Genetic analysis began to be used in prenatal diagnosis relatively recently, but is already included in the list of recommended tests for expectant mothers. It allows you to identify fetal pathologies in early pregnancy, and also gives the most complete picture of the process of fetal development. Thanks to screening, the doctor who is caring for the pregnancy knows what the risks are, as well as how the fetus is developing. However, many myths and “horror stories” still circulate around this test, which interfere with a full examination of a pregnant woman and can affect the future of both her and her child.
Indications for genetic screening
The main indications for genetic analysis during pregnancy are:
- Mother's age is more than 35 years.
- The presence in the family of a child with a chromosomal pathology.
- The presence of genetic diseases in one or both parents, as well as in the parents’ immediate relatives.
- The presence of markers of genetic diseases in the results of ultrasound examinations and other screening procedures.
Since each of the genetic tests has its own advantages and disadvantages, the decision to conduct them always requires consultation with a doctor: both an obstetrician leading the pregnancy and a geneticist.
How are DNA test results deciphered?
DNA testing, decoding and examination of the genome takes place in several main stages:
- Researchers isolate cells of interest. At this stage, it is possible to determine the presence of infections and viruses, even if the content of foreign DNA in the sample is the minimum possible.
- Synthesis (reproduction) of isolated cells using the polymerase chain reaction method. It is thanks to this method that it is possible to conduct a detailed study of the genetic code with a minimum amount of biomaterial for research.
- Sequencing. Determination of the nucleotide and amino acid sequence of DNA. At this stage, either specific sections of deoxyribonucleic acid are isolated for deeper analysis, or the entire chain, if it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive study. These areas are so small that for ease of study they have to be tinted with special fluorescent paint.
- Decoding the results. A competent specialist draws up a detailed report on the results of the study and recommendations for it, if necessary.
Types of genetic tests
There are two general types of fetal genetic tests: invasive and non-invasive. The first type of manipulation requires direct contact of the screening equipment with the fetus or the tissues immediately surrounding it. Non-invasive techniques include taking the mother's blood and then measuring circulating biomarkers or other similar methods. They do not require access to the fetus, and therefore are considered more comfortable and safe.
The main non-invasive tests used include the so-called “non-invasive prenatal test”. Its essence is to take blood from the mother and then determine the biomarkers in it. In addition to zero trauma for both the woman and the child, its great advantage is the ability to obtain results at the earliest possible date, from 9 weeks. However, if problems are identified, doctors still recommend an additional invasive test, since they cannot always be interchangeable. (We recommend the article: “Genetic analysis in agriculture”)
The biggest disadvantage of this test is the fairly large number of false positive results. This is due to the peculiarities of diagnostics, namely the impossibility of taking fetal tissue directly for examination. As a result, cells circulating in the blood can be influenced by third-party factors, for example, a twin if the pregnancy is multiple.
The number of invasive tests available is much greater, they are more difficult to perform, and they also require careful consideration when choosing the stage of pregnancy to perform them.
For example, karyotyping of chorionic villi, which is one of the safest ways to determine a violation of the chromosome set, can be done only up to 14-15 weeks, since then the villi become inaccessible.
The most well-known invasive test is amniocentesis, amniocyte karyotyping. It can be done from the 15th week, and the process is quite traumatic. Its essence lies in the fact that the doctor needs to use a needle to collect amniotic fluid, which is subsequently analyzed. Amniocentesis is minimally traumatic for the child and allows additional analysis of the material for many other pathologies (for example, placental mosaicism).

In addition to the procedures described, cord blood analysis is also used. This is the most accurate method of karyotyping available, but it is traumatic not only for the mother, but also for the fetus. For this reason, it is carried out only in cases where the use of other methods was impossible, most often in the case of late registration of the mother or danger to the child.
Test reliability
DNA testing is a highly accurate technique for studying the microcosm of an organism and the microprocesses in it. The test is deciphered based on the genetic base, which many world scientists and institutes are working to replenish. There are currently no more accurate diagnostic methods that offer different testing options.
Paternity: index
DNA paternity testing is one of the most famous studies in society, causing the greatest public outcry. The results of such research have legal force and are sufficient grounds for making a decision in court. What is the essence of testing?
Undoubtedly, many people know that the human DNA helix has a double structure. Thus, the child borrows part of the genotype from the mother, and part from the father. Comparing the alleles (different forms of the same gene) of the child and the father (and in some cases the mother) can confirm the probability of paternity with up to 99.99% accuracy. It is believed that a 100% result is not possible, since there is always the possibility of a potential father having twins. Paternity is 100% refuted.
