s, third generation tests appeared. Their main difference is that they have higher sensitivity. This testing is based on the specific interaction of an antibody produced by the body and a hostile antigen from the virus.
Nowadays, the fourth generation test is most often used. It, like previous tests, detects antibodies, but at the same time, it is also sensitive to HIV antigens. This shortens the seronegative period and gives more accurate results.
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent test method, or ELISA, is currently the most popular and used. Its accuracy is about 99%. But in addition to enzyme immunoassay, other methods for determining HIV are often used. If ELISA is usually carried out as a screening test, i.e. During the initial examination, immunoblotting is used to make an accurate diagnosis of HIV. It is much more difficult to carry out, but gives a more accurate result because it is more sensitive and specific. For IB, blood from a vein is also used, after which it undergoes special treatment and is then applied to a special strip of nylon filter or nitrocellulose. A reaction occurs and the result is displayed on the strip - it becomes visible. If stripes appear in certain places, then this confirms that the blood contains antibodies to HIV.
Another method for detecting HIV in the body is the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
However, it is much more difficult to use and requires a lot of skill. PCR analysis examines nucleic acids, which are DNA and RNA, so it turns out that it determines the genetic material of a microorganism. This research method is very accurate - up to 98% - 99%. But high-quality reagents and highly qualified professionals are needed who can correctly conduct research and make a diagnosis. These are the most popular HIV testing methods currently available. As mentioned above, no test can give a result with 100% accuracy. Therefore, an additional method is always used for confirmation. Only by going through several testing methods will doctors be able to make a final diagnosis. What kind of testing will be carried out for the patient is also determined by the doctor, based on the individual characteristics of the body.
Tests for coronavirus
- Test for coronavirus
- Coronavirus test for organizations
- Testing for coronavirus at home
- Testing for coronavirus at home in 12 hours!
- Testing for coronavirus in Lyubertsy in 12 hours!
- Testing for coronavirus in Nekrasovka in 12 hours!
- Testing for coronavirus in Korolev in 12 hours!
- Test for coronavirus on the Sokol metro station
- Coronavirus test at Kolomenskaya metro station
- Coronavirus test at Voykovskaya metro station
- Test for coronavirus in Nekrasovka
- Coronavirus test in Korolev
- Test for coronavirus in Lyubertsy
- Test for coronavirus in Mytishchi
- Test for coronavirus at home Mytishchi
- Test for coronavirus at home Korolev
- Test for coronavirus at home Lyubertsy
- Test for coronavirus at home Nekrasovka
Any tests can be taken at clinics in the East Clinic network.
Complexes with this research
Examination during pregnancy.
1st trimester RUB 11,430 Composition Male infertility. Extended examination Analysis of male reproductive health 21,080 RUR Composition
Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure RUR 16,590 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Women's check-up No. 1 13,430 RUR
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 6,310 RUR
- Hospital complex 1,300 RUR
- Pregnancy planning. Diagnosis of infections 6,680 RUR
- Future dad 5,850 RUR
When do you need to take an AT and AG test for HIV 1/2 (screening, quality)?
1. Enlarged lymph nodes in more than two areas; 2. Leukopenia with lymphopenia; 3. Night sweats; 4. Sudden weight loss of unknown cause; 5. Diarrhea for more than three weeks of unknown cause; 6. Fever of unknown cause; 7. Planning pregnancy; 8. Preoperative preparation, hospitalization; 9. Identification of the following infections or combinations thereof: tuberculosis, manifest toxoplasmosis, often recurrent herpesvirus infection, candidiasis of internal organs, repeated herpes zoster neuralgia caused by mycoplasmas, pneumocystis or legionella pneumonia; 10. Kaposi's sarcoma at a young age; 11. Casual sex.
Detailed description of the study
RULES FOR CONDUCTING TESTING FOR HIV INFECTION
The primary stage (screening) of HIV testing.
Attention! When taking the AT and AG test for HIV 1/2 for the primary screening study, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, it is mandatory to provide the following data and documents:
1) For residents of Moscow and the Moscow region
- Full Name
- Day, month and year of birth
- Registration Information
- Passport
2) For residents of other regions of the Russian Federation and foreign citizens, additionally - a photocopy (scan) of the passport.
- Full Name
- Day, month and year of birth
- Registration Information
- Passport
If the above information is not provided, for patients with preliminary positive and questionable results of the screening test for HIV antibodies and antigens ½ (screening) (quality), the test result cannot be issued.
The analysis can be taken anonymously: in this case, the patient is registered as anonymous with an individual order number (clause 2, article 8 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 38-FZ), with the obligatory indication of the year of birth and place of residence (subject of the Russian Federation).
Draw your attention to! That the results of the primary (screening) study are only the results of a laboratory test and are not the result of an examination or a conclusion about the presence or absence of HIV infection. Based on the results of the screening study, you should contact the municipal AIDS center to conduct a voluntary examination for the presence of HIV.
The results of an HIV test, regardless of their outcome, are issued only if the patient personally contacts the laboratory department. When examining minors (under 14 years of age) - to the legal representative specified in the order.
Results are issued upon presentation of a contract, estimate and identification document of the patient himself or the patient’s representative specified in the order.
Research results are not communicated by phone or email.
With this test, test serum/plasma samples can be simultaneously tested for the presence of HIV type 1 and 2 antigen and HIV type 1 and 2 antibodies.
The human immunodeficiency virus belongs to the family of RNA-containing retroviruses and the subfamily of lentiviruses, i.e. viruses of slow infections. HIV is genetically and antigenically heterogeneous; according to its structure, it is divided into types 1 and 2. When introduced into human cells, the virus forms a DNA section in their genome, which subsequently forms new HIV in unlimited quantities. Viral antigens appear on the surface of damaged cells. The response to their appearance on the part of the immune system is the formation of specific antibodies to the virus of the first or second type. Over the past three years, the number of HIV-infected persons officially registered in Russia has been growing exponentially. The rapid spread of HIV infection in the country may become uncontrollable. Therefore, one of the main tasks at present is the use of more advanced methods of its diagnosis, ensuring the identification of infected individuals at the earliest stages of infection. These methods include laboratory serological tests that determine both the protein structures of the virus and specific antibodies to the virus.