Myoma is one of the most common gynecological diseases. According to some reports, it occurs in 80% of women aged 30–50 years. Previously, doctors recommended that many women with fibroid nodes undergo hysterectomy - surgery to remove the uterus. Currently, the understanding of the causes and mechanisms of the development of the disease, as well as approaches to its treatment, have changed greatly.
According to modern concepts, uterine fibroids are a chronic multifactorial disease in which nodes of smooth muscle cells with unpredictable growth dynamics are formed in the uterus. This pathology is not related to cancer. There is no increased risk of cancer with fibroids. And not all women need treatment.
Scientists admit: at the moment, the reasons for the development of uterine fibroids are not fully known. There are two theories:
- Embryonic . Smooth muscle cells in the uterine wall mature very late. They are in an unstable state until the 38th week of intrauterine development. By comparison, smooth muscle cells in the wall of the intestines and bladder mature by 16 weeks. Thus, the risk of defects in the myometrium is increased, and it is believed that they lead to fibroids.
- Traumatic . Myometrial disorders occur throughout life. The main reasons: repeated menstrual cycles, curettage and abortions, inflammatory processes, rough actions of obstetricians during childbirth.
Indications for myomectomy - removal of uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids do not always need to be treated. For many women, we can limit ourselves to dynamic observation: they only need to undergo periodic examinations by a gynecologist and ultrasound examinations. Currently, the indications for treatment are clearly defined:
- If uterine fibroids cause symptoms that reduce a woman's quality of life. These may be: pain and excessively heavy periods, anemia, dysfunction of the rectum and bladder as a result of compression by their nodes.
- A woman’s desire to become pregnant, while myomatous nodes will interfere with the onset and gestation of pregnancy.
- If fibroids are growing, based on the results of two or three ultrasound examinations performed over time.
But age is a relative contraindication to surgery. Typically, after menopause, the nodes stop growing and most often decrease in size.
Treatment methods for uterine fibroids vary. And hysterectomy - removal of the uterus - is in last place on this list. Currently, it is used as a last resort when other treatments are ineffective. Many women are candidates for uterine artery embolization , a procedure that does not require incisions or general anesthesia. The doctor makes a puncture in the upper part of the thigh, inserts a catheter through the femoral artery into the vessels feeding the fibroids and injects an embolic drug through it. The latter consists of microscopic particles that block the lumen of blood vessels. Myoma stops receiving oxygen and necessary substances, dies and is replaced by connective tissue.
The third type of treatment is myomectomy, surgical removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus. Surgeries and embolization of the uterine arteries are not competing techniques. Each of them is used in certain cases when it makes it possible to solve the problem of uterine fibroids most effectively and with minimal risks.
Euroonko employs doctors who have extensive experience in performing both uterine artery embolization (UAE) and myomectomy operations, including minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures. Consult our doctor: he will correctly assess your situation and recommend treatment methods that are optimal in your case.
Types of laparoscopy
Depending on the problems that laparoscopy is aimed at solving, it can be:
- Diagnostic. It is practiced for examining the abdominal organs (abdominal cavity), when it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis of infertility, “acute abdomen”, and other problems. Usually this stage precedes surgery. For fibroids, laparoscopy is not diagnostic, only surgical. A diagnostic type is transvaginal hydrolaparoscopy. It is used to examine the pelvic organs and check the patency of the fallopian tubes. The essence of the technique is to perform a puncture in the vagina and then inject a special solution into the abdominal cavity that straightens or tints the tissue, which improves visibility. Then a camera is inserted in a similar way, with the help of which the doctor assesses the condition of the reproductive system. It is performed under anesthesia.
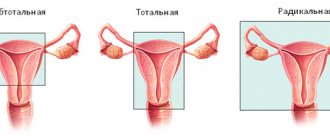
- Operational. It involves the removal of tumors in the PD or the correction of processes (in the presence of adhesions in the pelvic area). Laparoscopy is used to perform the entire range of gynecological operations, including hysterectomy.