The main indicator by which the relationship is calculated is called the “paternity index”. Without getting too technical, in general terms it is a measure of how similar the child's and potential father's alleles are in different areas of the gene code.
To standardize the results and eliminate possible errors in decoding the paternity test, the International Organization for Human Identification has established the following threshold values for determining paternity:
- 99.75 – 99.99% fully proven paternity
- 99 – 99.7% high probability of relationship
- 95 – 98.5 paternity is not excluded, but not proven
- 90 – 94.5 low probability of family connection
For kinship
In recent years, testing to determine nationality has become increasingly popular. And this is not only about people’s desire for self-identification: some need this to move to another country and obtain citizenship, while others want to restore their family tree and have an idea about their ancestors.
Often the results are surprising and have little in common with what the client imagined before receiving them. Sometimes the results of research are such that they can completely change a person’s attitude towards other nationalities, and expand the understanding of the deep interconnection between all people.
Also, testing can be carried out without the consent of the person being tested and the results can be provided to him as an original gift.

Congenital diseases
Timely testing for congenital diseases and predispositions to them can help you avoid many risks and prolong your life. Forewarned is forearmed. And this fully characterizes the usefulness of such an analysis. Today, specialists are able to identify up to 6,000 different viruses and infections, as well as determine genetic predisposition to the most dangerous diseases of our time.
Received data
Depending on the type of tests, the set of detected pathologies may be different:
- For the non-invasive test, the main pathologies detected are trisomies on chromosomes 13, 18 and 21, but the analysis does not detect fetal mosaicism or structural abnormalities.
- In addition to trisomies, invasive testing can detect mosaicism and structural abnormalities. Syndromes such as Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, etc. are identified. In parallel with the analysis for anomalies, parents also receive a determination of the sex of the fetus.
- In addition, both types of tests can identify pathologies of placental development.
- As a rule, in the report after the analysis, the laboratory indicates what abnormalities were identified and their probability (usually about 99% for invasive methods and about 97% for non-invasive methods). In addition, the type of violation is determined and a general recommendation for further actions is given.
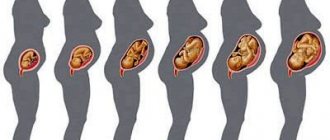
Pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy
In case of ectopic pregnancy
Before trying again, doctors recommend waiting about a year for the woman’s reproductive organs to fully recover.
- An ultrasound examination is required to check the patency of the fallopian tubes and the likelihood of the formation of adhesions. In addition, an ultrasound will make sure that there are no benign tumors, fibroids, cysts - all these problems could lead to or be the result of an ectopic pregnancy.
- It is important to undergo examination by an endocrinologist; the risk of encountering endocrinological disorders increases with an ectopic pregnancy.
- It is mandatory to be examined for chronic inflammation and tested for sexually transmitted infections.
Possible risks
At the moment, most methods of genetic diagnosis, including invasive ones, are as safe as possible for both the mother and the fetus. A lot still depends on the experience of the specialist performing the procedure, as well as the general traumatic nature of the collection of biomaterials. However, when using modern methods of pain relief, as well as high-precision equipment, the risks for mother and child are minimized. (We recommend the article: “Design and production of biopharmaceuticals”)
Regardless of how complex the analysis procedure seems, if the doctor suspects severe genetic diseases, it is recommended to undergo it. An analysis is very important for a correct diagnosis, as well as for determining possible illnesses of the child in the future.
Remember that genetic diseases can be dangerous and lead to very serious consequences for both the child and his parents. You should worry in advance about clarifying the presence or absence of problems and calmly go through all the examinations.
Planning pregnancy in difficult cases
Advance pregnancy planning is already a necessity for every married couple who dreams of healthy offspring, but special attention must be paid to planning in difficult cases. If the expectant mother has had miscarriages in the past, an ectopic pregnancy, she is over 40 years old, she has been prescribed antibiotics, or the woman is sick, for example, with diabetes - all these cases of an upcoming pregnancy are considered difficult, as they increase the risks of genetic pathologies in the fetus. However, the capabilities of modern medicine make it possible to solve almost all problems.
Professional specialists from the St. Petersburg clinic
“Diana” will help expectant parents effectively cope with
pregnancy planning
, regardless of the complexity of the case.