- Test. Necessary to check effectiveness after surgery. They resort to control when there has been postoperative treatment of endometriosis with hormonal drugs and it is necessary to assess the patient’s condition, as well as predict pregnancy.
Depending on the situation and the nature of the pathologies identified during the examination, laparoscopy can be emergency or planned.
Laparoscopic surgery: advantages and disadvantages
The main, obvious advantage of laparoscopic removal of uterine fibroids is that it is a minimally invasive operation. It is performed without incisions, through several punctures in the abdominal wall. At the same time, tissue is less injured, bleeding is minimized, and the recovery period is shortened. The woman can be discharged from the hospital earlier and return to her normal life.
When using laparoscopy, compared to open interventions, in the postoperative period there is less pain, and body temperature increases less frequently and less strongly. Lower risk of adhesions forming.
The disadvantage of laparoscopic interventions for the removal of uterine fibroids is that the possibilities of their use are limited. This operation cannot be performed on all women. Using laparoscopy, it is possible to remove only nodes that are subserosal (protrude externally above the surface of the organ) or intramural (in the thickness of the wall), are relatively small in size (up to 8–10 cm), and if there are no more than four of them.
The problem with any myomectomy is the relatively high risk of recurrence. Studies show that in 14% of women operated on, the nodes return within a year. Thus, after 4–5 years, approximately half of the patients are diagnosed with uterine fibroids again. After UAE, the risk of relapse is very low.
The advantage of a myomectomy over a hysterectomy is that the woman's uterus is preserved and she can become pregnant in the future. In addition, the uterus plays an important role in the body. posthysterectomy syndrome may develop , which manifests itself in the form of metabolic, neurovegetative disorders, and reduces the quality of life.
Treatment
For small subserous fibroids, if there are no complaints about health and fertility is not impaired, the woman may be offered observation with regular examinations. In the presence of clinical manifestations and a large size of fibroids, conservative therapy can be prescribed, but it must be understood that it is used only to reduce symptoms; for radical relief from the disease, surgical treatment is effective.
Today there are various surgical treatment methods. According to the recommendations of well-known specialists in the field of gynecology and European communities of obstetricians and gynecologists, the preservation of the organ is important both for patients expecting the birth of a child and for women who want to maintain menstrual function until natural menopause. Therefore, the “golden” standard in the treatment of fibroids is considered to be an organ-preserving operation - myomectomy - removal of nodes followed by suturing of the uterus. The presence of a capsule in fibroids allows for “husking” - removal of a node within the capsule, avoiding injury to the myometrium and without removing parts of the uterus.
Unfortunately, removing large nodes can be accompanied by certain difficulties. First of all, with laparoscopy there is a risk of bleeding, which often leads to the need to convert laparoscopic surgery to open surgery. When bleeding occurs, it becomes necessary to use coagulation; in this case, an incompetent scar may form. In addition, during the operation, visualization of the intervention area deteriorates, which also affects the quality of the suture.
Indications and contraindications for laparoscopy for fibroids
Often, after a woman is diagnosed with uterine fibroids, the question arises: which treatment method should be preferred: myomectomy or uterine artery embolization? The operation is indicated in the following cases:
- A woman is planning a pregnancy in the near future, not sometime in a few years. This is associated with the risk of relapse. If a woman decides to have a child in the long term, there is a high probability that the problem with fibroids will have to be solved again.
- The nodes are located superficially on the uterus, do not lead to deformation of its cavity, do not occupy the entire thickness of the wall of the organ, and are not located in the area of the isthmus and the confluence of large vessels.
- The surgeon is confident that the uterine cavity will not be opened during the operation.
- The surgeon is confident that after the operation a full-fledged scar will form, and it can be easily monitored using ultrasound during pregnancy.
Accordingly, if these conditions are not met, it is worth considering the possibility of conducting an EMA. Laparoscopically, it is possible to remove nodes no more than 8–10 cm in diameter, and their total number should not exceed four.
In addition, we should not forget that any operation, even minimally invasive, carries certain risks. They can be associated both with the surgical intervention itself and with anesthesia. Severe health problems in a woman may be a contraindication.
Carrying out the intervention
Laparoscopy is performed in an operating room, with strict adherence to the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. If surgeons preserve the reproductive organ, the operation is divided into the following stages:
- puncture of the anterior abdominal wall and filling the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide;
- examination of internal organs, clarification of the operation plan;
- removal of myomatous nodes;
- elimination of myometrial defects;
- repeated revision of internal organs after the fibroid has been removed;
- removing instruments, stitching punctures.
The operation to remove the uterus for multiple or large fibroids also takes place in stages:
- isolation and suturing of large vessels;
- intersection of the ligamentous apparatus;
- uterus removal.
When the fibroid is removed, the patient is transferred to the intensive care ward, where her condition is monitored by nursing staff and an anesthesiologist. After recovering from anesthesia, the woman is transferred to a specialized department.
Preparing for surgery
Laparoscopic myomectomy is performed routinely. The woman is first consulted by a doctor, and an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs is performed to assess the size, location, and number of myomatous nodes. The surgeon sets a date for hospitalization and surgery in advance and gives a list of tests that the woman needs to undergo. Typically, preoperative examination includes:
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- General urine analysis.
- Tests for infections.
- Determination of hormone levels in the blood.
- Blood clotting study.
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor.
- Smears from the cervix for cytology and flora.
- Electrocardiography.
- Ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities.
- Chest X-ray.
- According to indications - colposcopy, hysteroscopy, biopsy and other diagnostic methods.
During the consultation, the woman should tell the surgeon about what chronic diseases she suffers from, what medications and dietary supplements she takes, and whether she is allergic to medications. This information is needed in order to correctly assess the risks associated with surgery and anesthesia and take the necessary measures.
You should not eat anything 8 hours before surgery. On the day of surgery you should not drink. Before a woman is taken to the operating room, she is examined by an anesthesiologist and given premedication - drugs are administered that help her relax and calm down.
Clinical manifestations - what to look for
In 30% of patients, the disease occurs without pronounced manifestations and is detected only during examination, but there are certain symptoms that may indicate the presence of the disease, especially when fibroids reach large sizes:
- prolonged, heavy and painful menstruation;
- spotting between periods;
- bleeding;
- pain in the lower abdomen or lower back,
- palpable tumor in the abdomen.
The intensity of manifestations depends on the number and size of the tumor. For example, severe pain signals impaired blood circulation in the formation. If there is a node on the pedicle, torsion of the tumor is possible, as a result of which its blood supply is disrupted, necrosis is possible, followed by peritonitis. In such a situation, a woman needs emergency help from a surgeon. In addition, due to the changed size of the uterine cavity, blood circulation in the endometrium worsens, which leads to infertility or the inability to bear a child. Sometimes fibroids can deform the fallopian tube, which also causes secondary infertility.
For a written consultation, in order to choose treatment tactics in your case, you can send me a complete description of the ultrasound of the pelvic organs, indicate your age and main complaints [email protected] [email protected] Then I will be able to give a more accurate answer to your situation.
What happens in the operating room? Stages of the operation.
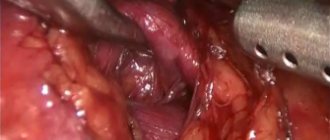
When the woman is already under anesthesia, the surgeon makes several punctures in her abdominal wall. Through one of them, usually in the navel area, a laparoscope is inserted - an instrument with a video camera and a light source. It broadcasts the image to the screen.
Through the remaining punctures, special instruments for laparoscopic interventions are inserted. The surgeon makes an incision in the wall of the uterus, enucleates and removes the fibroids, cauterizes the vessels and stops the bleeding. Stitches are then placed on the wall of the uterus. To better visualize the uterus and other anatomical structures, the abdominal cavity is filled with gas.
The operation is completed by suturing the skin at the puncture sites. In the future, small, barely noticeable scars remain.
What conclusions can be drawn?
Of course, it is impossible to recommend embolization to all women suffering from fibroids without exception. However, it is important to understand the fact that if there is an opportunity to reduce all risks, you should take it!
Removal without pain, long-term rehabilitation, or fear for one’s health is what many women dream about. Some of them plan to conceive and bear a healthy child in the future. The embolization technique allows you to achieve all your goals and reduce risks. Removal is as safe as possible and has a minimum number of contraindications. Myoma disappears quite quickly. Thanks to this, the patient does not suffer from various symptoms of the disease.
Have you decided to intervene?
Do you want fibroid therapy to be carried out by an experienced doctor?
Contact the endovascular surgery center prof. Kapranova! Here, only a progressive technique is used to remove fibroids.
You yourself will be able to choose a clinic for the intervention and determine the time of the procedure.
Call Sergei Anatolyevich on his personal numbers:
- +7,
- +7.
Discuss all conditions and features of the intervention. Talk about possible risks and complications. This will allow you to make the right decision.
Possible complications
As after any operation, after laparoscopy for fibroids there is a small risk of infection, suppuration in the suture area, and bleeding. Other possible complications:
- During the first days after surgery, you may experience slight pain. They are relieved with painkillers from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), for example, ibuprofen. If the pain is intense and intensifies, you should consult a doctor.
- The risk of adhesions is lower than after open surgery.
- Vascular thrombosis.
- Accidental damage to neighboring organs: intestines, ureters, bladder.
After removal of fibroids, a scar remains on the wall of the uterus. This is a weak point that threatens to rupture during pregnancy and childbirth. The surgeon must assess this risk well before surgery.
Features of fibroids
Uterine fibroids are a benign tumor that develops from muscle tissue and consists primarily of connective tissue elements. The disease develops in approximately 35-45% of women over the age of 35-40 years. The peak incidence occurs in the age group of 35-50 years. Recently about uterine fibroids. Even women of reproductive age are affected by the disease.
Types of tumor
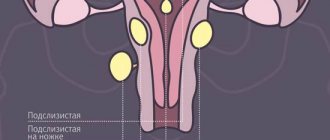
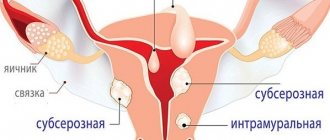
- Subserous myoma. This formation develops on the outside of the uterus. The tumor then grows down into the pelvic cavity. It does not interfere with the flow of menstruation, but can cause discomfort as it reaches a large size. The formation puts pressure on surrounding tissues.
- Intramural fibroids. This disease is more common than others. The growth of fibroids begins in the middle muscular layer of the uterus. This leads to a strong enlargement of the organ. As a result, menstrual irregularities occur. Patients often suffer from pain and feel pressure in the pelvic area.
- Submucosal (submucosal) fibroid. This form is less common than others. The formation appears inside the uterus, in a thin layer of the mucous membrane. Submucosal nodes and pedunculated nodes in the form of cysts often appear. This form of uterine fibroids is clearly defined and has obvious symptoms.
Why does the disease occur?
The following factors can lead to the development of fibroids:
- Hormonal disorders. Clinically, they manifest themselves in disruptions of the menstrual cycle. Usually there is an abundance of discharge and a late onset of menstruation. Patients with fibroids suffer from mood swings. They occur due to a decrease and increase in the level of estrogen and progesterone.
- Irregular sex life. Disharmony often leads to general malfunctions in the body. Myoma can be called one of them.
- Mechanical factors. Women with fibroids have had abortions and undergone curettage procedures in the past. Also, a number of patients suffered traumatic births.
- Genetic predisposition. Daughters of women with fibroids often face the same disease as their mothers.
- Presence of concomitant diseases. Often, uterine pathology is provoked by obesity, high blood pressure, thyroid pathologies, diabetes mellitus, etc.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
What formations are considered large?
Regardless of the type of formation, it is customary to classify by weeks of pregnancy. The affected uterus is equal in size to a healthy one at a certain stage of fetal development.
The following education parameters are distinguished:
- Small uterine fibroids. They are equivalent to 5-12 weeks of pregnancy.
- Large uterine fibroids. They are similar to 12-16 weeks of pregnancy.
- Giant fibroids. Such formations are equivalent to 16 or more weeks of pregnancy.
In some cases, myomatous nodes reach such a size (20 weeks) that the woman begins to show all the signs of future motherhood.
Among them:
- abdominal enlargement,
- absence of menstruation,
- fetal heartbeat.
The last symptom occurs due to pulsation of the aorta in the peritoneal space.
What signs of disease should I look out for?
Often, women live with uterine fibroids without even knowing that they are suffering from the disease. Its detection often becomes a discovery for the gynecologist, which he does during a standard preventive examination.
Situations often arise when the symptoms are smoothed out. They may be perceived as a variant of the norm.
The most pronounced signs of uterine fibroids appear when the formation is submucosal. Also, the symptoms are pronounced when the tumor is large.
What signs should alert the patient?
- Long and heavy menstruation. They are called menorrhagia. Such bleeding can be so profuse that a woman simply cannot leave the house. Often there is spotting that is not associated with menstruation at all. They are called "metrorrhagia". All secretions are dangerous! They can lead to decreased hemoglobin levels and iron deficiency anemia. The disease is expressed in pale skin, weakness, and drowsiness.
- Pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. They become acute when blood circulation in the myomatous node is disrupted. But usually the tumor grows gradually. In this case, with fibroids, the pain is aching in nature. At the same time, education is growing and becoming larger.
- Dysfunction of neighboring organs. Women suffering from fibroids often experience difficulty urinating and emptying the rectum. This is due to the fact that the fibroid grows and puts pressure on neighboring organs.
Request a call back Get a free consultation
Steal syndrome: what is it?
If fibroids have reached a large size, their negative impact on the body increases. The result is stealing syndrome. What it is?
The tumor is benign. However, she constantly needs oxygen and nutrition. The fibroid node can receive the elements necessary for life only from other organs and systems.
As a result, the liver, kidneys, and pancreas suffer. Disturbances in these organs affect metabolic processes. Therefore, a woman with fibroids is often exposed to many dangers. She may gain weight suddenly. Patients are often diagnosed with diabetes mellitus and other diseases. If oxygen enters the heart muscle in insufficient quantities, the formation can even provoke coronary disease, myocardial infarction.
The pathology also affects the functioning of the respiratory system. As a result, the woman suffers from laryngitis, bronchitis, and rhinitis.
When does steal syndrome occur?
Typically, the onset of the syndrome coincides with the formation of 12-14 weeks of pregnancy. The syndrome reaches its peak at educational parameters equal to the 16th week.
Does the method have any disadvantages?
Yes!
Critics of embolization include the following disadvantages:
- pain,
- probability of infection.
Important! Immediately after the manipulations, the woman undergoes anti-inflammatory prophylaxis. In addition, she receives painkillers. Moreover, the patient only needs the bandage on the first day. If no bleeding is observed from the puncture site, the bandage is removed. The patient can go home.
Full recovery occurs within 15-20 days. The rehabilitation period depends on the size of the nodes and their number.
Request a call back Get a free consultation
What are emboli and how do they work?
When performing UAE, 2 types of substances are supplied to the artery:
- Contrasting connections. They allow you to see the vessels on the screen of a special X-ray machine.
- Emboli (also called blockers).
Let's consider the features of the latter.
Emboli are tiny (diameter 300-700 microns) polymer balls. They are made of a special polymer and are able to move freely through large arteries, but get stuck in small ones. Thus, emboli allow artificial thrombosis of the vessel.